Important
この SDK の詳細については、Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK v4 リリース ノート、 Maven リポジトリ、Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK v4 のパフォーマンスに関するヒント、および Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK v4 のトラブルシューティング ガイドを参照してください。
Important
Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK v4 には最大 20% の拡張スループット、TCP ベースのダイレクト モード、最新のバックエンド サービス機能のサポートがあるため、次の機会に v4 にアップグレードすることをお勧めします。 詳細については、以下を参照してください。
Azure Cosmos DB が提供する機能を最大限に活用するために、最新の Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK に更新してください。競争力のあるパフォーマンスを備えた管理された非リレーショナルデータベースサービス、99.999% の可用性、独自のリソースガバナンスなどが含まれています。 この記事では、古い Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK を使用している既存の Java アプリケーションを、新しい Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK 4.0 for API for NoSQL にアップグレードする方法について説明します。 Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK v4 は、 com.azure.cosmos パッケージに対応します。 次のいずれかの Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK からアプリケーションを移行する場合は、このドキュメントの手順を使用できます。
- Sync Java SDK 2.x.x
- Async Java SDK 2.x.x
- Java SDK 3.x.x
Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK とパッケージ マッピング
次の表に、さまざまな Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK、パッケージ名、リリース情報を示します。
| Java SDK | リリース日 | バンドルされた API | Maven Jar | Java パッケージ名 | API リファレンス | リリース ノート | 廃止日 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Async 2.x.x | 2018 年 6 月 | Async(RxJava) | com.microsoft.azure::azure-cosmosdb |
com.microsoft.azure.cosmosdb.rx |
API | リリース ノート | 2024 年 8 月 31 日 |
| 同期 2.x.x | 2018 年 9 月 | 同期 | com.microsoft.azure::azure-documentdb |
com.microsoft.azure.cosmosdb |
API | 2024 年 2 月 29 日 | |
| 3.x.x | 2019 年 7 月 | Async(Reactor)/Sync | com.microsoft.azure::azure-cosmos |
com.azure.data.cosmos |
API | - | 2024 年 8 月 31 日 |
| 4.0 | 2020 年 6 月 | Async(Reactor)/Sync | com.azure::azure-cosmos |
com.azure.cosmos |
API | - | - |
SDK レベルの実装の変更
さまざまな SDK の主な実装の違いを次に示します。
RxJava は、Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK バージョン 3.x.x および 4.0 のリアクタに置き換えられます
非同期プログラミングやリアクティブ プログラミングに慣れていない場合は、非同期プログラミングと Project Reactor の概要については、 Reactor パターン ガイド を参照してください。 このガイドは、過去に Azure Cosmos DB Sync Java SDK 2.x.x または Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK 3.x.x Sync API を使用している場合に便利です。
Azure Cosmos DB Async Java SDK 2.x.x を使用していて、4.0 SDK への移行を計画している場合は、Reactor を使用するように RxJava コードを変換する方法のガイダンスについては、 Reactor と RxJava のガイド を参照してください。
Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK v4 には、非同期 API と同期 API の両方で直接接続モードがあります
Azure Cosmos DB Sync Java SDK 2.x.x を使用している場合は、非同期 API と Sync API の両方に対して、(HTTP ではなく) TCP に基づく直接接続モードが Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK 4.0 に実装されていることに注意してください。
API レベルの変更
以前の SDK (Java SDK 3.x.x、Async Java SDK 2.x.x、Sync Java SDK 2.x.x) と比較した Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK 4.x.x の API レベルの変更を次に示します。
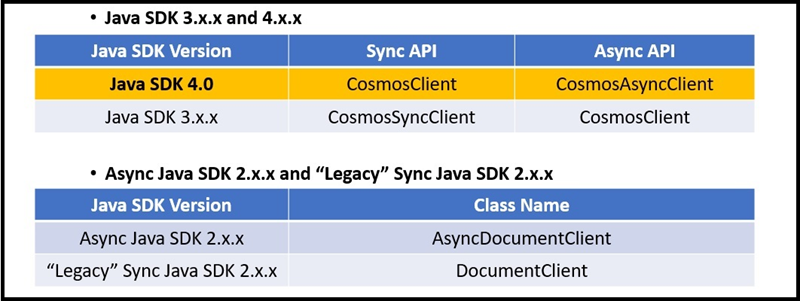
Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK 3.x.x および 4.0 は、クライアント リソースを
Cosmos<resourceName>として参照します。 たとえば、CosmosClient、CosmosDatabase、CosmosContainerなどです。 バージョン 2.x.x では、Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK には統一された名前付けスキームがありません。Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK 3.x.x と 4.0 では、同期 API と非同期 API の両方が提供されます。
Java SDK 4.0:
Asyncの後にクラス名にCosmosが付加されない限り、すべてのクラスは Sync API に属しています。Java SDK 3.x.x: クラス名が
Asyncの後にCosmosが追加されない限り、すべてのクラスは Async API に属します。Async Java SDK 2.x.x: クラス名は Sync Java SDK 2.x.x に似ていますが、名前は Async で始まります。
階層型 API の構造
Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK 4.0 および 3.x.x では、次の 4.0 SDK コード スニペットに示すように、クライアント、データベース、コンテナーを入れ子にして整理する階層型 API 構造が導入されています。
CosmosContainer container = client.getDatabase("MyDatabaseName").getContainer("MyContainerName");
Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK のバージョン 2.x.x では、リソースとドキュメントに対するすべての操作がクライアント インスタンスを介して実行されます。
ドキュメントの表現
Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK 4.0 では、カスタム POJO と JsonNodes は、Azure Cosmos DB からドキュメントを読み書きするための 2 つのオプションです。
Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK 3.x.x では、 CosmosItemProperties オブジェクトはパブリック API によって公開され、ドキュメント表現として機能します。 このクラスは、バージョン 4.0 では公開されなくなりました。
インポート
Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK 4.0 のパッケージは、
com.azure.cosmosで始まります。Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK 3.x.x パッケージは
com.azure.data.cosmosで始まりますAzure Cosmos DB Java SDK 2.x.x Sync API パッケージは
com.microsoft.azure.documentdbで始まります。Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK 4.0 では、入れ子になったパッケージ
com.azure.cosmos.modelsに複数のクラスが配置されます。 これらのパッケージの一部は次のとおりです。CosmosContainerResponseCosmosDatabaseResponseCosmosItemResponse- 上記のすべてのパッケージの Async API アナログ
CosmosContainerPropertiesFeedOptionsPartitionKeyIndexingPolicy-
IndexingMode...など。
Accessors
Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK 4.0 では、インスタンス メンバーにアクセスするための get メソッドと set メソッドが公開されています。 たとえば、 CosmosContainer インスタンスには container.getId() メソッドと container.setId() メソッドがあります。
これは、Fluent インターフェイスを公開する Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK 3.x.x とは異なります。 たとえば、CosmosSyncContainer インスタンスには、container.id()値を取得または設定するためにオーバーロードされたidがあります。
依存関係の競合を管理する
Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK V2 から V4 にアップグレードすると、SDK で使用されるライブラリが変更されたため、依存関係の競合が発生する可能性があります。 これらの競合を解決するには、依存関係を慎重に管理する必要があります。
新しい依存関係について: Azure Cosmos DB V4 SDK には、以前のバージョンとは異なる可能性がある独自の依存関係セットがあります。 次の依存関係を認識していることを確認します。
azure-cosmosreactor-corereactor-nettynetty-handlerguavaslf4j-apijackson-databindjackson-annotationsjackson-corecommons-lang3commons-collections4azure-coreazure-core-http-netty
競合する依存関係の削除: まず、
pom.xmlファイルから以前のバージョンの SDK に関連する依存関係を削除します。 これには、azure-cosmosdbと、古い SDK が持っていた可能性がある推移的な依存関係が含まれます。V4 SDK の依存関係の追加: V4 SDK とその依存関係を
pom.xmlに追加します。 次に例を示します。<dependency> <groupId>com.azure</groupId> <artifactId>azure-cosmos</artifactId> <version>4.x.x</version> <!-- Use the latest version available --> </dependency>依存関係の競合を確認する: Maven
dependency:treeコマンドを使用して依存関係ツリーを生成し、競合を特定します。 走れmvn dependency:tree競合するバージョンの依存関係を探します。 これらの競合は、多くの場合、
reactor-core、netty-handler、guava、jacksonなどのライブラリで発生します。依存関係管理の使用: バージョンの競合が発生した場合は、
<dependencyManagement>のpom.xmlセクションを使用して、問題のあるバージョンをオーバーライドすることが必要になる場合があります。 特定のバージョンのreactor-coreを適用する例を次に示します。<dependencyManagement> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>io.projectreactor</groupId> <artifactId>reactor-core</artifactId> <version>3.x.x</version> <!-- Use a compatible version --> </dependency> <!-- Repeat for any other conflicting dependencies --> </dependencies> </dependencyManagement>推移的な依存関係を除外する: 場合によっては、他の依存関係によって取り込まれる推移的な依存関係を除外する必要があります。 たとえば、別のライブラリが競合する古いバージョンの依存関係を取り込む場合は、次のように除外できます。
<dependency> <groupId>some.group</groupId> <artifactId>some-artifact</artifactId> <version>x.x.x</version> <exclusions> <exclusion> <groupId>conflicting.group</groupId> <artifactId>conflicting-artifact</artifactId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency>リビルドとテスト: これらの変更を行った後、プロジェクトをリビルドし、十分にテストして、新しい依存関係が正しく動作し、ランタイムの競合が発生しないようにします。
コード スニペットの比較
リソースの作成
次のコード スニペットは、4.0、3.x.x Async、2.x.x Sync、および 2.x.x Async API 間のリソースの作成方法の違いを示しています。
// Create Async client.
// Building an async client is still a sync operation.
CosmosAsyncClient client = new CosmosClientBuilder()
.endpoint("your.hostname")
.key("yourmasterkey")
.consistencyLevel(ConsistencyLevel.EVENTUAL)
.buildAsyncClient();
// Create database with specified name
client.createDatabaseIfNotExists("YourDatabaseName")
.flatMap(databaseResponse -> {
testDatabaseAsync = client.getDatabase("YourDatabaseName");
// Container properties - name and partition key
CosmosContainerProperties containerProperties =
new CosmosContainerProperties("YourContainerName", "/id");
// Provision manual throughput
ThroughputProperties throughputProperties = ThroughputProperties.createManualThroughput(400);
// Create container
return database.createContainerIfNotExists(containerProperties, throughputProperties);
}).flatMap(containerResponse -> {
testContainerAsync = database.getContainer("YourContainerName");
return Mono.empty();
}).subscribe();
アイテムの操作
次のコード スニペットは、4.0、3.x.x Async、2.x.x Sync、2.x.x Async API の項目操作の実行方法の違いを示しています。
// Container is created. Generate many docs to insert.
int number_of_docs = 50000;
ArrayList<JsonNode> docs = generateManyDocs(number_of_docs);
// Insert many docs into container...
Flux.fromIterable(docs)
.flatMap(doc -> testContainerAsync.createItem(doc))
.subscribe(); // ...Subscribing triggers stream execution.
インデックス作成
次のコード スニペットは、4.0、3.x.x Async、2.x.x Sync、2.x.x Async API のインデックス作成方法の違いを示しています。
CosmosContainerProperties containerProperties = new CosmosContainerProperties(containerName, "/lastName");
// Custom indexing policy
IndexingPolicy indexingPolicy = new IndexingPolicy();
indexingPolicy.setIndexingMode(IndexingMode.CONSISTENT);
// Included paths
List<IncludedPath> includedPaths = new ArrayList<>();
includedPaths.add(new IncludedPath("/*"));
indexingPolicy.setIncludedPaths(includedPaths);
// Excluded paths
List<ExcludedPath> excludedPaths = new ArrayList<>();
excludedPaths.add(new ExcludedPath("/name/*"));
indexingPolicy.setExcludedPaths(excludedPaths);
containerProperties.setIndexingPolicy(indexingPolicy);
ThroughputProperties throughputProperties = ThroughputProperties.createManualThroughput(400);
database.createContainerIfNotExists(containerProperties, throughputProperties);
CosmosAsyncContainer containerIfNotExists = database.getContainer(containerName);
ストアド プロシージャ
次のコード スニペットは、4.0、3.x.x Async、2.x.x Sync、2.x.x Async API 間でのストアド プロシージャの作成方法の違いを示しています。
logger.info("Creating stored procedure...\n");
String sprocId = "createMyDocument";
String sprocBody = "function createMyDocument() {\n" +
"var documentToCreate = {\"id\":\"test_doc\"}\n" +
"var context = getContext();\n" +
"var collection = context.getCollection();\n" +
"var accepted = collection.createDocument(collection.getSelfLink(), documentToCreate,\n" +
" function (err, documentCreated) {\n" +
"if (err) throw new Error('Error' + err.message);\n" +
"context.getResponse().setBody(documentCreated.id)\n" +
"});\n" +
"if (!accepted) return;\n" +
"}";
CosmosStoredProcedureProperties storedProcedureDef = new CosmosStoredProcedureProperties(sprocId, sprocBody);
container.getScripts()
.createStoredProcedure(storedProcedureDef,
new CosmosStoredProcedureRequestOptions()).block();
// ...
logger.info(String.format("Executing stored procedure %s...\n\n", sprocId));
CosmosStoredProcedureRequestOptions options = new CosmosStoredProcedureRequestOptions();
options.setPartitionKey(new PartitionKey("test_doc"));
container.getScripts()
.getStoredProcedure(sprocId)
.execute(null, options)
.flatMap(executeResponse -> {
logger.info(String.format("Stored procedure %s returned %s (HTTP %d), at cost %.3f RU.\n",
sprocId,
executeResponse.getResponseAsString(),
executeResponse.getStatusCode(),
executeResponse.getRequestCharge()));
return Mono.empty();
}).block();
変更フィード
次のコード スニペットは、4.0 と 3.x.x の非同期 API 間で変更フィード操作がどのように実行されるかの違いを示しています。
ChangeFeedProcessor changeFeedProcessorInstance =
new ChangeFeedProcessorBuilder()
.hostName(hostName)
.feedContainer(feedContainer)
.leaseContainer(leaseContainer)
.handleChanges((List<JsonNode> docs) -> {
logger.info("--->setHandleChanges() START");
for (JsonNode document : docs) {
try {
//Change Feed hands the document to you in the form of a JsonNode
//As a developer you have two options for handling the JsonNode document provided to you by Change Feed
//One option is to operate on the document in the form of a JsonNode, as shown below. This is great
//especially if you do not have a single uniform data model for all documents.
logger.info("---->DOCUMENT RECEIVED: " + OBJECT_MAPPER.writerWithDefaultPrettyPrinter()
.writeValueAsString(document));
//You can also transform the JsonNode to a POJO having the same structure as the JsonNode,
//as shown below. Then you can operate on the POJO.
CustomPOJO pojo_doc = OBJECT_MAPPER.treeToValue(document, CustomPOJO.class);
logger.info("----=>id: " + pojo_doc.getId());
} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
logger.info("--->handleChanges() END");
})
.buildChangeFeedProcessor();
// ...
changeFeedProcessorInstance.start()
.subscribeOn(Schedulers.boundedElastic())
.subscribe();
コンテナー レベルの有効期限(TTL: Time-To-Live)
次のコード スニペットは、4.0、3.x.x Async、2.x.x Sync、2.x.x Async API の間で、コンテナー内のデータの有効期間を作成する方法の違いを示しています。
CosmosAsyncContainer container;
// Create a new container with TTL enabled with default expiration value
CosmosContainerProperties containerProperties = new CosmosContainerProperties("myContainer", "/myPartitionKey");
containerProperties.setDefaultTimeToLiveInSeconds(90 * 60 * 60 * 24);
ThroughputProperties throughputProperties = ThroughputProperties.createManualThroughput(400);
database.createContainerIfNotExists(containerProperties, throughputProperties).block();
container = database.getContainer("myContainer");
アイテムレベルのタイム・トゥ・リブ(TTL)
次のコード スニペットは、4.0、3.x.x Async、2.x.x Sync、および 2.x.x Async API 間の項目の有効期間を作成する方法の違いを示しています。
// Include a property that serializes to "ttl" in JSON
class SalesOrder
{
private String id;
private String customerId;
private Integer ttl;
public SalesOrder(String id, String customerId, Integer ttl) {
this.id = id;
this.customerId = customerId;
this.ttl = ttl;
}
public String getId() {return this.id;}
public void setId(String new_id) {this.id = new_id;}
public String getCustomerId() {return this.customerId;}
public void setCustomerId(String new_cid) {this.customerId = new_cid;}
public Integer getTtl() {return this.ttl;}
public void setTtl(Integer new_ttl) {this.ttl = new_ttl;}
//...
}
// Set the value to the expiration in seconds
SalesOrder salesOrder = new SalesOrder(
"SO05",
"CO18009186470",
60 * 60 * 24 * 30 // Expire sales orders in 30 days
);
次のステップ
- V4 SDK を使用して Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL データを管理する Java アプリを構築する
- Reactor ベースの Java SDK について学習する
- Reactor vs RxJava ガイドを使用して RxJava 非同期コードを Reactor 非同期コードに変換する方法について説明します
- Azure Cosmos DB への移行のための容量計画を実行しようとしていますか?
- 既存のデータベース クラスター内の仮想コアとサーバーの数のみがわかっている場合は、仮想コアまたは vCPU を使用した要求ユニットの見積もりに関するページを参照してください
- 現在のデータベース ワークロードに対する通常の要求レートがわかっている場合は、Azure Cosmos DB Capacity Planner を使用した要求ユニットの見積もりに関するページを参照してください