Investigate malicious email that was delivered in Microsoft 365
Tip
Did you know you can try the features in Microsoft Defender XDR for Office 365 Plan 2 for free? Use the 90-day Defender for Office 365 trial at the Microsoft Defender portal trials hub. Learn about who can sign up and trial terms on Try Microsoft Defender for Office 365.
Microsoft 365 organizations that have Microsoft Defender for Office 365 included in their subscription or purchased as an add-on have Explorer (also known as Threat Explorer) or Real-time detections. These features are powerful, near real-time tools to help Security Operations (SecOps) teams investigate and respond to threats. For more information, see About Threat Explorer and Real-time detections in Microsoft Defender for Office 365.
Threat Explorer and Real-time detections allow you to investigate activities that put people in your organization at risk, and to take action to protect your organization. For example:
- Find and delete messages.
- Identify the IP address of a malicious email sender.
- Start an incident for further investigation.
This article explains how to use Threat Explorer and Real-time detections to find malicious email in recipient mailboxes.
Tip
To go directly to the remediation procedures, see Remediate malicious email delivered in Office 365.
For other email scenarios using Threat Explorer and Real-time detections, see the following articles:
What do you need to know before you begin?
Threat Explorer is included in Defender for Office 365 Plan 2. Real-time detections is included in Defender for Office Plan 1:
- The differences between Threat Explorer and Real-time detections are described in About Threat Explorer and Real-time detections in Microsoft Defender for Office 365.
- The differences between Defender for Office 365 Plan 2 and Defender for Office Plan 1 are described in the Defender for Office 365 Plan 1 vs. Plan 2 cheat sheet.
For filter properties that require you to select one or more available values, using the property in the filter condition with all values selected has the same result as not using the property in the filter condition.
For permissions and licensing requirements for Threat Explorer and Real-time detections, see Permissions and licensing for Threat Explorer and Real-time detections.
Find suspicious email that was delivered
Use one of the following steps to open Threat Explorer or Real-time detections:
- Threat Explorer: In the Defender portal at https://security.microsoft.com, go to Email & Security > Explorer. Or, to go directly to the Explorer page, use https://security.microsoft.com/threatexplorerv3.
- Real-time detections: In the Defender portal at https://security.microsoft.com, go to Email & Security > Real-time detections. Or, to go directly to the Real-time detections page, use https://security.microsoft.com/realtimereportsv3.
On the Explorer or Real-time detections page, select an appropriate view:
- Threat Explorer: Verify the All email view is selected.
- Real-time detections: Verify the Malware view is selected, or select the Phish view.
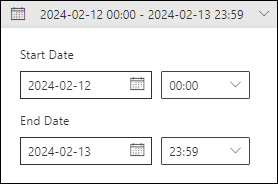
Select the date/time range. The default is yesterday and today.
Create one or more filter conditions using some or all of the following targeted properties and values. For complete instructions, see Property filters in Threat Explorer and Real-time detections. For example:
Delivery action: The action taken on an email due to existing policies or detections. Useful values are:
- Delivered: Email delivered to the user's Inbox or other folder where the user can access the message.
- Junked: Email delivered to the user's Junk Email folder or Deleted Items folder where the user can access the message.
- Blocked: Email messages that were quarantined, that failed delivery, or were dropped.
Original delivery location: Where email went before any automatic or manual post-delivery actions by the system or admins (for example, ZAP or moved to quarantine). Useful values are:
- Deleted items folder
- Dropped: The message was lost somewhere in mail flow.
- Failed: The message failed to reach the mailbox.
- Inbox/folder
- Junk folder
- On-prem/external: The mailbox doesn't exist in the Microsoft 365 organization.
- Quarantine
- Unknown: For example, after delivery, an Inbox rule moved the message to a default folder (for example, Draft or Archive) instead of to the Inbox or Junk Email folder.
Last delivery location: Where email ended-up after any automatic or manual post-delivery actions by the system or admins. The same values are available from Original delivery location.
Directionality: Valid values are:
- Inbound
- Intra-org
- Outbound
This information can help identify spoofing and impersonation. For example, messages from internal domain senders should be Intra-org, not Inbound.
Additional action: Valid values are:
- Automated remediation (Defender for Office 365 Plan 2)
- Dynamic Delivery: For more information, see Dynamic Delivery in Safe Attachments policies.
- Manual remediation
- None
- Quarantine release
- Reprocessed: The message was retroactively identified as good.
- ZAP: For more information, see Zero-hour auto purge (ZAP) in Microsoft Defender for Office 365.
Primary override: If organization or user settings allowed or blocked messages that would have otherwise been blocked or allowed. Values are:
- Allowed by organization policy
- Allowed by user policy
- Blocked by organization policy
- Blocked by user policy
- None
These categories are further refined by the Primary override source property.
Primary override source The type of organization policy or user setting that allowed or blocked messages that would have otherwise been blocked or allowed. Values are:
- 3rd Party Filter
- Admin initiated time travel
- Antimalware policy block by file type: Common attachments filter in anti-malware policies
- Antispam policy settings
- Connection policy: Configure connection filtering
- Exchange transport rule (mail flow rule)
- Exclusive mode (User override): The Only trust email from addresses in my Safe senders and domains list and Safe mailing lists setting in the safelist collection on a mailbox.
- Filtering skipped due to on-prem organization
- IP region filter from policy: The From these countries filter in anti-spam policies.
- Language filter from policy: The Contains specific languages filter in anti-spam policies.
- Phishing Simulation: Configure third-party phishing simulations in the advanced delivery policy
- Quarantine release: Release quarantined email
- SecOps Mailbox: Configure SecOps mailboxes in the advanced delivery policy
- Sender address list (Admin Override): The allowed senders list or blocked senders list in anti-spam policies.
- Sender address list (User override): Sender email addresses in the Blocked Senders list in the safelist collection on a mailbox.
- Sender domain list (Admin Override): The allowed domains list or blocked domains list in anti-spam policies.
- Sender domain list (User override): Sender domains in the Blocked Senders list in the safelist collection on a mailbox.
- Tenant Allow/Block List file block: Create block entries for files
- Tenant Allow/Block List sender email address block: Create block entries for domains and email addresses
- Tenant Allow/Block List spoof block: Create block entries for spoofed senders
- Tenant Allow/Block List URL block: Create block entries for URLs
- Trusted contact list (User override): The Trust email from my contacts setting in the safelist collection on a mailbox.
- Tenant Allow/Block List file block: Create block entries for files
- Trusted domain (User override): Sender domains in the Safe Senders list in the safelist collection on a mailbox.
- Trusted recipient (User override): Recipient email addresses or domains in the Safe Recipients list in the safelist collection on a mailbox.
- Trusted senders only (User override): The Safe Lists Only: Only mail from people or domains on your Safe Senders List or Safe Recipients List will be delivered to your Inbox setting in the safelist collection on a mailbox.
Override source: Same available values as Primary override source.
URL threat: Valid values are:
- Malware
- Phish
- Spam
When you're finished configuring date/time and property filters, select Refresh.
The Email tab (view) in the details area of the All email, Malware, or Phish views contains the details you need to investigate suspicious email.
For example, Use the Delivery Action, Original delivery location, and Last delivery location columns in the Email tab (view) to get a complete picture of where the affected messages went. The values were explained in Step 4.
Use ![]() Export to selectively export up to 200,000 filtered or unfiltered results to a CSV file.
Export to selectively export up to 200,000 filtered or unfiltered results to a CSV file.
Remediate malicious email that was delivered
After you identify the malicious email messages that were delivered, you can remove them from recipient mailboxes. For instructions, see Remediate malicious email delivered in Microsoft 365.
Related articles
Remediate malicious email delivered in Office 365