Exchange X12 messages using workflows in Azure Logic Apps
Applies to: Azure Logic Apps (Consumption + Standard)
To send and receive X12 messages in workflows that you create using Azure Logic Apps, use the X12 connector, which provides operations that support and manage X12 communication.
This how-to guide shows how to add the X12 encoding and decoding actions to an existing logic app workflow. The X12 connector doesn't include any triggers, so you can use any trigger to start your workflow. The examples in this guide use the Request trigger.
Connector technical reference
The X12 connector has one version across workflows in multitenant Azure Logic Apps and single-tenant Azure Logic Apps. For technical information about the X12 connector, see the following documentation:
Connector reference page, which describes the triggers, actions, and limits as documented by the connector's Swagger file
Prerequisites
An Azure account and subscription. If you don't have an Azure subscription yet, sign up for a free Azure account.
An integration account resource where you define and store artifacts, such as trading partners, agreements, certificates, and so on, for use in your enterprise integration and B2B workflows. This resource has to meet the following requirements:
Both your integration account and logic app resource must exist in the same Azure subscription and Azure region.
Defines at least two trading partners that participate in the X12 operation used in your workflow. The definitions for both partners must use the same X12 business identity qualifier.
Defines an X12 agreement between the trading partners that participate in your workflow. Each agreement requires a host partner and a guest partner. The content in the messages between you and the other partner must match the agreement type. For information about agreement settings to use when receiving and sending messages, see X12 message settings.
Important
If you're working with Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) schemas, you have to add a
schemaReferencessection to your agreement. For more information, see HIPAA schemas and message types.Defines the schemas to use for XML validation.
Important
If you're working with Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) schemas, make sure to review HIPAA schemas and message types.
Based on whether you're working on a Consumption or Standard logic app workflow, your logic app resource might require a link to your integration account:
Logic app workflow Link required? Consumption Connection and link to integration account are required. You can create the connection when you add the X12 operation to your workflow. Standard Connection to integration account required, but no link required. You can create the connection when you add the X12 operation to your workflow. The logic app resource and workflow where you want to use the X12 operations.
For more information, see the following documentation:
Encode X12 messages
The Encode to X12 message operation performs the following tasks:
- Resolves the agreement by matching sender and receiver context properties.
- Serializes the EDI interchange and converts XML-encoded messages into EDI transaction sets in the interchange.
- Applies transaction set header and trailer segments.
- Generates an interchange control number, a group control number, and a transaction set control number for each outgoing interchange.
- Replaces separators in the payload data.
- Validates EDI and partner-specific properties.
- Schema validation of transaction-set data elements against the message schema.
- EDI validation on transaction-set data elements.
- Extended validation on transaction-set data elements.
- Requests a Technical and Functional Acknowledgment, if configured.
- Generates a Technical Acknowledgment as a result of header validation. The technical acknowledgment reports the status of the processing of an interchange header and trailer by the address receiver.
- Generates a Functional Acknowledgment as a result of body validation. The functional acknowledgment reports each error encountered while processing the received document.
In the Azure portal, open your logic app resource and workflow in the designer.
In the designer, follow these general steps to add the X12 action named Encode to X12 message by agreement name to your workflow.
Note
If you want to use Encode to X12 message by identities action instead, you later have to provide different values, such as the Sender identifier and Receiver identifier that's specified by your X12 agreement. You also have to specify the XML message to encode, which can be the output from the trigger or a preceding action.
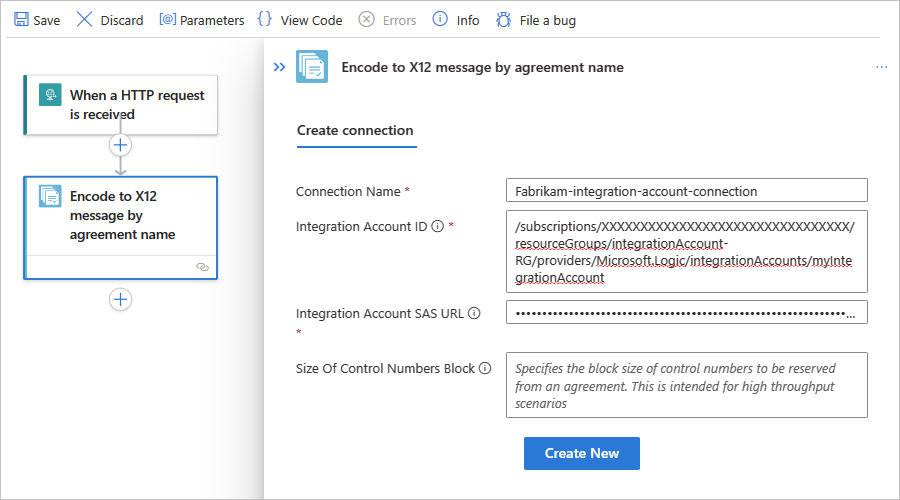
When prompted, provide the following connection information for your integration account:
Property Required Description Connection name Yes A name for the connection Integration Account Yes From the list of available integration accounts, select the account to use. For example:
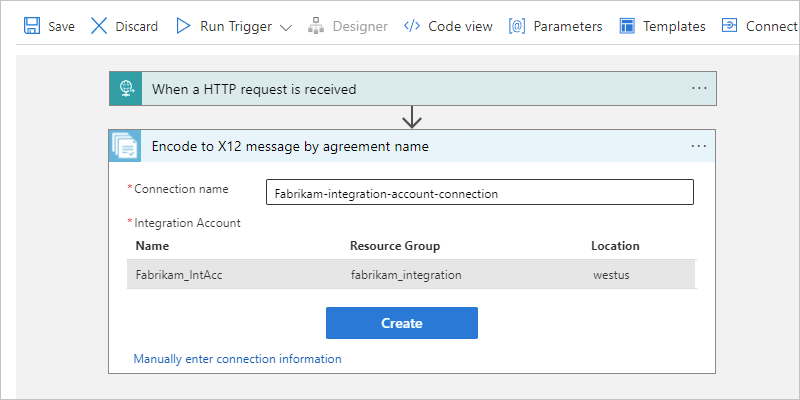
When you're done, select Create.
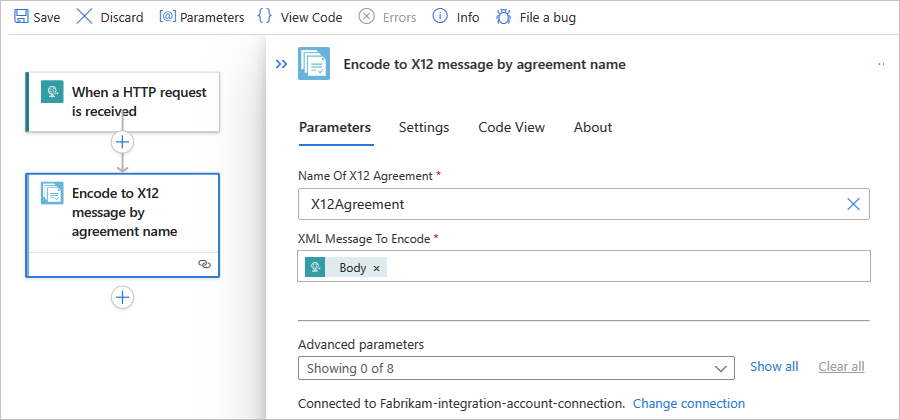
In the X12 action information box, provide the following property values:
Property Required Description Name of X12 agreement Yes The X12 agreement to use. XML message to encode Yes The XML message to encode Other parameters No This operation includes the following other parameters:
- Data element separator
- Component separator
- Replacement character
- Segment terminator
- Segment terminator suffix
- Control Version Number
- Application Sender Identifier/Code GS02
- Application Receiver Identifier/Code GS03
For more information, review X12 message settings.For example, you can use the Body content output from the Request trigger as the XML message payload:

Decode X12 messages
The Decode X12 message operation performs the following tasks:
Validates the envelope against trading partner agreement.
Validates EDI and partner-specific properties.
- EDI structural validation and extended schema validation
- Interchange envelope structural validation
- Schema validation of the envelope against the control schema
- Schema validation of the transaction set data elements against the message schema
- EDI validation on transaction-set data elements
Verifies that the interchange, group, and transaction set control numbers aren't duplicates.
- Checks the interchange control number against previously received interchanges.
- Checks the group control number against other group control numbers in the interchange.
- Checks the transaction set control number against other transaction set control numbers in that group.
Splits an interchange into transaction sets, or preserves the entire interchange:
Split the interchange into transaction sets or suspend transaction sets on error: Parse each transaction set. The X12 decode action outputs only the transaction sets that fail validation to
badMessages, and outputs the remaining transactions sets togoodMessages.Split the interchange into transaction sets or suspend interchange on error: Parse each transaction set. If one or more transaction sets in the interchange fail validation, the X12 decode action outputs all the transaction sets in that interchange to
badMessages.Preserve the interchange or suspend transaction sets on error: Preserve the interchange and process the entire batched interchange. The X12 decode action outputs only the transaction sets that fail validation to
badMessages, and outputs the remaining transactions sets togoodMessages.Preserve the interchange or suspend interchange on error: Preserve the interchange and process the entire batched interchange. If one or more transaction sets in the interchange fail validation, the X12 decode action outputs all the transaction sets in that interchange to
badMessages.
Generates a Technical and Functional Acknowledgment, if configured.
- Generates a Technical Acknowledgment as a result of header validation. The technical acknowledgment reports the status of the processing of an interchange header and trailer by the address receiver.
- Generates a Functional Acknowledgment as a result of body validation. The functional acknowledgment reports each error encountered while processing the received document.
In the Azure portal, open your logic app resource and workflow in the designer.
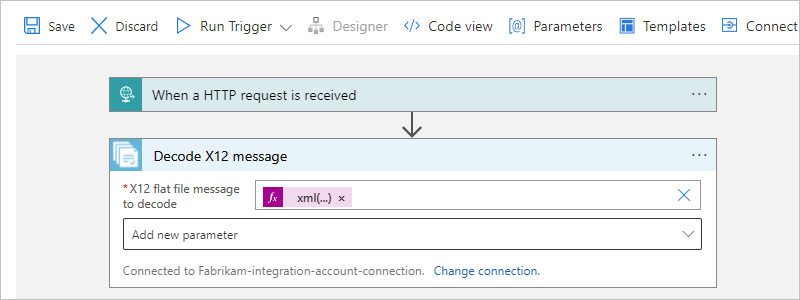
In the designer, follow these general steps to add the X12 action named Decode X12 message to your workflow.
When prompted, provide the following connection information for your integration account:
Property Required Description Connection name Yes A name for the connection Integration Account Yes From the list of available integration accounts, select the account to use. For example:
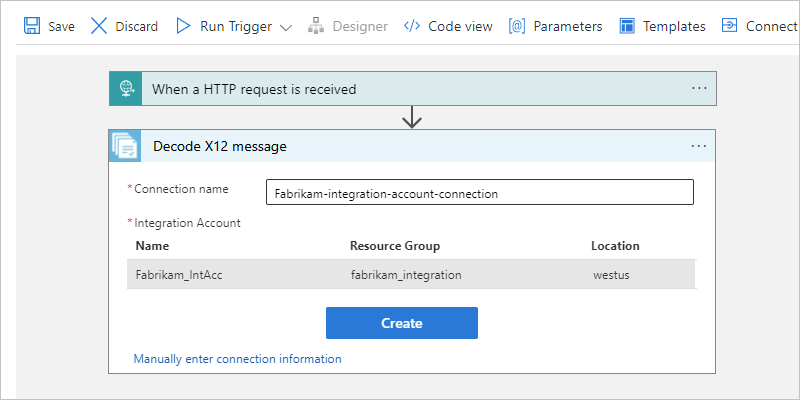
When you're done, select Create.
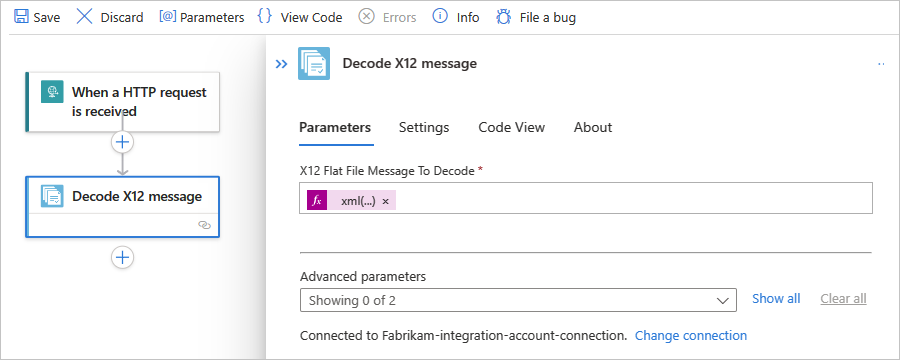
In the X12 action information box, provide the following property values:
Property Required Description X12 flat file message to decode Yes The X12 message in flat file format to decode
Note: The XML message payload or content for the message array, good or bad, is base64 encoded. So, you must use an expression that processes this content. For example, the following expression processes the message content as XML:xml(base64ToBinary(item()?['Body']))Other parameters No This operation includes the following other parameters:
- Preserve Interchange
- Suspend Interchange on Error
For more information, review X12 message settings.For example, you can use the Body content output from the Request trigger as the XML message payload, but you must first preprocess this content using an expression: