TextPatternRange.Move(TextUnit, Int32) Metodo
Definizione
Importante
Alcune informazioni sono relative alla release non definitiva del prodotto, che potrebbe subire modifiche significative prima della release definitiva. Microsoft non riconosce alcuna garanzia, espressa o implicita, in merito alle informazioni qui fornite.
Sposta l'intervallo di testo di un numero specificato di unità di testo.
public:
int Move(System::Windows::Automation::Text::TextUnit unit, int count);public int Move (System.Windows.Automation.Text.TextUnit unit, int count);member this.Move : System.Windows.Automation.Text.TextUnit * int -> intPublic Function Move (unit As TextUnit, count As Integer) As IntegerParametri
- unit
- TextUnit
Limite di unità di testo.
- count
- Int32
Numero di unità di testo da spostare. Un valore positivo consente di spostare l'intervallo di testo in avanti, un valore negativo consente di spostare l'intervallo di testo indietro e 0 non ha effetto.
Restituisce
Numero di unità effettivamente spostate. Può essere inferiore al numero richiesto se uno dei nuovi endpoint di intervallo di testo è maggiore o minore degli endpoint di DocumentRange.
Esempio
/// -------------------------------------------------------------------
/// <summary>
/// Starts the target application and returns the AutomationElement
/// obtained from the targets window handle.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="exe">
/// The target application.
/// </param>
/// <param name="filename">
/// The text file to be opened in the target application
/// </param>
/// <returns>
/// An AutomationElement representing the target application.
/// </returns>
/// -------------------------------------------------------------------
private AutomationElement StartTarget(string exe, string filename)
{
// Start text editor and load with a text file.
Process p = Process.Start(exe, filename);
// targetApp --> the root AutomationElement.
AutomationElement targetApp =
AutomationElement.FromHandle(p.MainWindowHandle);
return targetApp;
}
''' -------------------------------------------------------------------
''' <summary>
''' Starts the target application and returns the AutomationElement
''' obtained from the targets window handle.
''' </summary>
''' <param name="exe">
''' The target application.
''' </param>
''' <param name="filename">
''' The text file to be opened in the target application
''' </param>
''' <returns>
''' An AutomationElement representing the target application.
''' </returns>
''' -------------------------------------------------------------------
Private Function StartTarget( _
ByVal exe As String, ByVal filename As String) As AutomationElement
' Start text editor and load with a text file.
Dim p As Process = Process.Start(exe, filename)
' targetApp --> the root AutomationElement.
Dim targetApp As AutomationElement
targetApp = AutomationElement.FromHandle(p.MainWindowHandle)
Return targetApp
End Function
/// -------------------------------------------------------------------
/// <summary>
/// Obtain the text control of interest from the target application.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="targetApp">
/// The target application.
/// </param>
/// <returns>
/// An AutomationElement that represents a text provider..
/// </returns>
/// -------------------------------------------------------------------
private AutomationElement GetTextElement(AutomationElement targetApp)
{
// The control type we're looking for; in this case 'Document'
PropertyCondition cond1 =
new PropertyCondition(
AutomationElement.ControlTypeProperty,
ControlType.Document);
// The control pattern of interest; in this case 'TextPattern'.
PropertyCondition cond2 =
new PropertyCondition(
AutomationElement.IsTextPatternAvailableProperty,
true);
AndCondition textCondition = new AndCondition(cond1, cond2);
AutomationElement targetTextElement =
targetApp.FindFirst(TreeScope.Descendants, textCondition);
// If targetText is null then a suitable text control was not found.
return targetTextElement;
}
''' -------------------------------------------------------------------
''' <summary>
''' Obtain the text control of interest from the target application.
''' </summary>
''' <param name="targetApp">
''' The target application.
''' </param>
''' <returns>
''' An AutomationElement. representing a text control.
''' </returns>
''' -------------------------------------------------------------------
Private Function GetTextElement(ByVal targetApp As AutomationElement) As AutomationElement
' The control type we're looking for; in this case 'Document'
Dim cond1 As PropertyCondition = _
New PropertyCondition( _
AutomationElement.ControlTypeProperty, _
ControlType.Document)
' The control pattern of interest; in this case 'TextPattern'.
Dim cond2 As PropertyCondition = _
New PropertyCondition( _
AutomationElement.IsTextPatternAvailableProperty, _
True)
Dim textCondition As AndCondition = New AndCondition(cond1, cond2)
Dim targetTextElement As AutomationElement = _
targetApp.FindFirst(TreeScope.Descendants, textCondition)
' If targetText is null then a suitable text control was not found.
Return targetTextElement
End Function
/// -------------------------------------------------------------------
/// <summary>
/// Moves a text range a specified number of text units. The text range
/// is the current selection.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="targetTextElement">
/// The AutomationElment that represents a text control.
/// </param>
/// <param name="textUnit">
/// The text unit value.
/// </param>
/// <param name="units">
/// The number of text units to move.
/// </param>
/// <param name="direction">
/// Direction to move the text range. Valid values are -1, 0, 1.
/// </param>
/// <returns>
/// The number of text units actually moved. This can be less than the
/// number requested if either of the new text range endpoints is
/// greater than or less than the DocumentRange endpoints.
/// </returns>
/// <remarks>
/// Moving the text range does not modify the text source in any way.
/// Only the text range starting and ending endpoints are modified.
/// </remarks>
/// -------------------------------------------------------------------
private Int32 MoveSelection(
AutomationElement targetTextElement,
TextUnit textUnit,
int units,
int direction)
{
TextPattern textPattern =
targetTextElement.GetCurrentPattern(TextPattern.Pattern)
as TextPattern;
if (textPattern == null)
{
// Target control doesn't support TextPattern.
return -1;
}
TextPatternRange[] currentSelection = textPattern.GetSelection();
if (currentSelection.Length > 1)
{
// For this example, we cannot move more than one text range.
return -1;
}
return currentSelection[0].Move(textUnit, Math.Sign(direction) * units);
}
''' -------------------------------------------------------------------
''' <summary>
''' Moves a text range a specified number of text units.
''' </summary>
''' <param name="targetTextElement">
''' The AutomationElement that represents a text control.
''' </param>
''' <param name="textUnit">
''' The text unit value.
''' </param>
''' <param name="units">
''' The number of text units to move.
''' </param>
''' <param name="direction">
''' Direction to move the text range. Valid values are -1, 0, 1.
''' </param>
''' <returns>
''' The number of text units actually moved. This can be less than the
''' number requested if either of the new text range endpoints is
''' greater than or less than the DocumentRange endpoints.
''' </returns>
''' <remarks>
''' Moving the text range does not modify the text source in any way.
''' Only the text range starting and ending endpoints are modified.
''' </remarks>
''' -------------------------------------------------------------------
Private Function MoveSelection( _
ByVal targetTextElement As AutomationElement, _
ByVal textUnit As TextUnit, _
ByVal units As Integer, _
ByVal direction As Integer) As Integer
Dim textPattern As TextPattern = _
DirectCast( _
targetTextElement.GetCurrentPattern(textPattern.Pattern), _
TextPattern)
If (textPattern Is Nothing) Then
' Target control doesn't support TextPattern.
Return -1
End If
Dim currentSelection As TextPatternRange() = _
textPattern.GetSelection()
If (currentSelection.Length > 1) Then
' For this example, we cannot move more than one text range.
Return -1
End If
Return currentSelection(0).Move(textUnit, Math.Sign(direction) * units)
End Function
Commenti
Quando è necessario scorrere il contenuto di un intervallo di testo, per garantire una corretta esecuzione del metodo Move è prevista una serie di passaggi dietro le quinte.
L'intervallo di testo viene normalizzato, ovvero viene compresso in un intervallo degenerato all'endpoint Start . Ciò rende superfluo l'endpoint End . Questo passaggio è necessario per rimuovere l'ambiguità nelle situazioni in cui un intervallo di testo si estende
unitsu limiti, ad esempio "{La riga https://www.microsoft.com/ U}è incorporata nel testo" in cui "{" e "}" sono gli endpoint dell'intervallo di testo.L'intervallo risultante viene spostato indietro in DocumentRange all'inizio del limite
unitrichiesto.L'intervallo viene spostato avanti o indietro in DocumentRange per il numero richiesto di limiti
unit.L'intervallo viene quindi espanso dallo stato di intervallo degenerato spostando l'endpoint End di un limite
unitrichiesto.
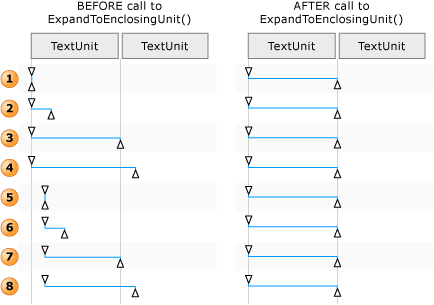
Esempi di regolazione di un intervallo di testo per Move() ed ExpandToEnclosingUnit()
Il contenuto testuale (o testo interno) di un contenitore di testo e di un oggetto incorporato, ad esempio un collegamento ipertestuale o una cella di tabella, viene esposto come un singolo flusso di testo continuo sia nella visualizzazione controllo che nella visualizzazione contenuto dell'albero Automazione interfaccia utente; i limiti degli oggetti vengono ignorati. Se un client di automazione interfaccia utente sta recuperando il testo a scopo di esposizione, interpretazione o analisi, è necessario verificare l'eventuale presenza di casi speciali nell'intervallo di testo, ad esempio una tabella con contenuto testuale o altri oggetti incorporati. A tale scopo, è possibile chiamare GetChildren per ottenere un AutomationElement oggetto per ogni oggetto incorporato e quindi chiamare RangeFromChild per ottenere un intervallo di testo per ogni elemento. Questa operazione viene eseguita in modo ricorsivo fino a quando non viene recuperato tutto il contenuto testuale.
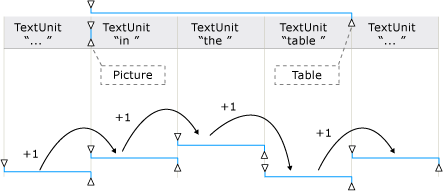
Esempio di un flusso di testo con oggetti incorporati e le estensioni degli intervalli corrispondenti
Move rispetta sia il testo nascosto che quello visibile. Il client Automazione interfaccia utente può verificare la visibilità del IsHiddenAttribute testo.
Move rinvia al successivo più grande TextUnit supportato se il dato TextUnit non è supportato dal controllo .
L'ordine, dall'unità più piccola alla più grande, è elencato di seguito.
Nota
Il testo non viene modificato in alcun modo perché l'intervallo di testo si estende solo su una parte diversa del testo.
