Nota
L'accesso a questa pagina richiede l'autorizzazione. È possibile provare ad accedere o modificare le directory.
L'accesso a questa pagina richiede l'autorizzazione. È possibile provare a modificare le directory.
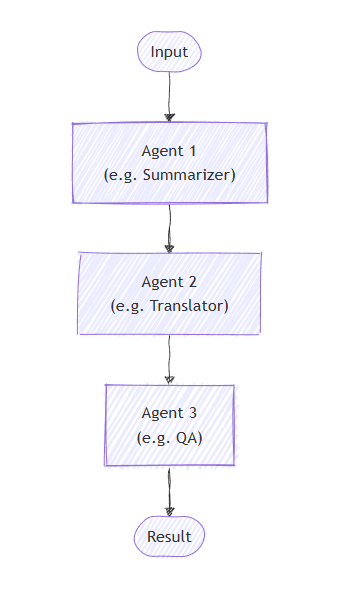
Nell'orchestrazione sequenziale gli agenti sono organizzati in una pipeline. Ogni agente elabora l'attività a sua volta, passando l'output all'agente successivo nella sequenza. Questo è ideale per i flussi di lavoro in cui ogni passaggio si basa su quello precedente, ad esempio la revisione dei documenti, le pipeline di elaborazione dei dati o il ragionamento a più fasi.
Importante
La cronologia completa della conversazione degli agenti precedenti viene passata all'agente successivo nella sequenza. Ogni agente può visualizzare tutti i messaggi precedenti, consentendo l'elaborazione compatibile con il contesto.
Cosa Imparerai
- Come creare una pipeline sequenziale di agenti
- Come concatenare gli agenti in cui ognuno si basa sull'output precedente
- Come combinare agenti con executor personalizzati per attività specializzate
- Come tenere traccia del flusso della conversazione attraverso la pipeline
Definire gli agenti
Nell'orchestrazione sequenziale, gli agenti sono organizzati in una pipeline in cui ogni agente elabora l'attività a sua volta, passando l'output all'agente successivo nella sequenza.
Configurare il client OpenAI di Azure
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Azure.AI.OpenAI;
using Azure.Identity;
using Microsoft.Agents.AI.Workflows;
using Microsoft.Extensions.AI;
using Microsoft.Agents.AI;
// 1) Set up the Azure OpenAI client
var endpoint = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT") ??
throw new InvalidOperationException("AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT is not set.");
var deploymentName = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("AZURE_OPENAI_DEPLOYMENT_NAME") ?? "gpt-4o-mini";
var client = new AzureOpenAIClient(new Uri(endpoint), new DefaultAzureCredential())
.GetChatClient(deploymentName)
.AsIChatClient();
Avviso
DefaultAzureCredential è utile per lo sviluppo, ma richiede un'attenta considerazione nell'ambiente di produzione. Nell'ambiente di produzione prendere in considerazione l'uso di credenziali specifiche ,ad esempio ManagedIdentityCredential, per evitare problemi di latenza, probe di credenziali indesiderate e potenziali rischi per la sicurezza dai meccanismi di fallback.
Creare agenti specializzati che funzioneranno in sequenza:
// 2) Helper method to create translation agents
static ChatClientAgent GetTranslationAgent(string targetLanguage, IChatClient chatClient) =>
new(chatClient,
$"You are a translation assistant who only responds in {targetLanguage}. Respond to any " +
$"input by outputting the name of the input language and then translating the input to {targetLanguage}.");
// Create translation agents for sequential processing
var translationAgents = (from lang in (string[])["French", "Spanish", "English"]
select GetTranslationAgent(lang, client));
Configurare l'orchestrazione sequenziale
Compilare il flusso di lavoro usando AgentWorkflowBuilder:
// 3) Build sequential workflow
var workflow = AgentWorkflowBuilder.BuildSequential(translationAgents);
Eseguire il flusso di lavoro sequenziale
Eseguire il flusso di lavoro ed elaborare gli eventi:
// 4) Run the workflow
var messages = new List<ChatMessage> { new(ChatRole.User, "Hello, world!") };
StreamingRun run = await InProcessExecution.StreamAsync(workflow, messages);
await run.TrySendMessageAsync(new TurnToken(emitEvents: true));
List<ChatMessage> result = new();
await foreach (WorkflowEvent evt in run.WatchStreamAsync().ConfigureAwait(false))
{
if (evt is AgentResponseUpdateEvent e)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{e.ExecutorId}: {e.Data}");
}
else if (evt is WorkflowOutputEvent outputEvt)
{
result = (List<ChatMessage>)outputEvt.Data!;
break;
}
}
// Display final result
foreach (var message in result)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{message.Role}: {message.Content}");
}
Output di esempio
French_Translation: User: Hello, world!
French_Translation: Assistant: English detected. Bonjour, le monde !
Spanish_Translation: Assistant: French detected. ¡Hola, mundo!
English_Translation: Assistant: Spanish detected. Hello, world!
Concetti chiave
- Elaborazione sequenziale: ogni agente elabora l'output dell'agente precedente nell'ordine
- AgentWorkflowBuilder.BuildSequential(): crea un flusso di lavoro della pipeline da una raccolta di agenti
- ChatClientAgent: rappresenta un agente supportato da un client di chat con istruzioni specifiche
- StreamingRun: fornisce l'esecuzione in tempo reale con funzionalità di streaming di eventi
-
Gestione eventi: monitorare l'avanzamento attraverso
AgentResponseUpdateEvente il completamento attraversoWorkflowOutputEvent
Nell'orchestrazione sequenziale, ogni agente elabora l'attività a sua volta, con il flusso dell'output che passa da uno a quello successivo. Per iniziare, definire gli agenti per un processo in due fasi:
from agent_framework.azure import AzureChatClient
from azure.identity import AzureCliCredential
# 1) Create agents using AzureChatClient
chat_client = AzureChatClient(credential=AzureCliCredential())
writer = chat_client.as_agent(
instructions=(
"You are a concise copywriter. Provide a single, punchy marketing sentence based on the prompt."
),
name="writer",
)
reviewer = chat_client.as_agent(
instructions=(
"You are a thoughtful reviewer. Give brief feedback on the previous assistant message."
),
name="reviewer",
)
Configurare l'orchestrazione sequenziale
La SequentialBuilder classe crea una pipeline in cui gli agenti elaborano le attività in ordine. Ogni agente vede la cronologia completa della conversazione e aggiunge la risposta:
from agent_framework.orchestrations import SequentialBuilder
# 2) Build sequential workflow: writer -> reviewer
workflow = SequentialBuilder(participants=[writer, reviewer]).build()
Eseguire il flusso di lavoro sequenziale
Eseguire il flusso di lavoro e raccogliere la conversazione finale che mostra il contributo di ogni agente:
from agent_framework import Message, WorkflowEvent
# 3) Run and print final conversation
output_evt: WorkflowEvent | None = None
async for event in workflow.run_stream("Write a tagline for a budget-friendly eBike."):
if event.type == "output":
output_evt = event
if output_evt:
print("===== Final Conversation =====")
messages: list[Message] | Any = output_evt.data
for i, msg in enumerate(messages, start=1):
name = msg.author_name or ("assistant" if msg.role == "assistant" else "user")
print(f"{'-' * 60}\n{i:02d} [{name}]\n{msg.text}")
Output di esempio
===== Final Conversation =====
------------------------------------------------------------
01 [user]
Write a tagline for a budget-friendly eBike.
------------------------------------------------------------
02 [writer]
Ride farther, spend less—your affordable eBike adventure starts here.
------------------------------------------------------------
03 [reviewer]
This tagline clearly communicates affordability and the benefit of extended travel, making it
appealing to budget-conscious consumers. It has a friendly and motivating tone, though it could
be slightly shorter for more punch. Overall, a strong and effective suggestion!
Avanzato: integrazione di agenti con executor personalizzati
L'orchestrazione sequenziale supporta la combinazione di agenti con executor personalizzati per l'elaborazione specializzata. Ciò è utile quando è necessaria una logica personalizzata che non richiede un LLM:
Definire un executor personalizzato
from agent_framework import Executor, WorkflowContext, handler
from agent_framework import Message
class Summarizer(Executor):
"""Simple summarizer: consumes full conversation and appends an assistant summary."""
@handler
async def summarize(
self,
conversation: list[Message],
ctx: WorkflowContext[list[Message]]
) -> None:
users = sum(1 for m in conversation if m.role == "user")
assistants = sum(1 for m in conversation if m.role == "assistant")
summary = Message(
role="assistant",
contents=[f"Summary -> users:{users} assistants:{assistants}"]
)
await ctx.send_message(list(conversation) + [summary])
Creare un flusso di lavoro sequenziale misto
# Create a content agent
content = chat_client.as_agent(
instructions="Produce a concise paragraph answering the user's request.",
name="content",
)
# Build sequential workflow: content -> summarizer
summarizer = Summarizer(id="summarizer")
workflow = SequentialBuilder(participants=[content, summarizer]).build()
Output di esempio con executor personalizzato
------------------------------------------------------------
01 [user]
Explain the benefits of budget eBikes for commuters.
------------------------------------------------------------
02 [content]
Budget eBikes offer commuters an affordable, eco-friendly alternative to cars and public transport.
Their electric assistance reduces physical strain and allows riders to cover longer distances quickly,
minimizing travel time and fatigue. Budget models are low-cost to maintain and operate, making them accessible
for a wider range of people. Additionally, eBikes help reduce traffic congestion and carbon emissions,
supporting greener urban environments. Overall, budget eBikes provide cost-effective, efficient, and
sustainable transportation for daily commuting needs.
------------------------------------------------------------
03 [assistant]
Summary -> users:1 assistants:1
Concetti chiave
- Contesto condiviso: ogni partecipante riceve la cronologia completa della conversazione, inclusi tutti i messaggi precedenti
-
L'ordine è importante: gli agenti vengono eseguiti rigorosamente nell'ordine specificato nell'elenco
participants() - Partecipanti flessibili: è possibile combinare agenti ed esecutori personalizzati in qualsiasi ordine
- Flusso di conversazione: ciascun agente/esecutore aggiunge alla conversazione, creando un dialogo completo.