Quickstart: Move and transform data with dataflows and data pipelines
In this tutorial, you discover how the dataflow and data pipeline experience can create a powerful and comprehensive Data Factory solution.
Prerequisites
To get started, you must have the following prerequisites:
- A tenant account with an active subscription. Create a free account.
- Make sure you have a Microsoft Fabric enabled Workspace: Create a workspace that isn’t the default My Workspace.
- An Azure SQL database with table data.
- A Blob Storage account.
Dataflows compared to pipelines
Dataflows Gen2 lets you to use a low-code interface and 300+ data and AI-based transformations to you easily clean, prep, and transform data with more flexibility than any other tool. Data Pipelines enable rich out-of-the-box data orchestration capabilities to compose flexible data workflows that meet your enterprise needs. In a pipeline, you can create logical groupings of activities that perform a task, which might include calling a Dataflow to clean and prep your data. While there's some functionality overlap between the two, the choice of which to use for a specific scenario depends on whether you require the full richness of pipelines or can use the simpler but more limited capabilities of dataflows. For more information, see the Fabric decision guide
Transform data with dataflows
Follow these steps to set up your dataflow.
Step 1: Create a dataflow
Choose your Fabric enabled workspace, and then select New. Then select Dataflow Gen2.
The dataflow editor window appears. Select the Import from SQL Server card.
Step 2: Get data
On the Connect to data source dialog presented next, enter the details to connect to your Azure SQL database, then select Next. For this example, you use the AdventureWorksLT sample database configured when you set up the Azure SQL database in the prerequisites.
Select the data you’d like to transform and then select Create. For this quickstart, select SalesLT.Customer from the AdventureWorksLT sample data provided for Azure SQL DB, and then the Select related tables button to automatically include two other related tables.
Step 3: Transform your data
If it isn't selected, select the Diagram view button along the status bar at the bottom of the page, or select Diagram view under the View menu at the top of the Power Query editor. Either of these options can toggle the diagram view.
Right-click your SalesLT Customer query, or select the vertical ellipsis on the right of the query, then select Merge queries.
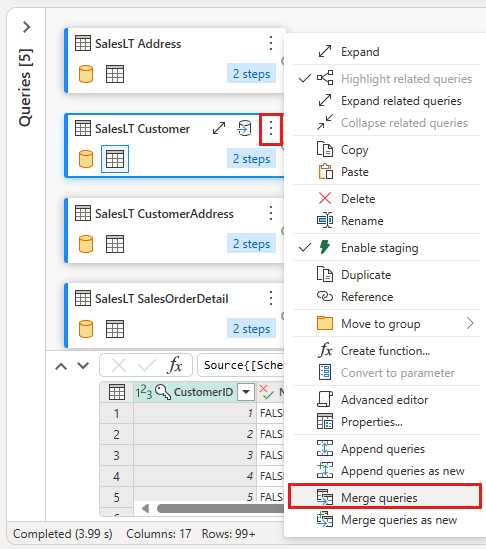
Configure the merge by selecting the SalesLTOrderHeader table as the right table for the merge, the CustomerID column from each table as the join column, and Left outer as the join kind. Then select OK to add the merge query.

Select the Add data destination button, which looks like a database symbol with an arrow above it, from the new merge query you created. Then select Azure SQL database as the destination type.
Provide the details for your Azure SQL database connection where the merge query is to be published. In this example, you can use the AdventureWorksLT database we used as the data source for the destination too.

Choose a database to store the data, and provide a table name, then select Next.

You can leave the default settings on the Choose destination settings dialog, and just select Save settings without making any changes here.

Select Publish back on the dataflow editor page, to publish the dataflow.
Move data with data pipelines
Now that you created a Dataflow Gen2, you can operate on it in a pipeline. In this example, you copy the data generated from the dataflow into text format in an Azure Blob Storage account.
Step 1: Create a new data pipeline
From your workspace, select New, and then select Data pipeline.

Name your pipeline then select Create.

Step 2: Configure your dataflow
Add a new dataflow activity to your data pipeline by selecting Dataflow in the Activities tab.

Select the dataflow on the pipeline canvas, and then the Settings tab. Choose the dataflow you created previously from the drop-down list.

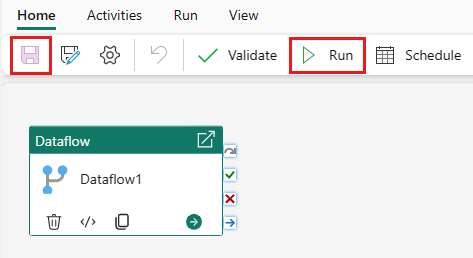
Select Save, and then Run to run the dataflow to initially populate its merged query table you designed in the prior step.
Step 3: Use the copy assistant to add a copy activity
Select Copy data on the canvas to open the Copy Assistant tool to get started. Or select Use copy assistant from the Copy data drop down list under the Activities tab on the ribbon.

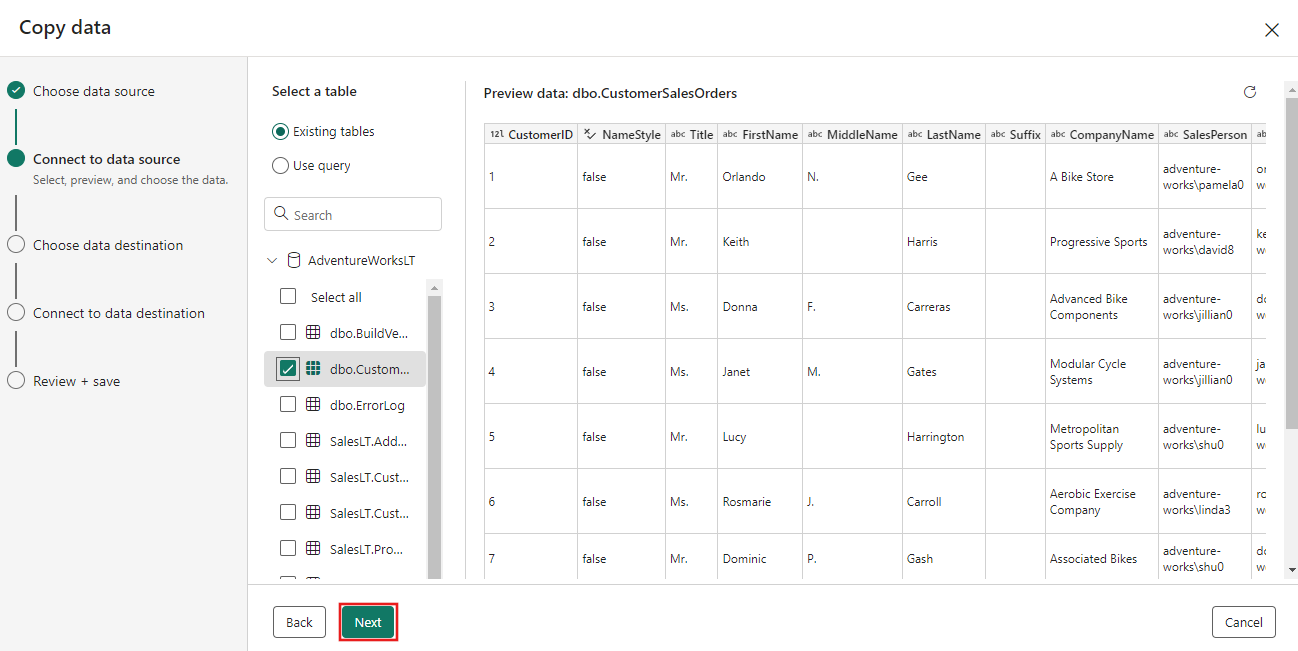
Choose your data source by selecting a data source type. In this tutorial, you use the Azure SQL Database used previously when you created the dataflow to generate a new merge query. Scroll down below the sample data offerings and select the Azure tab, then Azure SQL Database. Then select Next to continue.

Create a connection to your data source by selecting Create new connection. Fill in the required connection information on the panel, and enter the AdventureWorksLT for the database, where we generated the merge query in the dataflow. Then select Next.

Select the table you generated in the dataflow step earlier, and then select Next.
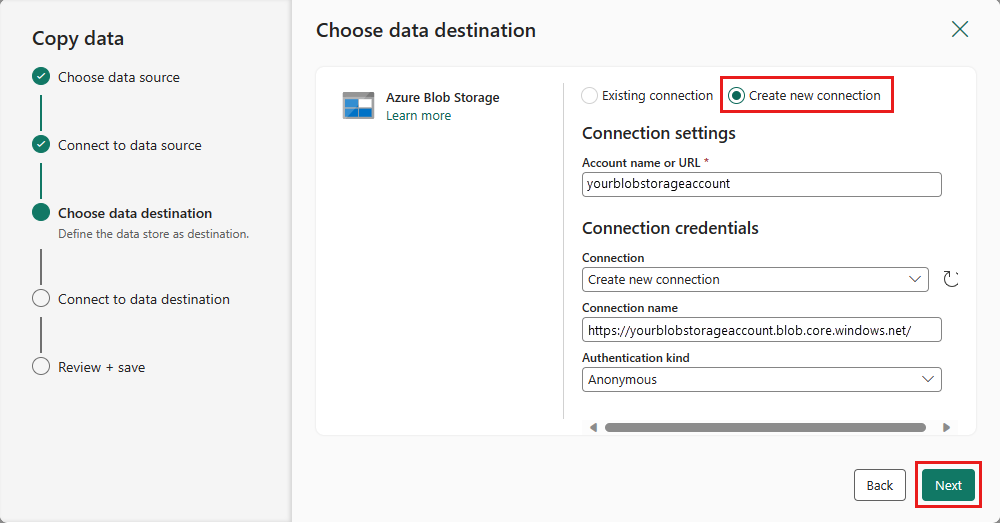
For your destination, choose Azure Blob Storage and then select Next.

Create a connection to your destination by selecting Create new connection. Provide the details for your connection, then select Next.
Select your Folder path and provide a File name, then select Next.

Select Next again to accept the default file format, column delimiter, row delimiter and compression type, optionally including a header.
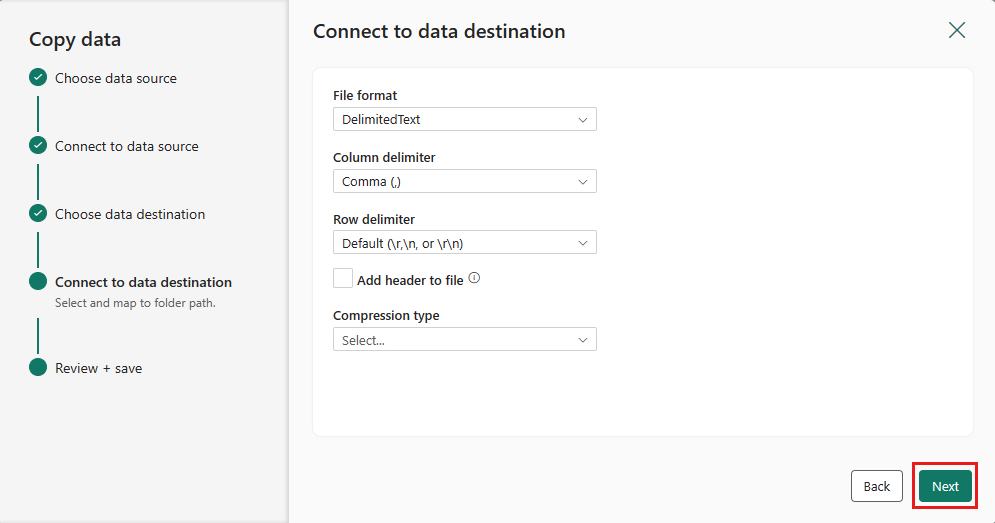
Finalize your settings. Then, review and select Save + Run to finish the process.

Step 5: Design your data pipeline and save to run and load data
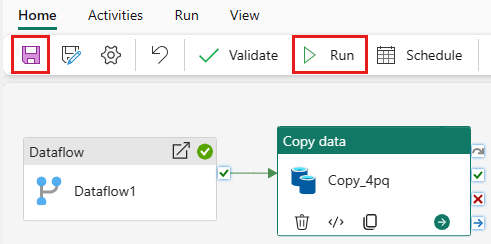
To run the Copy activity after the Dataflow activity, drag from Succeeded on the Dataflow activity to the Copy activity. The Copy activity only runs after the Dataflow activity succeeds.

Select Save to save your data pipeline. Then select Run to run your data pipeline and load your data.
Schedule pipeline execution
Once you finish developing and testing your pipeline, you can schedule it to execute automatically.
On the Home tab of the pipeline editor window, select Schedule.

Configure the schedule as required. The example here schedules the pipeline to execute daily at 8:00 PM until the end of the year.

Related content
This sample shows you how to create and configure a Dataflow Gen2 to create a merge query and store it in an Azure SQL database, then copy data from the database into a text file in Azure Blob Storage. You learned how to:
- Create a dataflow.
- Transform data with the dataflow.
- Create a data pipeline using the dataflow.
- Order the execution of steps in the pipeline.
- Copy data with the Copy Assistant.
- Run and schedule your data pipeline.
Next, advance to learn more about monitoring your pipeline runs.






