Nóta
Aðgangur að þessari síðu krefst heimildar. Þú getur prófað aðskrá þig inn eða breyta skráasöfnum.
Aðgangur að þessari síðu krefst heimildar. Þú getur prófað að breyta skráasöfnum.
This article demonstrates how to develop Apache Spark applications on Azure HDInsight using the Azure Toolkit plug-in for the IntelliJ IDE. Azure HDInsight is a managed, open-source analytics service in the cloud. The service allows you to use open-source frameworks like Hadoop, Apache Spark, Apache Hive, and Apache Kafka.
You can use the Azure Toolkit plug-in in a few ways:
- Develop and submit a Scala Spark application to an HDInsight Spark cluster.
- Access your Azure HDInsight Spark cluster resources.
- Develop and run a Scala Spark application locally.
In this article, you learn how to:
- Use the Azure Toolkit for IntelliJ plug-in
- Develop Apache Spark applications
- Submit an application to Azure HDInsight cluster
Prerequisites
An Apache Spark cluster on HDInsight. For instructions, see Create Apache Spark clusters in Azure HDInsight. Only HDInsight clusters in public cloud are supported while other secure cloud types (e.g. government clouds) are not.
Oracle Java Development kit. This article uses Java version 8.0.202.
IntelliJ IDEA. This article uses IntelliJ IDEA Community 2018.3.4.
Azure Toolkit for IntelliJ. See Installing the Azure Toolkit for IntelliJ.
Install Scala plugin for IntelliJ IDEA
Steps to install the Scala plugin:
Open IntelliJ IDEA.
On the welcome screen, navigate to Configure > Plugins to open the Plugins window.
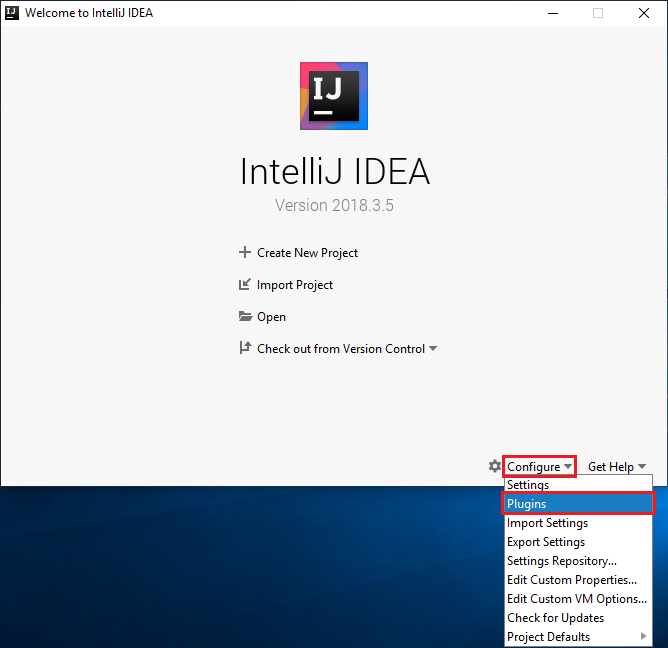
Select Install for the Scala plugin that is featured in the new window.
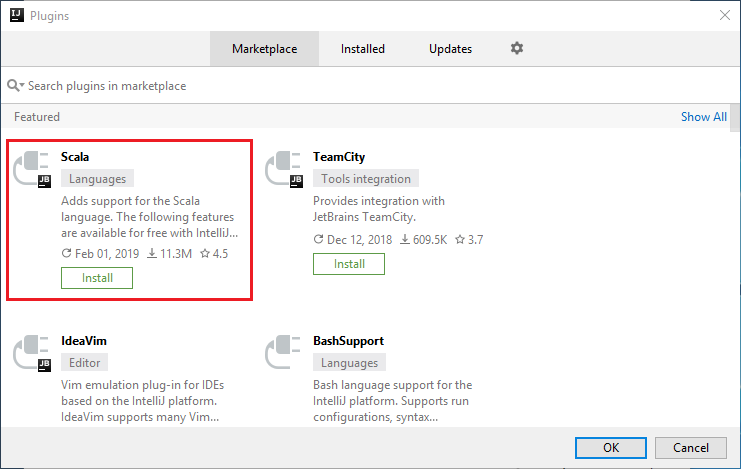
After the plugin installs successfully, you must restart the IDE.
Create a Spark Scala application for an HDInsight Spark cluster
Start IntelliJ IDEA, and select Create New Project to open the New Project window.
Select Azure Spark/HDInsight from the left pane.
Select Spark Project (Scala) from the main window.
From the Build tool drop-down list, select one of the following options:
Maven for Scala project-creation wizard support.
SBT for managing the dependencies and building for the Scala project.
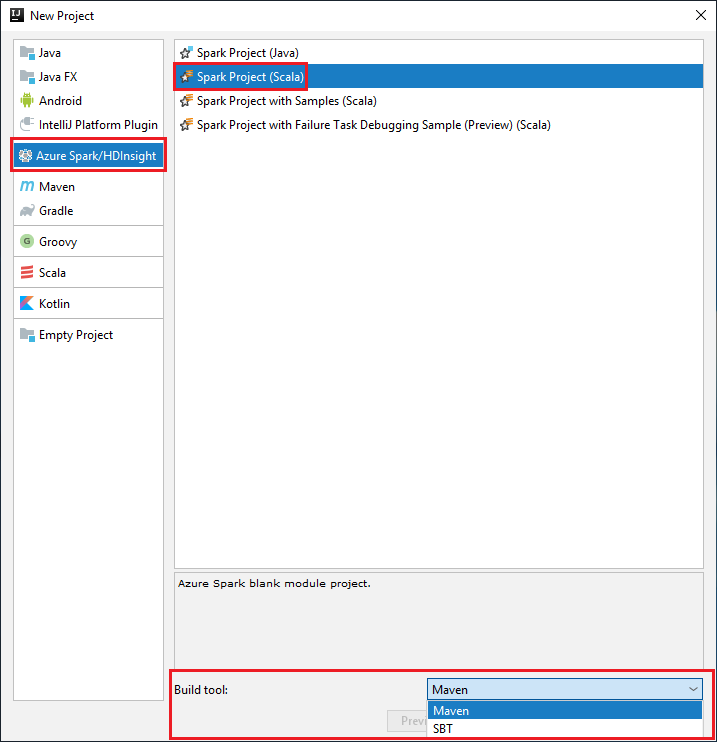
Select Next.
In the New Project window, provide the following information:
Property Description Project name Enter a name. This article uses myApp.Project location Enter the location to save your project. Project SDK This field might be blank on your first use of IDEA. Select New... and navigate to your JDK. Spark Version The creation wizard integrates the proper version for Spark SDK and Scala SDK. If the Spark cluster version is earlier than 2.0, select Spark 1.x. Otherwise, select Spark2.x. This example uses Spark 2.3.0 (Scala 2.11.8). 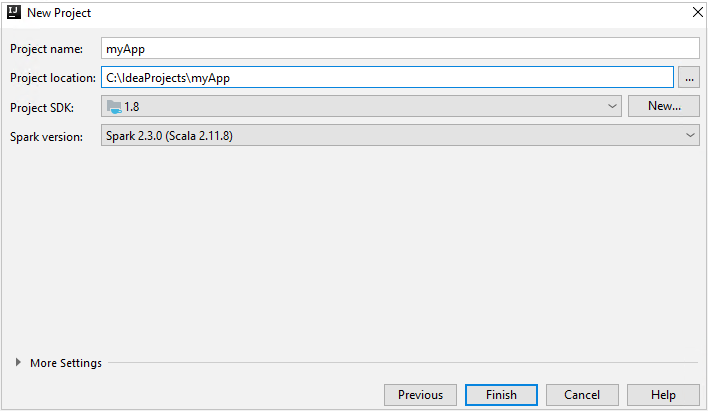
Select Finish. It may take a few minutes before the project becomes available.
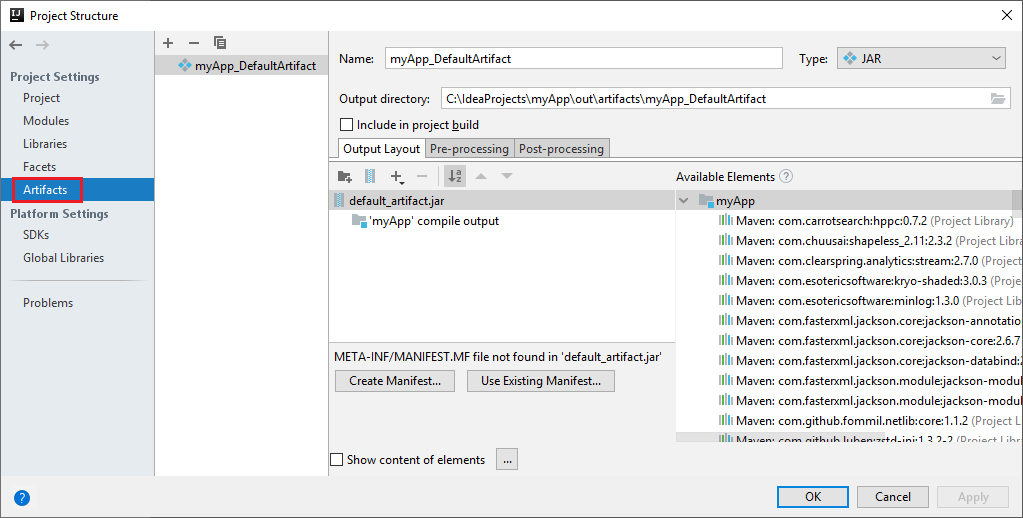
The Spark project automatically creates an artifact for you. To view the artifact, do the following steps:
a. From the menu bar, navigate to File > Project Structure....
b. From the Project Structure window, select Artifacts.
c. Select Cancel after viewing the artifact.
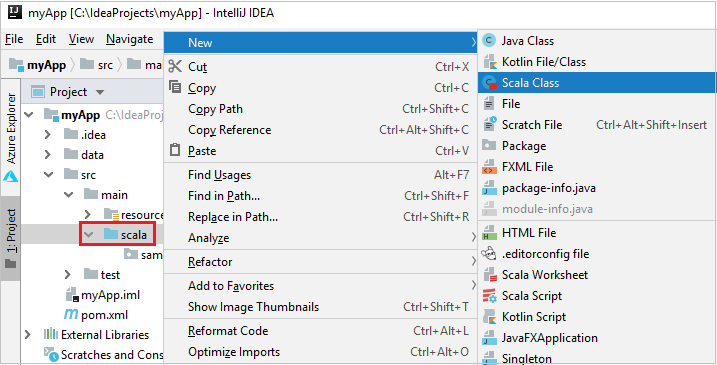
Add your application source code by doing the following steps:
a. From Project, navigate to myApp > src > main > scala.
b. Right-click scala, and then navigate to New > Scala Class.
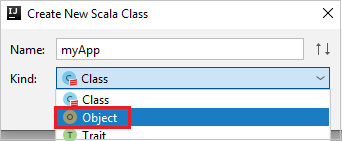
c. In the Create New Scala Class dialog box, provide a name, select Object in the Kind drop-down list, and then select OK.
d. The myApp.scala file then opens in the main view. Replace the default code with the code found below:
import org.apache.spark.SparkConf import org.apache.spark.SparkContext object myApp{ def main (arg: Array[String]): Unit = { val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("myApp") val sc = new SparkContext(conf) val rdd = sc.textFile("wasbs:///HdiSamples/HdiSamples/SensorSampleData/hvac/HVAC.csv") //find the rows that have only one digit in the seventh column in the CSV file val rdd1 = rdd.filter(s => s.split(",")(6).length() == 1) rdd1.saveAsTextFile("wasbs:///HVACOut") } }The code reads the data from HVAC.csv (available on all HDInsight Spark clusters), retrieves the rows that have only one digit in the seventh column in the CSV file, and writes the output to
/HVACOutunder the default storage container for the cluster.
Connect to your HDInsight cluster
User can either sign in to your Azure subscription, or link a HDInsight cluster. Use the Ambari username/password or domain joined credential to connect to your HDInsight cluster.
Sign in to your Azure subscription
From the menu bar, navigate to View > Tool Windows > Azure Explorer.
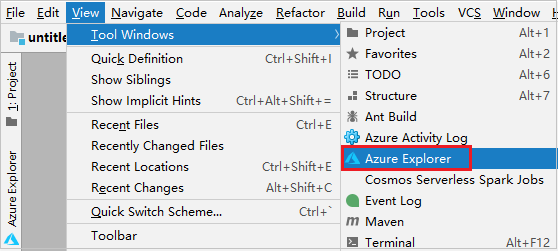
From Azure Explorer, right-click the Azure node, and then select Sign In.
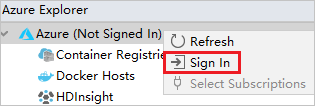
In the Azure Sign In dialog box, choose Device Login, and then select Sign in.
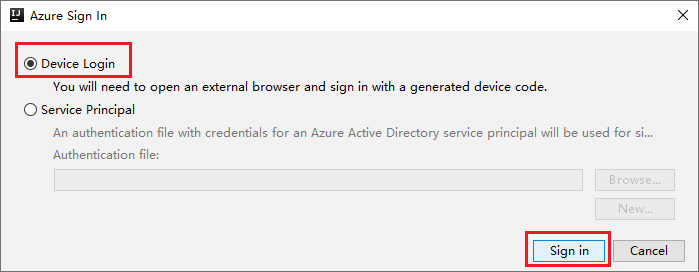
In the Azure Device Login dialog box, click Copy&Open.
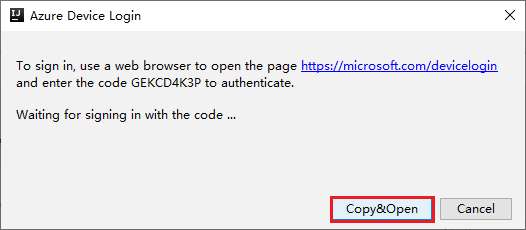
In the browser interface, paste the code, and then click Next.
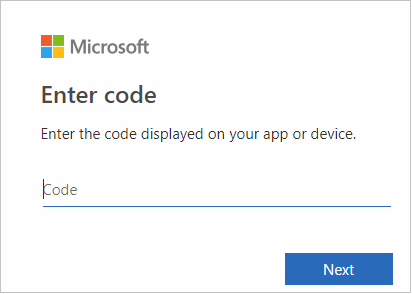
Enter your Azure credentials, and then close the browser.
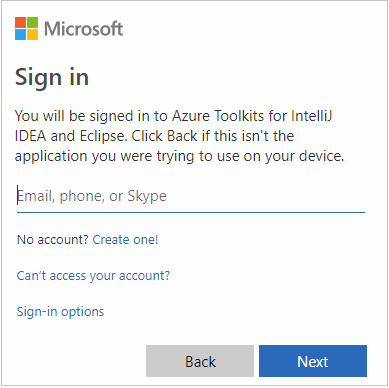
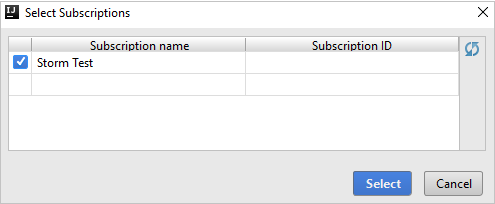
After you're signed in, the Select Subscriptions dialog box lists all the Azure subscriptions that are associated with the credentials. Select your subscription and then select the Select button.
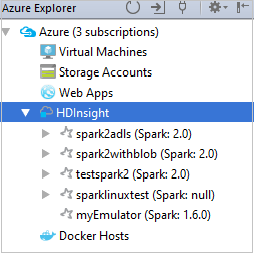
From Azure Explorer, expand HDInsight to view the HDInsight Spark clusters that are in your subscriptions.
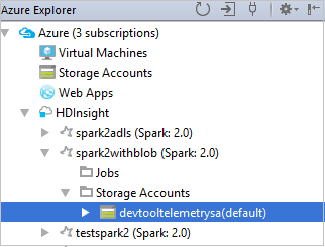
To view the resources (for example, storage accounts) that are associated with the cluster, you can further expand a cluster-name node.
Link a cluster
You can link an HDInsight cluster by using the Apache Ambari managed username. Similarly, for a domain-joined HDInsight cluster, you can link by using the domain and username, such as user1@contoso.com. Also you can link Livy Service cluster.
From the menu bar, navigate to View > Tool Windows > Azure Explorer.
From Azure Explorer, right-click the HDInsight node, and then select Link A Cluster.
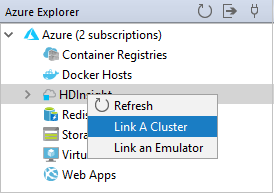
The available options in the Link A Cluster window will vary depending on which value you select from the Link Resource Type drop-down list. Enter your values and then select OK.
HDInsight Cluster
Property Value Link Resource Type Select HDInsight Cluster from the drop-down list. Cluster Name/URL Enter cluster name. Authentication Type Leave as Basic Authentication User Name Enter cluster user name, default is admin. Password Enter password for user name. 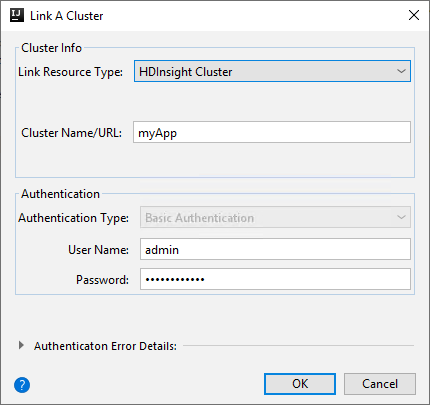
Livy Service
Property Value Link Resource Type Select Livy Service from the drop-down list. Livy Endpoint Enter Livy Endpoint Cluster Name Enter cluster name. Yarn Endpoint Optional. Authentication Type Leave as Basic Authentication User Name Enter cluster user name, default is admin. Password Enter password for user name. 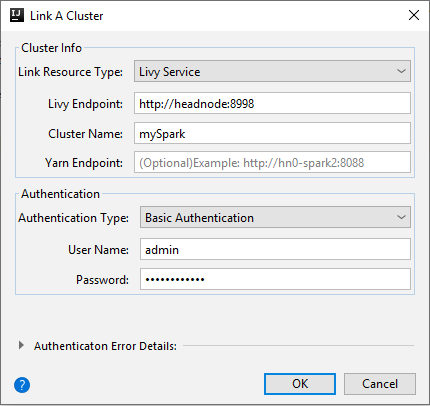
You can see your linked cluster from the HDInsight node.
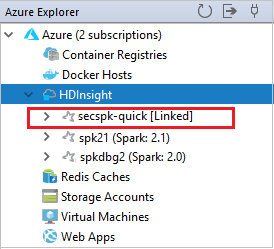
You also can unlink a cluster from Azure Explorer.
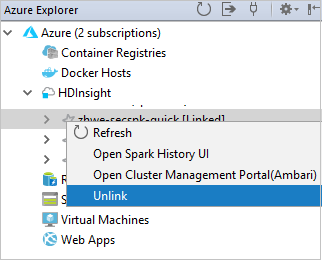
Run a Spark Scala application on an HDInsight Spark cluster
After creating a Scala application, you can submit it to the cluster.
From Project, navigate to myApp > src > main > scala > myApp. Right-click myApp, and select Submit Spark Application (It will likely be located at the bottom of the list).
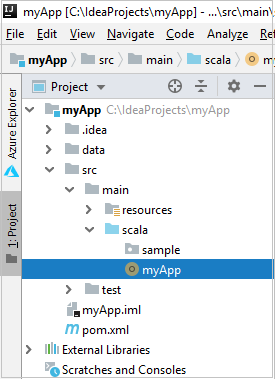
In the Submit Spark Application dialog window, select 1. Spark on HDInsight.
In the Edit configuration window, provide the following values and then select OK:
Property Value Spark clusters (Linux only) Select the HDInsight Spark cluster on which you want to run your application. Select an Artifact to submit Leave default setting. Main class name The default value is the main class from the selected file. You can change the class by selecting the ellipsis(...) and choosing another class. Job configurations You can change the default keys and, or values. For more information, see Apache Livy REST API. Command-line arguments You can enter arguments separated by space for the main class if needed. Referenced Jars and Referenced Files You can enter the paths for the referenced Jars and files if any. You can also browse files in the Azure virtual file system, which currently only supports ADLS Gen 2 cluster. For more information: Apache Spark Configuration. See also, How to upload resources to cluster. Job Upload Storage Expand to reveal additional options. Storage Type Select Use Azure Blob to upload from the drop-down list. Storage Account Enter your storage account. Storage Key Enter your storage key. Storage Container Select your storage container from the drop-down list once Storage Account and Storage Key has been entered. 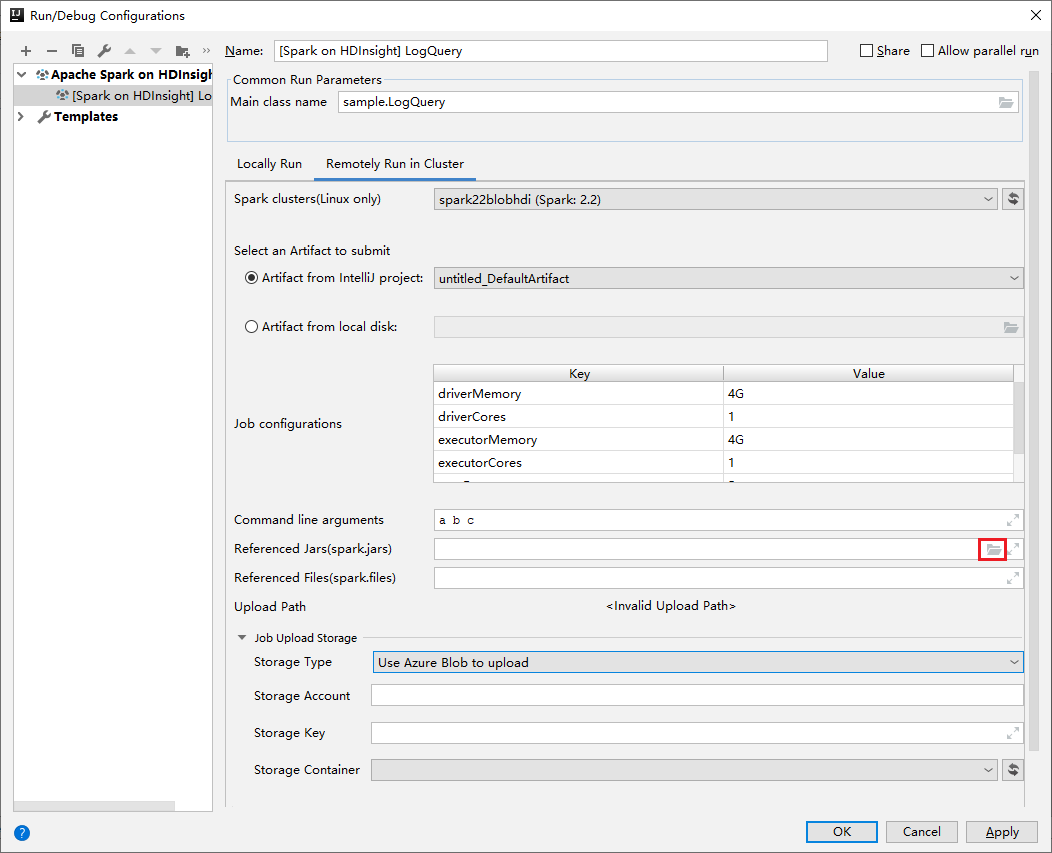
Select SparkJobRun to submit your project to the selected cluster. The Remote Spark Job in Cluster tab displays the job execution progress at the bottom. You can stop the application by clicking the red button.
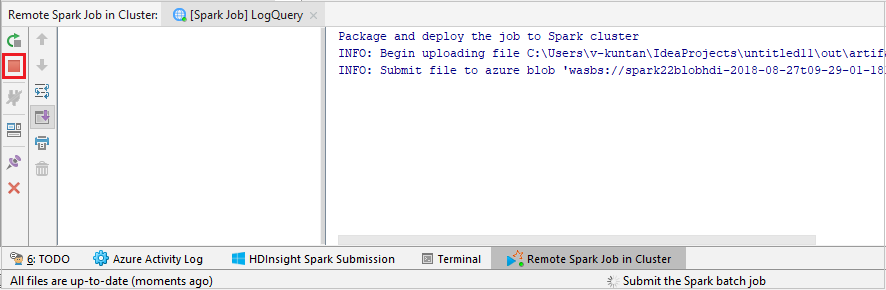
Debug Apache Spark applications locally or remotely on an HDInsight cluster
We also recommend another way of submitting the Spark application to the cluster. You can do so by setting the parameters in the Run/Debug configurations IDE. See Debug Apache Spark applications locally or remotely on an HDInsight cluster with Azure Toolkit for IntelliJ through SSH.
Access and manage HDInsight Spark clusters by using Azure Toolkit for IntelliJ
You can do various operations by using Azure Toolkit for IntelliJ. Most of the operations are started from Azure Explorer. From the menu bar, navigate to View > Tool Windows > Azure Explorer.
Access the job view
From Azure Explorer, navigate to HDInsight > <Your Cluster> > Jobs.
In the right pane, the Spark Job View tab displays all the applications that were run on the cluster. Select the name of the application for which you want to see more details.
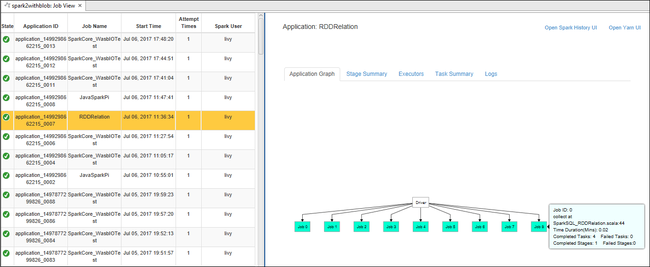
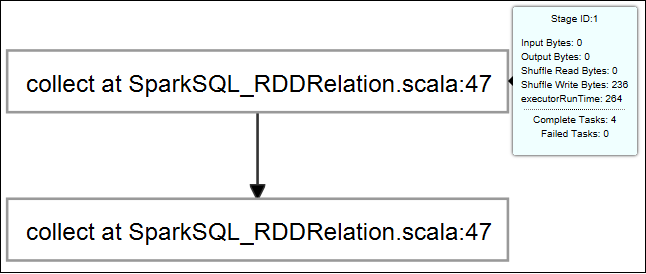
To display basic running job information, hover over the job graph. To view the stages graph and information that every job generates, select a node on the job graph.
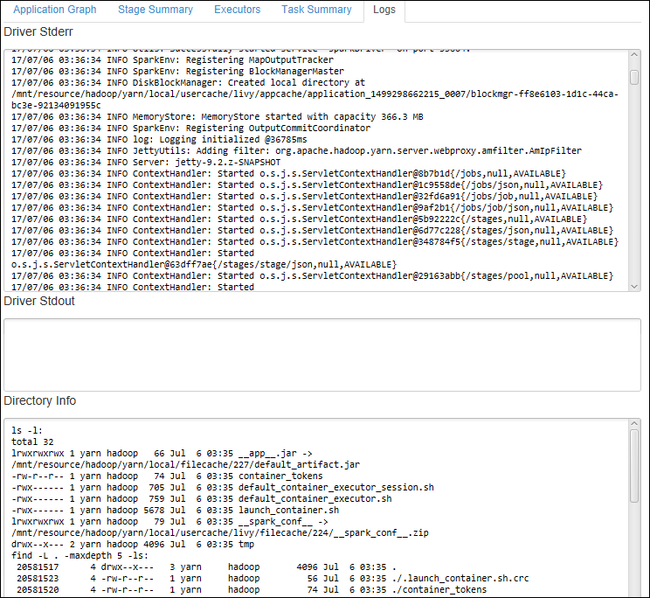
To view frequently used logs, such as Driver Stderr, Driver Stdout, and Directory Info, select the Log tab.
You can view the Spark history UI and the YARN UI (at the application level). Select a link at the top of the window.
Access the Spark history server
From Azure Explorer, expand HDInsight, right-click your Spark cluster name, and then select Open Spark History UI.
When you're prompted, enter the cluster's admin credentials, which you specified when you set up the cluster.
On the Spark history server dashboard, you can use the application name to look for the application that you just finished running. In the preceding code, you set the application name by using
val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("myApp"). Your Spark application name is myApp.
Start the Ambari portal
From Azure Explorer, expand HDInsight, right-click your Spark cluster name, and then select Open Cluster Management Portal(Ambari).
When you're prompted, enter the admin credentials for the cluster. You specified these credentials during the cluster setup process.
Manage Azure subscriptions
By default, Azure Toolkit for IntelliJ lists the Spark clusters from all your Azure subscriptions. If necessary, you can specify the subscriptions that you want to access.
From Azure Explorer, right-click the Azure root node, and then select Select Subscriptions.
From the Select Subscriptions window, clear the check boxes next to the subscriptions that you don't want to access, and then select Close.
Spark Console
You can run Spark Local Console(Scala) or run Spark Livy Interactive Session Console(Scala).
Spark Local Console(Scala)
Ensure you've satisfied the WINUTILS.EXE prerequisite.
From the menu bar, navigate to Run > Edit Configurations....
From the Run/Debug Configurations window, in the left pane, navigate to Apache Spark on HDInsight > [Spark on HDInsight] myApp.
From the main window, select the
Locally Runtab.Provide the following values, and then select OK:
Property Value Job main class The default value is the main class from the selected file. You can change the class by selecting the ellipsis(...) and choosing another class. Environment variables Ensure the value for HADOOP_HOME is correct. WINUTILS.exe location Ensure the path is correct. 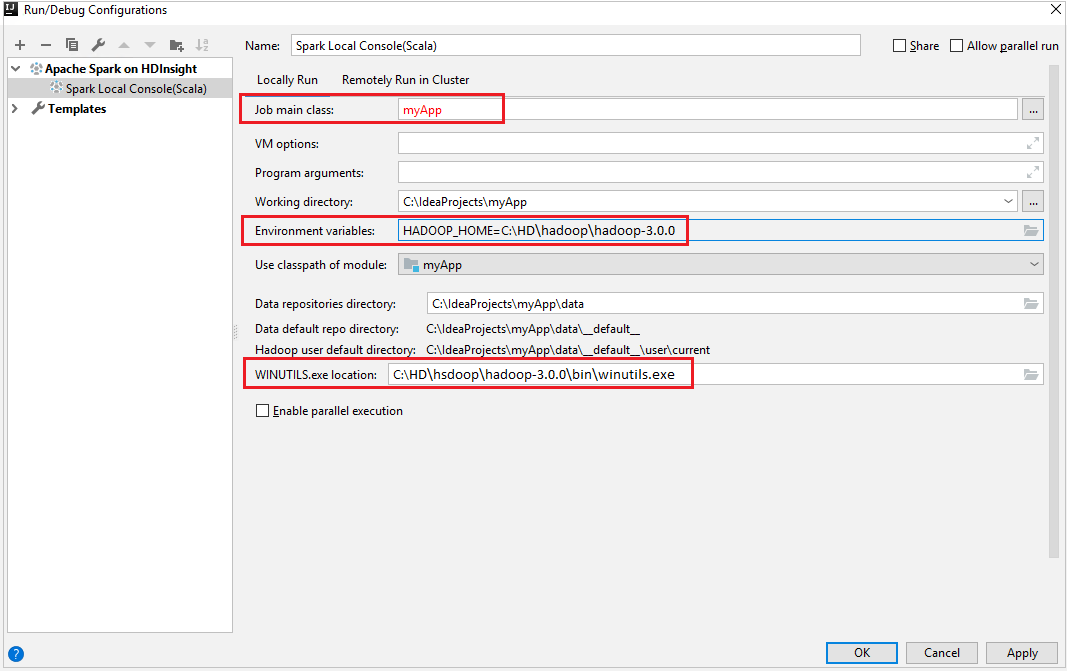
From Project, navigate to myApp > src > main > scala > myApp.
From the menu bar, navigate to Tools > Spark Console > Run Spark Local Console(Scala).
Then two dialogs may be displayed to ask you if you want to auto fix dependencies. If so, select Auto Fix.
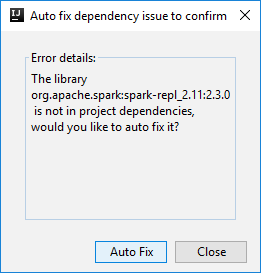
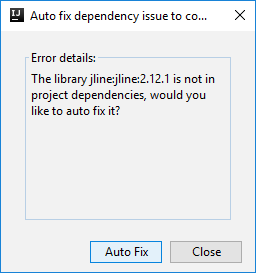
The console should look similar to the picture below. In the console window type
sc.appName, and then press ctrl+Enter. The result will be shown. You can end the local console by clicking red button.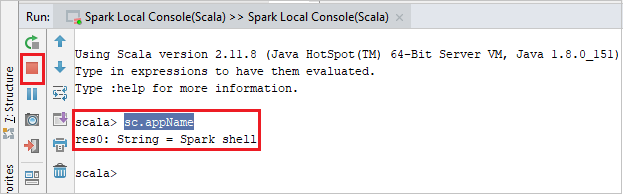
Spark Livy Interactive Session Console(Scala)
From the menu bar, navigate to Run > Edit Configurations....
From the Run/Debug Configurations window, in the left pane, navigate to Apache Spark on HDInsight > [Spark on HDInsight] myApp.
From the main window, select the
Remotely Run in Clustertab.Provide the following values, and then select OK:
Property Value Spark clusters (Linux only) Select the HDInsight Spark cluster on which you want to run your application. Main class name The default value is the main class from the selected file. You can change the class by selecting the ellipsis(...) and choosing another class. 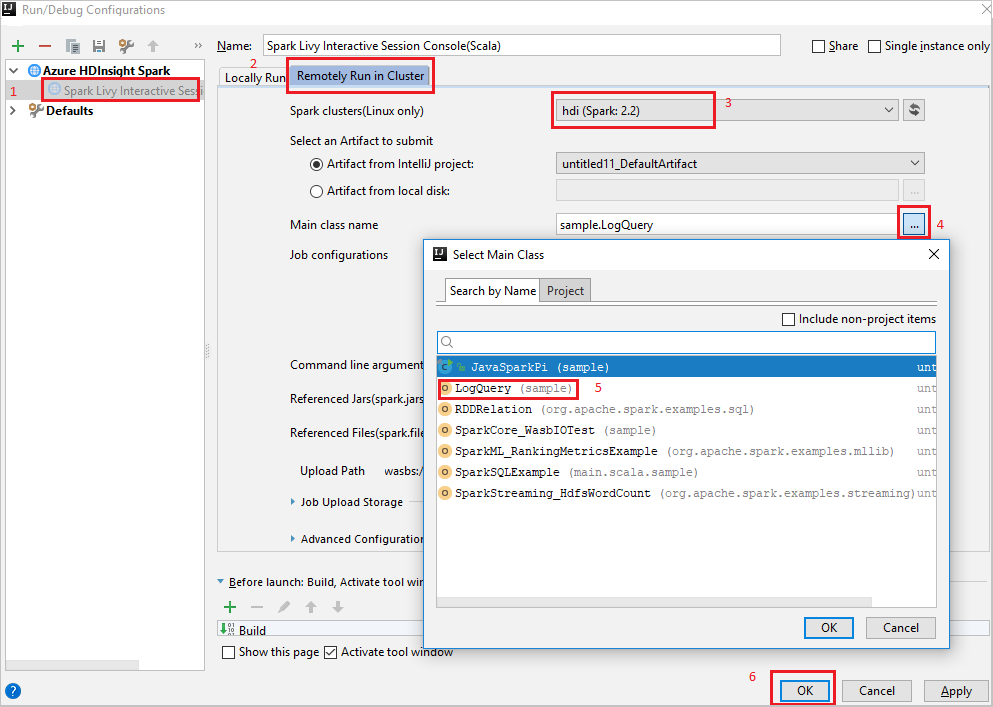
From Project, navigate to myApp > src > main > scala > myApp.
From the menu bar, navigate to Tools > Spark Console > Run Spark Livy Interactive Session Console(Scala).
The console should look similar to the picture below. In the console window type
sc.appName, and then press ctrl+Enter. The result will be shown. You can end the local console by clicking red button.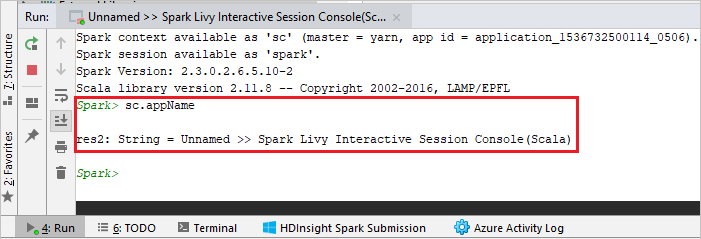
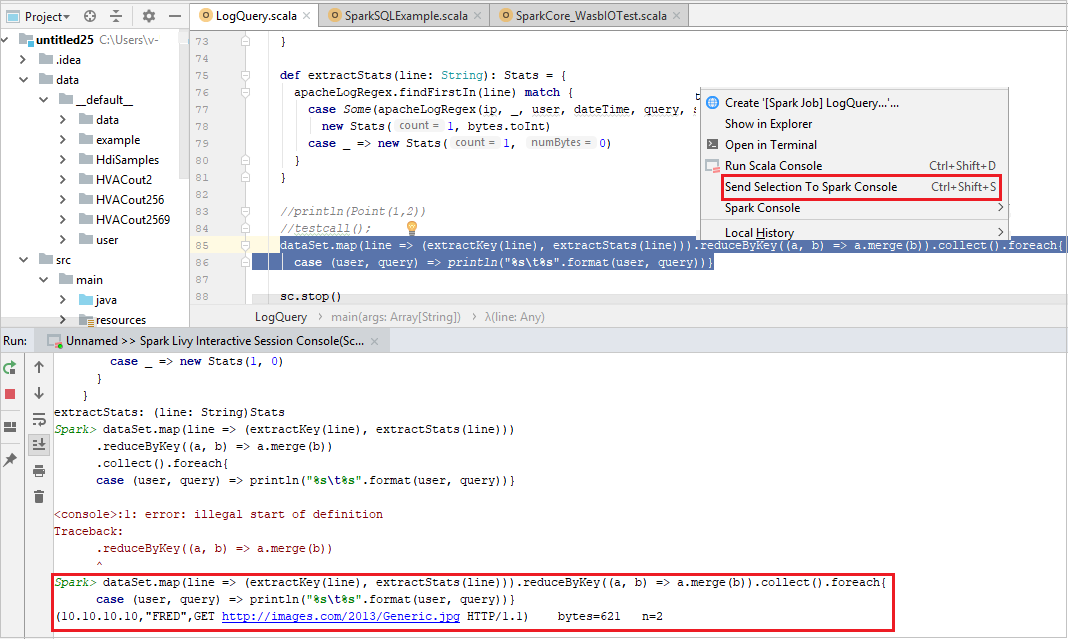
Send Selection to Spark Console
It's convenient for you to foresee the script result by sending some code to the local console or Livy Interactive Session Console(Scala). You can highlight some code in the Scala file, then right-click Send Selection To Spark Console. The selected code will be sent to the console. The result will be displayed after the code in the console. The console will check the errors if existing.
Integrate with HDInsight Identity Broker (HIB)
Connect to your HDInsight ESP cluster with ID Broker (HIB)
You can follow the normal steps to sign in to Azure subscription to connect to your HDInsight ESP cluster with ID Broker (HIB). After sign-in, you'll see the cluster list in Azure Explorer. For more instructions, see Connect to your HDInsight cluster.
Run a Spark Scala application on an HDInsight ESP cluster with ID Broker (HIB)
You can follow the normal steps to submit job to HDInsight ESP cluster with ID Broker (HIB). Refer to Run a Spark Scala application on an HDInsight Spark cluster for more instructions.
We upload the necessary files to a folder named with your sign-in account, and you can see the upload path in the configuration file.

Spark console on an HDInsight ESP cluster with ID Broker (HIB)
You can run Spark Local Console(Scala) or run Spark Livy Interactive Session Console(Scala) on an HDInsight ESP cluster with ID Broker (HIB). Refer to Spark Console for more instructions.
Note
For the HDInsight ESP cluster with Id Broker (HIB), link a cluster and debug Apache Spark applications remotely is not supported currently.
Reader-only role
When users submit job to a cluster with reader-only role permission, Ambari credentials is required.
Link cluster from context menu
Sign in with reader-only role account.
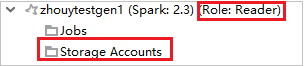
From Azure Explorer, expand HDInsight to view HDInsight clusters that are in your subscription. The clusters marked "Role:Reader" only have reader-only role permission.
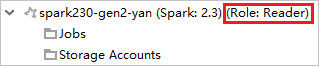
Right-click the cluster with reader-only role permission. Select Link this cluster from context menu to link cluster. Enter the Ambari username and Password.
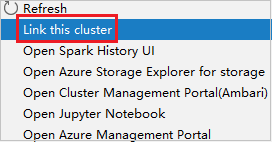
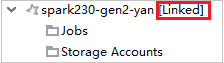
If the cluster is linked successfully, HDInsight will be refreshed. The stage of the cluster will become linked.
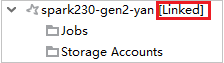
Link cluster by expanding Jobs node
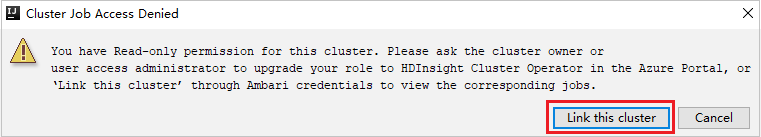
Click Jobs node, Cluster Job Access Denied window pops up.
Click Link this cluster to link cluster.
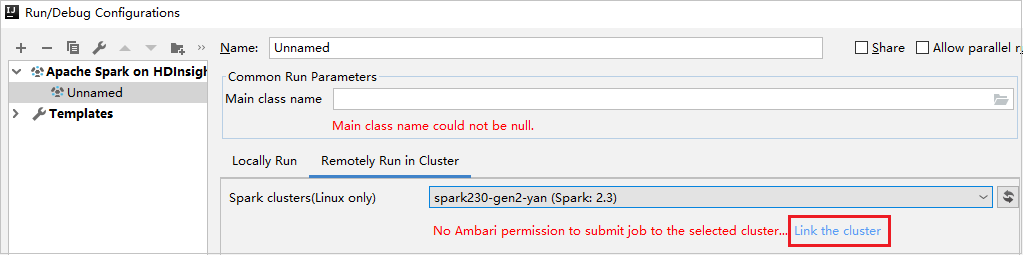
Link cluster from Run/Debug Configurations window
Create an HDInsight Configuration. Then select Remotely Run in Cluster.
Select a cluster, which has reader-only role permission for Spark clusters(Linux only). Warning message shows out. You can Click Link this cluster to link cluster.
View Storage Accounts
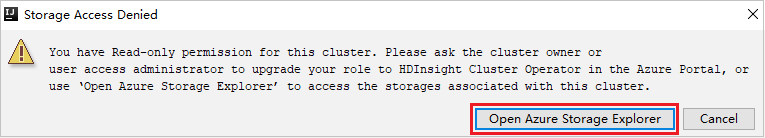
For clusters with reader-only role permission, click Storage Accounts node, Storage Access Denied window pops up. You can click Open Azure Storage Explorer to open Storage Explorer.
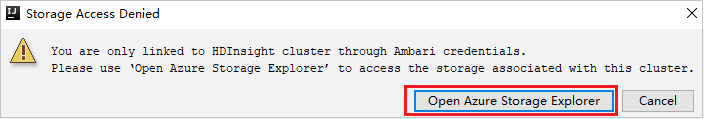
For linked clusters, click Storage Accounts node, Storage Access Denied window pops up. You can click Open Azure Storage to open Storage Explorer.
Convert existing IntelliJ IDEA applications to use Azure Toolkit for IntelliJ
You can convert the existing Spark Scala applications that you created in IntelliJ IDEA to be compatible with Azure Toolkit for IntelliJ. You can then use the plug-in to submit the applications to an HDInsight Spark cluster.
For an existing Spark Scala application that was created through IntelliJ IDEA, open the associated
.imlfile.At the root level, is a module element like the following text:
<module org.jetbrains.idea.maven.project.MavenProjectsManager.isMavenModule="true" type="JAVA_MODULE" version="4">Edit the element to add
UniqueKey="HDInsightTool"so that the module element looks like the following text:<module org.jetbrains.idea.maven.project.MavenProjectsManager.isMavenModule="true" type="JAVA_MODULE" version="4" UniqueKey="HDInsightTool">Save the changes. Your application should now be compatible with Azure Toolkit for IntelliJ. You can test it by right-clicking the project name in Project. The pop-up menu now has the option Submit Spark Application to HDInsight.
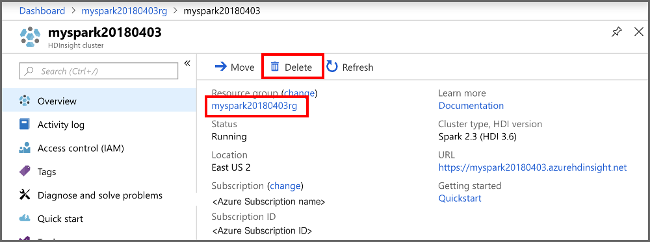
Clean up resources
If you're not going to continue to use this application, delete the cluster that you created with the following steps:
Sign in to the Azure portal.
In the Search box at the top, type HDInsight.
Select HDInsight clusters under Services.
In the list of HDInsight clusters that appears, select the ... next to the cluster that you created for this article.
Select Delete. Select Yes.
Errors and solution
Unmark the src folder as Sources if you get build failed errors as below:
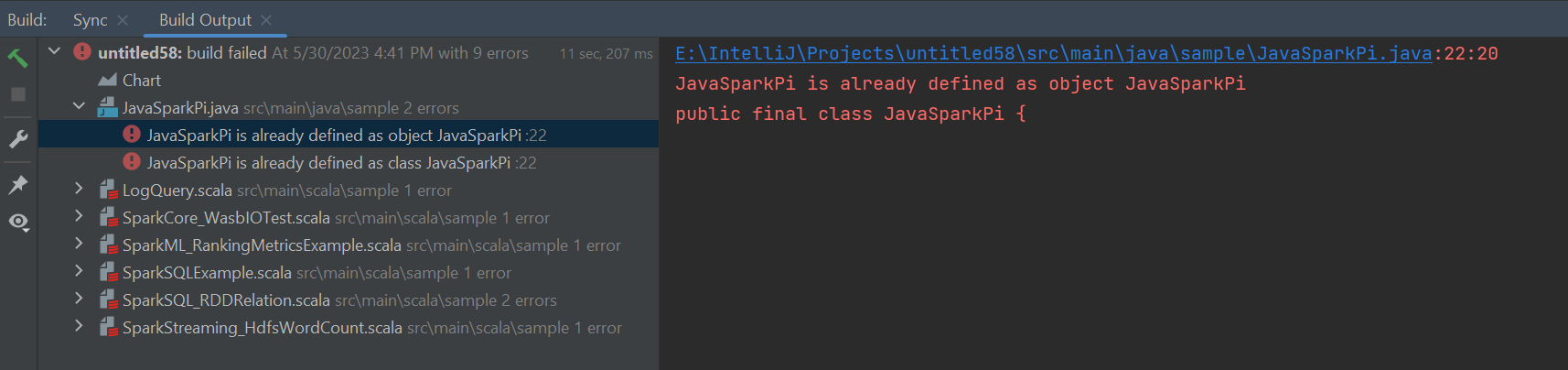
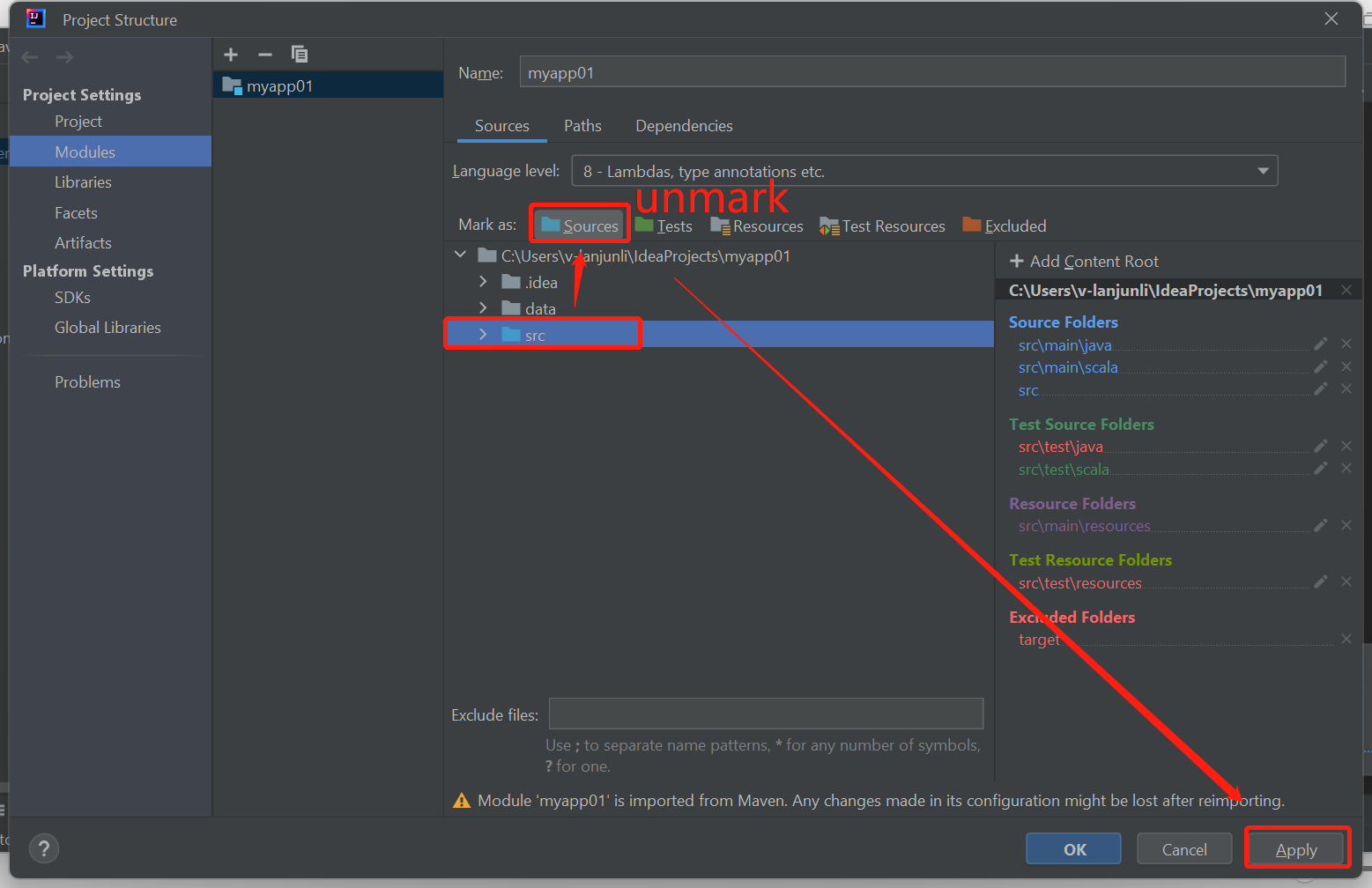
Unmark the src folder as Sources to solution this issue:
Navigate to File and select the Project Structure.
Select the Modules under the Project Settings.
Select the src file and unmark as Sources.
Click on Apply button and then click on OK button to close the dialog.
Next steps
In this article, you learned how to use the Azure Toolkit for IntelliJ plug-in to develop Apache Spark applications written in Scala. Then submitted them to an HDInsight Spark cluster directly from the IntelliJ integrated development environment (IDE). Advance to the next article to see how the data you registered in Apache Spark can be pulled into a BI analytics tool such as Power BI.