Rand and RandBetween functions
Applies to:
Canvas apps
Desktop flows
Model-driven apps
Power Pages
Power Platform CLI
Returns a pseudo-random number.
Description
The Rand function returns a pseudo-random number that's greater than or equal to 0 and less than 1. For example, Rand() might return 0.43147 and could return 0 but not 1.
The RandBetween function returns a pseudo-random integer (whole number with no decimal portion) that is between two numbers, inclusive. For example, RandBetween( 1, 3 ) may return 1, 2, or 3.
Volatile Functions
Rand and RandBetween are volatile function. Each time the function is evaluated it returns a different value.
When used in a data flow formula, a volatile function will only return a different value if the formula in which it appears is reevaluated. If nothing else changes in the formula then it will have the same value throughout the execution of your app.
For example, a label control with Label1.Text = Rand() won't change while your app is active. Only closing and reopening the app will result in a new value.
The function will be reevaluated if it's part of a formula in which something else has changed. For example, if we change our example to involve a slider control with Label1.Text = Slider1.Value + Rand() then a new random number is generated each time the Slider control's value changes and the label's text property is reevaluated. See below for this example.
When used in a behavior formula, Rand and RandBetween will be evaluated each time the behavior formula is evaluated. See below for an example.
Syntax
Rand()
RandBetween( Bottom, Top )
- Bottom - Required. The smallest integer that the function can return.
- Top - Required. The largest integer that the function can return. Must be equal to or greater than Bottom.
Examples
Basic usage
| Formula | Description | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Rand() | Returns a pseudo-random number that's greater than or equal to 0 and less than 1. | Varies with each evaluation, for example 0.874252. |
| Rand() * 100 | Building on the previous example, uses multiplication to extend the range to greater than or equal to 0 and less than 100. | Varies with each evaluation, for example 78.42521. |
| Int( Rand() * 100 ) | Building on the previous example, uses the Int function to remove the decimal portion, resulting in an integer greater than or equal to 0 and less than 100 | Varies with each evaluation, for example 84. |
| RandBetween( 0, 99 ) | Building on the previous example, performs the same operation using the RandBetween function | Varies with each evaluation, for example 21. |
| RandBetween( -1, 1 ) | Returns a pseudo-random number that is between -1 and 1 inclusive: -1, 0, or 1. | Varies with each evaluation, for example -1. |
Display a different random number as user input changes with Rand
Add a Slider control, and rename it Slider1 if it has a different name.
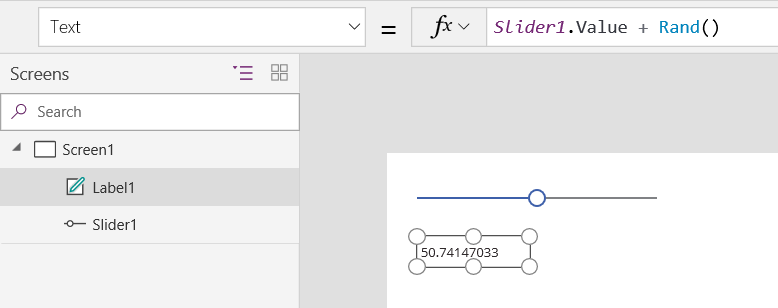
Add a Label control, and set its Text property to this formula:
Slider1.Value + Rand()
The label shows 50 (the default value for the slider) plus a random decimal:
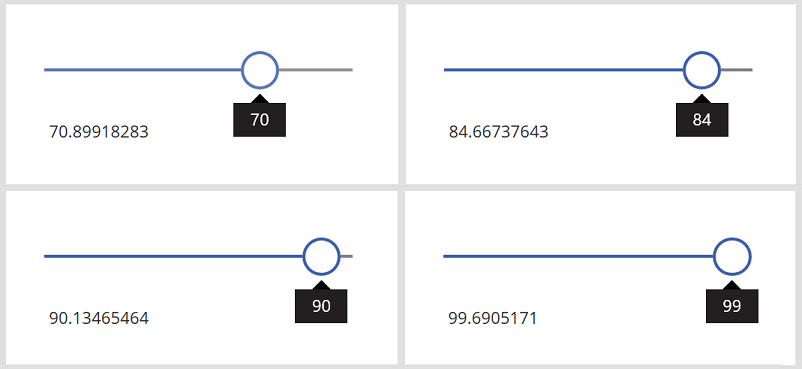
While holding down the Alt key, change the value of the slider.
Every time you change the value of the slider, the decimal portion of the label shows a different random number:
Create a table of random numbers with RandBetween
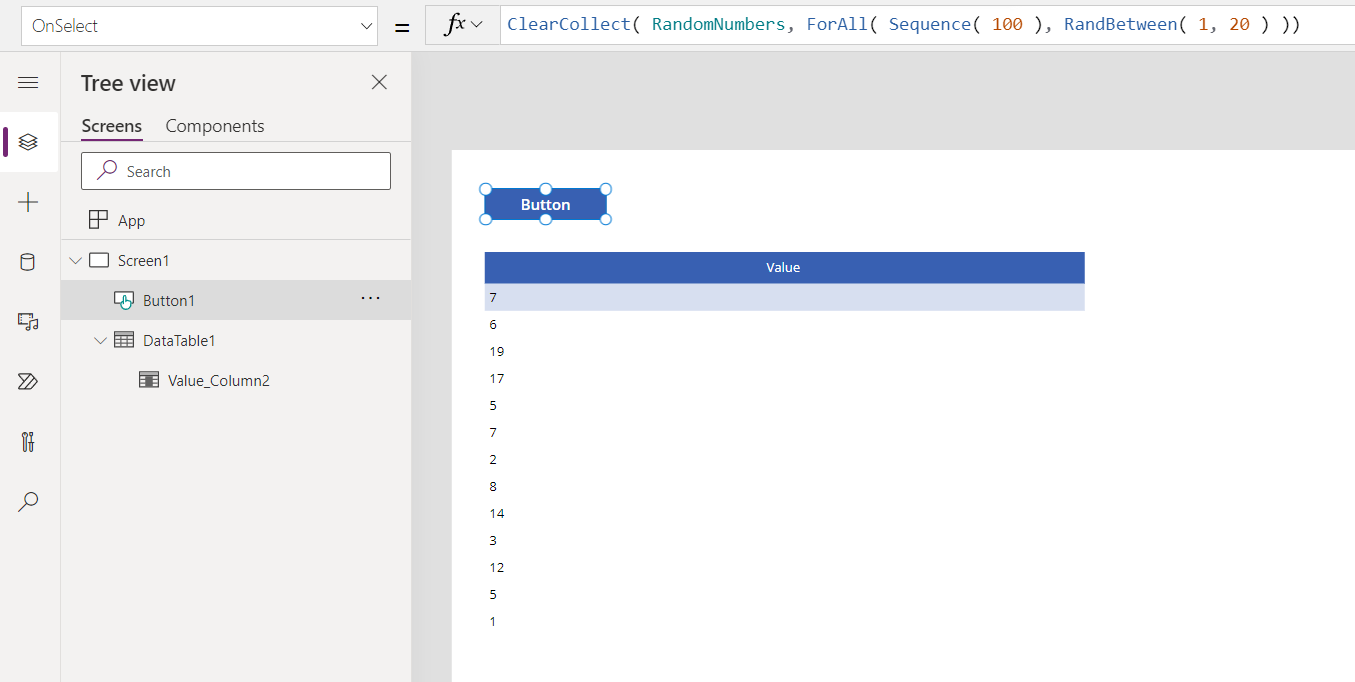
Add a Button control, and set its OnSelect property to this formula:
ClearCollect( RandomNumbers, ForAll( Sequence( 100 ), RandBetween( 1, 20 ) ))
This formula creates a single-column table that's used to iterate 100 times, resulting in 100 random numbers.
Add a Data table, set its Items property to RandomNumbers, and show the Value field.
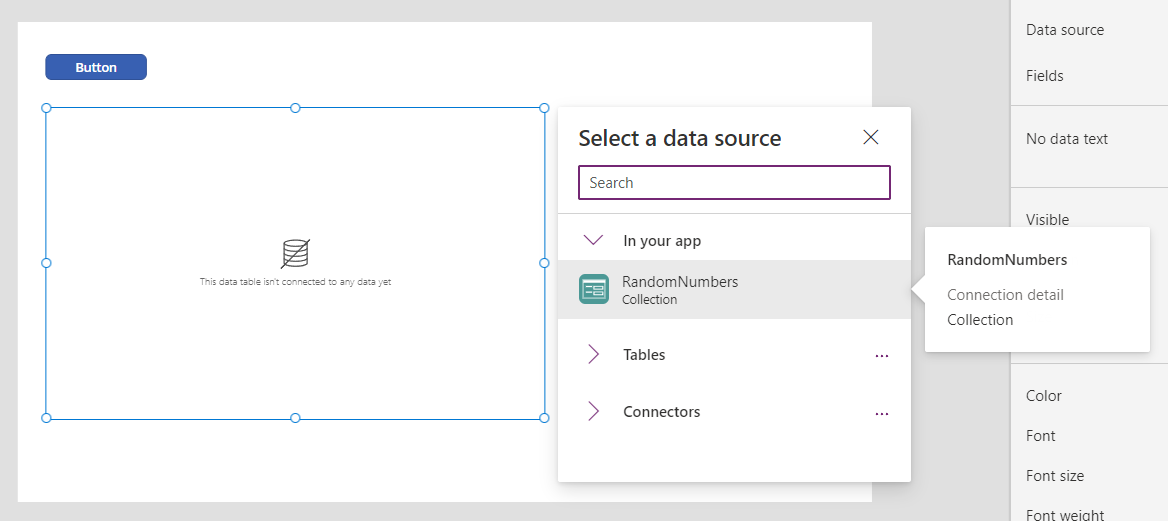
While holding down the Alt key, select the button by clicking or tapping it.
The data table shows 100 hundred random numbers between 1 and 20:
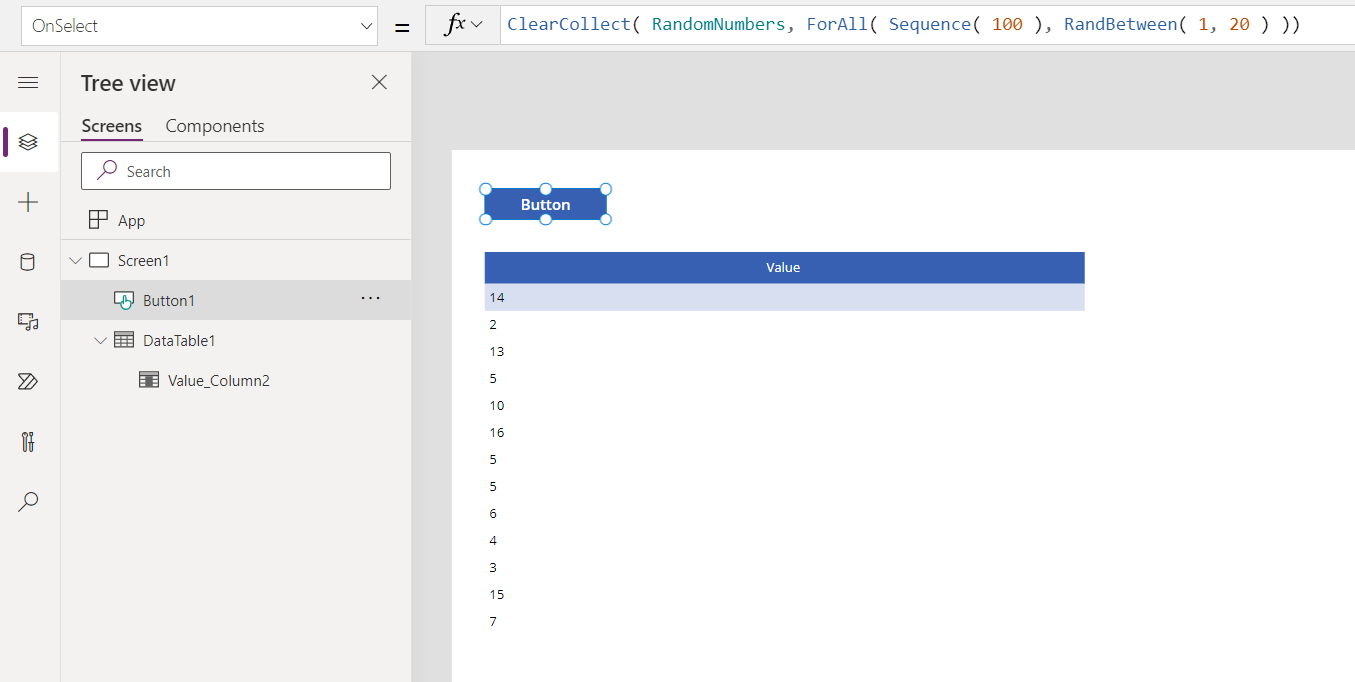
Select the button again to show a different list of random numbers:
To generate a single random number instead of a table, use Set( RandomNumber, Rand() ) or Set( RandNumber, RandBetween( 1, 20 ) ).