Use automation dictionary to pass parameter keys
The automation dictionary maintains the contextual data for sessions. You can use the keys from the automation dictionary to pass the parameter in an action.
While creating templates and macros in the admin app, you can pass parameter keys such as title of a session, title of notification, title of an application tab template, and custom parameter values for application tab types. These keys are replaced based on the contextual information available at the time of execution.
Pass data parameter in templates
Let's take a scenario for templates with the notifications.
The notification shows certain fields and values, which are called Field header and Value, respectively.
Kenny Smith, a customer, initiated a conversation and when the agent sees the notification, it displays Customer Name as Kenny Smith.
Here, Field header is Customer Name and the Value is Kenny Smith.
For templates to identify the name of the customer as Kenny Smith, you (the administrator) must pass the parameter as keys.
Similarly, for session and notification titles, you can pass the data parameters. More information: Automation dictionary formats to data parameter keys
The system replaces these parameter keys with the actual values based on the context of the session, channel provider, Microsoft Dataverse, and user actions. More information: Types of context data parameters
Pass data parameter in macros and agent scripts
Macros are a set of configured sequential actions that are run on demand by the user. As an administrator, you need to configure the actions that a macro must perform. To configure the actions, you need to pass the data parameters. More information: Automation dictionary formats to pass data parameter keys
When the agent runs the macro, the system replaces these parameter keys with the actual values based on the context of the session, channel provider, Dataverse, and user actions.
When the context is from a session, the macro action is run based on the information for a current session, where the information is obtained from an Anchor tab or current tab that's in focus. For example, to create a case, you need to define the actions that contain the incident entity form and the GUID of the form (optional). More information: Types of context data parameter
Types of context data parameters
The automation dictionary uses the context data parameters that are available from the following sources:
- Context data from the channel provider
- Context data from user actions
- Context data from Dataverse
- Context data from other macro actions
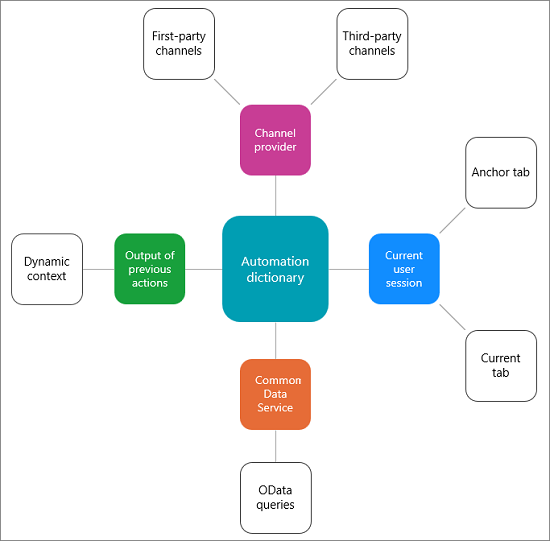
Context data from the channel provider
This context data is from the first-party channel provider such as Omnichannel for Customer Service or a third-party channel provider that uses the widget exposed by Dynamics 365 Channel Integration Framework. The context data from Omnichannel for Customer Service are pre-conversation survey, visitor portal navigation, and so on.
Context data from user actions
This data is populated as and when agents perform some activities in the session. An example is opening a new customer record, case, and so on.
Context data from Dataverse
The organizational data is stored in Dataverse, and you can fetch the data with the use of OData queries. More information: OData queries
Context data from other macro actions
An action in a macro generates context data that is consumed by other actions in that macro.
For example, there are two action steps in the following order:
- Open a new form to create a record.
- Open an email form with a predefined template.
While creating the Open an email form with predefined template action, you can get the context data parameter keys from the Open a new form to create a record macro action step.
The context data parameter from the first macro action are as follows:
- Entity Logical Name
- Page Type
- Tab Id
Note
The context data parameters from other macro actions are specific to macros, and aren't applicable to templates.
Automation dictionary formats to pass data parameter keys
The automation dictionary maintains the contextual data for sessions. The keys in the automation dictionary can be passed as parameters to the action in macros. The system replaces these parameter keys with the actual value based on the context of the session, channel provider, Dataverse, and user actions.
The automation dictionary supports the following formats:
Slugs
A slug is a replacement parameter that the system populates at runtime based on context. Use the following list of slugs only for macros and agent scripts, and to set an agent script as the default by using the agent script expression builder. More information: Productivity tools
Slugs for productivity tools (macros and agent scripts)
Macros and agent scripts support the following slugs:
| Slug | Description |
|---|---|
${customerName} |
The name of the customer who initiated the conversation. |
${caseId} |
The unique ID of a case. The system displays the case ID only if a case is linked to the conversation. |
${caseTitle} |
The title of the case. The system displays the title of the case only if the case is linked to the conversation. |
${LiveWorkItemId} |
The unique ID of the conversation. |
${queueId} |
The unique ID of a queue. This alphanumeric string is displayed in the queue page URL. |
${visitorLanguage} |
The language of the customer who initiated the conversation. |
${visitorDevice} |
The device of the customer who initiated the conversation. |
${entityRoutingLogicalName} |
The name of the entity, if the notification is for an entity record. |
${customerEntityName} |
The name of the entity (contact or account), if the customer is authenticated. |
${customerRecordId} |
The unique ID of the entity (contact or account), if the customer is authenticated. |
${<name of the pre-conversation survey questions>} |
All the pre-conversation survey questions that are configured for a workstream will have the slug name as the name of the question. |
Note
Only the ${anchor.<attribute_name>} slug is supported in the macros and scripts for Customer Service workspace.
Slug for reconnection link
The following slug is used to generate a reconnection link that can be shared with customers to connect back to the same agent and conversation. More information: Configure a reconnection to a previous chat
| Slug | Description |
|---|---|
{ReconnectUrl{ReconnectID}} |
Used in quick replies to generate the reconnect link. |
Format for slugs for productivity tools
The ${Slug} parameter format that retrieves the context from the channel provider, current user session, output of other macro actions, or Dataverse.
Productivity automation context
When you want to execute a slug in the productivity automation context, which is used to perform operations related to model-driven apps in Dynamics 365, use the ${</slug/>} format. For example: ${customerName}
Session connector context
When you want to execute a slug in the session context, you must use the ${$session.<slug>} format. For example: ${$session.customerName}
Slugs that are available for session context include:
${$session.visitorDevice}${$session.visitorDevice}${$session.entityRoutingLogicalName}${$session.entityRoutingRecordId}${$session.<name of the pre-chat survey questions>
Omnichannel connector context
When you want to execute a slug in the Omnichannel for Customer Service context, you must use the ${$oc.<slug>} format. For example: ${$oc.customerName}
The Session.CurrentTab.<Attribute> and Session.AnchorTab.<Attribute> parameters provide context data based on the current session and the anchor tab or the current tab in focus. The following are the supported attribute types:
- EntityName
- EntityId
Examples:
Session.CurrentTab.<EntityName>Session.CurrentTab.<EntityId>Session.AnchorTab.<EntityName>Session.AnchorTab.<EntityId>
Note
The Session.CurrentTab.<Attribute> and Session.AnchorTab.<Attribute> parameters are only applicable to macros and aren't applicable to templates.
Slugs for templates
The list of supported slugs are:
| Slug | Description |
|---|---|
{anchor.<attribute_name>} |
Is used to access attributes of the record that is loaded in the anchor tab. |
{customerName} |
The name of the customer who initiated the conversation. |
{caseId} |
The unique ID of a case. The system displays the case ID only if the case is linked to the conversation. |
{caseTitle} |
The title of the case. The system displays the title of the case only if the case is linked to the conversation. |
{queueId} |
The unique ID of a queue. This alphanumeric string is displayed in the queue page URL. |
{visitorLanguage} |
The language of the customer who initiated the conversation. |
{visitorDevice} |
The device of the customer who initiated the conversation. |
{entityRoutingLogicalName} |
The name of the entity, if the notification is for an entity record. |
{entityRoutingRecordId} |
The unique ID of the entity record, if the notification is for an entity record. |
{customerRecordId} |
The unique ID of the entity (contact or account), if the customer is authenticated. |
{<name of the pre-chat survey questions>} |
All the pre-chat survey questions that are configured for a workstream will have the slug name as the name of the question. |
Format for slugs for templates
The {Slug} parameter format that retrieves the template context from the channel provider, current user session, or Dataverse. For example: {caseId}
OData queries
You can use OData queries to get the contexts that are available from Dataverse.
The OData query format is:
{$odata.<entityName>.<entityAttributeName>.<?options>}
Examples:
{$odata.account.name.?$filter=accountid eq '{customerRecordId}'}{$odata.incident.prioritycode.?$filter=incidentid eq '{caseId}'&$select=prioritycode}{$odata.incident.title.?$filter=incidentid eq '{caseId}'&$select=title}
Static values
These are hard-coded values that you update based on your business requirements. For every hard-coded attribute you choose, follow the format type for the particular attribute.
Example (Macro):
You want a case title to always be appended with Contoso -. You use the Open a new form to create a record action with following fields.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Entity Logical Name | incident |
| Attribute Name | Case title |
| Attribute value | Contoso - {caseTitle} |
Here, Contoso - is the hard-coded static value.
Example (Templates):
For an incoming chat request, you want to provide the static title to the session and notification template that agents see at runtime.
Notification title = New chat request
Session title = Chat conversation
Related information
Manage session templates
Manage application tab templates
Manage notification templates
Associate templates with workstreams