Nóta
Aðgangur að þessari síðu krefst heimildar. Þú getur prófað aðskrá þig inn eða breyta skráasöfnum.
Aðgangur að þessari síðu krefst heimildar. Þú getur prófað að breyta skráasöfnum.
This tutorial helps you create and manage a virtual network gateway (VPN gateway) using the Azure portal. The VPN gateway is one part of the connection architecture that helps you securely access resources within a virtual network using VPN Gateway.
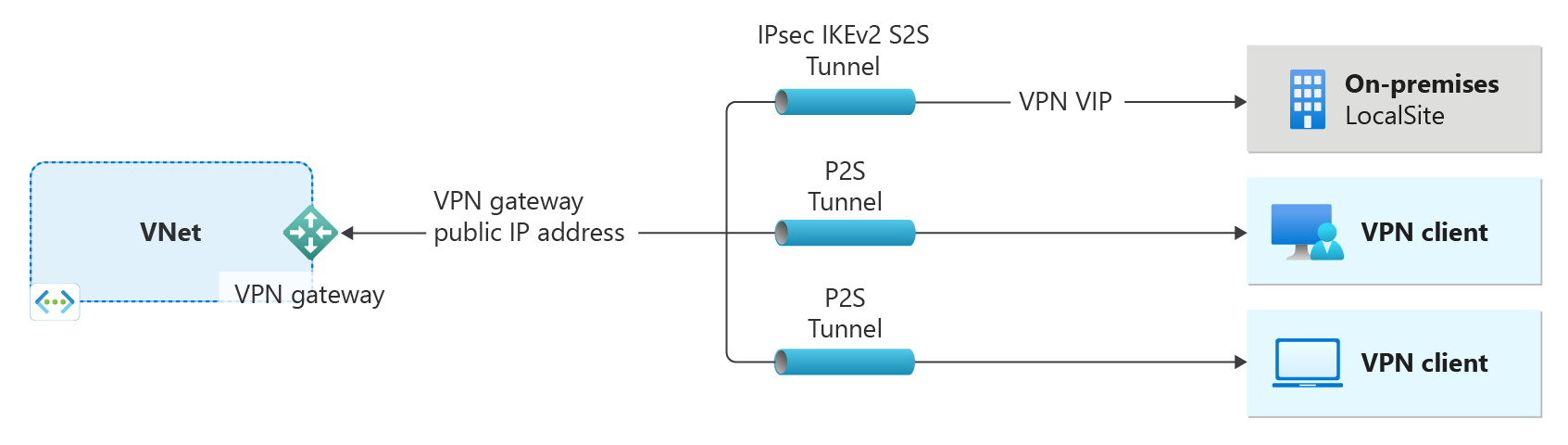
- The left side of the diagram shows the virtual network and the VPN gateway that you create by using the steps in this article.
- You can later add different types of connections, as shown on the right side of the diagram. For example, you can create site-to-site and point-to-site connections. To view different design architectures that you can build, see VPN gateway design.
- For more information about Azure VPN Gateway, see What is Azure VPN Gateway? If you want to learn more about the configuration settings used in this tutorial, see About VPN Gateway configuration settings.
In this tutorial, you learn how to:
- Create a virtual network.
- Create an active-active mode zone-redundant VPN gateway.
- View the gateway public IP address.
- Upgrade a VPN gateway SKU.
- Reset a VPN gateway.
Note
The steps in this article use the gateway SKU VpnGw2AZ, which is a SKU that supports Azure availability zones. Effective May 2025, all regions will accept an AZ SKU, regardless of whether availability zones are supported in that region. For more information about gateway SKUs, see About gateway SKUs.
Prerequisites
You need an Azure account with an active subscription. If you don't have one, create one for free.
Create a virtual network
This article uses the Azure portal to create a virtual network. You can also use a different tool or method to create a virtual network. For more information or steps, see Create a virtual network. For this exercise, the virtual network doesn't require the configuration of additional services, such as Azure Bastion or DDoS Protection. However, you can add these services if you want to use them.
| Setting | Example value |
|---|---|
| Resource Group | TestRG1 |
| Virtual Network Name | VNet1 |
| Region | East US |
| IPv4 address space | 10.1.0.0/16 |
| Subnet name | FrontEnd |
| Subnet address space | 10.1.0.0/24 |
- Sign in to the Azure portal.
- In Search resources, service, and docs (G+/) at the top of the portal page, enter virtual network. Select Virtual network from the Marketplace search results to open the Virtual network page.
- On the Virtual network page, select Create to open the Create virtual network page.
- Fill out the required values for the Basics tab.
- Select Next or Security to go to the Security tab. For this exercise, leave the default values for all the services on this page.
- Select IP Addresses to go to the IP Addresses tab. On the IP Addresses tab, configure the required settings.
- Review the IP addresses page and remove any address spaces or subnets that you don't need.
- Select Review + create to validate the virtual network settings.
- After the settings are validated, select Create to create the virtual network.
Create a gateway subnet
Virtual network gateway resources are deployed to a specific subnet named GatewaySubnet. The gateway subnet is part of the virtual network IP address range that you specify when you configure your virtual network.
If you don't have a subnet named GatewaySubnet, when you create your VPN gateway, it fails. We recommend that you create a gateway subnet that uses a /27 (or larger). For example, /27 or /26. For more information about the gateway subnet, see VPN Gateway settings - Gateway Subnet.
- On the page for your virtual network, on the left pane, select Subnets to open the Subnets page.
- At the top of the page, select + Subnet to open the Add subnet pane.
- For Subnet purpose, select Virtual Network Gateway from the dropdown.
- The name is automatically entered as GatewaySubnet. Adjust starting IP address and size if necessary. For example, 10.1.255.0/27.
- Don't adjust the other values on the page. Click Add to add the subnet.
For more information about adding a subnet to your virtual network, see Add, change, or delete a virtual network subnet. For steps to add an address range to your virtual network, see Add or remove an address range.
Important
NSGs on the gateway subnet aren't supported. Associating a network security group to this subnet might cause your virtual network gateway (VPN and ExpressRoute gateways) to stop functioning as expected. For more information about network security groups, see What is a network security group?.
Create a VPN gateway
In this section, you create the virtual network gateway (VPN gateway) for your virtual network. Creating a gateway can often take 45 minutes or more, depending on the selected gateway SKU. Use the following steps to create a VPN gateway. Note that the VPN Gateway Basic SKU is only available in PowerShell or CLI.
In Search resources, services, and docs (G+/), enter virtual network gateway. Locate Virtual network gateway in the Marketplace search results and select it to open the Create virtual network gateway page.
On the Basics tab, fill in the values for Project details and Instance details.
Setting Value Name Example: VNet1GW Region The region for the gateway must be the same as the virtual network. Gateway type Select VPN. VPN gateways use the virtual network gateway type VPN. SKU Example: VpnGw2AZ. We recommend that you select a Gateway SKU that ends in AZ if your region supports availability zones. Generation Generation 2 Virtual network Example: VNet1. If your virtual network isn't available in the dropdown, you need to adjust the region you selected. Subnet Example: 10.1.255.0/27, A subnet named GatewaySubnet is required to create a VPN gateway. If the gateway subnet doesn't autopopulate, and you don't see the option to create one on this page, go back to your virtual network page and create the gateway subnet.
Specify the values for Public IP address. These settings specify the public IP address object that gets associated to the VPN gateway. The public IP address is assigned to this object when the VPN gateway is created. The only time the primary public IP address changes is when the gateway is deleted and re-created.
Setting Value Public IP address name Example: VNet1GWpip1 Availability zone This setting is available for AZ SKUs in regions that support availability zones. Example: Zone-redundant. Enable active-active mode - Select Enabled to take advantage of the benefits of an active-active gateway. An active-active gateway requires an additional public IP address.
- If you plan to use this gateway for site-to-site connections, verify the active-active design that you want to use.
- Connections with your on-premises VPN device must be configured specifically to take advantage of active-active mode.
- Some VPN devices don't support active-active mode. If you're not sure, check with your VPN device vendor. If you're using a VPN device that doesn't support active-active mode, you can select Disabled for this setting.Second public IP address name Only available for active-active mode gateways. Example: VNet1GWpip2 Availability zone Example: Zone-redundant. Configure BGP Select Disabled, unless your configuration specifically requires this setting. If you do require this setting, the default ASN is 65515. Enable Key Vault Access Select Disabled unless you have a specific requirement to enable this setting. Select Review + create to run validation.
After validation passes, select Create to deploy the VPN gateway.
You can see the deployment status on the Overview page for your gateway. Once the gateway is created, you can view the IP address assigned to it by looking at the virtual network in the portal. The gateway appears as a connected device.
View public IP address
To view public IP addresses associated to your virtual network gateway, navigate to your gateway in the portal.
- On the Virtual network gateway portal page, under Settings, open the Properties page.
- To view more information about the IP address object, click the associated IP address link.
Upgrade a gateway SKU
There are specific rules for upgrading a gateway SKU. Not all SKUs can be upgraded. For more information, see Upgrade a gateway SKU.
- Go to the Configuration page for your virtual network gateway.
- On the right side of the page, select the dropdown arrow to show a list of available SKUs. Notice that the list only populates SKUs that you're able to select.
- Select the SKU from the dropdown list and save your changes.
Reset a gateway
Gateway resets behave differently, depending on your gateway configuration. For more information, see Reset a VPN gateway or a connection.
- In the portal, go to the virtual network gateway that you want to reset.
- On the Virtual network gateway page, in the left pane, scroll and locate Help -> Reset.
- On the Reset page, select Reset. After the command is issued, the current active instance of Azure VPN gateway is rebooted immediately. Resetting the gateway causes a gap in VPN connectivity and might limit future root cause analysis of the issue.
Clean up resources
If you're not going to continue to use this application or go to the next tutorial, delete these resources.
- Enter the name of your resource group in the Search box at the top of the portal and select it from the search results.
- Select Delete resource group.
- Enter your resource group for TYPE THE RESOURCE GROUP NAME and select Delete.
Next steps
After you create a VPN gateway, you can configure more gateway settings and connections. The following articles help you create a few of the most common configurations: