Nóta
Aðgangur að þessari síðu krefst heimildar. Þú getur prófað aðskrá þig inn eða breyta skráasöfnum.
Aðgangur að þessari síðu krefst heimildar. Þú getur prófað að breyta skráasöfnum.
Learn how to use C# user-defined functions (UDF) with Apache Hive and Apache Pig on HDInsight.
Important
The steps in this document work with Linux-based HDInsight clusters. Linux is the only operating system used on HDInsight version 3.4 or greater. For more information, see HDInsight component versioning.
Both Hive and Pig can pass data to external applications for processing. This process is known as streaming. When you use a .NET application, the data is passed to the application on STDIN, and the application returns the results on STDOUT. To read and write from STDIN and STDOUT, you can use Console.ReadLine() and Console.WriteLine() from a console application.
Prerequisites
A familiarity with writing and building C# code that targets .NET Framework 4.5.
Use whatever IDE you want. We recommend Visual Studio or Visual Studio Code. The steps in this document use Visual Studio 2019.
A way to upload .exe files to the cluster and run Pig and Hive jobs. We recommend Data Lake Tools for Visual Studio, Azure PowerShell, and Azure CLI. The steps in this document use the Data Lake Tools for Visual Studio to upload the files and run the example Hive query.
For information on other ways to run Hive queries, see What is Apache Hive and HiveQL on Azure HDInsight?.
A Hadoop on HDInsight cluster. For more information on creating a cluster, see Create HDInsight clusters.
.NET on HDInsight
Linux-based HDInsight clusters use Mono (https://mono-project.com) to run .NET applications. Mono version 4.2.1 is included with HDInsight version 3.6.
For more information on Mono compatibility with .NET Framework versions, see Mono compatibility.
For more information on the version of the .NET Framework and Mono included with HDInsight versions, see HDInsight component versions.
Create the C# projects
The following sections describe how to create a C# project in Visual Studio for an Apache Hive UDF and an Apache Pig UDF.
Apache Hive UDF
To create a C# project for an Apache Hive UDF:
Launch Visual Studio.
Select Create a new project.
In the Create a new project window, choose the Console App (.NET Framework) template (the C# version). Then select Next.
In the Configure your new project window, enter a Project name of HiveCSharp, and navigate to or create a Location to save the new project in. Then select Create.
In the Visual Studio IDE, replace the contents of Program.cs with the following code:
using System; using System.Security.Cryptography; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace HiveCSharp { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { string line; // Read stdin in a loop while ((line = Console.ReadLine()) != null) { // Parse the string, trimming line feeds // and splitting fields at tabs line = line.TrimEnd('\n'); string[] field = line.Split('\t'); string phoneLabel = field[1] + ' ' + field[2]; // Emit new data to stdout, delimited by tabs Console.WriteLine("{0}\t{1}\t{2}", field[0], phoneLabel, GetMD5Hash(phoneLabel)); } } /// <summary> /// Returns an MD5 hash for the given string /// </summary> /// <param name="input">string value</param> /// <returns>an MD5 hash</returns> static string GetMD5Hash(string input) { // Step 1, calculate MD5 hash from input MD5 md5 = System.Security.Cryptography.MD5.Create(); byte[] inputBytes = System.Text.Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(input); byte[] hash = md5.ComputeHash(inputBytes); // Step 2, convert byte array to hex string StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); for (int i = 0; i < hash.Length; i++) { sb.Append(hash[i].ToString("x2")); } return sb.ToString(); } } }From the menu bar, select Build > Build Solution to build the project.
Close the solution.
Apache Pig UDF
To create a C# project for an Apache Hive UDF:
Open Visual Studio.
In the Start window, select Create a new project.
In the Create a new project window, choose the Console App (.NET Framework) template (the C# version). Then select Next.
In the Configure your new project window, enter a Project name of PigUDF, and go to or create a Location to save the new project in. Then select Create.
In the Visual Studio IDE, replace the contents of Program.cs with the following code:
using System; namespace PigUDF { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { string line; // Read stdin in a loop while ((line = Console.ReadLine()) != null) { // Fix formatting on lines that begin with an exception if(line.StartsWith("java.lang.Exception")) { // Trim the error info off the beginning and add a note to the end of the line line = line.Remove(0, 21) + " - java.lang.Exception"; } // Split the fields apart at tab characters string[] field = line.Split('\t'); // Put fields back together for writing Console.WriteLine(String.Join("\t",field)); } } } }This code parses the lines sent from Pig and reformats lines that begin with
java.lang.Exception.From the menu bar, choose Build > Build Solution to build the project.
Leave the solution open.
Upload to storage
Next, upload the Hive and Pig UDF applications to storage on a HDInsight cluster.
In Visual Studio, navigate to View > Server Explorer.
From Server Explorer, right-click Azure, select Connect to Microsoft Azure Subscription, and complete the sign-in process.
Expand the HDInsight cluster that you wish to deploy this application to. An entry with the text (Default Storage Account) is listed.
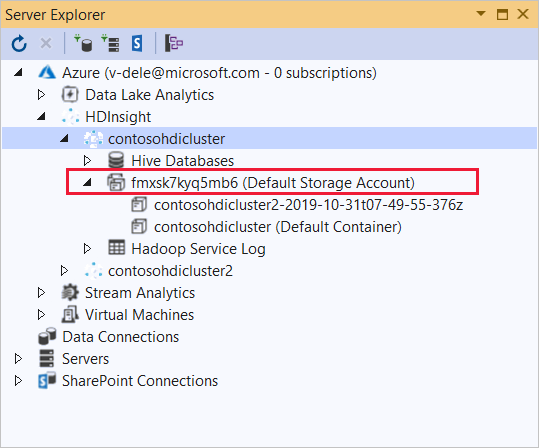
If this entry can be expanded, you're using an Azure Storage Account as default storage for the cluster. To view the files on the default storage for the cluster, expand the entry and then double-click the (Default Container).
If this entry can't be expanded, you're using Azure Data Lake Storage as the default storage for the cluster. To view the files on the default storage for the cluster, double-click the (Default Storage Account) entry.
To upload the .exe files, use one of the following methods:
If you're using an Azure Storage Account, select the Upload Blob icon.

In the Upload New File dialog box, under File name, select Browse. In the Upload Blob dialog box, go to the
bin\debugfolder for the HiveCSharp project, and then choose the HiveCSharp.exe file. Finally, select Open and then OK to complete the upload.If you're using Azure Data Lake Storage, right-click an empty area in the file listing, and then select Upload. Finally, choose the HiveCSharp.exe file and select Open.
Once the HiveCSharp.exe upload has finished, repeat the upload process for the PigUDF.exe file.
Run an Apache Hive query
Now you can run a Hive query that uses your Hive UDF application.
In Visual Studio, navigate to View > Server Explorer.
Expand Azure, and then expand HDInsight.
Right-click the cluster that you deployed the HiveCSharp application to, and then select Write a Hive Query.
Use the following text for the Hive query:
-- Uncomment the following if you are using Azure Storage -- add file wasbs:///HiveCSharp.exe; -- Uncomment the following if you are using Azure Data Lake Storage Gen1 -- add file adl:///HiveCSharp.exe; -- Uncomment the following if you are using Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 -- add file abfs:///HiveCSharp.exe; SELECT TRANSFORM (clientid, devicemake, devicemodel) USING 'HiveCSharp.exe' AS (clientid string, phoneLabel string, phoneHash string) FROM hivesampletable ORDER BY clientid LIMIT 50;Important
Uncomment the
add filestatement that matches the type of default storage used for your cluster.This query selects the
clientid,devicemake, anddevicemodelfields fromhivesampletable, and then it passes the fields to the HiveCSharp.exe application. The query expects the application to return three fields, which are stored asclientid,phoneLabel, andphoneHash. The query also expects to find HiveCSharp.exe in the root of the default storage container.Switch the default Interactive to Batch, and then Select Submit to submit the job to the HDInsight cluster. The Hive Job Summary window opens.
Select Refresh to refresh the summary until Job Status changes to Completed. To view the job output, select Job Output.
Run an Apache Pig job
You can also run a Pig job that uses your Pig UDF application.
Use SSH to connect to your HDInsight cluster. (For example, run the command
ssh sshuser@<clustername>-ssh.azurehdinsight.net.) For more information, see Use SSH withHDInsight.Use the following command to start the Pig command line:
pigA
grunt>prompt is displayed.Enter the following to run a Pig job that uses the .NET Framework application:
DEFINE streamer `PigUDF.exe` CACHE('/PigUDF.exe'); LOGS = LOAD '/example/data/sample.log' as (LINE:chararray); LOG = FILTER LOGS by LINE is not null; DETAILS = STREAM LOG through streamer as (col1, col2, col3, col4, col5); DUMP DETAILS;The
DEFINEstatement creates an alias ofstreamerfor the PigUDF.exe application, andCACHEloads it from default storage for the cluster. Later,streameris used with theSTREAMoperator to process the single lines contained inLOGand return the data as a series of columns.Note
The application name that is used for streaming must be surrounded by the
`(backtick) character when aliased, and by the'(single quote) character when used withSHIP.Once you enter the last line, the job should start. It returns output similar to the following text:
(2019-07-15 16:43:25 SampleClass5 [WARN] problem finding id 1358451042 - java.lang.Exception) (2019-07-15 16:43:25 SampleClass5 [DEBUG] detail for id 1976092771) (2019-07-15 16:43:25 SampleClass5 [TRACE] verbose detail for id 1317358561) (2019-07-15 16:43:25 SampleClass5 [TRACE] verbose detail for id 1737534798) (2019-07-15 16:43:25 SampleClass7 [DEBUG] detail for id 1475865947)Use
exitto exit pig.
Next steps
In this document, you've learned how to use a .NET Framework application from Hive and Pig on HDInsight. If you would like to learn how to use Python with Hive and Pig, see Use Python with Apache Hive and Apache Pig in HDInsight.
For other ways to use Hive, and to learn about using MapReduce, see the following articles: