Megjegyzés
Az oldalhoz való hozzáféréshez engedély szükséges. Megpróbálhat bejelentkezni vagy módosítani a címtárat.
Az oldalhoz való hozzáféréshez engedély szükséges. Megpróbálhatja módosítani a címtárat.
Original product version: SQL Server (all supported versions)
Original KB number: 935897
This article provides more information about servicing channels for currently supported versions of Microsoft SQL Server. The criteria for fixes includes workaround availability, customer effect, reproducibility, the complexity of the code that must be changed, and so on.
To determine the version, edition, and the latest updates of your SQL Server instance, review Determine the version, edition, and update level of SQL Server and its components. For details about the support cycle for each product, check mainstream lifecycle. To understand the various options that are available for SQL Server products that have reached the end of support, review SQL Server end of support options.
Delivery mechanisms for SQL Server updates
The SQL Server team uses a scheduled delivery model for releasing fixes and product updates. In the scheduled delivery model, a customer can receive a fix to address their most critical situations in a reasonable time. Additionally, a customer can receive a fix that has undergone rigorous testing and that is released on a scheduled basis. Therefore, the SQL Server team has created the following delivery mechanisms.
Cumulative update (CU)
| Description | SQL Server 2017 and later versions (both Windows and Linux platforms) | SQL Server 2016 and earlier versions |
|---|---|---|
| Contains | All the fixes, improvements, and feature enhancements since the release version of the product. | All the fixes, improvements, and feature enhancements since the release version (RTM) or since the latest installed baseline Service Pack. |
| Release frequency | Every month for the first year after a SQL Server release, and every two months for the remaining four years of the full 5-year mainstream lifecycle. | Every two months for a given baseline. |
| Localized content | Will accommodate localized content, allowing new feature completeness and supportability enhancements to be delivered faster. | |
| Example | KB5016394 - Cumulative Update 17 for SQL Server 2019 (microsoft.com) | B5001092 - Cumulative Update 17 for SQL Server 2016 SP2 (microsoft.com) |
| Notes | CU31 for 2017 is the last CU for SQL Server 2017. We'll ship only on-demand fixes and security updates for SQL Server 2017. | We no longer ship CUs for SQL Server 2016 and earlier versions. Only on-demand fixes and security updates will be shipped. For products that reached Extended Support End date, you will require Extended Security Update (ESU) subscription for receiving security updates. |
Note
The update can be requested by any customer, regardless of their support offering.
On-demand fixes (OD)
Contains critical fix requests that satisfy all these conditions:
- You can't wait for the scheduled Cumulative Update release.
- There's no reasonable mitigation or workaround.
- The problem causes significant impact to product or application functionality.
The hotfix can be requested by any customer, regardless of their support offering.
The hotfix is released on or before a mutually agreed-upon date based on the customer's need. The hotfix is targeted for a specific baseline, such as a cumulative update or a service pack.
This hotfix build can contain one or more fixes.
There's no defined frequency.
Example: KB4510083 - On-demand hotfix update package 2 for SQL Server 2017 CU15
General distribution release (GDR)
A GDR addresses an issue that has a broad customer impact, security implications, or both. A GDR is determined and issued by Microsoft as appropriate and when appropriate. The number of GDRs is kept to a minimum.
A GDR can't be requested by a customer. Microsoft internally determines whether a reported hotfix is classified as and delivered as a GDR.
A GDR is released through the download center. A GDR is also released through Microsoft Update, Windows Update, or both.
For fixes to SQL Server versions that are out of extended support, review What are Extended Security Updates for SQL Server?.
Example: KB5014356 - Description of the security update for SQL Server 2019 GDR: June 14, 2022
Note
By default, hotfixes are serviced through GDR, CU, and OD releases. When a product's hotfix request volume gets low, the SQL Server team stops CU releases and delivers hotfixes through GDR and OD releases. The SQL Server team makes the decision based on support trends and customer demand.
A GDR can have either an RTM baseline or a CU baseline. The latest GDR version for each baseline is cumulative and includes fixes from all the previous GDRs for the corresponding baseline.
Examples
Determine the latest GDR for RTM baseline:
The following are the RTM GDRs that are available for SQL Server 2019 as of February 6, 2023 when you filter on RTM-GDR in Cumulative Update or Security ID column in builds spreadsheet.
| Build number | KB number | KB URL | Release Date | Service Pack Level | Cumulative Update or Security ID | Servicing Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15.0.2095.3 | 5014356 | https://support.microsoft.com/kb/5014356 | 2022-06-14 | NA | RTM-GDR | GDR |
| 15.0.2080.9 | 4583458 | https://support.microsoft.com/kb/4583458 | 2021-01-12 | NA | RTM-GDR | GDR |
| 15.0.2070.41 | 4517790 | https://support.microsoft.com/kb/4517790 | 2019-11-04 | NA | RTM-GDR | GDR |
If you're a customer who opted for only GDR updates to the RTM version and no CUs, 15.0.2095.3 is the latest GDR build for your RTM-baseline.
Determine the latest GDRs for a CU baseline:
If you're using CUs for your SQL Server instance, you can check whether there's a GDR available for a given CU by reviewing the Cumulative Update or Security ID column for the corresponding version in the builds spreadsheet, and checking the CU<nn>-GDR entry (where nn is the current CU that's installed for your SQL Server version). For example, if you want to know whether there are any GDRs for SQL Server 2017 CU29, checking for "CU29-GDR" in Cumulative Update or Security ID reveals the following row.
| Build number | KB number | KB URL | Release Date | Service Pack Level | Cumulative Update or Security ID | Servicing Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14.0.3445.2 | 5014553 | https://support.microsoft.com/kb/5014553 | 2022-06-14 | NA | CU29-GDR | Cumulative Update with GDR |
Note
If there's a CU that has a later version number than a CU<nn>-GDR version, the later version includes the GDR fixes. Microsoft always recommends that you install the latest CU that's available for a given SQL Server version.
Service pack (SP)
Service packs are no longer released for SQL Server 2017 and later versions.
Service packs include hotfixes and fixes to issues that are reported through the Microsoft SQL Server community. Service packs can also include product and feature improvements.
Service packs are typically released on a yearly schedule.
Service packs might also include issues that our support organization feels must be addressed. The most common issues that are included affect customer support cases and customer satisfaction. These updates and components are conveniently bundled for easy downloading.
Service packs are cumulative. Each new service pack contains all the fixes that are in previous service packs, together with any new fixes. You don't have to install a previous service pack before you install the latest service pack. To find the list of fixes and cumulative updates that a service pack includes, review its release documentation.
Example: KB5003279 - SQL Server 2016 Service Pack 3 release information
Security fixes and security updates
Security fixes: Fixes that are generally shipped in a CU for which components in a fix list table for the corresponding CU are set to SQL Security. (For more information, see Explanation of Fix areas column in the Fix list KB articles for cumulative updates and service packs). Or, for which a component for the corresponding fix is set to Security Infrastructure in the detailed fix list table in the builds spreadsheet. These are the fixes that are made to the security components of a SQL Server database engine.
Security updates: A security fix to address vulnerabilities that can be used to compromise your SQL Server installation. These are released through a GDR (either an RTM-GDR or a CU-GDR). Subsequent CUs or GDRs include these security updates. Microsoft advises customers to install the latest product releases, security updates, service packs, and cumulative updates to remain as secure as possible. For more information, see Fixed Lifecycle Policy.
To check whether a GDR is a security update, you should review the release documentation for the corresponding GDR. Security updates always have an associated Common Vulnerability and Exposure (CVE) note. For example, the documentation for CU29-GDR ("KB5014553 - Description of the security update for SQL Server 2017 CU29: June 14, 2022") has a link to CVE-2022-29143 that opens in the Security Update Guide on the Microsoft - MSRC website. For more information, see Coming Soon: New Security Update Guide Notification System.
Note
GDRs don't necessarily have to be security updates. For example, "KB4517790 - Servicing Update for SQL Server 2019 RTM" is a non-security GDR release.
Support phase and release vehicle matrix
| Support phase | Mainstream support | Extended support | Extended security updates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Available release vehicles | CU, OD, GDR, SP (SQL Server 2016 and earlier versions only) | GDR/Security updates | GDR/Security updates with agreement |
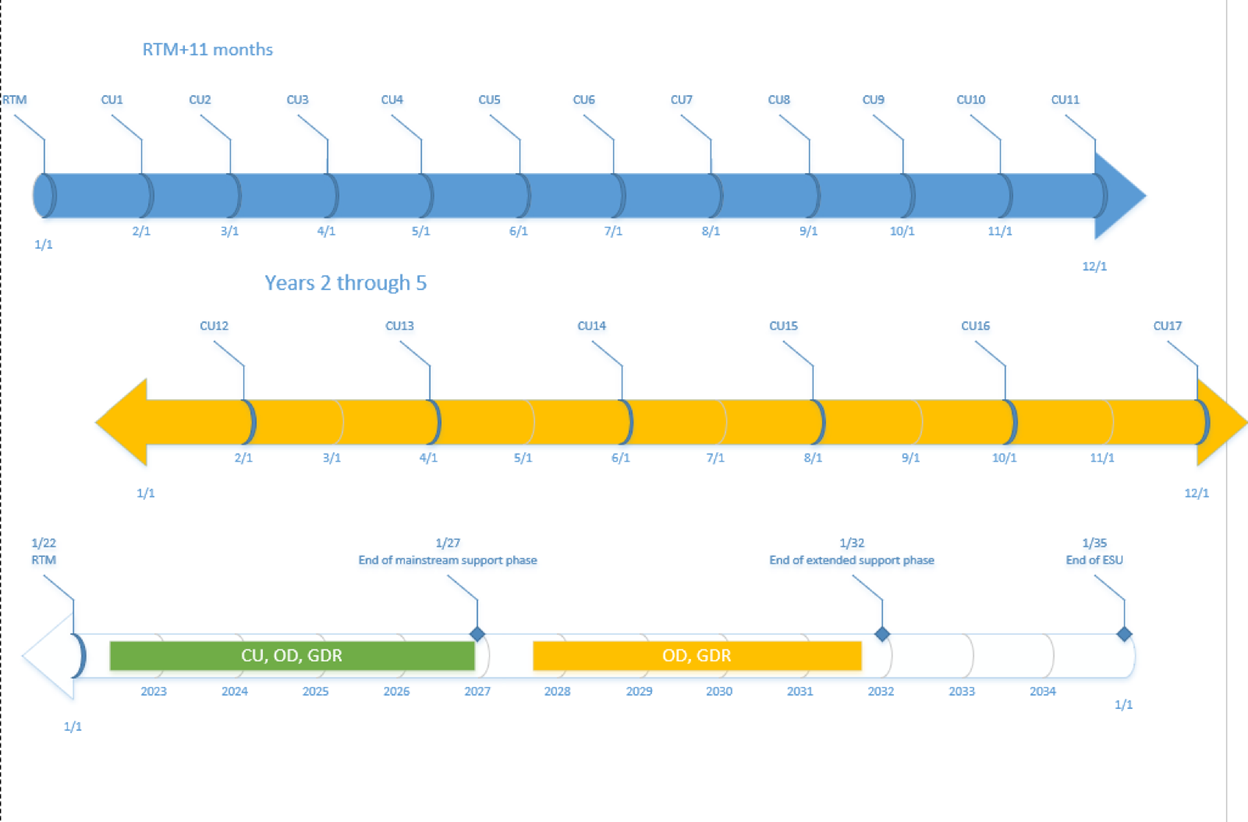
SQL Server 2017 and later versions
The following figure shows an overview of the support cycle for a typical product. This kind of timeline also applies to all future releases of a product.
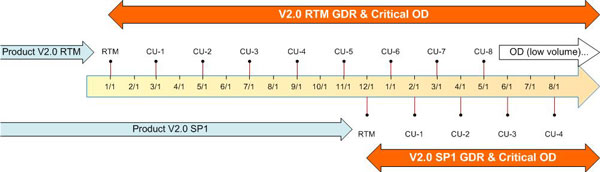
SQL Server 2016 and earlier versions
The following figure shows an overview of the support cycle for a typical product. Both the original release version support cycle and the first service pack support cycle are shown.