Use private endpoints for access control
You can use private endpoints for your Azure Web PubSub resource to allow clients in a virtual network (VNet) to securely access data over a private link. The private endpoint uses an IP address from the VNet address space for your Web PubSub resource. Network traffic between the clients on the VNet and your Web PubSub resource traverses a private link on the Microsoft network, eliminating exposure on the public internet.
Using private endpoints for your Web PubSub resource helps you:
- Secure your Web PubSub resource by using network access control to block all connections on the public endpoint for Web PubSub.
- Increase security for the VNet by enabling you to block exfiltration of data from the VNet.
- Securely connect to Web PubSub from on-premises networks that connect to the VNet by using a VPN or Azure ExpressRoute with private peering.
Use private endpoints in a virtual network
A private endpoint is a special network interface for an Azure service in your VNet. When you create a private endpoint for your Web PubSub resource, it provides secure connectivity between clients on your VNet and your service. The private endpoint is assigned an IP address from the IP address range of your VNet. The connection between the private endpoint and Web PubSub uses a secure private link.
Applications in the VNet can connect to Web PubSub resources seamlessly by using the private endpoint. The applications use the same connection strings and authorization mechanisms that they would use otherwise.
Private endpoints can be used with all protocols that the Web PubSub resource supports, including REST API.
When you create a private endpoint for a Web PubSub resource in your VNet, a consent request is sent for approval to the Web PubSub resource owner. If the user who requests the private endpoint is also an owner of the Web PubSub resource, this consent request is automatically approved.
You can manage consent requests and private endpoints for your Web PubSub resource on the Private endpoints tab in the Azure portal.
Tip
If you want to restrict access to your Web PubSub resource through the private endpoint only, set up network access control to deny or control access through the public endpoint.
Connect to a private endpoint
Clients on a VNet that uses a private endpoint should use the same connection string for the Web PubSub resource that clients that connect via a public endpoint use. We rely on Domain Name System (DNS) resolution to automatically route the connections from the VNet to Web PubSub over a private link.
Important
Use the same connection string to connect to Web PubSub by using private endpoints as you would use for a public endpoint. Don't connect to Web PubSub by using its privatelink subdomain URL.
We create a private DNS zone attached to the VNet with the necessary updates for the private endpoints, by default. If you're using your own DNS server, you might need to make other changes to your DNS configuration. The next section describes the updates that are required for private endpoints.
DNS changes for private endpoints
When you create a private endpoint, the DNS CNAME resource record for your Web PubSub resource is updated to an alias in a subdomain that has the prefix privatelink. By default, we also create a private DNS zone that corresponds to the privatelink subdomain, with the DNS A resource records for the private endpoints.
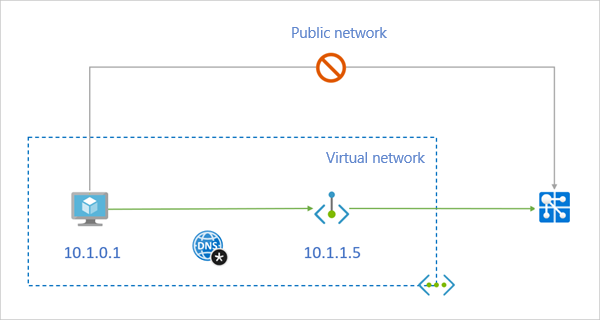
When you resolve your Web PubSub resource domain name from outside the VNet with the private endpoint, it resolves to the public endpoint of the Web PubSub resource. When resolved from the VNet hosting the private endpoint, the domain name resolves to the private endpoint's IP address.
For the preceding illustrated example, the DNS resource records for the Web PubSub resource sample when it's resolved from outside the VNet hosting the private endpoint:
| Name | Type | Value |
|---|---|---|
sample.webpubsub.azure.com |
CNAME | sample.privatelink.webpubsub.azure.com |
sample.privatelink.webpubsub.azure.com |
A | <Web PubSub public IP address> |
You can deny or control access for clients outside the VNet through the public endpoint by using network access control.
The DNS resource records for the Web PubSub resource sample when it's resolved by a client in the VNet that hosts the private endpoint is similar to this example:
| Name | Type | Value |
|---|---|---|
sample.webpubsub.azure.com |
CNAME | sample.privatelink.webpubsub.azure.com |
sample.privatelink.webpubsub.azure.com |
A | 10.1.1.5 |
This approach gives access to Web PubSub by using the same connection string for clients on the VNet that hosts the private endpoint and to clients outside the VNet.
If you use a custom DNS server on your network, clients must be able to resolve the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) for the Web PubSub resource endpoint to the private endpoint IP address. You should configure your DNS server to delegate your private link subdomain to the private DNS zone for the VNet or configure the A records for sample.privatelink.webpubsub.azure.com to use the private endpoint IP address.
Tip
If you use a custom or on-premises DNS server, you should configure your DNS server to resolve the Web PubSub resource name in the privatelink subdomain to the private endpoint IP address. You can do this by delegating the privatelink subdomain to the private DNS zone of the VNet or by configuring the DNS zone on your DNS server and then adding the DNS A records.
We recommend that you use privatelink.webpubsub.azure.com for the DNS zone name for private endpoints in a Web PubSub resource.
For more information about configuring your own DNS server to support private endpoints, see the following articles:
Create a private endpoint
The following sections describe how to create a private endpoint and a new instance of Web PubSub and how to create a private endpoint for an existing instance of Web PubSub.
Create a private endpoint in a new instance of Web PubSub
In the Azure portal, create a new instance of Azure Web PubSub. On the Networking tab, for Connectivity method, select Private endpoint.
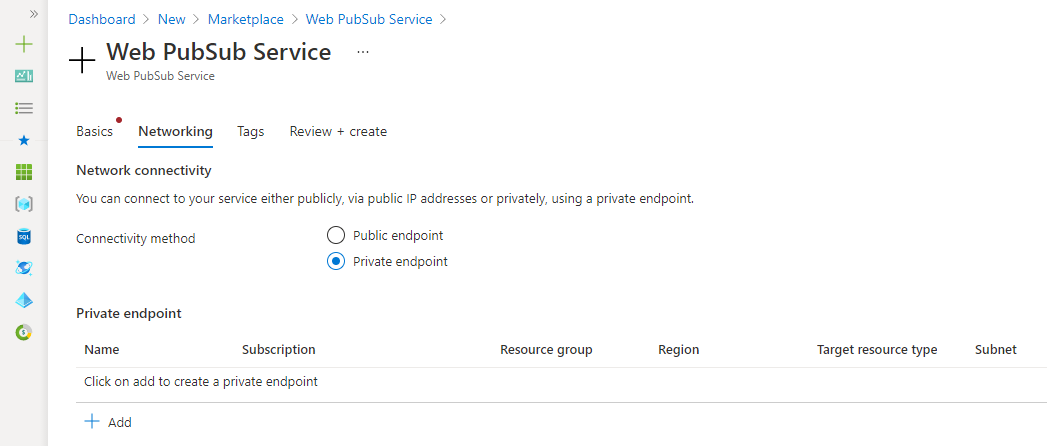
Select Add. Select or enter the subscription, the resource group name, the Azure region, and a name for the new private endpoint. Choose a virtual network and subnet to use.
Select Review + create.
Create a private endpoint for an existing Web PubSub resource
In the Azure portal, go to your Web PubSub resource.
On the left menu under Settings, select Private endpoint connections.
Select Private endpoint.
Select or enter values for subscription, resource group, resource name, and region for the new private endpoint.
Select the target Web PubSub resource.
Select the target virtual network.
Select Review + create.
Pricing
For pricing details, see Azure Private Link pricing.
Known issues
Keep in mind the following known issues about using private endpoints in Web PubSub.
Free tier constraints
An Azure Web PubSub instance that's created by using the free tier can't integrate with a private endpoint.
Access constraints for clients in VNets with private endpoints
Clients in VNets that have existing private endpoints have constraints when they access other Web PubSub instances that have private endpoints. For example, a VNet N1 has a private endpoint for a Web PubSub instance W1. If the Web PubSub instance W2 has a private endpoint in a VNet N2, then clients in VNet N1 must also access Web PubSub instance W2 by using a private endpoint.
If Web PubSub instance W2 doesn't have any private endpoints, then clients in VNet N1 can access the Web PubSub resource in that account without using a private endpoint. This constraint is a result of the DNS changes made when Web PubSub instance W2 creates a private endpoint.