Explore Windows network configuration
The Windows client network settings can be found in the Windows Setting App, under Network & Internet. Alternatively, you can select on the network connection icon on the right side of the taskbar, and then select Network & Internet Settings (Windows 10) or All Settings (Windows 11). Either will open the following submenu:
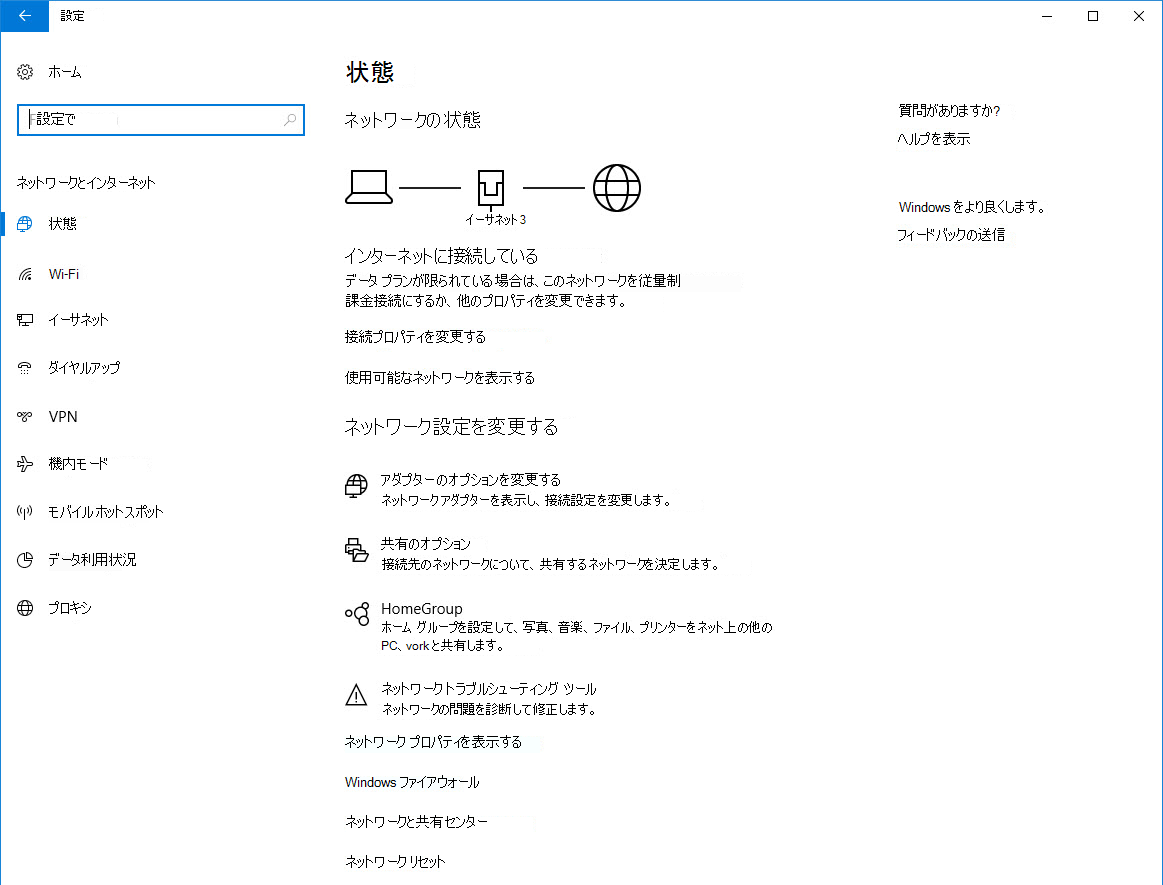
By default, you will see the Network Status page, which will indicate your current connection state. You’ll also notice additional sub-menus on the left side, such as Wi-Fi, Airplane mode, Data usage, VPN, Dial-up, Ethernet, and Proxy. These are the various methods available for connecting to a network – and will vary depending on what type of connections the individual device will support.
From within Ethernet or Wi-Fi, you can:
Change adapter options. You can configure the network adapter settings. A list of network adapters displays, and you can then configure the properties for each, including:
- Internet Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IPv6). Enables you to manually configure the IPv6 settings for a given adapter.
- Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4). Enables you to manually configure the IPv4 settings for a given adapter.
Change advanced sharing options. You can configure network discovery, file and print sharing, public folder sharing, media streaming options, and the encryption level to use for file sharing connections.
Launch the Network and Sharing Center. You can use this tool to configure most network settings. You will learn more about it in the next section.
Configure Internet options. You can configure the options your web browsers use.
Configure Windows Firewall. You can launch the Windows Firewall tool and configure Windows Firewall rules, notifications, and advanced settings.
From within Wi-Fi, you also can:
- View available networks. You can use this setting to view available networks, but not explicitly hidden wireless networks.
- View hardware properties. You can use this setting to view properties of your Wi-Fi connection such as its Service Set Identifier (SSID), protocol, and security type, in addition to the manufacturer and the physical MAC address of your Wi-Fi adapter.
- Manage known networks. You can use this setting to display the properties of the wireless networks you have connected to and remove (or forget, as referenced in the graphical user interface (GUI)) their settings.
- Configure Hotspot 2.0 networks. You can use this setting to use Online Sign-Up to connect to Hotspot 2.0 networks.
Network and Sharing Center
This tool is largely the same as it is in Windows 8.1. It provides a clear view of the status for any wired or wireless connection, and you can use it to create additional network connections by using a wizard-driven interface. The Network and Sharing Center also provides links for accessing other network-related tools, including:
- Change advanced sharing settings
- Internet Options
- Windows Firewall
- Network and Internet Troubleshooting Wizard