Service Fabric managed cluster node types
A virtual machine scale set backs each node type in a Service Fabric managed cluster. With managed clusters, you make any required changes through the Service Fabric managed cluster resource provider. The managed cluster provider creates and abstracts all of the underlying resources for the cluster on your behalf. Having the resource provider manage the resources helps to simplify cluster node type deployment and management. Management prevents operation errors such as deleting a seed node and helps apply best practices, such as validating a virtual machine (VM) SKU is safe to use.
The rest of this document covers how to adjust various settings, including:
- Creating a node type
- Adjusting node type instance count
- Enabling automatic OS image upgrades
- Changing the OS Image
- Configuring placement properties
- Setting computer name prefix
This document focuses on using Azure portal and Azure Resource Manager templates to make changes.
Important
At this time, Service Fabric Managed Clusters do not support custom OS images.
Note
You will not be able to modify the node type while a change is in progress. It is recommended to let any requested change complete before doing another.
Add a node type
You can add a node type to a Service Fabric managed cluster through Portal, an Azure Resource Manager template, or PowerShell.
Add with portal
Note
You can only add secondary node types using Portal
Sign in to Azure portal
Navigate to your cluster resource Overview page.

Select
Node typesunder theSettingssection
Select
Addat the top, fill in the required information, then select Add at the bottom, that's it!Wait for the new node type addition to be completed
Add with an ARM template
Add another resource type Microsoft.ServiceFabric/managedclusters/nodetypes with the required values and do a cluster deployment for the setting to take effect.
- The Service Fabric managed cluster resource apiVersion should be 2021-05-01 or later.
- Make sure to set
isPrimarytotrueif you're intending to replace an existing primary node type.
{
"apiVersion": "[variables('sfApiVersion')]",
"type": "Microsoft.ServiceFabric/managedclusters/nodetypes",
"name": "[concat(parameters('clusterName'), '/', parameters('nodeType2Name'))]",
"location": "[resourcegroup().location]",
"dependsOn": [
"[concat('Microsoft.ServiceFabric/managedclusters/', parameters('clusterName'))]"
],
"properties": {
"isPrimary": false,
"vmImagePublisher": "[parameters('vmImagePublisher')]",
"vmImageOffer": "[parameters('vmImageOffer')]",
"vmImageSku": "[parameters('vmImageSku')]",
"vmImageVersion": "[parameters('vmImageVersion')]",
"vmSize": "[parameters('nodeType2VmSize')]",
"vmInstanceCount": "[parameters('nodeType2VmInstanceCount')]",
"dataDiskSizeGB": "[parameters('nodeType2DataDiskSizeGB')]",
"dataDiskType": "[parameters('nodeType2managedDataDiskType')]"
}
}
For an example two node type configuration, see our sample two node type ARM template.
Add with PowerShell
To create a new node type, you need to define these properties:
- Resource Group: Resource group the cluster is in
- Cluster Name: Name of the managed cluster
- Node Type Name: Name that is unique from any existing node types in the cluster.
- Instance Count: Initial number of nodes of the new node type.
- VM Size: VM SKU for the nodes. If not specified, the default value Standard_D2 is used.
Note
If adding a primary node type, the -Primary property must be used.
$resourceGroup = "myResourceGroup"
$clusterName = "mysfcluster"
$nodeTypeName = "nt2"
$vmSize = "Standard_D2_v2"
New-AzServiceFabricManagedNodeType -ResourceGroupName $resourceGroup -ClusterName $clusterName -Name $nodeTypeName -InstanceCount 3 -vmSize $vmSize
Remove a node type
You can remove a Service Fabric managed cluster node type using Portal or PowerShell.
Note
To remove a primary node type from a Service Fabric managed cluster, you must use PowerShell and there must be more than one primary node type available.
Remove with portal
Sign in to Azure portal
Navigate to your cluster resource Overview page.

Select
Node typesunder theSettingssection
Select the
Node Typeyou want to remove and selectDeleteat the top.
Remove with PowerShell
Note
If removing a primary node type for scenarios such as upgrading the SKU it will take multiple hours and progress can be monitored by using SFX. Seed nodes will migrate one node per upgrade domain(UD) walk at a time.
To remove a node type, you need to define these properties:
- Resource Group: Resource group the cluster is in
- Cluster Name: Name of the managed cluster
- Node Type Name: Name that is unique from any existing node types in the cluster.
$resourceGroup = "myResourceGroup"
$clusterName = "myCluster"
$nodeTypeName = "nt2"
Remove-AzServiceFabricManagedNodeType -ResourceGroupName $resourceGroup -ClusterName $clusterName -Name $nodeTypeName
Scale a node type
You can scale a Service Fabric managed cluster node type with portal, ARM template, or PowerShell. You can also configure autoscale for a secondary node type if you want a fully automated solution.
Note
- A primary node type can't be set to auto-scale and you can only set it to manual scale.
- For the Primary node type, you will not be able to go below 3 nodes for a Basic SKU cluster, and 5 nodes for a Standard SKU cluster.
Scale using portal
In this walkthrough, you learn how to modify the node count for a node type using portal.
Sign in to Azure portal
Navigate to your cluster resource Overview page.

Select
Node Typesunder theSettingssectionSelect the
Node type nameyou want to modifyReview and update node type properties if needed.

Select
Manage node type scalingto configure the scaling settings and choose between custom autoscale and manual scale options. Autoscale is a built-in feature that helps applications perform their best when demand changes. You can choose to scale your resource manually to a specific instance count or via a custom autoscale policy that scales based on metric thresholds. You can also schedule instance counts to scale during designated time windows. Learn more about Azure Autoscale or view the how-to video.Custom autoscale: Select the appropriate
scale modeto define the custom Autoscale policy -Scale to a specific instance countorScale based on a metric. The latter is based on metric trigger rules, for example, increase instance count by 1 when CPU Percentage is above 70%. Once you define the policy, selectSaveat the top.
Manual scale: Adjust the
Node countto the new value you want and selectSaveat the top. In this screenshot, the value was3and adjusted to5.
Select
Applyat the bottom to configure these saved settings on the node type.The
Provisioning stateshows a status ofUpdatinguntil complete. When complete, it showsSucceededagain.
Scale a node type with a template
To adjust the node count for a node type using an ARM Template, adjust the vmInstanceCount property with the new value and do a cluster deployment for the setting to take effect. The cluster begins upgrading automatically. You see the additional nodes when complete.
- The Service Fabric managed cluster resource apiVersion should be 2021-05-01 or later.
Note
The managed cluster provider will block scale adjustments and return an error if the scaling request violates required minimums.
{
"apiVersion": "[variables('sfApiVersion')]",
"type": "Microsoft.ServiceFabric/managedclusters/nodetypes",
"name": "[concat(parameters('clusterName'), '/', parameters('nodeTypeName'))]",
"location": "[resourcegroup().location]",
"properties": {
...
"vmInstanceCount": "[parameters('nodeTypeVmInstanceCount')]",
...
}
}
Scale a node type with PowerShell
Change the instance count to increase or decrease the number of nodes on the node type that you would like to scale. You can find node type names in the Azure Resource Manager template (ARM template) from your cluster deployment, or in the Service Fabric Explorer.
$resourceGroup = "myResourceGroup"
$clusterName = "mysfcluster"
$nodeTypeName = "FE"
$instanceCount = "7"
Set-AzServiceFabricManagedNodeType -ResourceGroupName $resourceGroup -ClusterName $clusterName -name $nodeTypeName -InstanceCount $instanceCount -Verbose
The cluster begins upgrading automatically. You see the additional nodes when complete.
Enable automatic OS image upgrades
You can choose to enable automatic OS image upgrades to the virtual machines running your managed cluster nodes. Although the virtual machine scale set resources are managed on your behalf with Service Fabric managed clusters, it's your choice to enable automatic OS image upgrades for your cluster nodes. As with classic Service Fabric clusters, managed cluster nodes aren't upgraded by default, in order to prevent unintended disruptions to your cluster.
Note
Automatic OS image upgrade is supported for both marketplace and custom images.
To enable automatic OS upgrades:
- Use apiVersion
2021-05-01or later version of Microsoft.ServiceFabric/managedclusters and Microsoft.ServiceFabric/managedclusters/nodetypes resources - Set the cluster's property
enableAutoOSUpgradeto true - Set the cluster nodeTypes' resource property
vmImageVersionto latest
For example:
{
"apiVersion": "[variables('sfApiVersion')]",
"type": "Microsoft.ServiceFabric/managedclusters",
...
"properties": {
...
"enableAutoOSUpgrade": true
},
},
{
"apiVersion": "[variables('sfApiVersion')]",
"type": "Microsoft.ServiceFabric/managedclusters/nodetypes",
...
"properties": {
...
"vmImageVersion": "latest",
...
}
}
}
Once enabled, Service Fabric begins querying and tracking OS image versions in the managed cluster. If a new OS version is available, the cluster node types (virtual machine scale sets) are upgraded one at a time. Service Fabric runtime upgrades are performed only after confirming no cluster node OS image upgrades are in progress.
If an upgrade fails, Service Fabric will retry after 24 hours, for a maximum of three retries. Similar to classic (unmanaged) Service Fabric upgrades, unhealthy apps or nodes could block the OS image upgrade.
For more on image upgrades, see Automatic OS image upgrades with Azure virtual machine scale sets.
Modify the OS SKU for a node type
Service Fabric managed clusters enables you to modify the OS SKU for a node type in place. This process is helpful for scenarios such as migrating from Windows 2019 to Windows 2022 or if you want to switch to a Server (Core) SKU vs Server with Desktop Experience SKU.
Modify OS SKU with portal
In this walkthrough, you learn how to modify the OS image for a node type using portal.
Sign in to Azure portal
Navigate to your cluster resource Overview page.

Select
Node Typesunder theSettingssectionSelect the
Node type nameyou want to modifyAdjust the
OS Imageto the new value you want and selectApplyat the bottom. ![Sample showing changing the OS image][change-os-image]The
Provisioning stateshows a status ofUpdatingand performs one upgrade domain at a time. When complete, it showsSucceededagain.
Modify OS SKU with a template
To modify the OS image used for a node type using an ARM Template, adjust the vmImageSku property with the new value and do a cluster deployment for the setting to take effect. The managed cluster provider reimages each instance by upgrade domain.
- The Service Fabric managed cluster resource apiVersion should be 2021-05-01 or later.
{
"apiVersion": "[variables('sfApiVersion')]",
"type": "Microsoft.ServiceFabric/managedclusters/nodetypes",
"name": "[concat(parameters('clusterName'), '/', parameters('nodeTypeName'))]",
"location": "[resourcegroup().location]",
"properties": {
...
"vmImagePublisher": "[parameters('vmImagePublisher')]",
"vmImageOffer": "[parameters('vmImageOffer')]",
"vmImageSku": "[parameters('vmImageSku')]",
"vmImageVersion": "[parameters('vmImageVersion')]",
...
}
}
Configure placement properties for a node type
Placement properties are used to ensure that certain workloads run only on certain node types in the cluster. Service Fabric managed clusters support configuring these properties via portal, ARM template, or PowerShell.
Configure placement properties with portal
In this walkthrough, you learn how to modify a placement property for a node type using portal.
Sign in to Azure portal
Navigate to your cluster resource Overview page.

Select
Node Typesunder theSettingssectionSelect the
Node type nameyou want to modifyIn the
Placement propertiessection, add the name and value you want and selectApplyat the bottom. In this screenshot, theNameSSD_Premiumwas used withValueoftrue.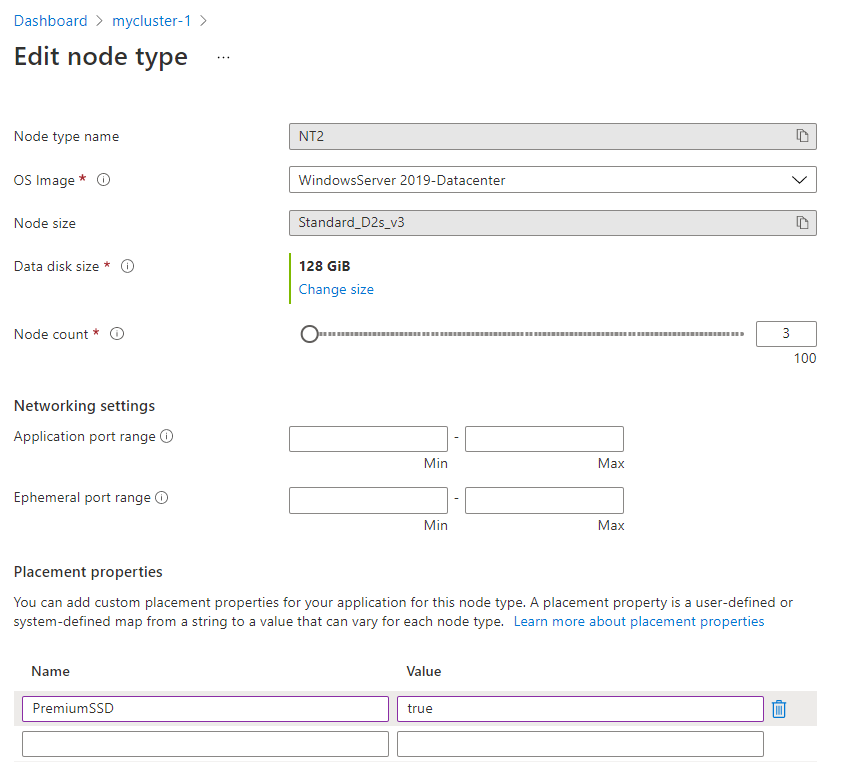
The
Provisioning stateshows a status ofUpdatinguntil complete. When complete, it showsSucceededagain.
Configure placement properties with a template
To adjust the placement properties for a node type using an ARM Template, adjust the placementProperties property with one or more new values and do a cluster deployment for the setting to take effect. The following sample shows three values being set for a node type.
- The Service Fabric managed cluster resource apiVersion should be 2021-05-01 or later.
{
"apiVersion": "[variables('sfApiVersion')]",
"type": "Microsoft.ServiceFabric/managedclusters/nodetypes",
"name": "[concat(parameters('clusterName'), '/', parameters('nodeTypeName'))]",
"location": "[resourcegroup().location]",
"properties": {
"placementProperties": {
"PremiumSSD": "true",
"NodeColor": "green",
"SomeProperty": "5"
}
}
}
Configure placement properties with PowerShell
The following example updates and overwrites any existing placement properties for a given node type.
$rgName = "testRG"
$clusterName = "testCluster"
$NodeTypeName = "nt1"
Set-AzServiceFabricManagedNodeType -ResourceGroupName $rgName -ClusterName $clusterName -name $NodeTypeName -PlacementProperty @{NodeColor="Red";SomeProperty="6";} -Verbose
Modify the VM SKU for a node type
To modify the VM SKU size used for a node type using an ARM Template, adjust the vmSize property with the new value and do a cluster deployment for the setting to take effect. The managed cluster provider reimages each instance by upgrade domain. For a list of SKU options, refer to the VM sizes - Azure Virtual Machines | Microsoft Learn.
{
"apiVersion": "[variables('sfApiVersion')]",
"type": "Microsoft.ServiceFabric/managedclusters/nodetypes",
"name": "[concat(parameters('clusterName'), '/', parameters('nodeTypeName'))]",
"location": "[resourcegroup().location]",
"properties": {
...
"vmSize": "[parameters('vmImageVersion')]",
...
}
}
Configure multiple managed disks
Service Fabric managed clusters by default configure one managed disk. By configuring the following optional property and values, you can add more managed disks to node types within a cluster. You're able to specify the drive letter, disk type, and size per disk.
Configure more managed disks by declaring additionalDataDisks property and required parameters in your Resource Manager template as follows:
Feature Requirements
- Lun must be unique per disk and can't use reserved lun 0 or 1
- Disk letter can't use reserved letters C or D and can't be modified once created. S is used by default if not specified.
- Must specify a supported disk type
- The Service Fabric managed cluster resource apiVersion should be 2022-01-01 or later.
{
"apiVersion": "[variables('sfApiVersion')]",
"type": "Microsoft.ServiceFabric/managedclusters/nodetypes",
"name": "[concat(parameters('clusterName'), '/', parameters('nodeTypeName'))]",
"location": "[resourcegroup().location]",
"properties": {
"additionalDataDisks": {
"lun": "2",
"diskSizeGB": "50",
"diskType": "Standard_LRS",
"diskLetter": "S"
}
}
}
See full list of parameters available.
Configure the Service Fabric data disk drive letter
Service Fabric managed clusters by default configure a Service Fabric data disk and automatically configure the drive letter on all nodes of a node type. By configuring this optional property and value, you can specify and retrieve the Service Fabric data disk letter if you have specific requirements for drive letter mapping.
Feature Requirements
- Disk letter can't use reserved letters C or D and can't be modified once created. S is used as default if not specified.
- The Service Fabric managed cluster resource apiVersion should be 2022-01-01 or later.
{
{
"apiVersion": "[variables('sfApiVersion')]",
"type": "Microsoft.ServiceFabric/managedclusters/nodetypes",
"name": "[concat(parameters('clusterName'), '/', parameters('nodeTypeName'))]",
"location": "[resourcegroup().location]",
"properties": {
"dataDiskLetter": "S"
}
}
}
Set computer name prefix
Customers who require longer names for their node type for more verbose description benefits from computer name prefix.
Note
Computer name prefix only works for Service Fabric API version 2024-04-01 or later.
Implement the following ARM template changes to set the computer name prefix:
{
"apiVersion": "2024-04-01",
"type": "Microsoft.ServiceFabric/managedclusters/nodetypes",
"name": "[concat(parameters('clusterName'), '/', 'BE-testResourceGroup-testRegion-test')]",
"location": "[parameters('clusterLocation')]",
"dependsOn": [
"[concat('Microsoft.ServiceFabric/managedclusters/', parameters('clusterName'))]"
],
"properties": {
"isPrimary": false,
"dataDiskSizeGB": "[parameters('dataDiskSizeGB')]",
"vmImagePublisher": "[parameters('vmImagePublisher')]",
"vmImageOffer": "[parameters('vmImageOffer')]",
"vmImageSku": "[parameters('vmImageSku')]",
"vmImageVersion": "[parameters('vmImageVersion')]",
"vmSize": "[parameters('vmSize')]",
"vmInstanceCount": "[parameters('vmInstanceCount')]",
"computerNamePrefix": "computerNamePrefix"
}
}