Microsoft Agent Framework の永続的なタスク拡張機能を使用すると、Azure 上のサーバーレス環境でステートフル AI エージェントとマルチエージェント決定論的オーケストレーションを構築できます。
Azure Functions は、インフラストラクチャを管理せずにオンデマンドでコードを実行できるサーバーレス コンピューティング サービスです。 永続的なタスク拡張機能は、この基盤に基づいて永続的な状態管理を提供します。つまり、エージェントの会話履歴と実行状態は確実に保持され、障害、再起動、実行時間の長い操作に耐えられます。
概要
非消耗品エージェントは、Agent Framework と Azure Durable Functions の機能を組み合わせて、次のエージェントを作成します。
- 関数呼び出し間で状態を自動的に保持する
- 会話コンテキストを失わずに失敗した後に再開する
- 需要に基づいて自動的にスケーリングする
- 信頼性の高い実行保証を使用してマルチエージェント ワークフローを調整する
非消耗品エージェントを使用する場合
必要に応じ、永続的なエージェントを選択します。
- 完全なコード制御: サーバーレスの利点を維持しながら、独自のコンピューティング環境をデプロイおよび管理する
- 複雑なオーケストレーション: 数日または数週間実行できる確定的で信頼性の高いワークフローで複数のエージェントを調整する
- イベント ドリブン オーケストレーション: Azure Functions トリガー (HTTP、タイマー、キューなど) およびイベント ドリブン エージェント ワークフローのバインドとの統合
- 自動会話状態: エージェントの会話履歴は自動的に管理され、コードで明示的な状態処理を必要とせずに保持されます
このサーバーレス ホスティングアプローチは、マネージド サービス ベースのエージェント ホスティング (Azure AI Foundry Agent Service など) とは異なります。これにより、Azure Functions アプリをデプロイまたは管理しなくても、フル マネージドインフラストラクチャが提供されます。 永続的なエージェントは、コード優先デプロイの柔軟性と永続的な状態管理の信頼性を組み合わせる必要がある場合に最適です。
Azure Functions Flex Consumption ホスティング プランでホストされている場合、エージェントは何千ものインスタンスまたは使用されていない場合はゼロ インスタンスにスケーリングでき、必要なコンピューティングに対してのみ料金を支払うことができます。
作業の開始
.NET Azure Functions プロジェクトで、必要な NuGet パッケージを追加します。
dotnet add package Azure.AI.OpenAI --prerelease
dotnet add package Azure.Identity
dotnet add package Microsoft.Agents.AI.OpenAI --prerelease
dotnet add package Microsoft.Agents.AI.Hosting.AzureFunctions --prerelease
注
これらのパッケージに加えて、プロジェクトで Microsoft.Azure.Functions.Worker パッケージのバージョン 2.2.0 以降を使用していることを確認します。
Python Azure Functions プロジェクトで、必要な Python パッケージをインストールします。
pip install azure-identity
pip install agent-framework-azurefunctions --pre
サーバーレス ホスティング
永続的なタスク拡張機能を使用すると、組み込みの HTTP エンドポイントとオーケストレーションベースの呼び出しを使用して、Azure Functions に Microsoft Agent Framework エージェントをデプロイしてホストできます。 Azure Functions は、自動スケーリングと最小限のインフラストラクチャ管理を使用して、イベントドリブンの呼び出しごとの料金を提供します。
非消耗品エージェントを構成すると、非消耗品タスク拡張機能によって、エージェントの HTTP エンドポイントが自動的に作成され、会話状態の格納、同時要求の処理、マルチエージェント ワークフローの調整のための基になるインフラストラクチャがすべて管理されます。
using System;
using Azure.AI.OpenAI;
using Azure.Identity;
using Microsoft.Agents.AI;
using Microsoft.Agents.AI.Hosting.AzureFunctions;
using Microsoft.Azure.Functions.Worker.Builder;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting;
var endpoint = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT");
var deploymentName = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("AZURE_OPENAI_DEPLOYMENT") ?? "gpt-4o-mini";
// Create an AI agent following the standard Microsoft Agent Framework pattern
AIAgent agent = new AzureOpenAIClient(new Uri(endpoint), new DefaultAzureCredential())
.GetChatClient(deploymentName)
.AsAIAgent(
instructions: "You are good at telling jokes.",
name: "Joker");
// Configure the function app to host the agent with durable thread management
// This automatically creates HTTP endpoints and manages state persistence
using IHost app = FunctionsApplication
.CreateBuilder(args)
.ConfigureFunctionsWebApplication()
.ConfigureDurableAgents(options =>
options.AddAIAgent(agent)
)
.Build();
app.Run();
import os
from agent_framework.azure import AzureOpenAIChatClient, AgentFunctionApp
from azure.identity import DefaultAzureCredential
endpoint = os.getenv("AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT")
deployment_name = os.getenv("AZURE_OPENAI_DEPLOYMENT_NAME", "gpt-4o-mini")
# Create an AI agent following the standard Microsoft Agent Framework pattern
agent = AzureOpenAIChatClient(
endpoint=endpoint,
deployment_name=deployment_name,
credential=DefaultAzureCredential()
).as_agent(
instructions="You are good at telling jokes.",
name="Joker"
)
# Configure the function app to host the agent with durable thread management
# This automatically creates HTTP endpoints and manages state persistence
app = AgentFunctionApp(agents=[agent])
会話履歴を含むステートフル エージェント スレッド
エージェントは、複数の相互作用にわたって存続する永続的なスレッドを維持します。 各スレッドは一意のスレッド ID で識別され、 Durable Task Scheduler によって管理される永続的ストレージに完全な会話履歴が格納されます。
このパターンにより、プロセスのクラッシュと再起動によってエージェントの状態が保持される会話の継続性が可能になり、ユーザー スレッド間で完全な会話履歴を維持できます。 永続ストレージにより、Azure Functions インスタンスが再起動したり、別のインスタンスにスケーリングされたりした場合でも、中断した場所から会話がシームレスに続行されます。
次の例では、同じスレッドに対する複数の HTTP 要求を示し、会話コンテキストがどのように保持されるかを示します。
# First interaction - start a new thread
curl -X POST https://your-function-app.azurewebsites.net/api/agents/Joker/run \
-H "Content-Type: text/plain" \
-d "Tell me a joke about pirates"
# Response includes thread ID in x-ms-thread-id header and joke as plain text
# HTTP/1.1 200 OK
# Content-Type: text/plain
# x-ms-thread-id: @dafx-joker@263fa373-fa01-4705-abf2-5a114c2bb87d
#
# Why don't pirates shower before they walk the plank? Because they'll just wash up on shore later!
# Second interaction - continue the same thread with context
curl -X POST "https://your-function-app.azurewebsites.net/api/agents/Joker/run?thread_id=@dafx-joker@263fa373-fa01-4705-abf2-5a114c2bb87d" \
-H "Content-Type: text/plain" \
-d "Tell me another one about the same topic"
# Agent remembers the pirate context from the first message and responds with plain text
# What's a pirate's favorite letter? You'd think it's R, but it's actually the C!
エージェントの状態は永続的ストレージで維持され、複数のインスタンス間で分散実行が可能になります。 中断または障害の後、任意のインスタンスがエージェントの実行を再開でき、継続的な操作が保証されます。
確定的なマルチエージェント オーケストレーション
永続的タスク拡張機能は、 Azure Durable Functions オーケストレーションを使用して複数のエージェントを調整する確定的なワークフローの構築をサポートします。
オーケストレーション は、複数の操作 (エージェント呼び出し、外部 API 呼び出し、タイマーなど) を信頼できる方法で調整するコードベースのワークフローです。 決定論的 とは、障害が発生した後に再生されたときにオーケストレーション コードが同じように実行され、ワークフローの信頼性とデバッグ性が向上することを意味します。オーケストレーションの履歴を再生すると、各ステップで何が起こったかを正確に確認できます。
オーケストレーションは、エージェントの呼び出しの間に障害が発生する場合でも、 安定して実行され、解除して続行できるように設計されており、予測可能で繰り返し可能なプロセスを提供します。 これにより、実行順序とフォールト トレランスを保証する必要がある複雑なマルチエージェント シナリオに最適です。
シーケンシャル オーケストレーション
順次マルチエージェント パターンでは、特殊化されたエージェントが特定の順序で実行され、各エージェントの出力が次のエージェントの実行に影響を与える可能性があります。 このパターンでは、エージェントの応答に基づく条件付きロジックと分岐がサポートされます。
オーケストレーションでエージェントを使用する場合は、 context.GetAgent() API を使用して DurableAIAgent インスタンスを取得する必要があります。これは、登録済みエージェントのいずれかをラップする標準 AIAgent 型の特殊なサブクラスです。
DurableAIAgent ラッパーを使用すると、永続的オーケストレーション フレームワークによってエージェント呼び出しが適切に追跡され、チェックポイント処理されます。
using Microsoft.Azure.Functions.Worker;
using Microsoft.DurableTask;
using Microsoft.Agents.AI.DurableTask;
[Function(nameof(SpamDetectionOrchestration))]
public static async Task<string> SpamDetectionOrchestration(
[OrchestrationTrigger] TaskOrchestrationContext context)
{
Email email = context.GetInput<Email>();
// Check if the email is spam
DurableAIAgent spamDetectionAgent = context.GetAgent("SpamDetectionAgent");
AgentSession spamSession = await spamDetectionAgent.CreateSessionAsync();
AgentResponse<DetectionResult> spamDetectionResponse = await spamDetectionAgent.RunAsync<DetectionResult>(
message: $"Analyze this email for spam: {email.EmailContent}",
session: spamSession);
DetectionResult result = spamDetectionResponse.Result;
if (result.IsSpam)
{
return await context.CallActivityAsync<string>(nameof(HandleSpamEmail), result.Reason);
}
// Generate response for legitimate email
DurableAIAgent emailAssistantAgent = context.GetAgent("EmailAssistantAgent");
AgentSession emailSession = await emailAssistantAgent.CreateSessionAsync();
AgentResponse<EmailResponse> emailAssistantResponse = await emailAssistantAgent.RunAsync<EmailResponse>(
message: $"Draft a professional response to: {email.EmailContent}",
session: emailSession);
return await context.CallActivityAsync<string>(nameof(SendEmail), emailAssistantResponse.Result.Response);
}
オーケストレーションでエージェントを使用する場合は、app.get_agent() メソッドを使用して持続可能なエージェント インスタンスを取得する必要があります。これは、登録済みエージェントの 1 つを対象とした特別なラッパーです。 永続的なエージェント ラッパーを使用すると、永続的オーケストレーション フレームワークによってエージェント呼び出しが適切に追跡され、チェックポイントが設定されます。
import azure.durable_functions as df
from typing import cast
from agent_framework.azure import AgentFunctionApp
from pydantic import BaseModel
class SpamDetectionResult(BaseModel):
is_spam: bool
reason: str
class EmailResponse(BaseModel):
response: str
app = AgentFunctionApp(agents=[spam_detection_agent, email_assistant_agent])
@app.orchestration_trigger(context_name="context")
def spam_detection_orchestration(context: df.DurableOrchestrationContext):
email = context.get_input()
# Check if the email is spam
spam_agent = app.get_agent(context, "SpamDetectionAgent")
spam_thread = spam_agent.create_session()
spam_result_raw = yield spam_agent.run(
messages=f"Analyze this email for spam: {email['content']}",
session=spam_thread,
response_format=SpamDetectionResult
)
spam_result = cast(SpamDetectionResult, spam_result_raw.get("structured_response"))
if spam_result.is_spam:
result = yield context.call_activity("handle_spam_email", spam_result.reason)
return result
# Generate response for legitimate email
email_agent = app.get_agent(context, "EmailAssistantAgent")
email_thread = email_agent.create_session()
email_response_raw = yield email_agent.run(
messages=f"Draft a professional response to: {email['content']}",
session=email_thread,
response_format=EmailResponse
)
email_response = cast(EmailResponse, email_response_raw.get("structured_response"))
result = yield context.call_activity("send_email", email_response.response)
return result
オーケストレーションは、複数のエージェント間の作業を調整し、エージェント呼び出し間で発生する障害にも対応できるようにします。 オーケストレーション コンテキストは、オーケストレーション内でホストされているエージェントを取得して操作するメソッドを提供します。
並列オーケストレーション
並列マルチエージェント パターンでは、複数のエージェントを同時に実行し、その結果を集計します。 このパターンは、多様なパースペクティブを収集したり、独立したサブタスクを同時に処理したりするのに役立ちます。
using Microsoft.Azure.Functions.Worker;
using Microsoft.DurableTask;
using Microsoft.Agents.AI.DurableTask;
[Function(nameof(ResearchOrchestration))]
public static async Task<string> ResearchOrchestration(
[OrchestrationTrigger] TaskOrchestrationContext context)
{
string topic = context.GetInput<string>();
// Execute multiple research agents in parallel
DurableAIAgent technicalAgent = context.GetAgent("TechnicalResearchAgent");
DurableAIAgent marketAgent = context.GetAgent("MarketResearchAgent");
DurableAIAgent competitorAgent = context.GetAgent("CompetitorResearchAgent");
// Start all agent runs concurrently
Task<AgentResponse<TextResponse>> technicalTask =
technicalAgent.RunAsync<TextResponse>($"Research technical aspects of {topic}");
Task<AgentResponse<TextResponse>> marketTask =
marketAgent.RunAsync<TextResponse>($"Research market trends for {topic}");
Task<AgentResponse<TextResponse>> competitorTask =
competitorAgent.RunAsync<TextResponse>($"Research competitors in {topic}");
// Wait for all tasks to complete
await Task.WhenAll(technicalTask, marketTask, competitorTask);
// Aggregate results
string allResearch = string.Join("\n\n",
technicalTask.Result.Result.Text,
marketTask.Result.Result.Text,
competitorTask.Result.Result.Text);
DurableAIAgent summaryAgent = context.GetAgent("SummaryAgent");
AgentResponse<TextResponse> summaryResponse =
await summaryAgent.RunAsync<TextResponse>($"Summarize this research:\n{allResearch}");
return summaryResponse.Result.Text;
}
import azure.durable_functions as df
from agent_framework.azure import AgentFunctionApp
app = AgentFunctionApp(agents=[technical_agent, market_agent, competitor_agent, summary_agent])
@app.orchestration_trigger(context_name="context")
def research_orchestration(context: df.DurableOrchestrationContext):
topic = context.get_input()
# Execute multiple research agents in parallel
technical_agent = app.get_agent(context, "TechnicalResearchAgent")
market_agent = app.get_agent(context, "MarketResearchAgent")
competitor_agent = app.get_agent(context, "CompetitorResearchAgent")
technical_task = technical_agent.run(messages=f"Research technical aspects of {topic}")
market_task = market_agent.run(messages=f"Research market trends for {topic}")
competitor_task = competitor_agent.run(messages=f"Research competitors in {topic}")
# Wait for all tasks to complete
results = yield context.task_all([technical_task, market_task, competitor_task])
# Aggregate results
all_research = "\n\n".join([r.get('response', '') for r in results])
summary_agent = app.get_agent(context, "SummaryAgent")
summary = yield summary_agent.run(messages=f"Summarize this research:\n{all_research}")
return summary.get('response', '')
並列実行は、タスクの一覧を使用して追跡されます。 自動チェックポイント処理により、集計中にエラーが発生した場合に、完了したエージェントの実行が繰り返されたり失われたりしないようにします。
Human-in-the-loop オーケストレーション
確定的なエージェント オーケストレーションは、コンピューティング リソースを消費することなく、人間の入力、承認、またはレビューのために一時停止できます。 永続的な実行により、オーケストレーションは、人間の応答を待機している間、数日または数週間待機できます。 サーバーレス ホスティングと組み合わせると、待機期間中にすべてのコンピューティング リソースがスピンダウンされ、人間が入力を提供するまでコンピューティング コストが削減されます。
using Microsoft.Azure.Functions.Worker;
using Microsoft.DurableTask;
using Microsoft.Agents.AI.DurableTask;
[Function(nameof(ContentApprovalWorkflow))]
public static async Task<string> ContentApprovalWorkflow(
[OrchestrationTrigger] TaskOrchestrationContext context)
{
string topic = context.GetInput<string>();
// Generate content using an agent
DurableAIAgent contentAgent = context.GetAgent("ContentGenerationAgent");
AgentResponse<GeneratedContent> contentResponse =
await contentAgent.RunAsync<GeneratedContent>($"Write an article about {topic}");
GeneratedContent draftContent = contentResponse.Result;
// Send for human review
await context.CallActivityAsync(nameof(NotifyReviewer), draftContent);
// Wait for approval with timeout
HumanApprovalResponse approvalResponse;
try
{
approvalResponse = await context.WaitForExternalEvent<HumanApprovalResponse>(
eventName: "ApprovalDecision",
timeout: TimeSpan.FromHours(24));
}
catch (OperationCanceledException)
{
// Timeout occurred - escalate for review
return await context.CallActivityAsync<string>(nameof(EscalateForReview), draftContent);
}
if (approvalResponse.Approved)
{
return await context.CallActivityAsync<string>(nameof(PublishContent), draftContent);
}
return "Content rejected";
}
import azure.durable_functions as df
from datetime import timedelta
from agent_framework.azure import AgentFunctionApp
app = AgentFunctionApp(agents=[content_agent])
@app.orchestration_trigger(context_name="context")
def content_approval_workflow(context: df.DurableOrchestrationContext):
topic = context.get_input()
# Generate content using an agent
content_agent = app.get_agent(context, "ContentGenerationAgent")
draft_content = yield content_agent.run(
messages=f"Write an article about {topic}"
)
# Send for human review
yield context.call_activity("notify_reviewer", draft_content)
# Wait for approval with timeout
approval_task = context.wait_for_external_event("ApprovalDecision")
timeout_task = context.create_timer(
context.current_utc_datetime + timedelta(hours=24)
)
winner = yield context.task_any([approval_task, timeout_task])
if winner == approval_task:
timeout_task.cancel()
approval_data = approval_task.result
if approval_data.get("approved"):
result = yield context.call_activity("publish_content", draft_content)
return result
return "Content rejected"
# Timeout occurred - escalate for review
result = yield context.call_activity("escalate_for_review", draft_content)
return result
確定的なエージェントオーケストレーションは、外部イベントを待ちながらその状態を耐久的に保持し、人間のフィードバックを待つ間も、障害や再起動、そして長期間の待機を乗り越えることができます。 人間の応答が到着すると、オーケストレーションは完全な会話コンテキストと実行状態をそのまま使用して自動的に再開します。
人間の入力を提供する
待機中のオーケストレーションに承認または入力を送信するには、Durable Functions クライアント SDK を使用して、オーケストレーション インスタンスに外部イベントを発生させます。 たとえば、校閲者は、次を呼び出す Web フォームを使用してコンテンツを承認できます。
await client.RaiseEventAsync(instanceId, "ApprovalDecision", new HumanApprovalResponse
{
Approved = true,
Feedback = "Looks great!"
});
approval_data = {
"approved": True,
"feedback": "Looks great!"
}
await client.raise_event(instance_id, "ApprovalDecision", approval_data)
コスト効率
永続的なエージェントを含む人間のループ内ワークフローは、 Azure Functions Flex 従量課金プランでホストされている場合、非常にコスト効率が高くなります。 承認を 24 時間待機しているワークフローでは、数秒間の実行時間 (コンテンツの生成、通知の送信、応答の処理の時間) についてのみ支払います。24 時間の待機時間は支払われません。 待機期間中は、コンピューティング リソースは消費されません。
Durable Task Scheduler を使用した可観測性
Durable Task Scheduler (DTS) は、優れたパフォーマンス、フル マネージドのインフラストラクチャ、および組み込みの可観測性を UI ダッシュボードで提供する、永続的なエージェントに推奨される永続的なバックエンドです。 Azure Functions では他のストレージ バックエンド (Azure Storage など) を使用できますが、DTS は永続的なワークロード専用に最適化され、優れたパフォーマンスと監視機能を提供します。
エージェント セッションの分析情報
- 会話履歴: すべてのメッセージ、ツール呼び出し、会話コンテキストなど、各エージェント セッションの完全なチャット履歴を任意の時点で表示する
- タスクのタイミング: 特定のタスクとエージェントの対話が完了するまでの時間を監視する
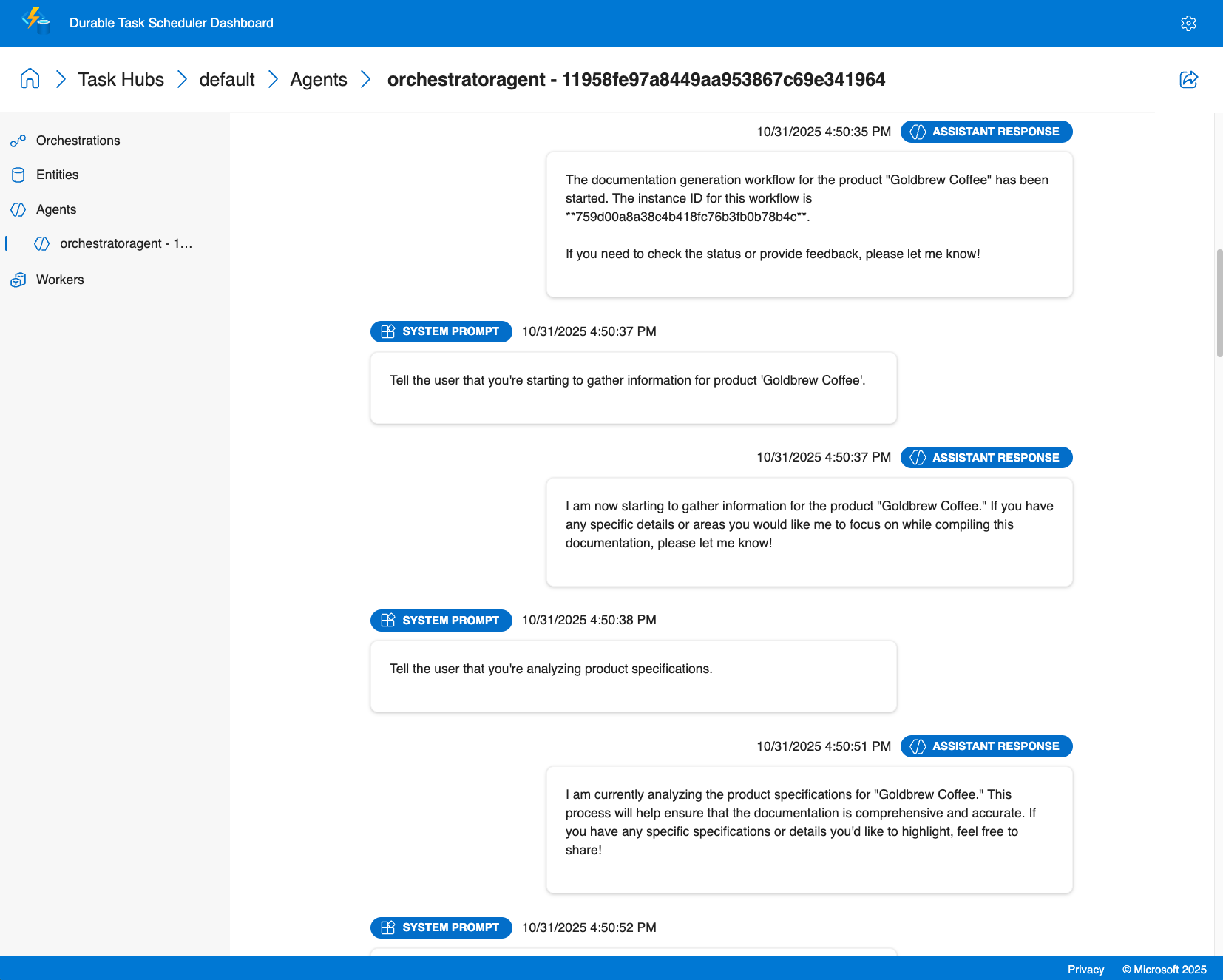
オーケストレーションの分析情報
- マルチエージェントの視覚化: 並列実行と条件付き分岐の視覚的表現を使用して複数の特殊なエージェントを呼び出すときの実行フローを確認する
- 実行履歴: 詳細な実行ログにアクセスする
- リアルタイム監視: デプロイ全体でアクティブなオーケストレーション、キューに置かれた作業項目、エージェントの状態を追跡する
- パフォーマンス メトリック: エージェントの応答時間、トークンの使用状況、オーケストレーションの期間を監視する
デバッグ機能
- 構造化されたエージェントの出力とツール呼び出しの結果を表示する
- トレース ツールの呼び出しとその結果
- 人間が介在するシナリオにおける外部イベント処理の監視
ダッシュボードを使用すると、エージェントの実行内容を正確に把握し、問題をすばやく診断し、実際の実行データに基づいてパフォーマンスを最適化できます。
チュートリアル: 非消耗品エージェントを作成して実行する
このチュートリアルでは、Microsoft Agent Framework の持続的タスク拡張機能を使用して、持続的 AI エージェントを作成して実行する方法について説明します。 組み込みの HTTP エンドポイントを使用してステートフル エージェントをホストする Azure Functions アプリを構築し、Durable Task Scheduler ダッシュボードを使用して監視する方法について説明します。
[前提条件]
開始する前に、次の前提条件を満たしていることを確認してください。
- .NET 9.0 SDK 以降
- Azure Functions Core Tools v4.x
- Azure Developer CLI (azd)
- Azure CLI のインストール と 認証
- Docker Desktop がインストールされ、実行されている (Azurite と Durable Task Scheduler エミュレーターを使用したローカル開発用)
- リソースを作成するアクセス許可を持つ Azure サブスクリプション
注
Microsoft Agent Framework は、アクティブにサポートされているすべてのバージョンの .NET でサポートされています。 このサンプルでは、.NET 9 SDK 以降のバージョンをお勧めします。
- Python 3.10 以降
- Azure Functions Core Tools v4.x
- Azure Developer CLI (azd)
- Azure CLI のインストール と 認証
- Docker Desktop がインストールされ、実行されている (Azurite と Durable Task Scheduler エミュレーターを使用したローカル開発用)
- リソースを作成するアクセス許可を持つ Azure サブスクリプション
クイック スタート プロジェクトをダウンロードする
Azure Developer CLI を使用して、Durable Agents クイック スタート テンプレートから新しいプロジェクトを初期化します。
プロジェクトの新しいディレクトリを作成し、そこに移動します。
mkdir MyDurableAgent cd MyDurableAgent
テンプレートからプロジェクトを初期化します。
azd init --template durable-agents-quickstart-dotnet環境名の入力を求められたら、
my-durable-agentなどの名前を入力します。
これにより、Azure Functions の構成、エージェント コード、コード テンプレートとしてのインフラストラクチャなど、必要なすべてのファイルを含むクイック スタート プロジェクトがダウンロードされます。
プロジェクトの新しいディレクトリを作成し、そこに移動します。
mkdir MyDurableAgent cd MyDurableAgent
テンプレートからプロジェクトを初期化します。
azd init --template durable-agents-quickstart-python環境名の入力を求められたら、
my-durable-agentなどの名前を入力します。仮想環境を作成してアクティブ化する:
python3 -m venv .venv source .venv/bin/activate
必要なパッケージをインストールします。
python -m pip install -r requirements.txt
これにより、Azure Functions の構成、エージェント コード、コード テンプレートとしてのインフラストラクチャなど、必要なすべてのファイルを含むクイック スタート プロジェクトがダウンロードされます。 また、必要な依存関係を持つ仮想環境も準備します。
Azure リソースをプロビジョニングする
Azure Developer CLI を使用して、永続エージェントに必要な Azure リソースを作成します。
インフラストラクチャをプロビジョニングします。
azd provisionこのコマンドを実行すると、次のものが作成されます。
- gpt-4o-mini デプロイを使用した Azure OpenAI サービス
- Flex Consumption ホスティング プランを使用した Azure Functions アプリ
- Azure Functions のランタイムと永続ストレージ用の Azure Storage アカウント
- エージェントの状態を管理するための Durable Task Scheduler インスタンス (従量課金プラン)
- 必要なネットワークと ID の構成
メッセージが表示されたら、Azure サブスクリプションを選択し、リソースの場所を選択します。
プロビジョニング プロセスには数分かかります。 完了すると、azd によって作成されたリソース情報が環境内に格納されます。
エージェント コードを確認する
次に、Durable Agent を定義するコードを調べてみましょう。
Program.csを開いて、エージェントの構成を確認します。
using Azure.AI.OpenAI;
using Azure.Identity;
using Microsoft.Agents.AI;
using Microsoft.Agents.AI.Hosting.AzureFunctions;
using Microsoft.Azure.Functions.Worker.Builder;
using Microsoft.Extensions.AI;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting;
using OpenAI;
var endpoint = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT")
?? throw new InvalidOperationException("AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT environment variable is not set");
var deploymentName = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("AZURE_OPENAI_DEPLOYMENT") ?? "gpt-4o-mini";
// Create an AI agent following the standard Microsoft Agent Framework pattern
AIAgent agent = new AzureOpenAIClient(new Uri(endpoint), new DefaultAzureCredential())
.GetChatClient(deploymentName)
.AsAIAgent(
instructions: "You are a helpful assistant that can answer questions and provide information.",
name: "MyDurableAgent");
using IHost app = FunctionsApplication
.CreateBuilder(args)
.ConfigureFunctionsWebApplication()
.ConfigureDurableAgents(options => options.AddAIAgent(agent))
.Build();
app.Run();
このコードによって以下が行われます。
- 環境変数から Azure OpenAI 構成を取得します。
- Azure 資格情報を使用して Azure OpenAI クライアントを作成します。
- 命令と名前を使用して AI エージェントを作成します。
- 永続的なスレッド管理を使用してエージェントをホストするように Azure Functions アプリを構成します。
function_app.pyを開いて、エージェントの構成を確認します。
import os
from agent_framework.azure import AzureOpenAIChatClient, AgentFunctionApp
from azure.identity import DefaultAzureCredential
endpoint = os.getenv("AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT")
if not endpoint:
raise ValueError("AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT is not set.")
deployment_name = os.getenv("AZURE_OPENAI_DEPLOYMENT_NAME", "gpt-4o-mini")
# Create an AI agent following the standard Microsoft Agent Framework pattern
agent = AzureOpenAIChatClient(
endpoint=endpoint,
deployment_name=deployment_name,
credential=DefaultAzureCredential()
).as_agent(
instructions="You are a helpful assistant that can answer questions and provide information.",
name="MyDurableAgent"
)
# Configure the function app to host the agent with durable thread management
app = AgentFunctionApp(agents=[agent])
このコードによって以下が行われます。
- 環境変数から Azure OpenAI 構成を取得します。
- Azure 資格情報を使用して Azure OpenAI クライアントを作成します。
- 命令と名前を使用して AI エージェントを作成します。
- 永続的なスレッド管理を使用してエージェントをホストするように Azure Functions アプリを構成します。
これで、エージェントを Azure Functions でホストする準備ができました。 永続的タスク拡張機能は、エージェントと対話するための HTTP エンドポイントを自動的に作成し、複数の要求にわたって会話の状態を管理します。
ローカル設定を構成する
プロジェクトに含まれるサンプル ファイルに基づいて、ローカル開発用の local.settings.json ファイルを作成します。
サンプル設定ファイルをコピーします。
cp local.settings.sample.json local.settings.json
プロビジョニングされたリソースから Azure OpenAI エンドポイントを取得します。
azd env get-value AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINTlocal.settings.jsonを開き、<your-resource-name>値のAZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINTを前のコマンドのエンドポイントに置き換えます。
local.settings.jsonは次のようになります。
{
"IsEncrypted": false,
"Values": {
// ... other settings ...
"AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT": "https://your-openai-resource.openai.azure.com",
"AZURE_OPENAI_DEPLOYMENT": "gpt-4o-mini",
"TASKHUB_NAME": "default"
}
}
注
local.settings.json ファイルはローカル開発にのみ使用され、Azure にはデプロイされません。 運用環境のデプロイの場合、これらの設定はインフラストラクチャ テンプレートによって Azure Functions アプリで自動的に構成されます。
ローカル開発の依存関係を開始する
永続エージェントをローカルで実行するには、次の 2 つのサービスを開始する必要があります。
- Azurite: Azure Storage サービスをエミュレートします (トリガーと内部状態を管理するために Azure Functions によって使用されます)。
- Durable Task Scheduler (DTS) エミュレーター: エージェントの永続的な状態 (会話履歴、オーケストレーション状態) とスケジュールを管理します
Azurite を起動する
Azurite は、Azure Storage サービスをローカルでエミュレートします。 Azure Functions では、内部状態の管理に使用されます。 これは、新しいターミナル ウィンドウで実行し、Durable Agent の開発とテスト中に実行し続ける必要があります。
新しいターミナル ウィンドウを開き、Azurite Docker イメージをプルします。
docker pull mcr.microsoft.com/azure-storage/azuriteターミナル ウィンドウで Azurite を起動します。
docker run -p 10000:10000 -p 10001:10001 -p 10002:10002 mcr.microsoft.com/azure-storage/azuriteAzurite は、BLOB (10000)、キュー (10001)、テーブル (10002) サービスの既定ポートで起動し、リッスンを開始します。
Durable Agent の開発とテスト中は、このターミナル ウィンドウを開いたままにしておきます。
ヒント
別のインストール方法を含む Azurite の詳細については、「 Azure Storage のローカル開発に Azurite エミュレーターを使用する」を参照してください。
Durable Task Scheduler エミュレーターを起動する
DTS エミュレーターは、エージェントの状態とオーケストレーションを管理するための永続的なバックエンドを提供します。 会話履歴が格納され、再起動後もエージェントの状態が維持されます。 また、永続性のあるオーケストレーションとエージェントもトリガーします。 これは、別の新しいターミナル ウィンドウで実行し、Durable Agent の開発とテスト中に実行し続ける必要があります。
別の新しいターミナル ウィンドウを開き、DTS エミュレーターの Docker イメージをプルします。
docker pull mcr.microsoft.com/dts/dts-emulator:latestDTS エミュレーターを実行します。
docker run -p 8080:8080 -p 8082:8082 mcr.microsoft.com/dts/dts-emulator:latestこのコマンドはエミュレーターを起動し、次を公開します。
- ポート 8080: Durable Task Scheduler の gRPC エンドポイント (Functions アプリで使用)
- ポート 8082: 管理ダッシュボード
ダッシュボードは、
http://localhost:8082で使用できるようになります。
Durable Agent の開発とテスト中は、このターミナル ウィンドウを開いたままにしておきます。
ヒント
複数のタスク ハブを構成してダッシュボードにアクセスする方法など、DTS エミュレーターの詳細については、「 Durable Task Scheduler を使用した開発」を参照してください。
関数アプリを実行する
これで、Durable Agent を使用して Azure Functions アプリを実行する準備ができました。
新しいターミナル ウィンドウ (Azurite と DTS エミュレーターの両方を別々のウィンドウで実行したまま) で、プロジェクト ディレクトリに移動します。
Azure Functions ランタイムを開始します。
func start関数アプリが実行されていることを示す出力 (エージェントの HTTP エンドポイントを含む) が表示されます。
Functions: http-MyDurableAgent: [POST] http://localhost:7071/api/agents/MyDurableAgent/run dafx-MyDurableAgent: entityTrigger
これらのエンドポイントは、会話の状態を自動的に管理します。スレッド オブジェクトを自分で作成または管理する必要はありません。
エージェントをローカルでテストする
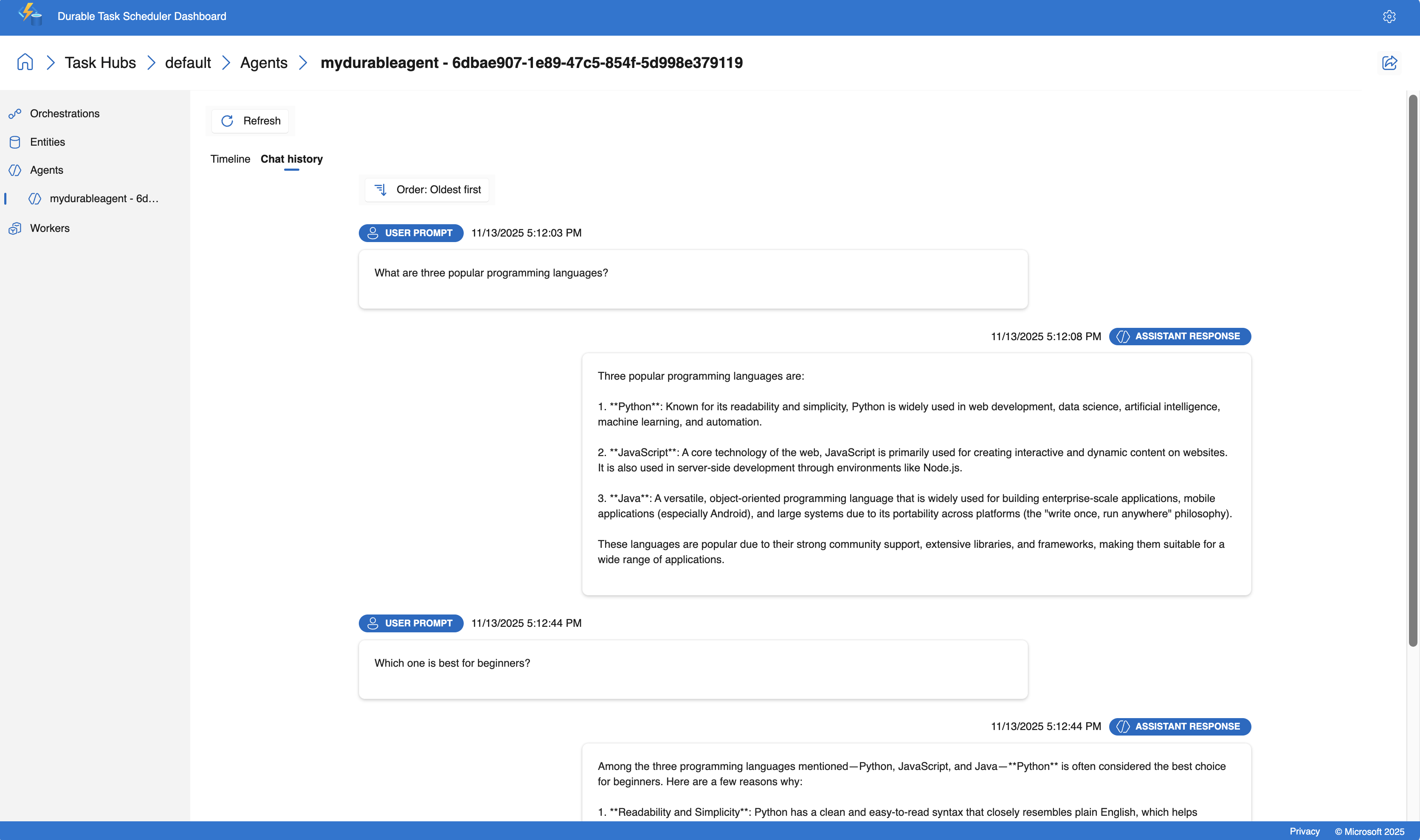
HTTP 要求を使用して永続エージェントと対話できるようになりました。 エージェントは、複数の要求にわたって会話状態を維持し、複数ターンの会話を有効にします。
会話を開始する
新しいスレッドを作成し、最初のメッセージを送信します。
curl -i -X POST http://localhost:7071/api/agents/MyDurableAgent/run \
-H "Content-Type: text/plain" \
-d "What are three popular programming languages?"
応答のサンプル ( x-ms-thread-id ヘッダーにスレッド ID が含まれていることに注意してください)。
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: text/plain
x-ms-thread-id: @dafx-mydurableagent@263fa373-fa01-4705-abf2-5a114c2bb87d
Content-Length: 189
Three popular programming languages are Python, JavaScript, and Java. Python is known for its simplicity and readability, JavaScript powers web interactivity, and Java is widely used in enterprise applications.
次の要求の x-ms-thread-id ヘッダー ( @dafx-mydurableagent@263fa373-fa01-4705-abf2-5a114c2bb87d など) からスレッド ID を保存します。
会話を続ける
スレッド ID をクエリ パラメーターとして含めることで、同じスレッドにフォローアップ メッセージを送信します。
curl -X POST "http://localhost:7071/api/agents/MyDurableAgent/run?thread_id=@dafx-mydurableagent@263fa373-fa01-4705-abf2-5a114c2bb87d" \
-H "Content-Type: text/plain" \
-d "Which one is best for beginners?"
@dafx-mydurableagent@263fa373-fa01-4705-abf2-5a114c2bb87dを、前の応答の x-ms-thread-id ヘッダーの実際のスレッド ID に置き換えます。
応答の例:
Python is often considered the best choice for beginners among those three. Its clean syntax reads almost like English, making it easier to learn programming concepts without getting overwhelmed by complex syntax. It's also versatile and widely used in education.
エージェントは、前のメッセージ (3 つのプログラミング言語) のコンテキストを記憶していることに注意してください。もう一度指定する必要はありません。 会話の状態は Durable Task Scheduler によって永続的に保存されるため、関数アプリを再起動した場合や、別のインスタンスによって会話が再開された場合でも、この履歴は保持されます。
Durable Task Scheduler ダッシュボードを使用して監視する
Durable Task Scheduler には、永続的なエージェントを監視およびデバッグするための組み込みのダッシュボードが用意されています。 ダッシュボードでは、エージェントの操作、会話履歴、実行フローを詳細に把握できます。
ダッシュボードにアクセスする
Web ブラウザーの
http://localhost:8082で、ローカル DTS エミュレーターのダッシュボードを開きます。一覧から 既定 のタスク ハブを選択すると、その詳細が表示されます。
右上隅にある歯車アイコンを選択して設定を開き、[プレビュー機能] の [エージェント ページを有効にする] オプションが選択されていることを確認します。
エージェントの会話を探索する
ダッシュボードで、[ エージェント ] タブに移動します。
一覧から永続的なエージェント スレッド (
mydurableagent - 263fa373-fa01-4705-abf2-5a114c2bb87dなど) を選択します。すべてのメッセージと応答を含む完全な会話履歴など、エージェント スレッドの詳細なビューが表示されます。
ダッシュボードには、会話のフローを理解するのに役立つタイムライン ビューが用意されています。 主な情報は次のとおりです。
- 各操作のタイムスタンプと期間
- プロンプトと応答のコンテンツ
- 使用されたトークンの数
ヒント
DTS ダッシュボードにはリアルタイムの更新プログラムが用意されているため、HTTP エンドポイントを介してエージェントを操作するときにエージェントの動作を確認できます。
Azure にデプロイ
Durable Agent をローカルでテストしたので、Azure にデプロイします。
アプリケーションをデプロイします。
azd deployこのコマンドは、アプリケーションをパッケージ化し、プロビジョニング中に作成された Azure Functions アプリにデプロイします。
デプロイが完了するまで待ちます。 出力は、エージェントが Azure で実行されていることを確認します。
デプロイされたエージェントをテストする
デプロイ後、Azure で実行されているエージェントをテストします。
関数キーを取得する
Azure Functions には、運用環境で HTTP によってトリガーされる関数の API キーが必要です。
API_KEY=`az functionapp function keys list --name $(azd env get-value AZURE_FUNCTION_NAME) --resource-group $(azd env get-value AZURE_RESOURCE_GROUP) --function-name http-MyDurableAgent --query default -o tsv`
Azure で新しい会話を開始する
新しいスレッドを作成し、デプロイされたエージェントに最初のメッセージを送信します。
curl -i -X POST "https://$(azd env get-value AZURE_FUNCTION_NAME).azurewebsites.net/api/agents/MyDurableAgent/run?code=$API_KEY" \
-H "Content-Type: text/plain" \
-d "What are three popular programming languages?"
x-ms-thread-id応答ヘッダーで返されたスレッド ID に注意してください。
Azure で会話を続ける
同じスレッドでフォローアップ メッセージを送信します。
<thread-id>を前の応答のスレッド ID に置き換えます。
THREAD_ID="<thread-id>"
curl -X POST "https://$(azd env get-value AZURE_FUNCTION_NAME).azurewebsites.net/api/agents/MyDurableAgent/run?code=$API_KEY&thread_id=$THREAD_ID" \
-H "Content-Type: text/plain" \
-d "Which is easiest to learn?"
エージェントは、ローカルで行ったのと同様に、Azure で会話コンテキストを維持し、エージェントの状態の持続性を示します。
デプロイされたエージェントを監視する
Azure の Durable Task Scheduler ダッシュボードを使用して、デプロイされたエージェントを監視できます。
Durable Task Scheduler インスタンスの名前を取得します。
azd env get-value DTS_NAMEAzure portal を開き、前の手順の Durable Task Scheduler 名を検索します。
Durable Task Scheduler リソースの [概要] ブレードで、一覧から 既定 のタスク ハブを選択します。
タスク ハブ ページの上部にある [ ダッシュボードを開く ] を選択して、監視ダッシュボードを開きます。
ローカル エミュレーターで行ったのと同じように、エージェントの会話を表示します。
Azure でホストされるダッシュボードには、ローカル エミュレーターと同じデバッグおよび監視機能が用意されており、会話履歴の検査、ツール呼び出しのトレース、運用環境でのパフォーマンスの分析を行うことができます。
チュートリアル: 非消耗品エージェントを調整する
このチュートリアルでは、ファンアウト/ファンイン パターンを使用して複数の持続的 AI エージェントを調整する方法について説明します。 前のチュートリアルの非消耗品エージェントを拡張して、ユーザーの質問を処理するマルチエージェント システムを作成し、応答を複数の言語に同時に変換します。
オーケストレーション パターンについて
ビルドするオーケストレーションは、次のフローに従います。
- ユーザー入力 - ユーザー からの質問またはメッセージ
-
メイン エージェント - 最初のチュートリアルの
MyDurableAgentが質問を処理する - ファンアウト - メイン エージェントの応答が両方の翻訳エージェントに同時に送信される
- 翻訳エージェント - 2 つの特殊なエージェントが応答を翻訳します (フランス語とスペイン語)
- ファンイン - 結果は、元の応答と翻訳を使用して 1 つの JSON 応答に集計されます
このパターンにより、同時処理が可能になり、連続変換と比較して合計応答時間が短縮されます。
起動時にエージェントを登録する
永続的オーケストレーションでエージェントを適切に使用するには、アプリケーションの起動時に登録します。 これらは、オーケストレーションの実行全体で使用できます。
既存のProgram.csと共に翻訳エージェントを登録するようにMyDurableAgentを更新します。
using System;
using Azure.AI.OpenAI;
using Azure.Identity;
using Microsoft.Agents.AI;
using Microsoft.Agents.AI.Hosting.AzureFunctions;
using Microsoft.Azure.Functions.Worker.Builder;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting;
using OpenAI;
using OpenAI.Chat;
// Get the Azure OpenAI configuration
string endpoint = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT")
?? throw new InvalidOperationException("AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT is not set.");
string deploymentName = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("AZURE_OPENAI_DEPLOYMENT")
?? "gpt-4o-mini";
// Create the Azure OpenAI client
AzureOpenAIClient client = new(new Uri(endpoint), new DefaultAzureCredential());
ChatClient chatClient = client.GetChatClient(deploymentName);
// Create the main agent from the first tutorial
AIAgent mainAgent = chatClient.AsAIAgent(
instructions: "You are a helpful assistant that can answer questions and provide information.",
name: "MyDurableAgent");
// Create translation agents
AIAgent frenchAgent = chatClient.AsAIAgent(
instructions: "You are a translator. Translate the following text to French. Return only the translation, no explanations.",
name: "FrenchTranslator");
AIAgent spanishAgent = chatClient.AsAIAgent(
instructions: "You are a translator. Translate the following text to Spanish. Return only the translation, no explanations.",
name: "SpanishTranslator");
// Build and configure the Functions host
using IHost app = FunctionsApplication
.CreateBuilder(args)
.ConfigureFunctionsWebApplication()
.ConfigureDurableAgents(options =>
{
// Register all agents for use in orchestrations and HTTP endpoints
options.AddAIAgent(mainAgent);
options.AddAIAgent(frenchAgent);
options.AddAIAgent(spanishAgent);
})
.Build();
app.Run();
既存のfunction_app.pyと共に翻訳エージェントを登録するようにMyDurableAgentを更新します。
import os
from azure.identity import DefaultAzureCredential
from agent_framework.azure import AzureOpenAIChatClient, AgentFunctionApp
# Get the Azure OpenAI configuration
endpoint = os.getenv("AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT")
if not endpoint:
raise ValueError("AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT is not set.")
deployment_name = os.getenv("AZURE_OPENAI_DEPLOYMENT", "gpt-4o-mini")
# Create the Azure OpenAI client
chat_client = AzureOpenAIChatClient(
endpoint=endpoint,
deployment_name=deployment_name,
credential=DefaultAzureCredential()
)
# Create the main agent from the first tutorial
main_agent = chat_client.as_agent(
instructions="You are a helpful assistant that can answer questions and provide information.",
name="MyDurableAgent"
)
# Create translation agents
french_agent = chat_client.as_agent(
instructions="You are a translator. Translate the following text to French. Return only the translation, no explanations.",
name="FrenchTranslator"
)
spanish_agent = chat_client.as_agent(
instructions="You are a translator. Translate the following text to Spanish. Return only the translation, no explanations.",
name="SpanishTranslator"
)
# Create the function app and register all agents
app = AgentFunctionApp(agents=[main_agent, french_agent, spanish_agent])
オーケストレーション関数を作成する
オーケストレーション関数は、複数のエージェント間でワークフローを調整します。 永続コンテキストから登録済みエージェントを取得し、その実行を調整し、最初にメイン エージェントを呼び出し、次に翻訳エージェントに同時にファンアウトします。
プロジェクト ディレクトリに AgentOrchestration.cs という名前の新しいファイルを作成します。
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.Agents.AI;
using Microsoft.Agents.AI.DurableTask;
using Microsoft.Azure.Functions.Worker;
using Microsoft.DurableTask;
namespace MyDurableAgent;
public static class AgentOrchestration
{
// Define a strongly-typed response structure for agent outputs
public sealed record TextResponse(string Text);
[Function("agent_orchestration_workflow")]
public static async Task<Dictionary<string, string>> AgentOrchestrationWorkflow(
[OrchestrationTrigger] TaskOrchestrationContext context)
{
var input = context.GetInput<string>() ?? throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(context), "Input cannot be null");
// Step 1: Get the main agent's response
DurableAIAgent mainAgent = context.GetAgent("MyDurableAgent");
AgentResponse<TextResponse> mainResponse = await mainAgent.RunAsync<TextResponse>(input);
string agentResponse = mainResponse.Result.Text;
// Step 2: Fan out - get the translation agents and run them concurrently
DurableAIAgent frenchAgent = context.GetAgent("FrenchTranslator");
DurableAIAgent spanishAgent = context.GetAgent("SpanishTranslator");
Task<AgentResponse<TextResponse>> frenchTask = frenchAgent.RunAsync<TextResponse>(agentResponse);
Task<AgentResponse<TextResponse>> spanishTask = spanishAgent.RunAsync<TextResponse>(agentResponse);
// Step 3: Wait for both translation tasks to complete (fan-in)
await Task.WhenAll(frenchTask, spanishTask);
// Get the translation results
TextResponse frenchResponse = (await frenchTask).Result;
TextResponse spanishResponse = (await spanishTask).Result;
// Step 4: Combine results into a dictionary
var result = new Dictionary<string, string>
{
["original"] = agentResponse,
["french"] = frenchResponse.Text,
["spanish"] = spanishResponse.Text
};
return result;
}
}
オーケストレーション関数を function_app.py ファイルに追加します。
import azure.durable_functions as df
@app.orchestration_trigger(context_name="context")
def agent_orchestration_workflow(context: df.DurableOrchestrationContext):
"""
Orchestration function that coordinates multiple agents.
Returns a dictionary with the original response and translations.
"""
input_text = context.get_input()
# Step 1: Get the main agent's response
main_agent = app.get_agent(context, "MyDurableAgent")
main_response = yield main_agent.run(input_text)
agent_response = main_response.text
# Step 2: Fan out - get the translation agents and run them concurrently
french_agent = app.get_agent(context, "FrenchTranslator")
spanish_agent = app.get_agent(context, "SpanishTranslator")
parallel_tasks = [
french_agent.run(agent_response),
spanish_agent.run(agent_response)
]
# Step 3: Wait for both translation tasks to complete (fan-in)
translations = yield context.task_all(parallel_tasks) # type: ignore
# Step 4: Combine results into a dictionary
result = {
"original": agent_response,
"french": translations[0].text,
"spanish": translations[1].text
}
return result
オーケストレーションをテストする
最初のチュートリアルのローカル開発の依存関係が引き続き実行されていることを確認します。
- 1 つのターミナル ウィンドウで Azurite
- 別のターミナル ウィンドウの Durable Task Scheduler エミュレーター
ローカル開発の依存関係が実行されている場合:
新しいターミナル ウィンドウで Azure Functions アプリを起動します。
func startDurable Functions 拡張機能は、オーケストレーションを管理するための組み込みの HTTP エンドポイントを自動的に作成します。 組み込みの API を使用してオーケストレーションを開始します。
curl -X POST http://localhost:7071/runtime/webhooks/durabletask/orchestrators/agent_orchestration_workflow \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d '"\"What are three popular programming languages?\""'
応答には、オーケストレーション インスタンスを管理するための URL が含まれています。
{ "id": "abc123def456", "statusQueryGetUri": "http://localhost:7071/runtime/webhooks/durabletask/instances/abc123def456", "sendEventPostUri": "http://localhost:7071/runtime/webhooks/durabletask/instances/abc123def456/raiseEvent/{eventName}", "terminatePostUri": "http://localhost:7071/runtime/webhooks/durabletask/instances/abc123def456/terminate", "purgeHistoryDeleteUri": "http://localhost:7071/runtime/webhooks/durabletask/instances/abc123def456" }statusQueryGetUriを使用してオーケストレーションの状態を照会します (abc123def456を実際のインスタンス ID に置き換えます)。curl http://localhost:7071/runtime/webhooks/durabletask/instances/abc123def456
runtimeStatusがCompletedされるまで、状態エンドポイントをポーリングします。 完了すると、メイン エージェントの応答とその翻訳を含むオーケストレーション出力が表示されます。{ "name": "agent_orchestration_workflow", "instanceId": "abc123def456", "runtimeStatus": "Completed", "output": { "original": "Three popular programming languages are Python, JavaScript, and Java. Python is known for its simplicity...", "french": "Trois langages de programmation populaires sont Python, JavaScript et Java. Python est connu pour sa simplicité...", "spanish": "Tres lenguajes de programación populares son Python, JavaScript y Java. Python es conocido por su simplicidad..." } }
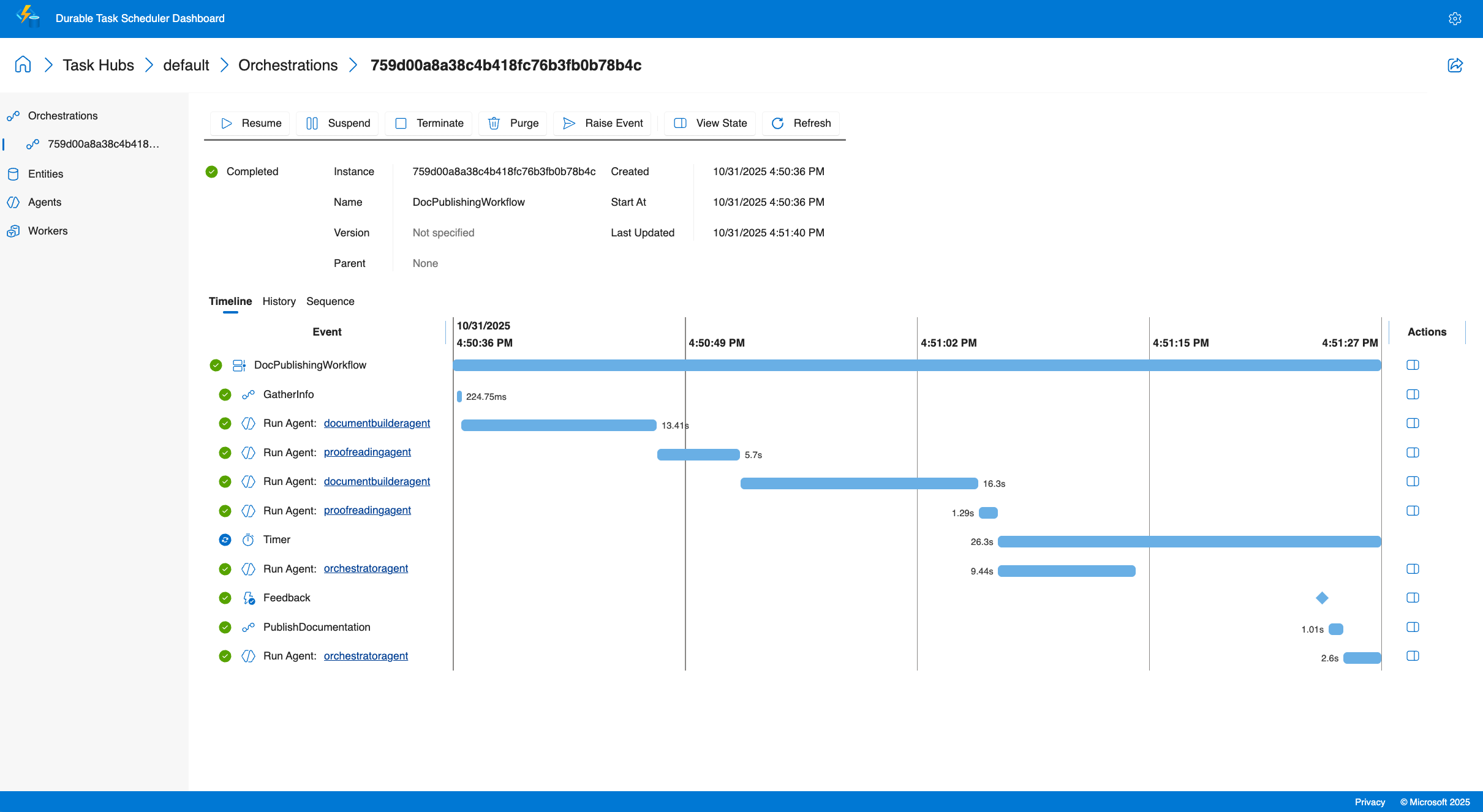
ダッシュボードでオーケストレーションを監視する
Durable Task Scheduler ダッシュボードでは、オーケストレーションに対する可視性が提供されます。
ブラウザーで
http://localhost:8082を開きます。"既定" タスク ハブを選択します。
[オーケストレーション] タブを選択します。
一覧でオーケストレーション インスタンスを見つけます。
表示するインスタンスを選択します。
- オーケストレーションのタイムライン
- メイン エージェントの実行後に同時翻訳エージェントが続く
- 各エージェントの実行順序(MyDurableAgent、続いてフランス語とスペイン語の翻訳プログラム)
- ファンアウトパターンとファンインパターンを視覚化
- 各ステップのタイミングと期間
オーケストレーションを Azure にデプロイする
Azure Developer CLI を使用して更新されたアプリケーションをデプロイします。
azd deploy
これにより、新しいオーケストレーション関数と追加のエージェントを含む更新されたコードが、最初のチュートリアルで作成された Azure Functions アプリにデプロイされます。
デプロイされたオーケストレーションをテストする
デプロイ後、Azure で実行されているオーケストレーションをテストします。
永続的拡張機能のシステム キーを取得します。
SYSTEM_KEY=$(az functionapp keys list --name $(azd env get-value AZURE_FUNCTION_NAME) --resource-group $(azd env get-value AZURE_RESOURCE_GROUP) --query "systemKeys.durabletask_extension" -o tsv)
組み込みの API を使用してオーケストレーションを開始します。
curl -X POST "https://$(azd env get-value AZURE_FUNCTION_NAME).azurewebsites.net/runtime/webhooks/durabletask/orchestrators/agent_orchestration_workflow?code=$SYSTEM_KEY" \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d '"\"What are three popular programming languages?\""'
- 応答の
statusQueryGetUriを用いて結果の完了を定期的に確認し、翻訳結果を表示します。
次のステップ
その他のリソース: