Install SQL Server 2016 R Services
Applies to:
SQL Server 2016 (13.x) only
Learn how to install SQL Server 2016 R Services on Windows. You can use R Services to execute R scripts in-database.
Note
In SQL Server 2017 and later, R is included in Machine Learning Services along with Python. If you want R and have SQL Server 2017 or later, see Install SQL Server Machine Learning Services to add the feature.
Pre-install checklist
A database engine instance is required. You can't install R only, although you can add it incrementally to an existing instance.
For business continuity, Always On Availability Groups are supported for R Services. You have to install R Services, and configure packages, on each node.
Don't install R Services on a SQL Server Always On Failover Cluster Instance (FCI). The security mechanism used for isolating R processes is not compatible with a SQL Server Always On Failover Cluster Instance (FCI) environment.
Don't install R Services on a domain controller. The R Services portion of setup will fail.
Don't install Shared Features > R Server (Standalone) on the same computer running an in-database instance.
Side-by-side installation with other versions of R is supported but not recommended. It is supported because the SQL Server instance uses its own copies of the open-source R distribution. However, running code that uses R on the SQL Server computer outside SQL Server can lead to various problems:
- You use a different library and different executable, and get different results, than you do when you are running in SQL Server.
- R scripts running in external libraries cannot be managed by SQL Server, leading to resource contention.
Important
After setup is complete, be sure to complete the additional post-configuration steps described in this article. These steps include enabling SQL Server to use external scripts, and adding accounts required for SQL Server to run R jobs on your behalf. Configuration changes generally require a restart of the instance, or a restart of the Launchpad service.
Get the installation media
The download location for SQL Server depends on the edition:
SQL Server Enterprise, Standard, and Express editions. These editions are licensed for production use. For the Enterprise and Standard editions, contact your software vendor for the installation media. You can find purchasing information and a directory of Microsoft partners on the Microsoft purchasing website.
Install patch requirement
Microsoft has identified a problem with the specific version of Microsoft VC++ 2013 Runtime binaries that are installed as a prerequisite by SQL Server. If this update to the VC runtime binaries is not installed, SQL Server may experience stability issues in certain scenarios. Before you install SQL Server follow the instructions at SQL Server Release Notes to see if your computer requires a patch for the VC runtime binaries.
Run setup
For local installations, you must run Setup as an administrator. If you install SQL Server from a remote share, you must use a domain account that has read and execute permissions on the remote share.
Start the setup wizard for SQL Server 2016.
On the Installation tab, select New SQL Server stand-alone installation or add features to an existing installation.
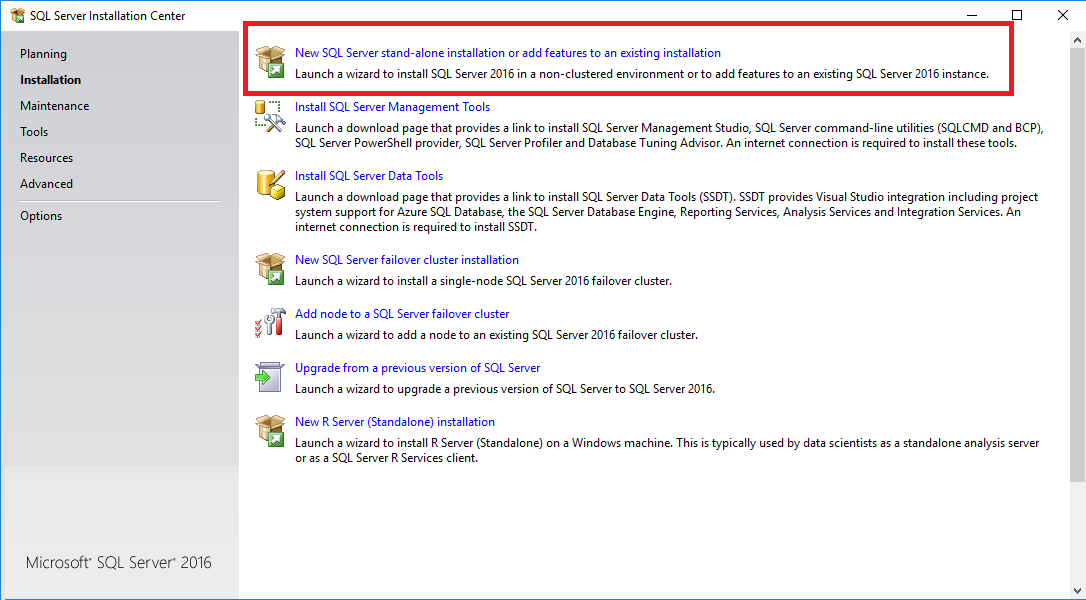
On the Feature Selection page, select the following options:
- Select Database Engine Services. The database engine is required in each instance that uses machine learning.
- Select R Services (In-Database). Installs support for in-database use of R.
Important
Do not install R Server and R Services at the same time.
On the Consent to Install Microsoft R Open page, click Accept.
This license agreement is required to download Microsoft R Open, which includes a distribution of the open-source R base packages and tools, together with enhanced R packages and connectivity providers from the Microsoft R development team.
After you have accepted the license agreement, there is a brief pause while the installer is prepared. Click Next when the button becomes available.
On the Ready to Install page, verify that the following items are included, and then select Install.
- Database Engine Services
- R Services (In-Database)
After setup is complete, if you are instructed to restart the computer, do so now. It is important to read the message from the Installation Wizard when you have finished with Setup. For more information, see View and Read SQL Server Setup Log Files.
Set environment variables
For R feature integration only, you should set the MKL_CBWR environment variable to ensure consistent output from Intel Math Kernel Library (MKL) calculations.
In Control Panel, click System and Security > System > Advanced System Settings > Environment Variables.
Create a new User or System variable.
- Set variable name to
MKL_CBWR - Set the variable value to
AUTO
- Set variable name to
This step requires a server restart. You can hold off on the restart until all of the configuration work is done.
Enable script execution
Open SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) or Azure Data Studio.
Connect to the instance where you installed R Services, click New Query to open a query window, and run the following command:
sp_configureThe value for the property,
external scripts enabled, should be 0 at this point. That is because the feature is turned off by default. The feature must be explicitly enabled by an administrator before you can run R scripts.To enable the external scripting feature, run the following statement:
EXEC sp_configure 'external scripts enabled', 1 RECONFIGURE WITH OVERRIDE
Restart the service
When the installation is complete, restart the database engine before continuing to the next, enabling script execution.
Restarting the service also automatically restarts the related SQL Server Launchpad service.
You can restart the service using the right-click Restart command for the instance in SSMS or by using SQL Server Configuration Manager.
Verify installation
Use the following steps to verify that all components used to launch external script are running.
In SQL Server Management Studio, open a new query window, and run the following command:
EXEC sp_configure 'external scripts enabled'The run_value should now be set to 1.
Open SQL Server Configuration Manager, and verify SQL Server Launchpad service is running. You should have one service for every database engine instance that has R installed. For more information about the service, see Extensibility framework.
If Launchpad is running, you should be able to run simple R to verify that external scripting runtimes can communicate with SQL Server.
Open a new Query window in SQL Server Management Studio or Azure Data Studio, and then run a script such as the following:
EXEC sp_execute_external_script @language =N'R', @script=N' OutputDataSet <- InputDataSet; ', @input_data_1 =N'SELECT 1 AS hello' WITH RESULT SETS (([hello] int not null)); GOThe script can take a little while to run, the first time the external script runtime is loaded. The results should be something like this:
hello 1
Apply updates
We recommend that you apply the latest service pack and cumulative update to both the database engine and machine learning components.
On internet-connected devices, cumulative updates are typically applied through Windows Update, but you can also use the steps below for controlled updates. When you apply the update for the database engine, Setup pulls in the cumulative updates for R libraries you installed on the same instance.
On disconnected servers, extra steps are required. For more information, see Install on computers with no internet access > Apply cumulative updates.
Start with a baseline instance already installed: SQL Server 2016 initial release, SQL Server 2016 SP 1, or SQL Server 2016 SP 2.
Go to the cumulative update list: Latest updates for Microsoft SQL Server
Select the latest service pack (of not already installed as the baseline instance) and cumulative update. An executable is downloaded and extracted automatically.
Run Setup. Accept the licensing terms, and on the Feature selection page, review the features for which cumulative updates are applied. You should see every feature installed for the current instance, including R Services. Setup downloads the CAB files necessary to update all features.
Continue through the wizard, accepting the licensing terms for the R distribution.
Note
Cumulative Update (CU) 14 and later for SQL Server 2016 SP2 include a newer version of the R runtime. For more information, see Change the default language runtime version.
Additional configuration
If the external script verification step was successful, you can run R commands from SQL Server Management Studio, Azure Data Studio, or any other client that can send T-SQL statements to the server.
If you got an error when running the command, review the additional configuration steps in this section. You might need to make additional appropriate configurations to the service or database.
At the instance level, additional configuration might include:
- Firewall configuration for SQL Server Machine Learning Services.
- Enable additional network protocols.
- Enable remote connections.
- Manage disk quotas to avoid external scripts running tasks that exhaust disk space.
On the database, you might need the following configuration updates:
Note
Not all the listed changes are required, and none might be required. Requirements depend on your security schema, where you installed SQL Server, and how you expect users to connect to the database and run external scripts. Additional installation guidance can be found here: Install SQL Server Machine Learning Services
Suggested optimizations
You might also want to optimize the server to support machine learning with R or install pretrained models.
Add more worker accounts
If you think you might use R heavily, or if you expect many users to be running scripts concurrently, you can increase the number of worker accounts that are assigned to the Launchpad service. For more information, see Scale concurrent execution of external scripts in SQL Server Machine Learning Services.
Optimize the server for external script execution
The default settings for SQL Server setup are intended to optimize the balance of the server for a variety of services that are supported by the database engine, which might include extract, transform, and load (ETL) processes, reporting, auditing, and applications that use SQL Server data. Therefore, under the default settings, you might find that resources for machine learning are sometimes restricted or throttled, particularly in memory-intensive operations.
To ensure that machine learning jobs are prioritized and resourced appropriately, we recommend that you use SQL Server Resource Governor to configure an external resource pool. You might also want to change the amount of memory that's allocated to the SQL Server database engine, or increase the number of accounts that run under the SQL Server Launchpad service.
To configure a resource pool for managing external resources, see Create an external resource pool.
To change the amount of memory reserved for the database, see Server memory configuration options.
To change the number of R accounts that can be started by SQL Server Launchpad, see Scale concurrent execution of external scripts in SQL Server Machine Learning Services.
If you are using Standard Edition and do not have Resource Governor, you can use Dynamic Management Views (DMVs) and Extended Events, as well as Windows event monitoring, to help manage the server resources that are used by R.
Install additional R packages
The R solutions you create for SQL Server can call basic R functions, functions from the proprietary packages installed with SQL Server, and third-party R packages compatible with the version of open-source R installed by SQL Server.
Packages that you want to use from SQL Server must be installed in the default library that is used by the instance. If you have a separate installation of R on the computer, or if you installed packages to user libraries, you won't be able to use those packages from T-SQL.
The process for installing and managing R packages is different in SQL Server 2016 and SQL Server 2017. In SQL Server 2016, a database administrator must install R packages that users need. In SQL Server 2017, you can set up user groups to share packages on a per-database level, or configure database roles to enable users to install their own packages. For more information, see Install packages with R tools.
Next steps
R developers can get started with some simple examples, and learn the basics of how R works with SQL Server. For your next step, see the following links: