Nóta
Aðgangur að þessari síðu krefst heimildar. Þú getur prófað aðskrá þig inn eða breyta skráasöfnum.
Aðgangur að þessari síðu krefst heimildar. Þú getur prófað að breyta skráasöfnum.
Applies to:
Canvas apps
Copilot Studio
Model-driven apps
Power Platform CLI
Dataverse functions
Power Pages
Generates a JSON text string for a table, a record, or a value.
Description
The JSON function returns the JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) representation of a data structure as text so that it's suitable for storing or transmitting across a network. [ECMA-404](https://www.ecma-international.org/publications/files/ECMA-ST/ECMA-404.pdf and IETF RFC 8259 describe the format, which is widely used by JavaScript and other programming languages.
Canvas apps support the data types that this table lists with details about their text representation:
| Data type | Description | Result example |
|---|---|---|
| Boolean | true or false. | true |
| Color | String that contains the 8-digit hexadecimal representation for the color. This representation takes the format #rrggbbaa, where rr is the red component, gg is green, bb is blue, and aa is the alpha channel. For the alpha channel, 00 is fully transparent, and ff is fully opaque. You can pass the string to the ColorValue function. | "#102030ff" |
| Currency | Number that uses the appropriate decimal separator for the user's language. Scientific notation is used if needed. | 1.345 |
| Date | String that contains the date in ISO 8601 yyyy-mm-dd format. | "2019-03-31" |
| DateTime | String that contains an ISO 8601 date/time. Date/time values are in UTC, as the ending "Z" indicates. | "2019-03-31T22:32:06.822Z" |
| GUID | String that contains the GUID value. Letters are lowercase. | "751b58ac-380e-4a04-a925-9f375995cc40" |
| Image, Media | If JSONFormat.IncludeBinaryData is specified, media files are encoded in a string. Web references that use the http: or https: URL scheme aren't modified. References to in-memory binary data are encoded with the "data:mimetype;base64,..." format. In-memory data includes images that users capture by using the Camera control and any other references with the appres: and blob: URL schemes. | "data:image/jpeg;base64,/9j/4AA..." |
| Number | Number that uses the appropriate decimal separator for the user's language. Scientific notation is used if needed. | 1.345 |
| Option set | Numeric value of the choice, not the label that's used for display. The numeric value is used because it's language independent. | 1001 |
| Time | String that contains an ISO 8601 hh:mm:ss.fff format. | "23:12:49.000" |
| Record | Comma-delimited list, between { and }, of fields and their values. This notation resembles that for records in canvas apps, but the name is always between double quotation marks. This format doesn't support records that are based on many-to-one relationships. | { "First Name": "Fred", "Age": 21 } |
| Table | Comma-delimited list, between [ and ], of records. This format doesn't support tables that are based on one-to-many relationships. Use the JSONFormat.FlattenValueTables option to remove the record for single column tables with the column named Value. | [ { "First Name": "Fred", "Age": 21 }, { "First Name": "Jean", "Age": 20 } ] |
| Two option | Boolean value of the two option, true or false, not the label that's used for display. The Boolean value is used because it's language independent. | false |
| Hyperlink, Text | String between double quotation marks. The function escapes embedded double-quotation marks with a backslash, replaces newlines with "\n", and makes other standard JavaScript replacements. | "This is a string." |
Specify the optional Format argument to control how readable the result is and how unsupported and binary data types are handled. By default, the output is as compact as possible with no unnecessary spaces or newlines, and unsupported data types and binary data aren't allowed. You can combine multiple formats if you specify the & operator.
| JSONFormat enum | Description |
|---|---|
| JSONFormat.Compact | Default. The output is as compact as possible with no added spaces or newlines. |
| JSONFormat.FlattenValueTables | As a Value table, [1,2,3] notation results in a table containing records where each record has a single Value column. In JSON, that same notation represents an array of three numbers. To make interoperability between the two easier, this option flattens a Power Fx Value table to a JSON friendly array instead of an array of records. |
| JSONFormat.IndentFour | To improve readability, the output contains a newline for each column and nesting level and uses four spaces for each indentation level. |
| JSONFormat.IncludeBinaryData | The result includes image, video, and audio-clip columns. This format can dramatically increase the result's size and degrade your app's performance. |
| JSONFormat.IgnoreBinaryData | The result doesn't include image, video, or audio-clip columns. If you specify neither JSONFormat.IncludeBinaryData nor JSONFormat.IgnoreBinaryData, the function produces an error if it encounters binary data. |
| JSONFormat.IgnoreUnsupportedTypes | Unsupported data types are allowed, but the result won't include them. By default, unsupported data types produce an error. |
Use the ShowColumns and DropColumns functions to control which data the result includes and to remove unsupported data types.
Because JSON can be both memory and compute intensive, you can use this function only in behavior functions. You can capture the result from JSON into a variable, which you can then use in data flow.
If a column has both a display name and a logical name, the result contains the logical name. Display names reflect the language of the app user and are, therefore, inappropriate for data transfer to a common service.
Syntax
JSON( DataStructure [, Format ] )
- DataStructure – Required. The data structure to convert to JSON. Tables, records, and primitive values are supported, arbitrarily nested.
- Format - Optional. JSONFormat enum value. The default value is JSONFormat.Compact, which doesn't add newlines or spaces and blocks binary data and unsupported columns.
Examples
Hierarchical data
Insert a Button control, and set its OnSelect property to this formula.
ClearCollect( CityPopulations, { City: "London", Country: "United Kingdom", Population: 8615000 }, { City: "Berlin", Country: "Germany", Population: 3562000 }, { City: "Madrid", Country: "Spain", Population: 3165000 }, { City: "Hamburg", Country: "Germany", Population: 1760000 }, { City: "Barcelona", Country: "Spain", Population: 1602000 }, { City: "Munich", Country: "Germany", Population: 1494000 } ); ClearCollect( CitiesByCountry, GroupBy( CityPopulations, "Country", "Cities" ) )Select the button while holding down the Alt key.
The CitiesByCountry collection is created with this data structure, which you can show by selecting Collections on the File menu and then selecting the name of the collection.
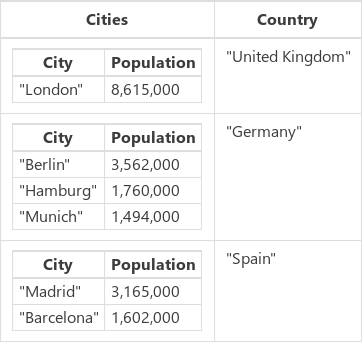
You can also show this collection by selecting Settings > Upcoming features > Enable formula bar result view, selecting the name of the collection in the formula bar, and then selecting the down arrow next to the name of the collection under the formula bar.
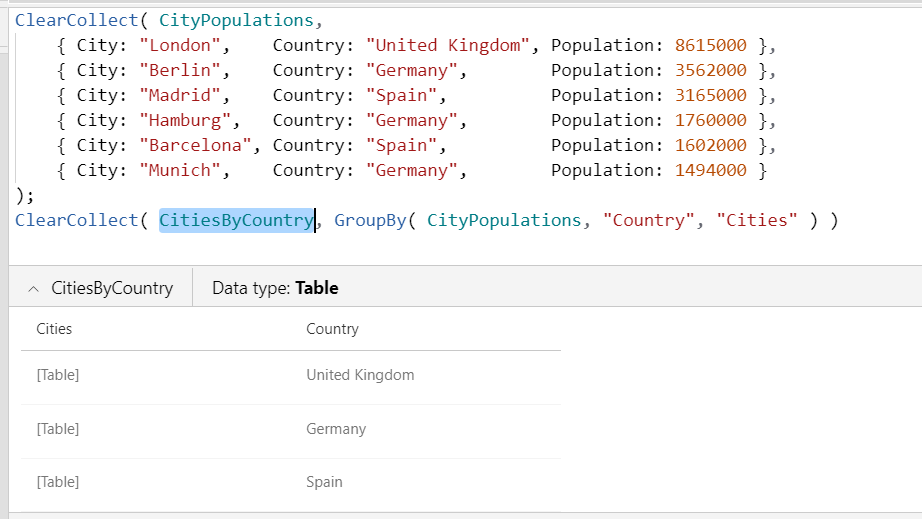
Insert another button, and set its OnSelect property to this formula:
Set( CitiesByCountryJSON, JSON( CitiesByCountry ) )This formula sets the global variable CitiesByCountryJSON to the JSON representation for CitiesByCountry.
Select the button while holding down the Alt key.
Insert a Label control, and set its Text property to this variable.
CitiesByCountryJSONThe label shows this result, all on a single line with no spaces, suitable for transmission across a network:
[ { "Cities": [{ "City": "London", "Population": 8615000 }], "Country": "United Kingdom" }, { "Cities": [ { "City": "Berlin", "Population": 3562000 }, { "City": "Hamburg", "Population": 1760000 }, { "City": "Munich", "Population": 1494000 } ], "Country": "Germany" }, { "Cities": [ { "City": "Madrid", "Population": 3165000 }, { "City": "Barcelona", "Population": 1602000 } ], "Country": "Spain" } ]Change the second button's formula to make the output more readable.
Set( CitiesByCountryJSON, JSON(CitiesByCountry, JSONFormat.IndentFour ))Select the second button while holding down the Alt key.
The label shows the more readable result.
[ { "Cities": [ { "City": "London", "Population": 8615000 } ], "Country": "United Kingdom" }, { "Cities": [ { "City": "Berlin", "Population": 3562000 }, { "City": "Hamburg", "Population": 1760000 }, { "City": "Munich", "Population": 1494000 } ], "Country": "Germany" }, { "Cities": [ { "City": "Madrid", "Population": 3165000 }, { "City": "Barcelona", "Population": 1602000 } ], "Country": "Spain" } ]
Images and media in base64
Add an Image control.
This control brings SampleImage with it.
Add a Button control, and set its OnSelect property to this formula.
Set( ImageJSON, JSON( SampleImage, JSONFormat.IncludeBinaryData ) )Select the button while holding down the Alt key.
Add a label, and set its Text property to this variable.
ImageJSONResize the control and reduce the font size as needed to show most of the result.
The label shows the text string that the JSON function captured.
"data:image/svg+xml;base64,PD94bWwgdmVyc2lvbj0iMS4wIiBlbmNvZGluZz0idXRmLTgiPz4NCjxzdmcgdmVyc2lvbj0iMS4xIg0KCSB4bWxucz0iaHR0cDovL3d3dy53My5vcmcvMjAwMC9zdmciIHhtbG5zOnhsaW5rPSJodHRwOi8vd3d3LnczLm9yZy8xOTk5L3hsaW5rIiB4bWxuczphPSJodHRwOi8vbnMuYWRvYmUuY29tL0Fkb2JlU1ZHVmlld2VyRXh0ZW5zaW9ucy8zLjAvIg0KCSB4PSIwcHgiIHk9IjBweCIgd2lkdGg9IjI3MHB4IiBoZWlnaHQ9IjI3MHB4IiBlbmFibGUtYmFja2dyb3VuZD0ibmV3IDAgMCAyNzAgMjcwIiB4bWw6c3BhY2U9InByZXNlcnZlIj4NCgk8ZyBjbGFzcz0ic3QwIj4NCgkJPHJlY3QgeT0iMC43IiBmaWxsPSIjRTlFOUU5IiB3aWR0aD0iMjY5IiBoZWlnaHQ9IjI2OS4zIi8+DQoJCTxwb2x5Z29uIGZpbGw9IiNDQkNCQ0EiIHBvaW50cz0iMjc3LjksMTg3LjEgMjQ1LDE0My40IDE4OC42LDIwMi44IDc1LDgwLjUgLTQuMSwxNjUuMyAtNC4xLDI3MiAyNzcuOSwyNzIiLz4NCgkJPGVsbGlwc2UgZmlsbD0iI0NCQ0JDQSIgY3g9IjIwMi40IiBjeT0iODQuMSIgcng9IjI0LjQiIHJ5PSIyNC4zIi8+DQoJPC9nPg0KPC9zdmc+"
Value tables
This formula:
JSON( [1,2,3] )
produces the text string [{"Value":1},{"Value":2},{"Value":3}].
The same formula with the JSONFormat.FlattenValueTables option:
JSON( [1,2,3], JSONFormat.FlattenValueTables )
produces the text string [1,2,3].
Note that the FlattenValueTables option has no impact when using JSON with the CityPopulations or CitiesByCountry collections as these tables are not Value tables. A Value table has a single column and it must be named "Value".