Resource governance with application groups
Azure Event Hubs enables you to govern event streaming workloads of client applications that connect to Event Hubs. You can create logical groups known as application groups where each group is a collection of client applications, and then apply quota and access management policies for an application group (group of client applications).
Note
Application groups are available only in premium and dedicated tiers.
Application groups
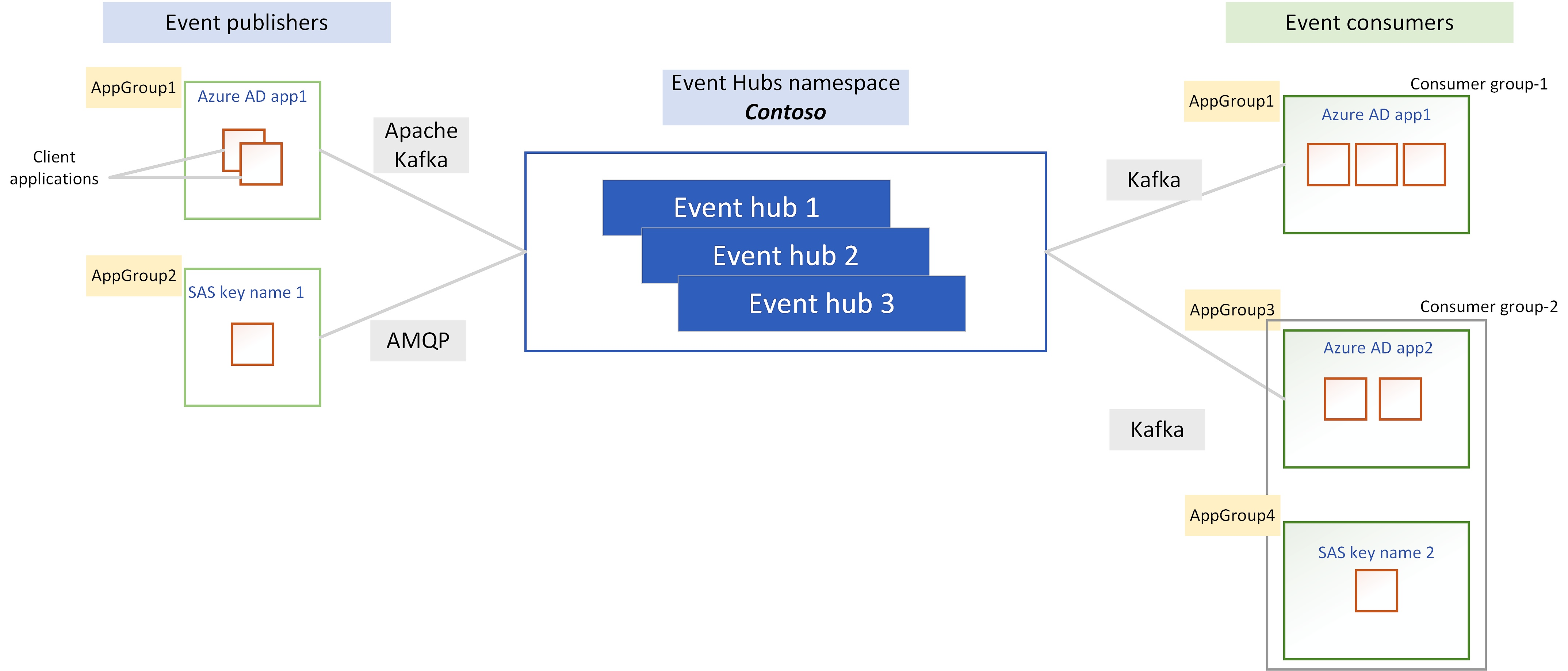
An application group is a collection of one or more client applications that interact with the Event Hubs data plane. Each application group can be scoped to a single Event Hubs namespace or event hubs (entity) within a namespace and should use a uniquely identifying condition such as the security context - shared access signatures (SAS) or Microsoft Entra application ID - of the client application.
Event Hubs currently supports using security contexts for creating application groups. Therefore, each application group must have a unique SAS policy or Microsoft Entra application ID associated with them. If preferred, you can use security context at event hub level to use an application group with a specific event hub within a namespace.
Application groups are logical entities that are created at the namespace level. Therefore, client applications interacting with event hubs don't need to be aware of the existence of an application group. Event Hubs can associate any client application to an application group by using the identifying condition.
As illustrated below, you can create application groups based on the security context that each client application uses. Therefore, application groups can span across multiple client applications using the same security context.
Application groups have no direct association with a consumer group. Depending on the application group identifier such as security context, one consumer group can have one or more application groups associated with it or one application group can span across multiple consumer groups.
These are the key attributes of an application group:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| name | Unique name of an application group. |
| clientAppGroupIdentifier | Associate an application group with a uniquely identifying condition (i.e security context such as SAS policy or Microsoft Entra application ID). |
| policies | List of policies, such as throttling policies that control event streaming between client applications and the Event Hubs namespace |
| isEnabled | Determine whether the client applications of an application group can access Event Hubs namespaces or not. |
Application group policies
Each application group can contain zero or more policies that control the data plane access of the client applications that are part of the application group. Application groups currently support throttling policies.
Throttling policies
You can have throttling policies specified using different ingress and egress metrics. Application groups support using the following metrics to throttle ingress or egress workloads of client applications.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| IncomingBytes | Publisher throughput in bytes per second. |
| OutgoingBytes | Consumer throughput in bytes per second. |
| IncomingMessages | Number of events published per second. |
| OutgoingMessages | Number of events consumed per second. |
When policies for application groups are applied, the client application workload may slow down or encounter server busy exceptions.
Throttling policy - threshold Limits
The following table shows minimum threshold limits that you can set for different metric ID in throttling policy:
| Metric ID | Minimum limit |
|---|---|
| IncomingByte | 1 KB |
| OutgoingByte | 1 KB |
| IncomingMessage | 1 |
| Outgoing message | 1 |
Note
Limits set on the throttling policy's threshold value would take precedence over any value set for Kafka topic properties. For example, IncomingBytes would have higher priority over message.max.bytes.
Application group throttling is expected to throttle consistent higher than permitted traffic scenarios (spanning across few minutes).Quick bursts in traffic for few seconds might not experience throttling via Application Groups. Looking at permitted throughput over the time horizon of few minutes is recommended approach to validate throttling.
Protocol support and error codes
Application group supports throttling operations happening via following protocols – AMQP, Kafka and HTTP. The following table provides you the expected error codes returned by application groups:
| Protocol | Operation | Error code | Error message |
|---|---|---|---|
| AMQP | Send | 50004 | SubCode:50013, Application group is throttled with application group ID & policy name |
| HTTP | Send | 503 | Subcode: 50013. Application group is throttled with application group ID and policy name |
| Kafka | Send | PolicyViolation | Broker: policy violation |
Due to restrictions at protocol level, error messages aren't supported during receive operation. When application groups are throttling on receive operations, you would experience sluggish consumption of messages at consumer side.
Disabling application groups
Application group is enabled by default and that means all the client applications can access Event Hubs namespace for publishing and consuming events by adhering to the application group policies.
When an application group is disabled, the client will still be able to connect to the event hub, but the authorization will fail and then the client connection gets closed. Therefore, you'll see lots of successful open and close connections, with same number of authorization failures in diagnostic logs.
Next steps
For instructions on how to create and manage application groups, see Resource governance for client applications using Azure portal