Catatan
Akses ke halaman ini memerlukan otorisasi. Anda dapat mencoba masuk atau mengubah direktori.
Akses ke halaman ini memerlukan otorisasi. Anda dapat mencoba mengubah direktori.
File yang dipetakan ke memori berisi konten dari sebuah file dalam memori virtual. Pemetaan antara file dan ruang memori ini memungkinkan aplikasi, termasuk beberapa proses, untuk memodifikasi file dengan membaca dan menulis langsung ke memori. Anda dapat menggunakan kode terkelola untuk mengakses file yang dipetakan memori dengan cara yang sama seperti fungsi Windows asli mengakses file yang dipetakan memori, seperti yang dijelaskan dalam Mengelola file Memory-Mapped.
Ada dua jenis file yang dipetakan memori:
File peta memori yang bertahan
File yang disimpan secara permanen adalah file memori yang dipetakan yang terkait dengan file sumber di dalam disk. Ketika proses terakhir telah selesai bekerja dengan file, data disimpan ke file sumber pada disk. File yang dipetakan memori ini cocok untuk bekerja dengan file sumber yang sangat besar.
File memori yang dipetakan dan tidak bertahan
File yang tidak bertahan adalah file yang dipetakan memori yang tidak terkait dengan file pada disk. Ketika proses terakhir selesai menggunakan file, data tersebut akan terhapus dan file tersebut diambil alih kembali oleh pengumpulan sampah. File-file ini cocok untuk membuat memori bersama untuk komunikasi antar-proses (IPC).
Proses, Tampilan, dan Pengelolaan Memori
File pemetaan memori dapat digunakan bersama oleh beberapa proses. Proses dapat memetakan ke file yang dipetakan memori yang sama dengan menggunakan nama umum yang ditetapkan oleh proses yang membuat file.
Untuk bekerja dengan file yang dipetakan memori, Anda harus membuat tampilan seluruh file yang dipetakan memori atau bagian darinya. Anda juga dapat membuat beberapa tampilan ke bagian yang sama dari file peta memori, sehingga memungkinkan memori ini diakses secara bersamaan. Agar dua tampilan tetap bersamaan, tampilan harus dibuat dari file yang dipetakan memori yang sama.
Beberapa tampilan mungkin juga diperlukan jika file lebih besar dari ukuran ruang memori logis aplikasi yang tersedia untuk pemetaan memori (2 GB pada komputer 32-bit).
Ada dua jenis tampilan: tampilan akses aliran dan tampilan akses acak. Gunakan tampilan akses aliran untuk akses berurutan ke file; ini direkomendasikan untuk file dan IPC yang tidak bertahan. Penayangan akses acak lebih disukai untuk bekerja dengan file yang disimpan.
File yang dipetakan memori diakses melalui manajer memori sistem operasi, sehingga file secara otomatis dipartisi ke dalam sejumlah halaman dan diakses sesuai kebutuhan. Anda tidak perlu menangani manajemen memori sendiri.
Ilustrasi berikut menunjukkan bagaimana proses-proses dapat memiliki beberapa tampilan yang saling tumpang tindih ke file yang dipetakan ke memori yang sama pada waktu yang bersamaan.
Gambar berikut menunjukkan beberapa tampilan yang saling tumpang tindih ke file yang dipetakan ke memori.
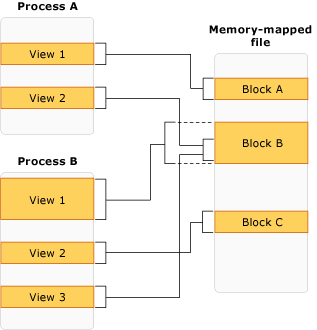
Pemrograman dengan File Memory-Mapped
Tabel berikut ini menyediakan panduan untuk menggunakan objek file yang dipetakan memori dan anggotanya.
| Tugas | Metode atau properti yang akan digunakan |
|---|---|
| Untuk mendapatkan MemoryMappedFile objek yang mewakili file yang dipetakan memori yang bertahan dari file pada disk. | MemoryMappedFile.CreateFromFile metode. |
| Untuk mendapatkan MemoryMappedFile objek yang mewakili file yang dipetakan memori yang tidak bertahan (tidak terkait dengan file pada disk). |
MemoryMappedFile.CreateNew metode. - atau - MemoryMappedFile.CreateOrOpen metode. |
| Untuk mendapatkan objek MemoryMappedFile dari file yang dipetakan memori yang sudah ada (baik yang bersifat persisten maupun tidak persisten). | MemoryMappedFile.OpenExisting metode. |
| Untuk mendapatkan UnmanagedMemoryStream objek untuk tampilan yang diakses secara berurutan ke file yang dipetakan ke memori. | MemoryMappedFile.CreateViewStream metode. |
| Untuk mendapatkan UnmanagedMemoryAccessor objek untuk tampilan akses acak ke file yang dipetakan memori. | MemoryMappedFile.CreateViewAccessor metode. |
| Untuk mendapatkan objek SafeMemoryMappedViewHandle untuk digunakan dengan kode yang tidak dikelola. |
MemoryMappedFile.SafeMemoryMappedFileHandle properti. - atau - MemoryMappedViewAccessor.SafeMemoryMappedViewHandle properti. - atau - MemoryMappedViewStream.SafeMemoryMappedViewHandle properti. |
| Untuk menunda alokasi memori hingga tampilan dibuat (file yang tidak bertahan saja). (Untuk menentukan ukuran halaman sistem saat ini, gunakan Environment.SystemPageSize properti .) |
CreateNew metode dengan MemoryMappedFileOptions.DelayAllocatePages nilai . - atau - CreateOrOpen metode yang memiliki MemoryMappedFileOptions enumerasi sebagai parameter. |
Keamanan
Anda dapat menerapkan hak akses saat membuat file yang dipetakan memori, dengan menggunakan metode berikut yang mengambil MemoryMappedFileAccess enumerasi sebagai parameter:
Anda dapat menentukan hak akses untuk membuka file yang dipetakan memori yang ada dengan menggunakan OpenExisting metode yang mengambil MemoryMappedFileRights sebagai parameter.
Selain itu, Anda dapat menyertakan MemoryMappedFileSecurity objek yang berisi aturan akses yang telah ditentukan sebelumnya.
Untuk menerapkan aturan akses baru atau yang diubah ke file yang dipetakan memori, gunakan metode .SetAccessControl Untuk mengambil aturan akses atau audit dari file yang ada, gunakan metode .GetAccessControl
Contoh
File Memory-Mapped yang Dipertahankan
Metode CreateFromFile membuat file yang dipetakan ke memori dari file yang sudah ada di disk.
Contoh berikut membuat tampilan yang dipetakan memori dari bagian dari file yang sangat besar dan memanipulasi sebagiannya.
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.IO.MemoryMappedFiles;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
long offset = 0x10000000; // 256 megabytes
long length = 0x20000000; // 512 megabytes
// Create the memory-mapped file.
using (var mmf = MemoryMappedFile.CreateFromFile(@"c:\ExtremelyLargeImage.data", FileMode.Open,"ImgA"))
{
// Create a random access view, from the 256th megabyte (the offset)
// to the 768th megabyte (the offset plus length).
using (var accessor = mmf.CreateViewAccessor(offset, length))
{
int colorSize = Marshal.SizeOf(typeof(MyColor));
MyColor color;
// Make changes to the view.
for (long i = 0; i < length; i += colorSize)
{
accessor.Read(i, out color);
color.Brighten(10);
accessor.Write(i, ref color);
}
}
}
}
}
public struct MyColor
{
public short Red;
public short Green;
public short Blue;
public short Alpha;
// Make the view brighter.
public void Brighten(short value)
{
Red = (short)Math.Min(short.MaxValue, (int)Red + value);
Green = (short)Math.Min(short.MaxValue, (int)Green + value);
Blue = (short)Math.Min(short.MaxValue, (int)Blue + value);
Alpha = (short)Math.Min(short.MaxValue, (int)Alpha + value);
}
}
Imports System.IO
Imports System.IO.MemoryMappedFiles
Imports System.Runtime.InteropServices
Class Program
Sub Main()
Dim offset As Long = &H10000000 ' 256 megabytes
Dim length As Long = &H20000000 ' 512 megabytes
' Create the memory-mapped file.
Using mmf = MemoryMappedFile.CreateFromFile("c:\ExtremelyLargeImage.data", FileMode.Open, "ImgA")
' Create a random access view, from the 256th megabyte (the offset)
' to the 768th megabyte (the offset plus length).
Using accessor = mmf.CreateViewAccessor(offset, length)
Dim colorSize As Integer = Marshal.SizeOf(GetType(MyColor))
Dim color As MyColor
Dim i As Long = 0
' Make changes to the view.
Do While (i < length)
accessor.Read(i, color)
color.Brighten(10)
accessor.Write(i, color)
i += colorSize
Loop
End Using
End Using
End Sub
End Class
Public Structure MyColor
Public Red As Short
Public Green As Short
Public Blue As Short
Public Alpha As Short
' Make the view brighter.
Public Sub Brighten(ByVal value As Short)
Red = CType(Math.Min(Short.MaxValue, (CType(Red, Integer) + value)), Short)
Green = CType(Math.Min(Short.MaxValue, (CType(Green, Integer) + value)), Short)
Blue = CType(Math.Min(Short.MaxValue, (CType(Blue, Integer) + value)), Short)
Alpha = CType(Math.Min(Short.MaxValue, (CType(Alpha, Integer) + value)), Short)
End Sub
End Structure
Contoh berikut membuka file peta memori yang sama untuk proses lain.
using System;
using System.IO.MemoryMappedFiles;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Assumes another process has created the memory-mapped file.
using (var mmf = MemoryMappedFile.OpenExisting("ImgA"))
{
using (var accessor = mmf.CreateViewAccessor(4000000, 2000000))
{
int colorSize = Marshal.SizeOf(typeof(MyColor));
MyColor color;
// Make changes to the view.
for (long i = 0; i < 1500000; i += colorSize)
{
accessor.Read(i, out color);
color.Brighten(20);
accessor.Write(i, ref color);
}
}
}
}
}
public struct MyColor
{
public short Red;
public short Green;
public short Blue;
public short Alpha;
// Make the view brigher.
public void Brighten(short value)
{
Red = (short)Math.Min(short.MaxValue, (int)Red + value);
Green = (short)Math.Min(short.MaxValue, (int)Green + value);
Blue = (short)Math.Min(short.MaxValue, (int)Blue + value);
Alpha = (short)Math.Min(short.MaxValue, (int)Alpha + value);
}
}
Imports System.IO.MemoryMappedFiles
Imports System.Runtime.InteropServices
Class Program
Public Shared Sub Main(ByVal args As String())
' Assumes another process has created the memory-mapped file.
Using mmf = MemoryMappedFile.OpenExisting("ImgA")
Using accessor = mmf.CreateViewAccessor(4000000, 2000000)
Dim colorSize As Integer = Marshal.SizeOf(GetType(MyColor))
Dim color As MyColor
' Make changes to the view.
Dim i As Long = 0
While i < 1500000
accessor.Read(i, color)
color.Brighten(30)
accessor.Write(i, color)
i += colorSize
End While
End Using
End Using
End Sub
End Class
Public Structure MyColor
Public Red As Short
Public Green As Short
Public Blue As Short
Public Alpha As Short
' Make the view brigher.
Public Sub Brighten(ByVal value As Short)
Red = CShort(Math.Min(Short.MaxValue, CInt(Red) + value))
Green = CShort(Math.Min(Short.MaxValue, CInt(Green) + value))
Blue = CShort(Math.Min(Short.MaxValue, CInt(Blue) + value))
Alpha = CShort(Math.Min(Short.MaxValue, CInt(Alpha) + value))
End Sub
End Structure
File Memory-Mapped yang Tidak Tersimpan Permanen
Metode CreateNew dan CreateOrOpen membuat file yang dipetakan memori yang tidak dipetakan ke file yang ada pada disk.
Contoh berikut terdiri dari tiga proses terpisah (aplikasi konsol) yang menulis nilai Boolean ke file yang dipetakan memori. Urutan tindakan berikut terjadi:
Process Amembuat file yang dipetakan dalam memori dan menulis nilai ke dalamnya.Process Bmembuka file yang dipetakan memori dan menulis nilai ke file tersebut.Process Cmembuka file yang dipetakan memori dan menulis nilai ke file tersebut.Process Amembaca dan menampilkan nilai dari file yang dipetakan memori.Setelah
Process Aselesai dengan file dengan pemetaan memori, file tersebut segera diambil kembali oleh pengumpulan sampah.
Untuk menjalankan contoh ini, lakukan hal berikut:
Kompilasi aplikasi dan buka tiga jendela Prompt Perintah.
Pada jendela Prompt Perintah pertama, jalankan
Process A.Di jendela Prompt Perintah kedua, jalankan
Process B.Kembali ke
Process Adan tekan ENTER.Pada jendela Prompt Perintah ketiga, jalankan
Process C.Kembali ke
Process Adan tekan ENTER.
Outputnya Process A adalah sebagai berikut:
Start Process B and press ENTER to continue.
Start Process C and press ENTER to continue.
Process A says: True
Process B says: False
Process C says: True
Proses A
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.IO.MemoryMappedFiles;
using System.Threading;
class Program
{
// Process A:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
using (MemoryMappedFile mmf = MemoryMappedFile.CreateNew("testmap", 10000))
{
bool mutexCreated;
Mutex mutex = new Mutex(true, "testmapmutex", out mutexCreated);
using (MemoryMappedViewStream stream = mmf.CreateViewStream())
{
BinaryWriter writer = new BinaryWriter(stream);
writer.Write(1);
}
mutex.ReleaseMutex();
Console.WriteLine("Start Process B and press ENTER to continue.");
Console.ReadLine();
Console.WriteLine("Start Process C and press ENTER to continue.");
Console.ReadLine();
mutex.WaitOne();
using (MemoryMappedViewStream stream = mmf.CreateViewStream())
{
BinaryReader reader = new BinaryReader(stream);
Console.WriteLine($"Process A says: {reader.ReadBoolean()}");
Console.WriteLine($"Process B says: {reader.ReadBoolean()}");
Console.WriteLine($"Process C says: {reader.ReadBoolean()}");
}
mutex.ReleaseMutex();
}
}
}
Imports System.IO
Imports System.IO.MemoryMappedFiles
Imports System.Threading
Module Module1
' Process A:
Sub Main()
Using mmf As MemoryMappedFile = MemoryMappedFile.CreateNew("testmap", 10000)
Dim mutexCreated As Boolean
Dim mTex As Mutex = New Mutex(True, "testmapmutex", mutexCreated)
Using Stream As MemoryMappedViewStream = mmf.CreateViewStream()
Dim writer As BinaryWriter = New BinaryWriter(Stream)
writer.Write(1)
End Using
mTex.ReleaseMutex()
Console.WriteLine("Start Process B and press ENTER to continue.")
Console.ReadLine()
Console.WriteLine("Start Process C and press ENTER to continue.")
Console.ReadLine()
mTex.WaitOne()
Using Stream As MemoryMappedViewStream = mmf.CreateViewStream()
Dim reader As BinaryReader = New BinaryReader(Stream)
Console.WriteLine("Process A says: {0}", reader.ReadBoolean())
Console.WriteLine("Process B says: {0}", reader.ReadBoolean())
Console.WriteLine("Process C says: {0}", reader.ReadBoolean())
End Using
mTex.ReleaseMutex()
End Using
End Sub
End Module
Proses B
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.IO.MemoryMappedFiles;
using System.Threading;
class Program
{
// Process B:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
using (MemoryMappedFile mmf = MemoryMappedFile.OpenExisting("testmap"))
{
Mutex mutex = Mutex.OpenExisting("testmapmutex");
mutex.WaitOne();
using (MemoryMappedViewStream stream = mmf.CreateViewStream(1, 0))
{
BinaryWriter writer = new BinaryWriter(stream);
writer.Write(0);
}
mutex.ReleaseMutex();
}
}
catch (FileNotFoundException)
{
Console.WriteLine("Memory-mapped file does not exist. Run Process A first.");
}
}
}
Imports System.IO
Imports System.IO.MemoryMappedFiles
Imports System.Threading
Module Module1
' Process B:
Sub Main()
Try
Using mmf As MemoryMappedFile = MemoryMappedFile.OpenExisting("testmap")
Dim mTex As Mutex = Mutex.OpenExisting("testmapmutex")
mTex.WaitOne()
Using Stream As MemoryMappedViewStream = mmf.CreateViewStream(1, 0)
Dim writer As BinaryWriter = New BinaryWriter(Stream)
writer.Write(0)
End Using
mTex.ReleaseMutex()
End Using
Catch noFile As FileNotFoundException
Console.WriteLine("Memory-mapped file does not exist. Run Process A first." & vbCrLf & noFile.Message)
End Try
End Sub
End Module
Proses C
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.IO.MemoryMappedFiles;
using System.Threading;
class Program
{
// Process C:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
using (MemoryMappedFile mmf = MemoryMappedFile.OpenExisting("testmap"))
{
Mutex mutex = Mutex.OpenExisting("testmapmutex");
mutex.WaitOne();
using (MemoryMappedViewStream stream = mmf.CreateViewStream(2, 0))
{
BinaryWriter writer = new BinaryWriter(stream);
writer.Write(1);
}
mutex.ReleaseMutex();
}
}
catch (FileNotFoundException)
{
Console.WriteLine("Memory-mapped file does not exist. Run Process A first, then B.");
}
}
}
Imports System.IO
Imports System.IO.MemoryMappedFiles
Imports System.Threading
Module Module1
' Process C:
Sub Main()
Try
Using mmf As MemoryMappedFile = MemoryMappedFile.OpenExisting("testmap")
Dim mTex As Mutex = Mutex.OpenExisting("testmapmutex")
mTex.WaitOne()
Using Stream As MemoryMappedViewStream = mmf.CreateViewStream(2, 0)
Dim writer As BinaryWriter = New BinaryWriter(Stream)
writer.Write(1)
End Using
mTex.ReleaseMutex()
End Using
Catch noFile As FileNotFoundException
Console.WriteLine("Memory-mapped file does not exist. Run Process A first, then B." & vbCrLf & noFile.Message)
End Try
End Sub
End Module
