適用対象: ✔️ Linux VM ✔️ Windows VM
この記事では、Azure Portal を使用して可用性ゾーン内に回復性の高い仮想マシンを作成する手順を説明します。 Azure 可用性ゾーンは、局所的な障害にトレラントな各 Azure リージョン内の物理的に分離された場所です。 可用性ゾーンを使用して、データセンターで発生する可能性の低い障害からアプリケーションとデータを保護します。
可用性ゾーンを使用するには、サポートされている Azure リージョンに仮想マシンを作成します。
Azure portal にサインインします。
[リソースの作成]>[コンピューティング]>[仮想マシン] をクリックします。
[仮想マシン] ページで、[作成] を選択してから [仮想マシン] を選択します。 [仮想マシンの作成] ページが開きます。
[基本] タブの [プロジェクトの詳細] で、正しいサブスクリプションが選択されていることを確認し、リソース グループを選択するか、新規に作成します。
[インスタンスの詳細] で、 仮想マシン名を入力します。
[可用性オプション] では、[可用性ゾーン] をデフォルトのままにします。
[可用性ゾーン] の場合、ドロップダウンの既定値は [ゾーン 1] です。 複数のゾーンを選択すると、各ゾーンにて新しい VM が作成されます。 たとえば、3 つのゾーンすべてを選択すると、3 つの VM が作成されます。 VM 名は、入力した元の名前であり、選択したゾーンの数に基づいて名前に -1、 -2、-3 が追加されます。 必要に応じて、既定の VM 名は編集できます。

通常どおりに、ページの残りの部分を完了します。 ロード バランサーを作成する場合は、[ネットワーク] タブの >[負荷分散] > [負荷分散オプション] に移動します。 Azure ロード バランサーまたはアプリケーション ゲートウェイのいずれかを選択できます。
Azure Load Balancer の場合:
- 既存のロード バランサーを選択するか、[ロード バランサーの作成] を選択します。
- 新しいロード バランサーを作成するには、[ロード バランサー名] にロード バランサーの名前を入力します。
- ロード バランサーの [種類] として、[パブリック] または [内部] を選択します。
- [プロトコル] で、[TCP] または [UDP] のどちらかを選択します。
- ポートとバックエンド ポートは既定値のままにすることも、必要に応じて変更することもできます。 選択したバックエンド ポートは、VM のネットワーク セキュリティ グループ (NSG) で開きます。
- 完了したら [作成] を選択します。
アプリケーション ゲートウェイの場合:
- 既存のアプリケーション ゲートウェイを選択するか、アプリケーション ゲートウェイを作成します。
- 新しいゲートウェイを作成するには、アプリケーション ゲートウェイの名前を入力します。 アプリケーション ゲートウェイでは、複数のアプリケーションを負荷分散できます。 仮想マシン名に特有のものにするのではなく、負荷分散するワークロードに応じて、ワークロードの名前を指定します。
- [ルーティング規則] に規則名を入力します。 規則名には、負荷分散するワークロードが記述されている必要があります。
- HTTP 負荷分散の場合は、既定値のままにして [作成] を選択できます。 HTTPS 負荷分散の場合は、次の 2 つのオプションがあります。
- 証明書をアップロードし、パスワードを追加します (アプリケーション ゲートウェイで証明書ストレージを管理します)。 [証明書名] に、証明書のフレンドリ名を入力します。
- キー コンテナーを使用します (アプリケーション ゲートウェイが、定義されたキー コンテナーから定義済みの証明書をプルします)。 使用するマネージド ID、キー コンテナー、証明書を選択します。
重要
VM とアプリケーション ゲートウェイがデプロイされた後、VM にログインして、アプリケーション ゲートウェイ証明書が VM にアップロードされているか、または VM 証明書のドメイン名がアプリケーション ゲートウェイのドメイン名と一致しているかを確認する必要があります。
Note
作成時に、アプリケーション ゲートウェイに別のサブネットが定義されます。 詳細については、「Application Gateway インフラストラクチャの構成」を参照してください。
残りの既定値はそのままにして、ページの一番下にある [Review + create] (確認および作成) ボタンを選択します。
[仮想マシンの作成] ページで、これから作成しようとしている VM の詳細を確認できます。 準備ができたら、 [作成] を選択します。
Linix VM を作成している時に [新しいキー ペアの生成] ウィンドウが開いたら、[Download private key and create resource (秘密キーをダウンロードし、リソースを作成する)] を選択します。 キー ファイルは myKey.pem としてダウンロードされます。
デプロイが完了したら、 [リソースに移動] を選択します。
Azure で選択したゾーンにゾーン仮想マシンを作成する
重要
これらの機能は、現在プレビュー段階です。 ベータ版、プレビュー版、または一般提供としてまだリリースされていない Azure の機能に適用される法律条項については、「Microsoft Azure プレビューの追加使用条件」を参照してください。
ゾーン仮想マシンの回復性の利点が必要で、ゾーンの選択に関するヘルプが必要な場合は、Azure でデプロイに最適なゾーンを選択できます。
Note
Azure で選択したゾーンを使用して VM をデプロイする前に、「制限」セクションを確認してください。
- このリンクを使用して Azure portal にサインインし、機能を有効にします。
- [基本] タブの [プロジェクトの詳細] で、正しいサブスクリプションが選択されていることを確認し、リソース グループを選択するか、新規に作成します。
- [インスタンスの詳細] で、 仮想マシン名を入力します。
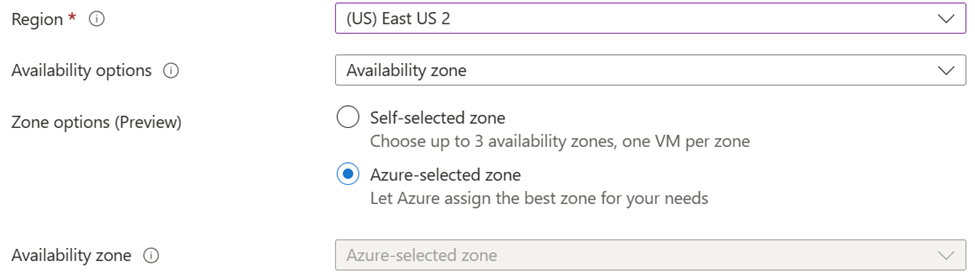
- [可用性オプション] で、[可用性ゾーン] ドロップダウンが選択されていることを確認します。
- [ゾーン オプション (プレビュー)] で、Azure で選択したゾーンを選択します。 可用性ゾーンの選択がグレー表示されます。
- デプロイ用に、仮想マシンの残りの部分を通常どおりに構成します。
制限
地域
Azure で選択したゾーンへの VM のデプロイは、次のリージョンを除くすべてのゾーン リージョンで使用できます。
- ブラジル南部
- CentralIndia
- EastUS
- JapanEast
- KoreaCentral
ディスク
現在、既存の OS およびデータ ディスクはサポートされていません。 新しいデータ ディスク ソースの種類は [なし] である必要があります。
サポートされているディスクの種類
- Standard HDD (ハード ディスク ドライブ)
- Premium SSD
- Premium SSD V2
- Ultra Disks
- Standard SSD ZRS
サポートされていないディスクの種類
- Standard SSD LRS

その他のリソース
- 既存のパブリック IP は、Azure で選択したゾーンではサポートされていません。 デプロイ後に追加できます。
- 新しいパブリック IP はゾーン冗長であるか、Azure で選択したゾーンを使用する必要があります。
- ロード バランサーと Application Gateway は、VM のデプロイ中にアタッチできるゾーン回復性がある必要があります。
- 近接配置グループ、容量予約グループ、Azure Dedicated Host はサポートされていません。
- Site Recovery の構成は、VM の作成時には使用できませんが、デプロイ後に構成できます。
次のステップ
この記事では、可用性ゾーン内に VM を作成する方法を説明しました。 Azure VM の可用性の詳細を確認してください。