Nota
L'accesso a questa pagina richiede l'autorizzazione. È possibile provare ad accedere o modificare le directory.
L'accesso a questa pagina richiede l'autorizzazione. È possibile provare a modificare le directory.
I dati geospaziali possono essere visualizzati come parte della query usando l'operatore di rendering come punti, pie o bolle su una mappa.
Per altre informazioni sul clustering geospaziale, vedere Clustering geospaziale.
Esempi
L'esempio seguente trova gli eventi storm e visualizza 100 su una mappa.
StormEvents
| take 100
| project BeginLon, BeginLat
| render scatterchart with (kind = map)

Nell'esempio seguente vengono visualizzate più serie di punti, in cui la coppia [Longitudine, Latitudine] definisce ogni punto e una terza colonna definisce la serie. In questo esempio la serie è EventType.
StormEvents
| take 100
| project BeginLon, BeginLat, EventType
| render scatterchart with (kind = map)
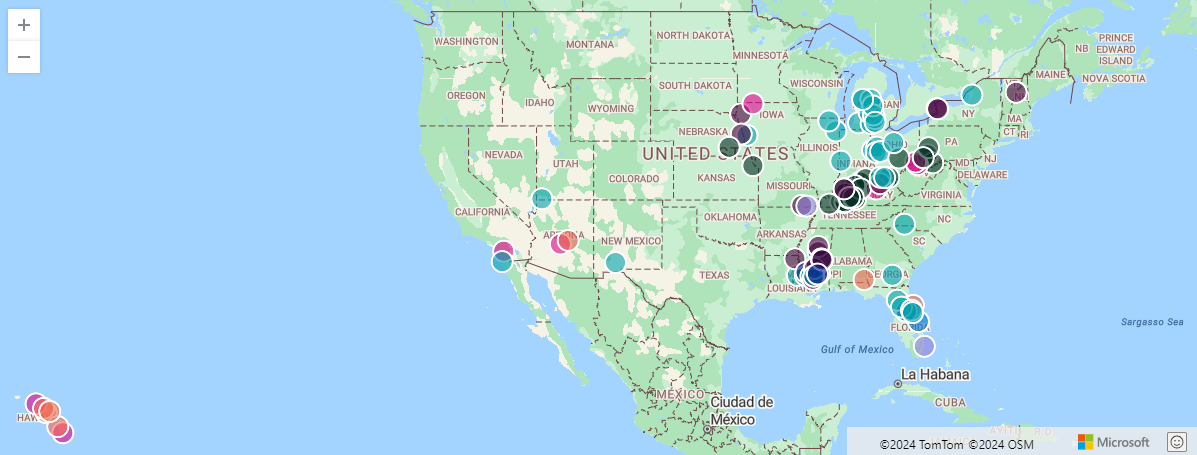
Nell'esempio seguente viene visualizzata una serie di punti su una mappa. Se sono presenti più colonne nel risultato, è necessario specificare le colonne da usare per xcolumn (Longitudine), ycolumn (Latitudine) e serie.
Annotazioni
La visualizzazione di più colonne è supportata solo in Kusto.Explorer.
StormEvents
| take 100
| render scatterchart with (kind = map, xcolumn = BeginLon, ycolumns = BeginLat, series = EventType)

L'esempio seguente visualizza i punti sulla mappa usando i valori dinamici GeoJSON per definire i punti.
StormEvents
| project BeginLon, BeginLat
| summarize by hash=geo_point_to_s2cell(BeginLon, BeginLat, 5)
| project geo_s2cell_to_central_point(hash)
| render scatterchart with (kind = map)

L'esempio seguente mostra gli eventi storm aggregati dalle celle S2. Il grafico aggrega gli eventi in bolle in base alla posizione in un unico colore.
StormEvents
| project BeginLon, BeginLat, EventType
| where geo_point_in_circle(BeginLon, BeginLat, real(-81.3891), 28.5346, 1000 * 100)
| summarize count() by EventType, hash = geo_point_to_s2cell(BeginLon, BeginLat)
| project geo_s2cell_to_central_point(hash), count_
| extend Events = "count"
| render piechart with (kind = map)

L'esempio seguente mostra gli eventi storm aggregati dalle celle S2. Il grafico aggrega gli eventi in base al tipo di evento nei grafici a torta in base alla posizione.
Annotazioni
La visualizzazione dell'asse dei colori è supportata solo in Kusto.Explorer.
StormEvents
| project BeginLon, BeginLat, EventType
| where geo_point_in_circle(BeginLon, BeginLat, real(-81.3891), 28.5346, 1000 * 100)
| summarize count() by EventType, hash = geo_point_to_s2cell(BeginLon, BeginLat)
| project geo_s2cell_to_central_point(hash), EventType, count_
| render piechart with (kind = map)

Contenuto correlato
- Clustering geospaziale
- Operatore Render
- Analisi dei dati per i veicoli di test automobilistici (caso d'uso di clustering geospaziale)
- Informazioni sull'architettura di Azure per l'elaborazione e l'analisi geospaziali dei dati