Back up an Azure Database for MySQL flexible server by using Azure Backup (preview)
Important
The preview solution for protecting Azure Database for MySQL flexible servers using Azure Backup is currently paused. Please refrain from configuring new backups until further notice. Rest assured, all existing backup data remains safe and available for restore. In the meantime, you can refer to the blog post instructions to create long-term backups manually, ensuring compliance with your immediate needs.
This article describes how to back up your Azure Database for MySQL flexible server by using Azure Backup.
Here are important considerations for this preview feature:
Currently, this feature supports only the weekly backup option. However, you can schedule the backups on multiple days of the week.
Retention duration ranges from 7 days to 10 years in the backup data store.
Each retention rule requires inputs for specific backups, data store, and retention duration for the backups.
The retention rules are evaluated in a predetermined order of priority. The priority is the highest for the yearly rule, followed by the monthly rule, and then the weekly rule.
Default retention settings are applied when no other rules qualify. For example, the same recovery point might be the first successful backup taken every week in addition to the first successful backup taken every month. However, because the priority of the monthly rule is higher than the priority of the weekly rule, the retention that corresponds to the first successful backup taken every month applies.
By default, the retention rule is set to 3 months if no retention rule is set.
Learn more about the supported scenarios, considerations, and limitations.
Create a backup policy for Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server
To create a backup policy, follow these steps:
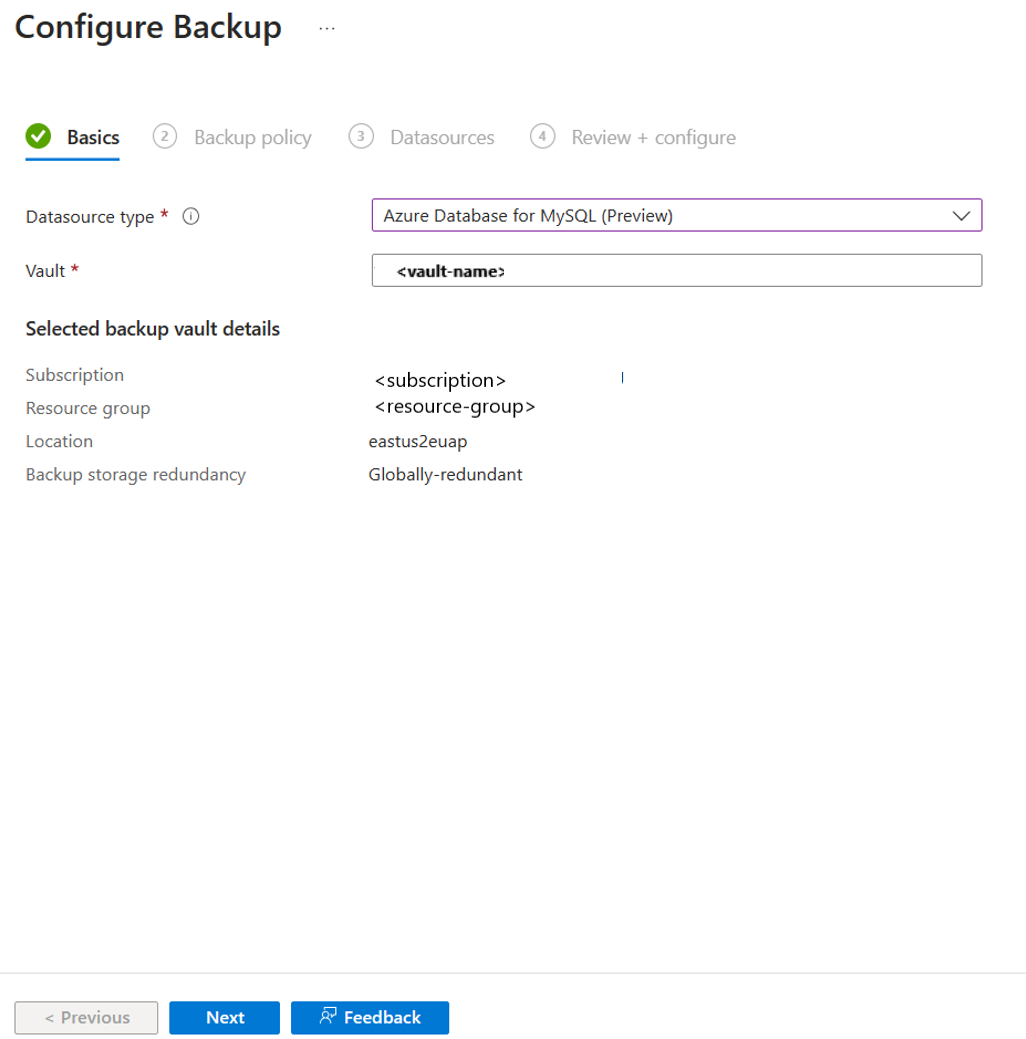
Go to the Backup vault, and then select +Backup to open the Configure backup pane.
Under Backup policy, select Create new.
On the Create Backup Policy pane, enter a name for the new policy, and then select Azure Database for MySQL (Preview) for Datasource type.
On the Schedule + retention tab, select the Backup schedule values.
Select the Retention settings values.
You can add one or more retention rules. To add more retention rules, select Add.
You can move the backups from the backup data store to an archive data store after they expire according to the backup policy. To archive backups on expiry, select On-expiry.
Select Review + create.
Configure a backup on Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server
You can configure a backup for the entire Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server instance.
To configure a backup, follow these steps:
In the Azure portal, go to the Backup vault, and then select +Backup.
Alternatively, go to Business Continuity Center > +Backup.
Select the backup policy that you created, which defines the backup schedule and the retention duration.
Select the Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server instance to back up.
You can choose an Azure Database for MySQL flexible server across subscriptions if it's in the same region as that of the vault.
Select Add and choose the Azure Database for MySQL flexible server that you want to back up.
After the selection, the backup readiness check validates that the configuration is correct.
To resolve any access problems, select Assign missing roles.
Review the configuration details, and then select Configure backup.
To track the progress, go to Backup Instances.
Run an on-demand backup
To trigger an on-demand backup (a backup that's not in the schedule specified in the policy), follow these steps:
Go to the Backup vault, select Backup instances, and then select the backup instance for which you want to take a backup.
Select Backup Now.
On the MySQL database instance pane, choose a retention rule from the list.
Select Backup now.
Monitor a backup job
Azure Backup creates a job for scheduled backups or if you trigger on-demand backup operation for tracking. To view the backup job's status, go to Backup jobs.
The Backup jobs dashboard shows the operations and status for the past 7 days. You can select the time range and other filters to narrow down your selection.
To view the status of all backup jobs, select All for Status. The ongoing and past jobs of the backup instance appear.