What is Designer (v1) in Azure Machine Learning?
The Azure Machine Learning designer is a drag-and-drop interface used to train and deploy models in Azure Machine Learning studio. This article describes the tasks you can do in the designer.
Important
Designer in Azure Machine Learning supports two types of pipelines that use classic prebuilt (v1) or custom (v2) components. The two component types aren't compatible within pipelines, and designer v1 isn't compatible with CLI v2 and SDK v2. This article applies to pipelines that use classic prebuilt (v1) components.
Classic prebuilt components (v1) include typical data processing and machine learning tasks like regression and classification. Azure Machine Learning continues to support the existing classic prebuilt components, but no new prebuilt components are being added. Also, deployment of classic prebuilt (v1) components doesn't support managed online endpoints (v2).
Custom components (v2) let you wrap your own code as components, enabling sharing across workspaces and seamless authoring across Azure Machine Learning studio, CLI v2, and SDK v2 interfaces. It's best to use custom components for new projects, because they're compatible with Azure Machine Learning v2 and continue to receive new updates. For more information about custom components and Designer (v2), see Azure Machine Learning designer (v2).
The following animated GIF shows how you can build a pipeline visually in Designer by dragging and dropping assets and connecting them.
To learn about the components available in the designer, see the Algorithm and component reference. To get started with the designer, see Tutorial: Train a no-code regression model.
Model training and deployment
The designer uses your Azure Machine Learning workspace to organize shared resources such as:
The following diagram illustrates how you can use the designer to build an end-to-end machine learning workflow. You can train, test, and deploy models, all in the designer interface.
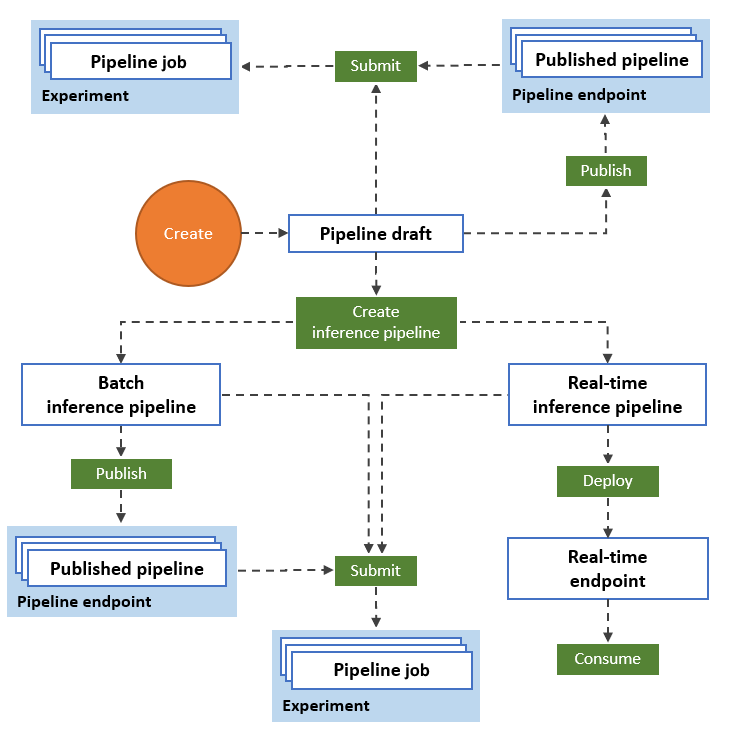
- Drag and drop data assets and components onto the designer visual canvas, and connect the components to create a pipeline draft.
- Submit a pipeline job that uses the compute resources in your Azure Machine Learning workspace.
- Convert your training pipelines to inference pipelines.
- Publish your pipelines to a REST pipeline endpoint to submit new pipelines that run with different parameters and data assets.
- Publish a training pipeline to reuse a single pipeline to train multiple models while changing parameters and data assets.
- Publish a batch inference pipeline to make predictions on new data by using a previously trained model.
- Deploy a real-time inference pipeline to an online endpoint to make predictions on new data in real time.
Data
A machine learning data asset makes it easy to access and work with your data. The designer includes several sample data assets for you to experiment with. You can register more data assets as you need them.
Components
A component is an algorithm that you can run on your data. The designer has several components ranging from data ingress functions to training, scoring, and validation processes.
A component can have parameters that you use to configure the component's internal algorithms. When you select a component on the canvas, the component's parameters and other settings display in a properties pane at the right of the canvas. You can modify the parameters and set the compute resources for individual components in that pane.
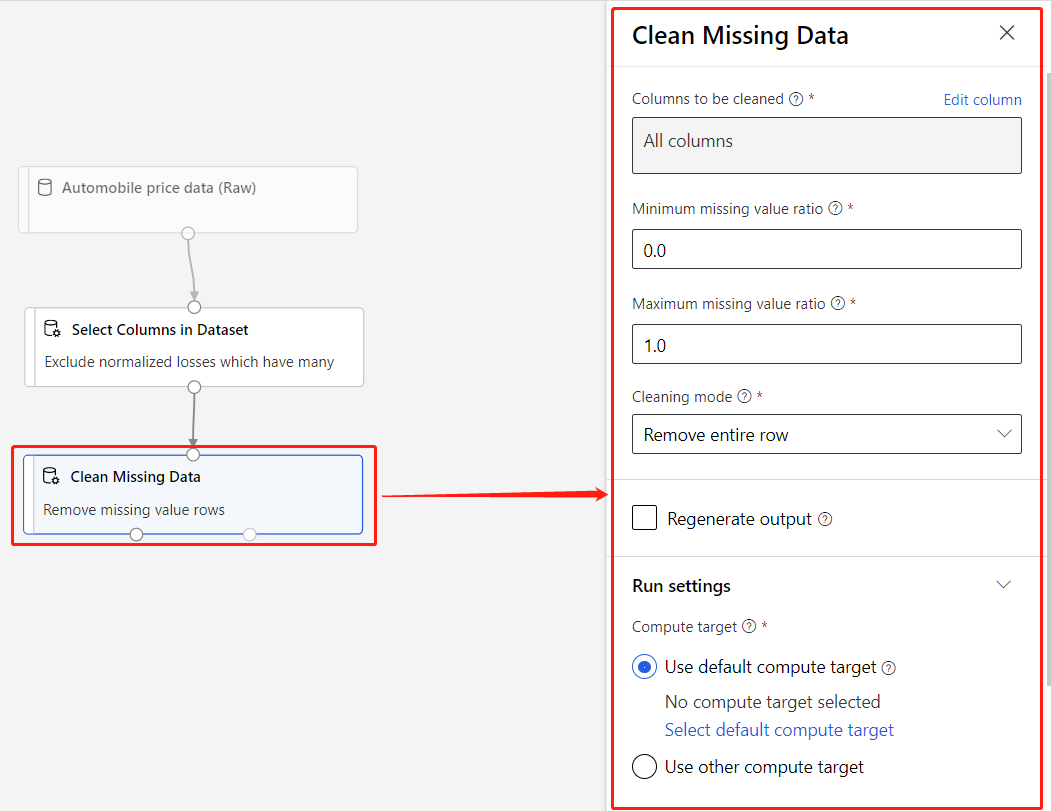
For more information about the library of available machine learning algorithms, see the Algorithm and component reference. For help with choosing an algorithm, see the Azure Machine Learning Algorithm Cheat Sheet.
Pipelines
A pipeline consists of data assets and analytical components that you connect. Pipelines help you reuse your work and organize your projects.
Pipelines have many uses. You can create pipelines that:
- Train a single model.
- Train multiple models.
- Make predictions in real time or in batch.
- Clean data only.
Pipeline drafts
As you edit a pipeline in the designer, your progress is saved as a pipeline draft. You can edit a pipeline draft at any point by adding or removing components, configuring compute targets, or setting parameters.
A valid pipeline has the following characteristics:
- Data assets can connect only to components.
- Components can connect only to data assets or to other components.
- All input ports for components must have some connection to the data flow.
- All required parameters for each component must be set.
When you're ready to run your pipeline draft, you save the pipeline and submit a pipeline job.
Pipeline jobs
Each time you run a pipeline, the configuration of the pipeline and its results are stored in your workspace as a pipeline job. Pipeline jobs are grouped into experiments to organize job history.
You can go back to any pipeline job to inspect it for troubleshooting or auditing. Clone a pipeline job to create a new pipeline draft to edit.
Compute resources
Compute targets are attached to your Azure Machine Learning workspace in Azure Machine Learning studio. Use compute resources from your workspace to run your pipeline and host your deployed models as online endpoints or as pipeline endpoints for batch inference. The supported compute targets are as follows:
| Compute target | Training | Deployment |
|---|---|---|
| Azure Machine Learning compute | ✓ | |
| Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) | ✓ |
Deploy
To do real-time inferencing, you must deploy a pipeline as an online endpoint. The online endpoint creates an interface between an external application and your scoring model. The endpoint is based on REST, a popular architecture choice for web programming projects. A call to an online endpoint returns prediction results to the application in real time.
To make a call to an online endpoint, you pass the API key that was created when you deployed the endpoint. Online endpoints must be deployed to an AKS cluster. To learn how to deploy your model, see Tutorial: Deploy a machine learning model with the designer.
Publish
You can also publish a pipeline to a pipeline endpoint. Similar to an online endpoint, a pipeline endpoint lets you submit new pipeline jobs from external applications by using REST calls. However, you can't send or receive data in real time by using a pipeline endpoint.
Published pipeline endpoints are flexible and can be used to train or retrain models, do batch inferencing, or process new data. You can publish multiple pipelines to a single pipeline endpoint and specify which pipeline version to run.
A published pipeline runs on the compute resources you define in the pipeline draft for each component. The designer creates the same PublishedPipeline object as the SDK.
Related content
- Learn the fundamentals of predictive analytics and machine learning with Tutorial: Predict automobile price with the designer.
- Learn how to modify existing designer samples to adapt them to your needs.