핸드오프 오케스트레이션을 사용하면 에이전트가 컨텍스트 또는 사용자 요청에 따라 서로 제어를 전송할 수 있습니다. 각 에이전트는 적절한 전문 지식을 갖춘 다른 에이전트에게 대화를 "전달"하여 올바른 에이전트가 작업의 각 부분을 처리하도록 할 수 있습니다. 이는 고객 지원, 전문가 시스템 또는 동적 위임이 필요한 시나리오에서 특히 유용합니다.
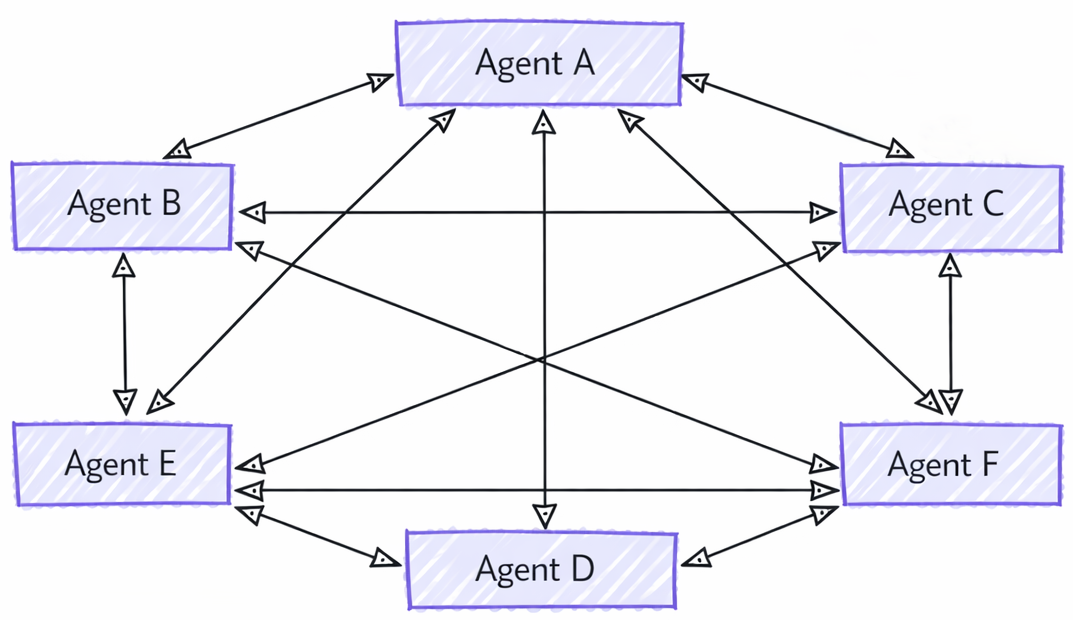
내부적으로 핸드오프 오케스트레이션은 에이전트가 오케스트레이터 없이 직접 연결되는 메시 토폴로지로 구현됩니다. 각 에이전트는 미리 정의된 규칙 또는 메시지 내용에 따라 대화를 전달할 시기를 결정할 수 있습니다.
비고
핸드오프 오케스트레이션은 Agent만 지원되며, 에이전트는 로컬 도구 실행을 지원해야 합니다.
핸드오프와 Agent-as-Tools의 차이점
에이전트를 도구로 사용하는 것은 보편적으로 멀티 에이전트 패턴으로 여겨지며 언뜻 보기에 핸드오프 방식과 유사하게 보일 수 있지만, 두 가지 간에는 근본적인 차이점이 있습니다.
- 제어 흐름: 핸드오프 오케스트레이션에서 정의된 규칙에 따라 에이전트 간에 제어가 명시적으로 전달됩니다. 각 에이전트는 전체 작업을 다른 에이전트에 전달하도록 결정할 수 있습니다. 워크플로를 관리하는 중앙 기관은 없습니다. 반면, 에이전트-as-tools에는 하위 작업을 다른 에이전트에 위임하는 기본 에이전트가 포함되며 에이전트가 하위 작업을 완료하면 컨트롤이 주 에이전트로 돌아갑니다.
- 작업 소유권: 핸드오프에서 핸드오프를 받는 에이전트는 작업의 전체 소유권을 맡습니다. 에이전트-as-tools에서 주 에이전트는 작업에 대한 전반적인 책임을 유지하지만 다른 에이전트는 특정 하위 작업을 지원하는 도구로 처리됩니다.
- 컨텍스트 관리: 핸드오프 오케스트레이션에서 대화는 완전히 다른 에이전트에 전달됩니다. 수신 에이전트에는 지금까지 수행된 작업의 전체 컨텍스트가 있습니다. 에이전트-as-tools에서 기본 에이전트는 전체 컨텍스트를 관리하고 필요에 따라 도구 에이전트에 관련 정보만 제공할 수 있습니다.
학습 내용
- 다른 도메인에 대한 특수 에이전트를 만드는 방법
- 에이전트 간에 핸드오프 규칙을 구성하는 방법
- 동적 에이전트 라우팅을 사용하여 대화형 워크플로를 빌드하는 방법
- 에이전트 전환으로 다중 턴 대화를 처리하는 방법
- 중요한 작업에 대한 도구 승인을 구현하는 방법(HITL)
- 내구적인 핸드오프 워크플로를 위한 체크포인트 사용 방법
핸드오프 오케스트레이션에서 에이전트는 컨텍스트에 따라 서로 제어를 전송하여 동적 라우팅 및 전문 지식 처리를 수행할 수 있습니다.
Azure OpenAI 클라이언트 설정
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Azure.AI.OpenAI;
using Azure.Identity;
using Microsoft.Agents.AI.Workflows;
using Microsoft.Extensions.AI;
using Microsoft.Agents.AI;
// 1) Set up the Azure OpenAI client
var endpoint = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT") ??
throw new InvalidOperationException("AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT is not set.");
var deploymentName = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("AZURE_OPENAI_DEPLOYMENT_NAME") ?? "gpt-4o-mini";
var client = new AzureOpenAIClient(new Uri(endpoint), new DefaultAzureCredential())
.GetChatClient(deploymentName)
.AsIChatClient();
경고
DefaultAzureCredential 은 개발에 편리하지만 프로덕션 환경에서 신중하게 고려해야 합니다. 프로덕션 환경에서는 특정 자격 증명(예: ManagedIdentityCredential)을 사용하여 대기 시간 문제, 의도하지 않은 자격 증명 검색 및 대체 메커니즘의 잠재적인 보안 위험을 방지하는 것이 좋습니다.
특수 에이전트 정의
라우팅을 위한 도메인별 에이전트 및 심사 에이전트를 만듭니다.
// 2) Create specialized agents
ChatClientAgent historyTutor = new(client,
"You provide assistance with historical queries. Explain important events and context clearly. Only respond about history.",
"history_tutor",
"Specialist agent for historical questions");
ChatClientAgent mathTutor = new(client,
"You provide help with math problems. Explain your reasoning at each step and include examples. Only respond about math.",
"math_tutor",
"Specialist agent for math questions");
ChatClientAgent triageAgent = new(client,
"You determine which agent to use based on the user's homework question. ALWAYS handoff to another agent.",
"triage_agent",
"Routes messages to the appropriate specialist agent");
핸드오프 규칙 구성
어떤 에이전트가 다른 에이전트에게 인계를 할 수 있는지 정의합니다.
// 3) Build handoff workflow with routing rules
var workflow = AgentWorkflowBuilder.StartHandoffWith(triageAgent)
.WithHandoffs(triageAgent, [mathTutor, historyTutor]) // Triage can route to either specialist
.WithHandoff(mathTutor, triageAgent) // Math tutor can return to triage
.WithHandoff(historyTutor, triageAgent) // History tutor can return to triage
.Build();
대화형 핸드오프 워크플로 실행
동적 에이전트 전환을 사용하여 다중 턴 대화를 처리합니다.
// 4) Process multi-turn conversations
List<ChatMessage> messages = new();
while (true)
{
Console.Write("Q: ");
string userInput = Console.ReadLine()!;
messages.Add(new(ChatRole.User, userInput));
// Execute workflow and process events
StreamingRun run = await InProcessExecution.StreamAsync(workflow, messages);
await run.TrySendMessageAsync(new TurnToken(emitEvents: true));
List<ChatMessage> newMessages = new();
await foreach (WorkflowEvent evt in run.WatchStreamAsync().ConfigureAwait(false))
{
if (evt is AgentResponseUpdateEvent e)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{e.ExecutorId}: {e.Data}");
}
else if (evt is WorkflowOutputEvent outputEvt)
{
newMessages = (List<ChatMessage>)outputEvt.Data!;
break;
}
}
// Add new messages to conversation history
messages.AddRange(newMessages.Skip(messages.Count));
}
샘플 상호 작용
Q: What is the derivative of x^2?
triage_agent: This is a math question. I'll hand this off to the math tutor.
math_tutor: The derivative of x^2 is 2x. Using the power rule, we bring down the exponent (2) and multiply it by the coefficient (1), then reduce the exponent by 1: d/dx(x^2) = 2x^(2-1) = 2x.
Q: Tell me about World War 2
triage_agent: This is a history question. I'll hand this off to the history tutor.
history_tutor: World War 2 was a global conflict from 1939 to 1945. It began when Germany invaded Poland and involved most of the world's nations. Key events included the Holocaust, Pearl Harbor attack, D-Day invasion, and ended with atomic bombs on Japan.
Q: Can you help me with calculus integration?
triage_agent: This is another math question. I'll route this to the math tutor.
math_tutor: I'd be happy to help with calculus integration! Integration is the reverse of differentiation. The basic power rule for integration is: ∫x^n dx = x^(n+1)/(n+1) + C, where C is the constant of integration.
데모용 몇 가지 도구 정의
@tool
def process_refund(order_number: Annotated[str, "Order number to process refund for"]) -> str:
"""Simulated function to process a refund for a given order number."""
return f"Refund processed successfully for order {order_number}."
@tool
def check_order_status(order_number: Annotated[str, "Order number to check status for"]) -> str:
"""Simulated function to check the status of a given order number."""
return f"Order {order_number} is currently being processed and will ship in 2 business days."
@tool
def process_return(order_number: Annotated[str, "Order number to process return for"]) -> str:
"""Simulated function to process a return for a given order number."""
return f"Return initiated successfully for order {order_number}. You will receive return instructions via email."
채팅 클라이언트 설정
from agent_framework.azure import AzureOpenAIChatClient
from azure.identity import AzureCliCredential
# Initialize the Azure OpenAI chat client
chat_client = AzureOpenAIChatClient(credential=AzureCliCredential())
특수 에이전트 정의
라우팅을 위한 코디네이터를 사용하여 도메인별 에이전트를 만듭니다.
# Create triage/coordinator agent
triage_agent = chat_client.as_agent(
instructions=(
"You are frontline support triage. Route customer issues to the appropriate specialist agents "
"based on the problem described."
),
description="Triage agent that handles general inquiries.",
name="triage_agent",
)
# Refund specialist: Handles refund requests
refund_agent = chat_client.as_agent(
instructions="You process refund requests.",
description="Agent that handles refund requests.",
name="refund_agent",
# In a real application, an agent can have multiple tools; here we keep it simple
tools=[process_refund],
)
# Order/shipping specialist: Resolves delivery issues
order_agent = chat_client.as_agent(
instructions="You handle order and shipping inquiries.",
description="Agent that handles order tracking and shipping issues.",
name="order_agent",
# In a real application, an agent can have multiple tools; here we keep it simple
tools=[check_order_status],
)
# Return specialist: Handles return requests
return_agent = chat_client.as_agent(
instructions="You manage product return requests.",
description="Agent that handles return processing.",
name="return_agent",
# In a real application, an agent can have multiple tools; here we keep it simple
tools=[process_return],
)
핸드오프 규칙 구성
HandoffBuilder를 사용하여 핸드오프 워크플로를 빌드합니다.
from agent_framework.orchestrations import HandoffBuilder
# Build the handoff workflow
workflow = (
HandoffBuilder(
name="customer_support_handoff",
participants=[triage_agent, refund_agent, order_agent, return_agent],
termination_condition=lambda conversation: len(conversation) > 0 and "welcome" in conversation[-1].text.lower(),
)
.with_start_agent(triage_agent) # Triage receives initial user input
.build()
)
기본적으로 모든 에이전트는 서로에게 인계할 수 있습니다. 고급 라우팅을 위해 핸드오프를 구성할 수 있습니다.
workflow = (
HandoffBuilder(
name="customer_support_handoff",
participants=[triage_agent, refund_agent, order_agent, return_agent],
termination_condition=lambda conversation: len(conversation) > 0 and "welcome" in conversation[-1].text.lower(),
)
.with_start_agent(triage_agent) # Triage receives initial user input
# Triage cannot route directly to refund agent
.add_handoff(triage_agent, [order_agent, return_agent])
# Only the return agent can handoff to refund agent - users wanting refunds after returns
.add_handoff(return_agent, [refund_agent])
# All specialists can handoff back to triage for further routing
.add_handoff(order_agent, [triage_agent])
.add_handoff(return_agent, [triage_agent])
.add_handoff(refund_agent, [triage_agent])
.build()
)
비고
사용자 지정 핸드오프 규칙이 있더라도 모든 에이전트는 여전히 메시 토폴로지에서 연결됩니다. 이는 에이전트가 대화 기록을 유지하기 위해 컨텍스트를 서로 공유해야 하기 때문입니다(자세한 내용은 컨텍스트 동기화 참조). 핸드오프 규칙은 다음에 대화를 인수할 수 있는 에이전트만 제어합니다.
핸드오프 에이전트 상호 작용을 실행하기
다른 오케스트레이션과 달리 에이전트가 매 턴마다 핸드오프를 결정하지 않을 수 있으므로 핸드오프는 대화형입니다. 에이전트가 전달하지 않는 경우 대화를 계속하려면 사용자 입력이 필요합니다. 이 요구 사항을 무시하려면 자치 모드 를 참조하세요. 다른 오케스트레이션에서는 에이전트가 응답한 후 컨트롤이 오케스트레이터 또는 다음 에이전트로 이동합니다.
에이전트가 핸드오프 워크플로에서 전달을 하지 않기로 결정하면(특별한 도구 호출에 의해 핸드오프가 트리거됨), 워크플로는 에이전트의 최신 메시지를 포함하는 WorkflowEvent 페이로드와 type="request_info" 을 HandoffAgentUserRequest 함께 내보냅니다. 워크플로를 계속하려면 사용자가 이 요청에 응답해야 합니다.
from agent_framework import WorkflowEvent
from agent_framework.orchestrations import HandoffAgentUserRequest
# Start workflow with initial user message
events = [event async for event in workflow.run_stream("I need help with my order")]
# Process events and collect pending input requests
pending_requests = []
for event in events:
if event.type == "request_info" and isinstance(event.data, HandoffAgentUserRequest):
pending_requests.append(event)
request_data = event.data
print(f"Agent {event.executor_id} is awaiting your input")
# The request contains the most recent messages generated by the
# agent requesting input
for msg in request_data.agent_response.messages[-3:]:
print(f"{msg.author_name}: {msg.text}")
# Interactive loop: respond to requests
while pending_requests:
user_input = input("You: ")
# Send responses to all pending requests
responses = {req.request_id: HandoffAgentUserRequest.create_response(user_input) for req in pending_requests}
# You can also send a `HandoffAgentUserRequest.terminate()` to end the workflow early
events = [event async for event in workflow.run(responses=responses)]
# Process new events
pending_requests = []
for event in events:
# Check for new input requests
자율 모드
핸드오프 오케스트레이션은 에이전트가 인계하지 않기로 결정할 때 사용자 입력이 필요한 대화형 시나리오를 위해 설계되었습니다. 그러나 실험적 기능으로 "자율 모드"를 사용하도록 설정하여 사람의 개입 없이 워크플로를 계속할 수 있습니다. 이 모드에서 에이전트가 전달하지 않기로 결정하면, 워크플로는 자동으로 기본 응답(예:User did not respond. Continue assisting autonomously.)을 에이전트에게 보내어 대화를 계속하도록 합니다.
팁 (조언)
핸드오프 오케스트레이션이 본질적으로 대화형인 이유는 무엇인가요? 에이전트가 응답한 후 수행할 경로가 하나뿐인 다른 오케스트레이션과 달리(예: 오케스트레이터 또는 다음 에이전트로 돌아가기) 핸드오프 오케스트레이션에서 에이전트는 다른 에이전트에 전달하거나 사용자 자체를 계속 지원할 수 있습니다. 또한 도구 호출을 통해 핸드오프가 수행되므로 에이전트가 핸드오프 도구를 호출하지 않고 대신 응답을 생성하는 경우 워크플로는 다음에 수행할 작업을 알 수 없고 추가 입력을 위해 사용자에게 다시 위임합니다. 에이전트가 의미 있는 응답을 생성할 수 없으므로 핸드오프 도구를 호출하도록 요구하여 에이전트가 항상 전달하도록 강제할 수도 없습니다.
자율 모드는 with_autonomous_mode()에서 HandoffBuilder을 호출하여 활성화됩니다. 이렇게 하면 기본 메시지를 사용하여 입력 요청에 자동으로 응답하도록 워크플로가 구성되므로 에이전트가 사용자 입력을 기다리지 않고 계속할 수 있습니다.
workflow = (
HandoffBuilder(
name="autonomous_customer_support",
participants=[triage_agent, refund_agent, order_agent, return_agent],
)
.with_start_agent(triage_agent)
.with_autonomous_mode()
.build()
)
에이전트 인스턴스 목록을 전달하여 에이전트 하위 집합에서만 자율 모드를 사용하도록 설정할 수도 있습니다 with_autonomous_mode().
workflow = (
HandoffBuilder(
name="partially_autonomous_support",
participants=[triage_agent, refund_agent, order_agent, return_agent],
)
.with_start_agent(triage_agent)
.with_autonomous_mode(agents=[triage_agent]) # Only triage_agent runs autonomously
.build()
)
기본 응답 메시지를 사용자 지정할 수 있습니다.
workflow = (
HandoffBuilder(
name="custom_autonomous_support",
participants=[triage_agent, refund_agent, order_agent, return_agent],
)
.with_start_agent(triage_agent)
.with_autonomous_mode(
agents=[triage_agent],
prompts={triage_agent.name: "Continue with your best judgment as the user is unavailable."},
)
.build()
)
사용자 입력을 요구하기 전에 에이전트가 자율적으로 실행할 수 있는 턴 수를 사용자 지정할 수 있습니다. 이렇게 하면 사용자 개입 없이 워크플로가 무기한 실행되지 않도록 방지할 수 있습니다.
workflow = (
HandoffBuilder(
name="limited_autonomous_support",
participants=[triage_agent, refund_agent, order_agent, return_agent],
)
.with_start_agent(triage_agent)
.with_autonomous_mode(
agents=[triage_agent],
turn_limits={triage_agent.name: 3}, # Max 3 autonomous turns
)
.build()
)
고급: 핸드오프 워크플로의 도구 승인
핸드오프 워크플로에는 실행 전에 사람의 승인이 필요한 도구가 있는 에이전트가 포함될 수 있습니다. 이는 환불 처리, 구매 또는 돌이킬 수 없는 작업 실행과 같은 중요한 작업에 유용합니다.
승인이 필요한 도구 정의
from typing import Annotated
from agent_framework import tool
@tool(approval_mode="always_require")
def process_refund(order_number: Annotated[str, "Order number to process refund for"]) -> str:
"""Simulated function to process a refund for a given order number."""
return f"Refund processed successfully for order {order_number}."
승인 필요 도구를 사용하여 에이전트 만들기
from agent_framework import Agent
from agent_framework.azure import AzureOpenAIChatClient
from azure.identity import AzureCliCredential
client = AzureOpenAIChatClient(credential=AzureCliCredential())
triage_agent = chat_client.as_agent(
instructions=(
"You are frontline support triage. Route customer issues to the appropriate specialist agents "
"based on the problem described."
),
description="Triage agent that handles general inquiries.",
name="triage_agent",
)
refund_agent = chat_client.as_agent(
instructions="You process refund requests.",
description="Agent that handles refund requests.",
name="refund_agent",
tools=[process_refund],
)
order_agent = chat_client.as_agent(
instructions="You handle order and shipping inquiries.",
description="Agent that handles order tracking and shipping issues.",
name="order_agent",
tools=[check_order_status],
)
사용자 입력 및 도구 승인 요청 모두 처리
from agent_framework import (
FunctionApprovalRequestContent,
WorkflowEvent,
)
from agent_framework.orchestrations import HandoffBuilder, HandoffAgentUserRequest
workflow = (
HandoffBuilder(
name="support_with_approvals",
participants=[triage_agent, refund_agent, order_agent],
)
.with_start_agent(triage_agent)
.build()
)
pending_requests: list[WorkflowEvent] = []
# Start workflow
async for event in workflow.run_stream("My order 12345 arrived damaged. I need a refund."):
if event.type == "request_info":
pending_requests.append(event)
# Process pending requests - could be user input OR tool approval
while pending_requests:
responses: dict[str, object] = {}
for request in pending_requests:
if isinstance(request.data, HandoffAgentUserRequest):
# Agent needs user input
print(f"Agent {request.executor_id} asks:")
for msg in request.data.agent_response.messages[-2:]:
print(f" {msg.author_name}: {msg.text}")
user_input = input("You: ")
responses[request.request_id] = HandoffAgentUserRequest.create_response(user_input)
elif isinstance(request.data, FunctionApprovalRequestContent):
# Agent wants to call a tool that requires approval
func_call = request.data.function_call
args = func_call.parse_arguments() or {}
print(f"\nTool approval requested: {func_call.name}")
print(f"Arguments: {args}")
approval = input("Approve? (y/n): ").strip().lower() == "y"
responses[request.request_id] = request.data.create_response(approved=approval)
# Send all responses and collect new requests
pending_requests = []
async for event in workflow.run(responses=responses):
if event.type == "request_info":
pending_requests.append(event)
elif event.type == "output":
print("\nWorkflow completed!")
지속성 워크플로를 위한 체크포인트 처리
장시간 실행되는 워크플로에서 도구 승인이 몇 시간 또는 며칠 후에 발생할 수 있는 경우, 체크포인트를 사용하세요.
from agent_framework import FileCheckpointStorage
storage = FileCheckpointStorage(storage_path="./checkpoints")
workflow = (
HandoffBuilder(
name="durable_support",
participants=[triage_agent, refund_agent, order_agent],
checkpoint_storage=storage,
)
.with_start_agent(triage_agent)
.build()
)
# Initial run - workflow pauses when approval is needed
pending_requests = []
async for event in workflow.run_stream("I need a refund for order 12345"):
if event.type == "request_info":
pending_requests.append(event)
# Process can exit here - checkpoint is saved automatically
# Later: Resume from checkpoint and provide approval
checkpoints = await storage.list_checkpoints()
latest = sorted(checkpoints, key=lambda c: c.timestamp, reverse=True)[0]
# Step 1: Restore checkpoint to reload pending requests
restored_requests = []
async for event in workflow.run_stream(checkpoint_id=latest.checkpoint_id):
if event.type == "request_info":
restored_requests.append(event)
# Step 2: Send responses
responses = {}
for req in restored_requests:
if isinstance(req.data, FunctionApprovalRequestContent):
responses[req.request_id] = req.data.create_response(approved=True)
elif isinstance(req.data, HandoffAgentUserRequest):
responses[req.request_id] = HandoffAgentUserRequest.create_response("Yes, please process the refund.")
async for event in workflow.run(responses=responses):
if event.type == "output":
print("Refund workflow completed!")
샘플 상호 작용
User: I need help with my order
triage_agent: I'd be happy to help you with your order. Could you please provide more details about the issue?
User: My order 1234 arrived damaged
triage_agent: I'm sorry to hear that your order arrived damaged. I will connect you with a specialist.
support_agent: I'm sorry about the damaged order. To assist you better, could you please:
- Describe the damage
- Would you prefer a replacement or refund?
User: I'd like a refund
triage_agent: I'll connect you with the refund specialist.
refund_agent: I'll process your refund for order 1234. Here's what will happen next:
1. Verification of the damaged items
2. Refund request submission
3. Return instructions if needed
4. Refund processing within 5-10 business days
Could you provide photos of the damage to expedite the process?
컨텍스트 동기화
에이전트 프레임워크의 에이전트는 에이전트 세션(AgentSession)을 사용하여 컨텍스트를 관리합니다. 핸드오프 오케스트레이션에서 에이전트는 동일한 세션 인스턴스를 공유 하지 않으며 참가자는 컨텍스트 일관성을 보장할 책임이 있습니다. 이를 위해 참가자는 응답을 생성할 때마다 워크플로의 다른 모든 사용자에게 수신된 응답 또는 사용자 입력을 브로드캐스트하여 모든 참가자가 다음 턴에 대한 최신 컨텍스트를 갖도록 합니다.

비고
핸드오프 도구 호출을 비롯한 도구 관련 콘텐츠는 다른 에이전트에 브로드캐스트되지 않습니다. 사용자 및 에이전트 메시지만 모든 참가자에 걸쳐 동기화됩니다.
팁 (조언)
에이전트 유형에 따라 추상화 구현이 다를 수 있으므로 에이전트 는 동일한 세션 인스턴스를 AgentSession 공유하지 않습니다. 동일한 세션 인스턴스를 공유하면 각 에이전트가 컨텍스트를 처리하고 유지 관리하는 방식이 불일치할 수 있습니다.
응답을 브로드캐스트한 후 참가자는 대화를 다른 에이전트에게 전달해야 하는지 여부를 확인합니다. 그렇다면 선택한 에이전트에 대화를 인수하라는 요청을 보냅니다. 그렇지 않으면 사용자 입력을 요청하거나 워크플로 구성에 따라 자율적으로 계속됩니다.
주요 개념
- 동적 라우팅: 에이전트는 컨텍스트에 따라 다음 상호 작용을 처리해야 하는 에이전트를 결정할 수 있습니다.
- AgentWorkflowBuilder.StartHandoffWith(): 워크플로를 시작하는 초기 에이전트를 정의합니다.
- WithHandoff() 및 WithHandoffs(): 특정 에이전트 간에 핸드오프 규칙을 구성합니다.
- 컨텍스트 보존: 전체 대화 기록은 모든 핸드오프에서 유지 관리됩니다.
- 다중 턴 지원: 원활한 에이전트 전환으로 진행 중인 대화 지원
- 전문 지식: 각 에이전트는 핸드오프를 통해 공동 작업하는 동안 도메인에 중점을 둡니다.
- 동적 라우팅: 에이전트는 컨텍스트에 따라 다음 상호 작용을 처리해야 하는 에이전트를 결정할 수 있습니다.
- HandoffBuilder: 자동 핸드오프 도구 등록을 사용하여 워크플로 만들기
- with_start_agent(): 먼저 사용자 입력을 수신하는 에이전트를 정의합니다.
- add_handoff(): 에이전트 간의 특정 핸드오프 관계 구성
- 컨텍스트 보존: 전체 대화 기록은 모든 핸드오프에서 유지 관리됩니다.
- 요청/응답 주기: 워크플로가 사용자 입력을 요청하고, 응답을 처리하며, 종료 조건이 충족될 때까지 계속됩니다.
-
도구 승인: 사용자 승인이 필요한 중요한 작업에 사용
@tool(approval_mode="always_require") -
FunctionApprovalRequestContent: 에이전트가 승인이 필요한 도구를 호출할 때 내보냅니다. 응답하는 데 사용
create_response(approved=...) -
체크포인팅: 프로세스가 재시작되는 동안 일시 중지하고 다시 시작할 수 있는 내구성 있는 워크플로에
with_checkpointing()를 사용 - 전문 지식: 각 에이전트는 핸드오프를 통해 공동 작업하는 동안 도메인에 중점을 둡니다.