Nóta
Aðgangur að þessari síðu krefst heimildar. Þú getur prófað aðskrá þig inn eða breyta skráasöfnum.
Aðgangur að þessari síðu krefst heimildar. Þú getur prófað að breyta skráasöfnum.
APPLIES TO: Basic | Basic v2 | Standard | Standard v2 | Premium | Premium v2
An Azure API Management service instance can scale automatically based on a set of rules. This behavior can be enabled and configured through Azure Monitor autoscale.
The article walks through the process of configuring autoscale and suggests optimal configuration of autoscale rules.
Note
- In service tiers that support multiple scale units, you can also manually scale your API Management instance.
- An API Management service in the Consumption tier scales automatically based on the traffic - without any additional configuration needed.
Important
Changes to your API Management service's infrastructure (such as configuring custom domains, adding CA certificates, scaling, virtual network configuration, availability zone changes, and region additions) can take 15 minutes or longer to complete, depending on the service tier and the size of the deployment. Expect longer times for an instance with a greater number of scale units or multi-region configuration. Rolling changes to API Management are executed carefully to preserve capacity and availability.
While the service is updating, other service infrastructure changes can't be made. However, you can configure APIs, products, policies, and user settings. The service will not experience gateway downtime, and API Management will continue to service API requests without interruption (except in the Developer tier).
Prerequisites
To follow the steps from this article, you must:
- Have an active Azure subscription.
- Have an Azure API Management instance. For more information, see Create an Azure API Management instance.
- Understand the concept of capacity of an API Management instance.
- Understand manual scaling of an API Management instance, including cost consequences.
Azure API Management autoscale limitations
Certain limitations and consequences of scaling decisions need to be considered before configuring autoscale behavior.
- The pricing tier of your API Management instance determines the maximum number of units you may scale to. For example, the Standard tier can be scaled to 4 units. You can add any number of units to the Premium tier.
- If the service is locked by another operation, the scaling request will fail and retry automatically.
- If your service instance is deployed in multiple regions (locations), only units in the Primary location can be autoscaled with Azure Monitor autoscale. Units in other locations can be scaled manually or using custom scaling tools.
- If your service instance is configured with availability zones in the Primary location, we recommend leaving the default Automatic setting for availability zones. If you select specific zones, the number of API Management units in autoscale rules and limits must be a multiple of the number of zones configured.
Enable and configure autoscale for an API Management instance
Follow these steps to configure autoscale for an Azure API Management service:
Sign in to the Azure portal, and navigate to your API Management instance.
In the left menu, select Deployment + infrastructure > Scale out (auto-scale), and then select Custom autoscale.
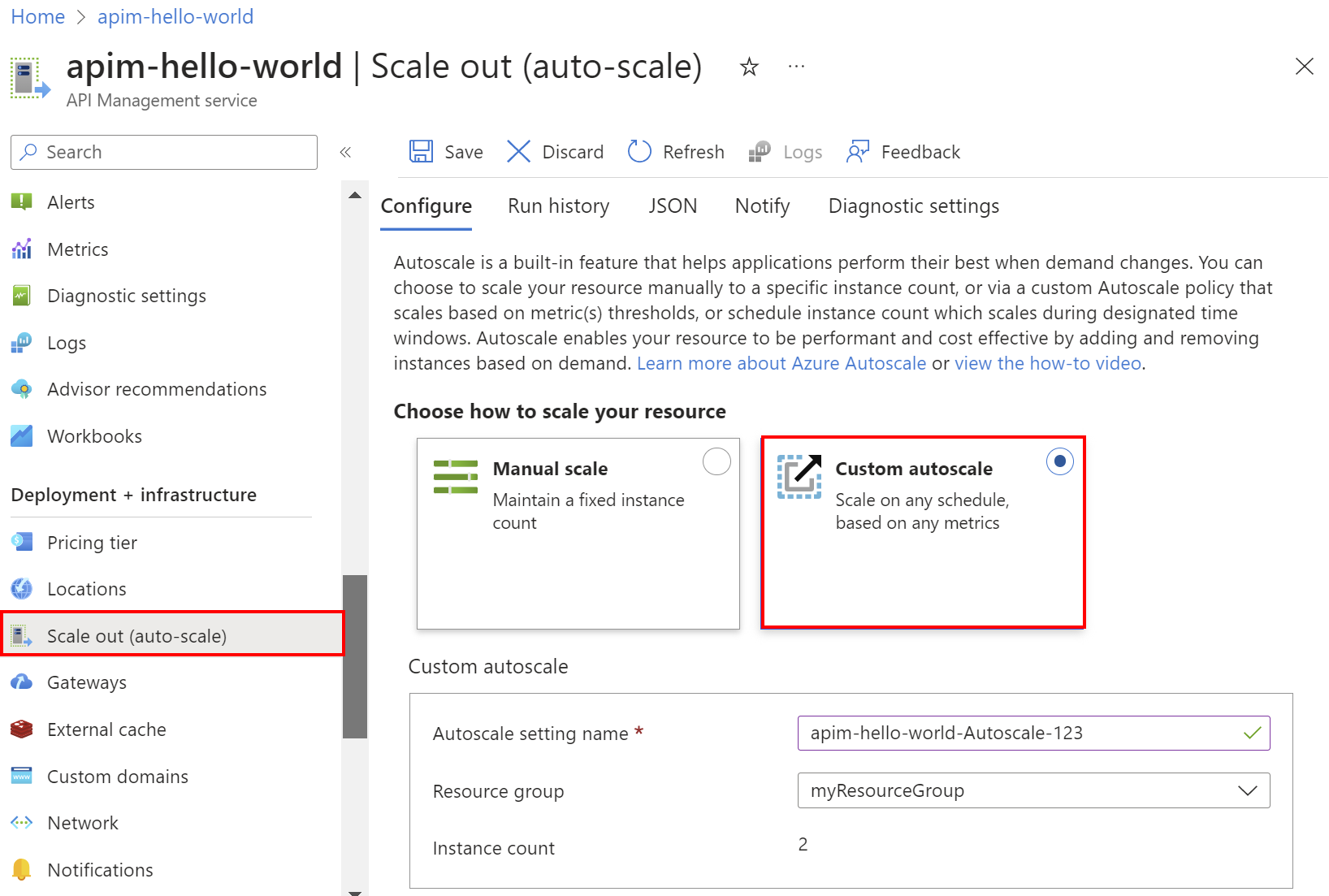
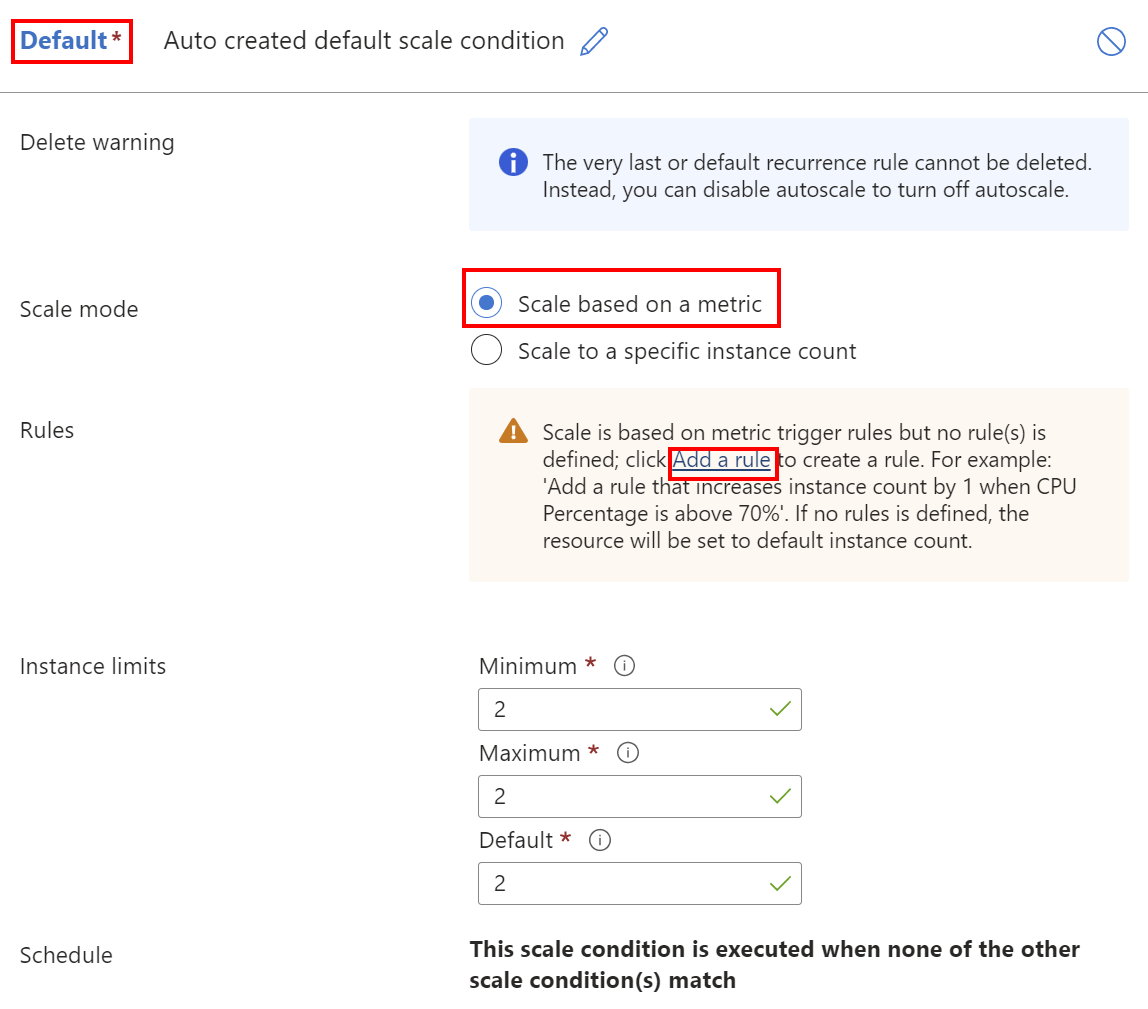
In the Default scale condition, select Scale based on a metric, and then select Add a rule.
Define a new scale-out rule.
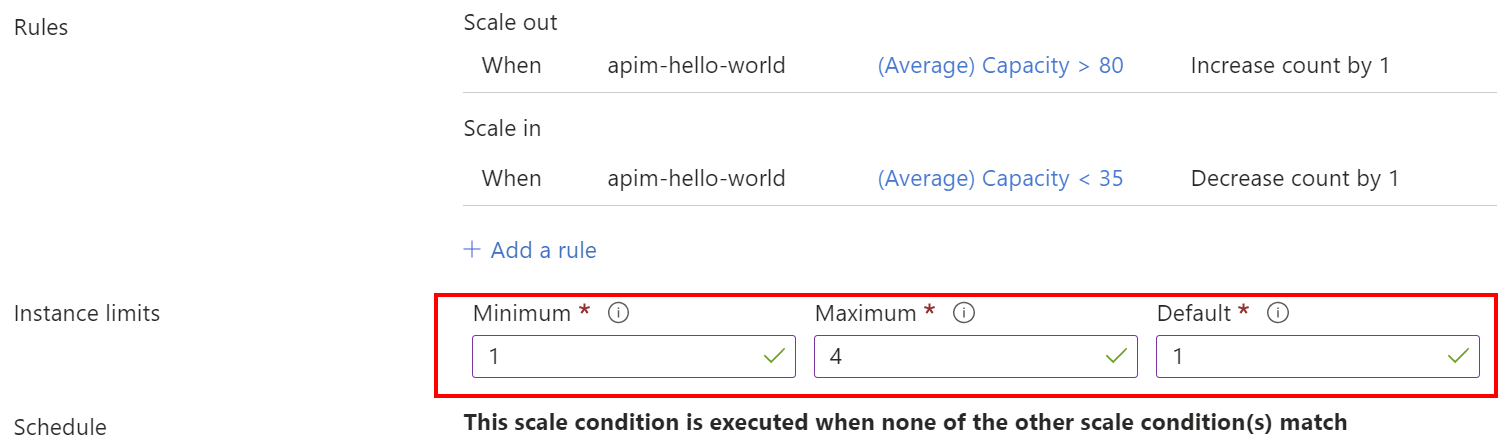
For example, a scale-out rule could trigger addition of 1 API Management unit, when the average capacity metric over the previous 30 minutes exceeds 70%. The following table provides an example configuration for such a rule. Review the preceding limitations when defining a scale-out rule in your environment.
Parameter Value Notes Metric source Current resource Define the rule based on the current API Management resource metrics. Criteria Metric name Capacity Capacity metric is one of the API Management metrics reflecting usage of resources by an Azure API Management instance. Choose a capacity metric supported in your API Management service tier. Location Select the primary location of the API Management instance Operator Greater than Metric threshold 70% The threshold for the averaged capacity metric. For considerations on setting this threshold, see Using capacity for scaling decisions. Duration (in minutes) 30 The timespan to average the capacity metric over is specific to usage patterns. The longer the duration, the smoother the reaction will be. Intermittent spikes will have less effect on the scale-out decision. However, it will also delay the scale-out trigger. Time grain statistic Average Action Operation Increase count by Instance count 1 Scale out the Azure API Management instance by 1 unit. Cool down (minutes) 60 In most cases, the cool down period of 60 minutes prevents from triggering many scale-outs. Select Add to save the rule.
To add another rule, select Add a rule.
This time, a scale-in rule needs to be defined. It ensures that resources aren't being wasted, when the usage of APIs decreases.
Define a new scale-in rule.
For example, a scale-in rule could trigger a removal of 1 API Management unit when the average capacity metric over the previous 30 minutes is lower than 35%. The following table provides an example configuration for such a rule.
Parameter Value Notes Metric source Current resource Define the rule based on the current API Management resource metrics. Criteria Time aggregation Average Metric name Capacity Same metric as the one used for the scale-out rule. Location Select the primary location of the API Management instance Operator Less than Threshold 35% As with the scale-out rule, this value heavily depends on the usage patterns of the API Management instance. Duration (in minutes) 30 Same value as the one used for the scale-out rule. Time grain statistic Average Action Operation Decrease count by Opposite to what was used for the scale-out rule. Instance count 1 Same value as the one used for the scale-out rule. Cool down (minutes) 90 Scale-in should be more conservative than a scale-out, so the cool down period should be longer. Select Add to save the rule.
In Instance limits, select the Minimum, Maximum, and Default number of API Management units.
Note
API Management has a limit of units an instance can scale out to. The limit depends on the service tier.
Select Save. Your autoscale is configured.