Atlassian Jira Cloud Microsoft Graph connector
The Atlassian Jira Cloud Microsoft Graph connector allows your organization to index Jira issues. After you configure the connector and index content from the Jira site, end users can search for those items in Microsoft Search and Microsoft 365 Copilot.
This article is for Microsoft 365 administrators or anyone who configures, runs, and monitors a Jira cloud Graph connector.
Important
The Atlassian Jira Cloud Microsoft Graph connector supports only Jira cloud-hosted instances. Jira Server and Jira Data Center versions are not supported by this connector.
Capabilities
- Index issues (or tickets) from Jira cloud
- Enable your end users to ask questions related to project tracking, support queries, or task execution in Copilot.
- Find the issue with mobile app not loading.
- Look for Jira tasks reported by John to update documentation about API migration.
- Summarize CP-1234.
- Use Semantic search in Copilot to enable users to find relevant content based on keywords, personal preferences, and social connections.
Limitations
- The connector doesn't support the "Any user logged in" application role to grant access of issues to users.
- The connector doesn't index attachments.
Prerequisites
You must be the search admin for your organization's Microsoft 365 tenant.
Jira cloud instance URL: To connect to your Jira data, you need your organization's Jira instance URL. Your organization's Jira instance URL typically looks like
https://<your-organization-domain>.atlassian.net. If you don't have an instance already, refer the page to create a test instance.Service Account: To connect to Jira and allow the Microsoft Graph Connector to update issues regularly, you need a service account with the following permissions granted to it.
Permission name Permission type Required for Browse projects Project permission Crawling Jira issues. This permission is mandatory for the projects that need to be indexed. Issue level security permissions Issue-level security Crawling different issue types. This permission is optional. Browse users and groups Global permission Security trimming based on access permissions of search results. This permission is optional and is required to select Only people with access to this data sourceoption in step 4 below.Administer Jira Global permission Security trimming based on access permissions of search results. This permission is optional and is required to select Only people with access to this data sourceoption in step 4 below.
Get Started
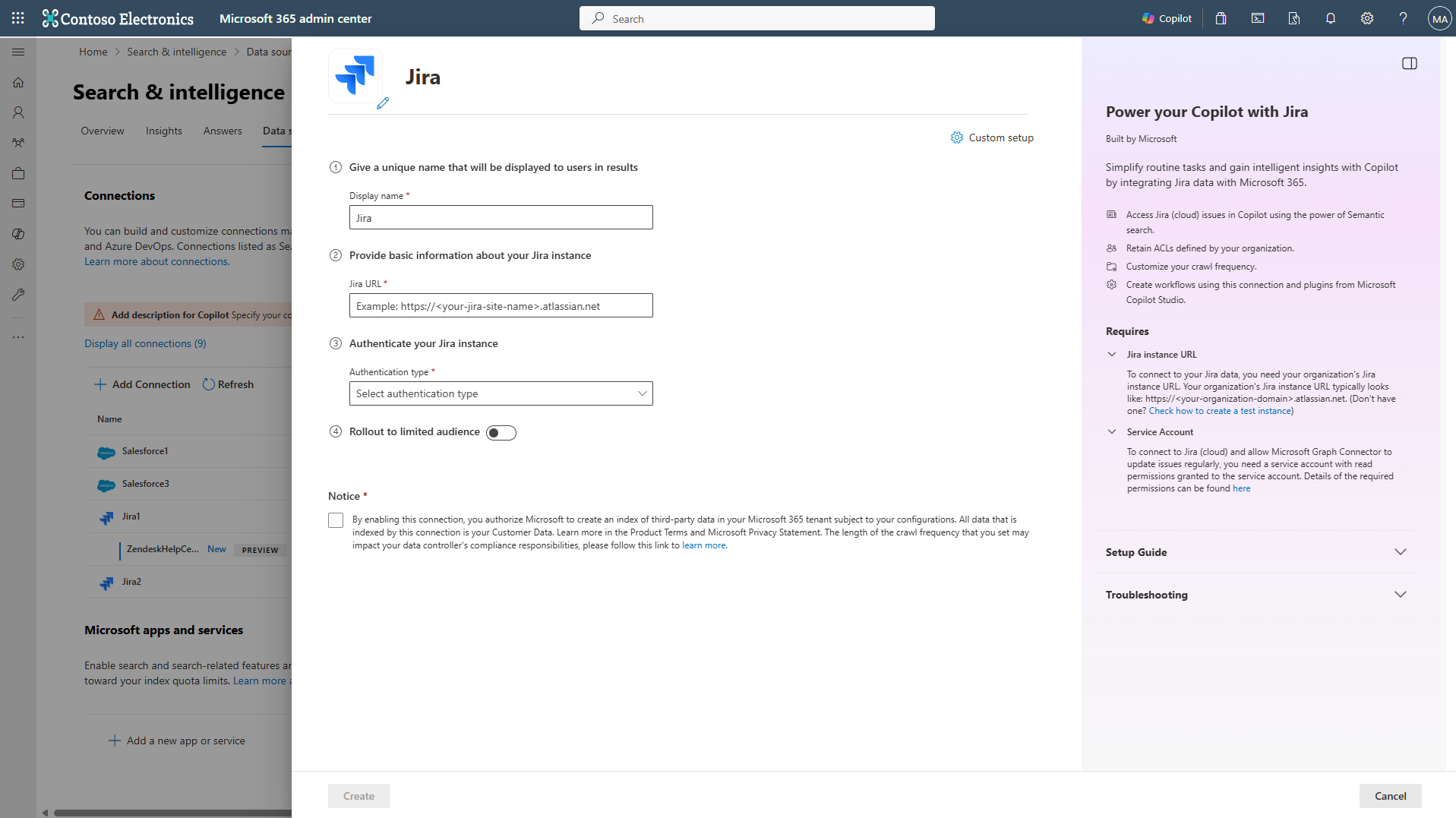
1. Display name
A display name is used to identify each citation in Copilot, helping users easily recognize the associated file or item. Display name also signifies trusted content. Display name is also used as a content source filter. A default value is present for this field, but you can customize it to a name that users in your organization recognize.
2. Jira cloud URL
To connect to your Jira cloud data, you need your organization's Jira instance URL. Your organization's Jira instance URL typically looks like https://<your-organization-domain>.atlassian.net.
3. Authentication Type
To authenticate and sync issues from Jira, choose one of the two supported methods:
a. Basic authentication
Enter your account's username (usually email ID) and API token to authenticate using basic auth. Refer Atlassian's documentation on how to manage API tokens for your Atlassian account to learn more about generating an API token.
b. Atlassian Jira OAuth 2.0 (Recommended)
To use the Jira OAuth for authentication, follow these steps.
Register an app in Atlassian Jira so the Microsoft Search app and Microsoft 365 Copilot can access the instance. To learn more, see Atlassian Support documentation on how to Enable OAuth 2.0.
The following steps provide guidance on how to register the app:
Sign in to Atlassian Developer console with your Atlassian Jira admin account.
Select on
Createand selectOAuth 2.0 integration.Provide an appropriate name for the application and create the new app.
Navigate to
Permissionsfrom the navigation pane on left. SelectAddforJira APIand click onConfigure. Under the 'Granular Permissions' header, add the following scopes.# Scope name Code 1 View fields read:field:jira2 View avatars read:avatar:jira3 View project categories read:project-category:jira4 View projects read:project:jira5 Read field configurations read:field-configuration:jira6 View issue types read:issue-type:jira7 View project properties read:project.property:jira8 View users read:user:jira9 View application roles read:application-role:jira10 View groups read:group:jira11 Read issue type hierarchies read:issue-type-hierarchy:jira12 View project versions read:project-version:jira13 View project components read:project.component:jira14 View issue details read:issue-details:jira15 View audit logs read:audit-log:jira16 View issue meta read:issue-meta:jira17 View project roles read:project-role:jira18 View issue security levels read:issue-security-level:jira19 View issue security schemes read:issue-security-scheme:jira20 View permission schemes read:permission-scheme:jira21 View permissions read:permission:jiraNavigate to
Authorizationfrom the navigation pane on the left. Add the callback URL for M365 Enterprise:https://gcs.office.com/v1.0/admin/oauth/callback, for M365 Government:https://gcsgcc.office.com/v1.0/admin/oauth/callbackand save the changes.Navigate to
Settingsfrom the navigation pane on the left to get theClient IDandSecretfrom this page.
Complete the connection settings step using the Client ID and Secret.
Note
- Refer to the list of scopes for OAuth 2.0 apps to learn more about Jira permissions.
- The original (Classic) OAuth permissions are being deprecated for the Jira cloud. Refer the changelog announcement to learn more.
4. Roll out to limited audience
Deploy this connection to a limited user base if you want to validate it in Copilot and other Search surfaces before expanding the rollout to a broader audience. To know more about limited rollout, see staged rollout.
At this point, you're ready to create the connection for Jira cloud. You can click Create to publish your connection and index issues from your Jira account.
For other settings, like Access Permissions, Data Inclusion Rules, Schema, Crawl frequency, etc., we have defaults based on what works best with Jira data. You can see the default values below:
| Users | Description |
|---|---|
| Access permissions | Only people with access to content in Data source. |
| Map Identities | Data source identities mapped using Microsoft Entra IDs. |
| Content | Description |
|---|---|
| Site projects | All projects are indexed. |
| Filter data | All issues are indexed. No time filter or JQL criteria is applied. |
| Manage Properties | To check default properties and their schema, see content |
| Sync | Description |
|---|---|
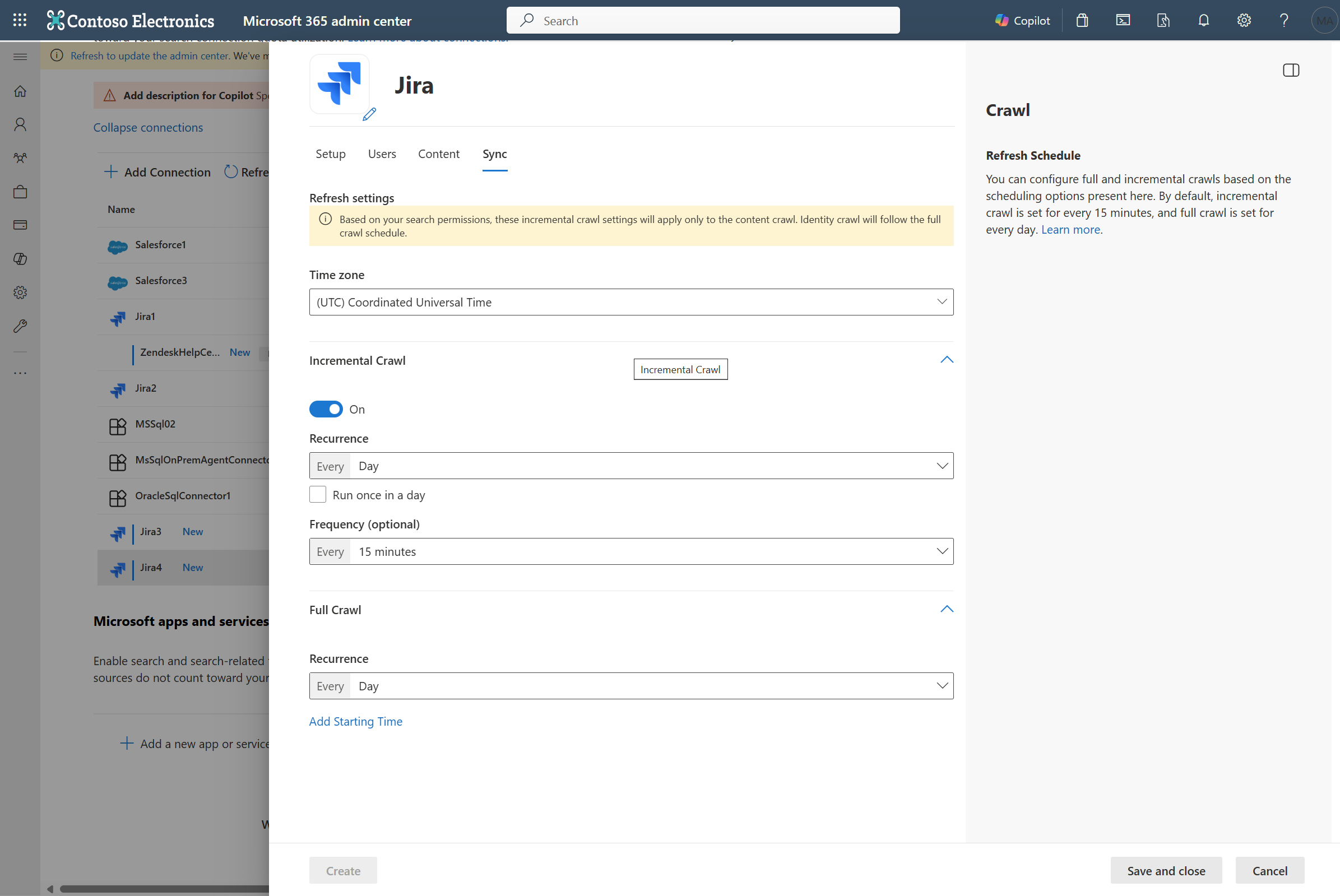
| Incremental Crawl | Frequency: Every 15 mins |
| Full Crawl | Frequency: Every Day |
If you want to edit any of these values, you need to choose the "Custom Setup" option.
Custom Setup
Custom setup is for those admins who want to edit the default values for settings listed in the above table. Once you click on the "Custom Setup" option, you see three more tabs - Users, Content, and Sync.
Users
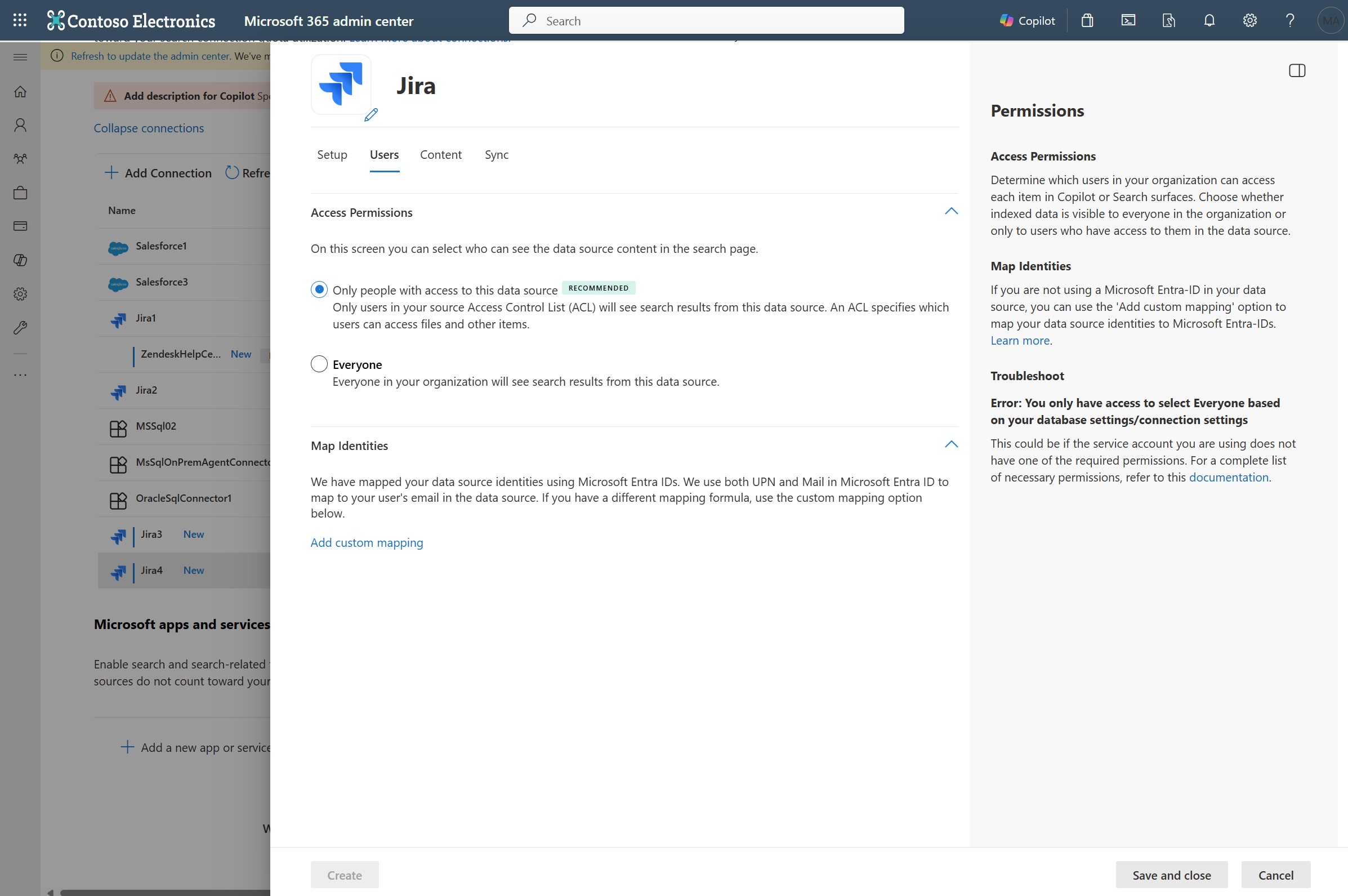
Access Permissions
The Atlassian Jira connector supports search permissions visible to Everyone or Only people with access to this data source. If you choose Everyone, indexed data will appear in the search results for all users. If you choose Only people with access to this data source, indexed data will appear in the search results for users who have access to them. In Atlassian Jira, security permissions are defined using project permission schemes containing site-level groups and project roles. Issue-level security can also be defined using issue-level permission schemes.
Important
The Jira cloud Microsoft Graph connector must be able to read a user’s email ID in Jira to appropriately assign security permissions in Microsoft Search and Microsoft 365 Copilot. This requires you to ensure either of the following:
- All users should have selected the ‘Anyone’ option for their profile visibility settings. To learn more about profile visibility settings, refer to the documentation by Atlassian.
- For organizations using ‘Managed accounts’ (All the Atlassian accounts with email addresses from your verified domain become managed accounts. Refer this documentation for more information) -
- All users, who are part of managed accounts, must have the managed account setting selected in profile visibility settings.
- Users who are not part of the managed account (same as crawling account), need to have ‘Anyone’ selected in their profile visibility settings.
- The crawling account used during connection configuration must have the managed account domain.
Mapping Identities
The default method for mapping your data source identities with Microsoft Entra ID is by checking whether the Email ID of Jira users is same as the UserPrincipalName (UPN), or Mail of the users in Microsoft Entra. If you believe the default mapping wouldn't work for your organization, you can provide a custom mapping formula. To know more about, mapping Non-Microsoft Entra ID identities, see Map your non-Azure AD Identities.
To identify which option is suitable for your organization:
- Choose the Microsoft Entra ID option if the Email ID of Jira users is the same as the UserPrincipalName (UPN) of users in Microsoft Entra ID.
- Choose the Non-Microsoft Entra ID option if the Email ID of Jira users is different from the UserPrincipalName (UPN) and Email of users in Microsoft Entra ID.
Note
Updates to groups governing access permissions are synced in full crawls only. Incremental crawls don't support processing of updates to permissions.
Content
Choose projects and filter data
Site projects
You can choose for the connection to index either the entire Jira site or specific projects only.
If you choose to index the entire Jira site, Jira issues in all projects in the site are indexed. New projects and issues are indexed during the next crawl after they're created.
If you choose individual projects, only Jira issues in the selected projects are indexed.
Note
When you grant the Browse projects permission to a Jira projects, it is listed in the project selection and can be crawled. If a project is missing, check the permissions for your account.
Filter data
You may further choose to filter the Jira issues that are indexed in two ways.
- Specify the issue modified time period. This option will only index the Jira issues that are created or modified in the time period selected on a rolling basis based on current crawl.
Tip
You may use the JQL filter to index only specific Jira issue types using "issueType in (Bug,Improvement)"
Manage Properties
Here, you can add or remove available properties from your Jira data source, assign a schema to the property (define whether a property is searchable, queryable, retrievable, or refinable), change the semantic label and add an alias to the property. Properties that are selected by default are listed below.
| Source Property | Label | Description | Schema |
|---|---|---|---|
| Authors | Authors | Name all the people who participated/collaborated on the item in the data source | Retrieve |
| Created | Created date time | Data and time that the item was created in the data source | Query, Retrieve |
| IssueDescription | Content | The description of the issue | Search |
| IssueIconURL | IconUrl | Icon url that represents the issue type. | Retrieve |
| IssueId | |||
| IssueKey | |||
| IssueLink | url | The target URL of the item in the data source | Query, Retrieve |
| IssueStatus | Query | ||
| IssueSummary | |||
| ProjectName | Query | ||
| ReporterEmailId | Created by | Retrieve | |
| ReporterName | Query, Retrieve | ||
| Title | Title | The title of the item that you want shown in Copilot and other search experiences | Search, Query, Retrieve |
| Updated | Last modified date time | Date and time the item was last modified in the data source. | Query, Retrieve |
Note
- The Atlassian Jira connector can index both default issue fields and custom created issue fields.
- If a selected custom created field is not present in some Jira issue type(s), the field will be ingested as NULL (blank).
The list of properties that you select here, can impact how you can filter, search and view your results in Copilot for Microsoft 365.
Preview Data
Use the preview results button to verify the sample values of the selected properties and query filter.
Sync
The refresh interval determines how often your data is synced between the data source and the Graph connector index. There are two types of refresh intervals - full crawl and incremental crawl. For more details, see refresh settings.
You can change the default values of refresh interval from here if you want to.
Set up search result page
After creating the connection, you need to customize the search results page with verticals and result types. To learn about customizing search results, review how to manage verticals and result types. You may also use the sample result layout for the Jira connector. Copy-paste the result layout JSON to get started after reviewing the schema of the connection with required schema for the sample layout.
Troubleshooting
After publishing your connection, you can review the status under the Data Sources tab in the admin center. To learn how to make updates and deletions, see Manage your connector. You can find troubleshooting steps for commonly seen issues in Troubleshooting guide for Atlassian Jira Cloud Microsoft Graph connector.
If you have issues or want to provide feedback, contact Microsoft Graph | Support.