패키지된 Windows 앱에서 기존 사용자 이름 및 암호 인증 시스템의 대안으로 Windows Hello를 사용하는 방법에 대한 전체 연습의 두 번째 부분입니다. 이 문서는 1부 Windows Hello 로그인 앱에서 끝난 지점부터 시작하여, Windows Hello를 기존 애플리케이션에 통합하는 방법을 보여주는 기능 확장을 설명합니다.
이 프로젝트를 빌드하려면 C#과 XAML에 대한 경험이 필요합니다. Windows 10 또는 Windows 11 컴퓨터에서도 Visual Studio 2022를 사용해야 합니다. 개발 환경 설정에 대한 전체 지침은 Windows 앱 개발 시작을 참조하세요.
연습 1: 서버 쪽 논리
이 연습에서는 첫 번째 랩에서 빌드된 Windows Hello 애플리케이션으로 시작하고 로컬 모의 서버 및 데이터베이스를 만듭니다. 이 실습 랩은 Windows Hello를 기존 시스템에 통합하는 방법을 학습하도록 설계되었습니다. 모의 서버와 모의 데이터베이스를 사용하면 관련 없는 설정이 많이 제거됩니다. 사용자 고유의 애플리케이션에서는 모의 개체를 실제 서비스 및 데이터베이스로 바꿔야 합니다.
시작하려면 첫 번째 Windows Hello Hands On Lab에서 WindowsHelloLogin 솔루션을 엽니다.
먼저 모의 서버 및 모의 데이터베이스를 구현합니다. "AuthService"라는 새 폴더를 만듭니다. 솔루션 탐색기에서 WindowsHelloLogin 프로젝트를 마우스 오른쪽 단추로 클릭하고새 폴더>를 선택합니다.
모의 데이터베이스에 저장할 데이터에 대한 모델 역할을 하는 UserAccount 및 WindowsHelloDevices 클래스를 만듭니다. UserAccount는 기존 인증 서버에서 구현된 사용자 모델과 유사합니다. AuthService 폴더를 마우스 오른쪽 단추로 클릭하고 "UserAccount"라는 새 클래스를 추가합니다.
클래스 범위를 public으로 변경하고 UserAccount 클래스에 대해 다음 public 속성을 추가합니다.
System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations네임스페이스에 using 문을 추가해야 합니다.using System; using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations; namespace WindowsHelloLogin.AuthService { public class UserAccount { [Key, Required] public Guid UserId { get; set; } [Required] public string Username { get; set; } public string Password { get; set; } // public List<WindowsHelloDevice> WindowsHelloDevices = new(); } }WindowsHelloDevices의 주석 처리된 목록을 발견했을 수 있습니다. 현재 구현에서 기존 사용자 모델을 수정해야 합니다. WindowsHelloDevices 목록에는 deviceID, Windows Hello에서 만든 공개 키 및 KeyCredentialAttestationResult가 포함됩니다. 이 연습에서는 TPM(신뢰할 수 있는 플랫폼 모듈) 칩이 있는 디바이스에서 Windows Hello에서만 제공되므로 keyAttestationResult 를 구현해야 합니다. KeyCredentialAttestationResult는 여러 속성의 조합으로, 이를 데이터베이스에 저장하고 로드하기 위해서는 분할해야 합니다.
AuthService 폴더에 "WindowsHelloDevice.cs"이라는 새 클래스를 만듭니다. 위에서 설명한 대로 Windows Hello 디바이스의 모델입니다. 클래스 범위를 public으로 변경하고 다음 속성을 추가합니다.
using System; namespace WindowsHelloLogin.AuthService { public class WindowsHelloDevice { // These are the new variables that will need to be added to the existing UserAccount in the Database // The DeviceName is used to support multiple devices for the one user. // This way the correct public key is easier to find as a new public key is made for each device. // The KeyAttestationResult is only used if the User device has a TPM (Trusted Platform Module) chip, // in most cases it will not. So will be left out for this hands on lab. public Guid DeviceId { get; set; } public byte[] PublicKey { get; set; } // public KeyCredentialAttestationResult KeyAttestationResult { get; set; } } }UserAccount.cs로 돌아가서 Windows Hello 디바이스 목록의 주석을 해제하세요.
using System.Collections.Generic; namespace WindowsHelloLogin.AuthService { public class UserAccount { [Key, Required] public Guid UserId { get; set; } [Required] public string Username { get; set; } public string Password { get; set; } public List<WindowsHelloDevice> WindowsHelloDevices = new(); } }UserAccount 및 WindowsHelloDevice에 대한 모델을 만들면 사용자 계정 목록을 로컬로 저장하고 로드할 모의 데이터베이스이므로 모의 데이터베이스 역할을 하는 또 다른 새 클래스를 AuthService 폴더에 만들어야 합니다. 실제 세계에서는 이것이 데이터베이스 구현이 될 것입니다. "MockStore.cs"이라는 AuthService 폴더에 새 클래스를 만듭니다. 클래스 범위를 public으로 변경합니다.
모의 저장소는 사용자 계정 목록을 로컬로 저장하고 로드하므로 XmlSerializer를 사용하여 해당 목록을 저장하고 로드하는 논리를 구현할 수 있습니다. 또한 파일 이름을 기억하고 위치를 저장해야 합니다. MockStore.cs에 다음을 구현하세요.
using System.Collections.Generic; using System; using System.IO; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Xml.Serialization; using Windows.Storage; namespace WindowsHelloLogin.AuthService { public class MockStore { private const string USER_ACCOUNT_LIST_FILE_NAME = "userAccountsList.txt"; // This cannot be a const because the LocalFolder is accessed at runtime private string _userAccountListPath = Path.Combine( ApplicationData.Current.LocalFolder.Path, USER_ACCOUNT_LIST_FILE_NAME); private List<UserAccount> _mockDatabaseUserAccountsList; #region Save and Load Helpers /// <summary> /// Create and save a useraccount list file. (Replacing the old one) /// </summary> private async Task SaveAccountListAsync() { string accountsXml = SerializeAccountListToXml(); if (File.Exists(_userAccountListPath)) { StorageFile accountsFile = await StorageFile.GetFileFromPathAsync(_userAccountListPath); await FileIO.WriteTextAsync(accountsFile, accountsXml); } else { StorageFile accountsFile = await ApplicationData.Current.LocalFolder.CreateFileAsync(USER_ACCOUNT_LIST_FILE_NAME); await FileIO.WriteTextAsync(accountsFile, accountsXml); } } /// <summary> /// Gets the useraccount list file and deserializes it from XML to a list of useraccount objects. /// </summary> /// <returns>List of useraccount objects</returns> private async Task LoadAccountListAsync() { if (File.Exists(_userAccountListPath)) { StorageFile accountsFile = await StorageFile.GetFileFromPathAsync(_userAccountListPath); string accountsXml = await FileIO.ReadTextAsync(accountsFile); DeserializeXmlToAccountList(accountsXml); } // If the UserAccountList does not contain the sampleUser Initialize the sample users // This is only needed as it in a Hand on Lab to demonstrate a user being migrated. // In the real world, user accounts would just be in a database. if (!_mockDatabaseUserAccountsList.Any(f => f.Username.Equals("sampleUsername"))) { //If the list is empty, call InitializeSampleAccounts and return the list //await InitializeSampleUserAccountsAsync(); } } /// <summary> /// Uses the local list of accounts and returns an XML formatted string representing the list /// </summary> /// <returns>XML formatted list of accounts</returns> private string SerializeAccountListToXml() { var xmlizer = new XmlSerializer(typeof(List<UserAccount>)); var writer = new StringWriter(); xmlizer.Serialize(writer, _mockDatabaseUserAccountsList); return writer.ToString(); } /// <summary> /// Takes an XML formatted string representing a list of accounts and returns a list object of accounts /// </summary> /// <param name="listAsXml">XML formatted list of accounts</param> /// <returns>List object of accounts</returns> private List<UserAccount> DeserializeXmlToAccountList(string listAsXml) { var xmlizer = new XmlSerializer(typeof(List<UserAccount>)); TextReader textreader = new StreamReader(new MemoryStream(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(listAsXml))); return _mockDatabaseUserAccountsList = (xmlizer.Deserialize(textreader)) as List<UserAccount>; } #endregion } }LoadAccountListAsync 메서드에서 InitializeSampleUserAccountsAsync 메서드가 주석 처리된 것을 확인할 수 있습니다. MockStore.cs 이 메서드를 만들어야 합니다. 이 메서드는 로그인이 수행될 수 있도록 사용자 계정 목록을 채웁니다. 실제 환경에서는 사용자 데이터베이스가 이미 채워져 있습니다. 이 단계에서는 사용자 목록을 초기화하고 LoadAccountListAsync를 호출하는 생성자도 만듭니다.
namespace WindowsHelloLogin.AuthService { public class MockStore { private const string USER_ACCOUNT_LIST_FILE_NAME = "userAccountsList.txt"; // This cannot be a const because the LocalFolder is accessed at runtime private string _userAccountListPath = Path.Combine( ApplicationData.Current.LocalFolder.Path, USER_ACCOUNT_LIST_FILE_NAME); private List<UserAccount> _mockDatabaseUserAccountsList; public MockStore() { _mockDatabaseUserAccountsList = new List<UserAccount>(); _ = LoadAccountListAsync(); } private async Task InitializeSampleUserAccountsAsync() { // Create a sample Traditional User Account that only has a Username and Password // This will be used initially to demonstrate how to migrate to use Windows Hello var sampleUserAccount = new UserAccount() { UserId = Guid.NewGuid(), Username = "sampleUsername", Password = "samplePassword", }; // Add the sampleUserAccount to the _mockDatabase _mockDatabaseUserAccountsList.Add(sampleUserAccount); await SaveAccountListAsync(); } } }이제 InitializeSampleUserAccountsAsync 메서드가 존재하므로, LoadAccountListAsync 메서드에서 메서드 호출을 주석에서 해제하세요.
private async Task LoadAccountListAsync() { if (File.Exists(_userAccountListPath)) { StorageFile accountsFile = await StorageFile.GetFileFromPathAsync(_userAccountListPath); string accountsXml = await FileIO.ReadTextAsync(accountsFile); DeserializeXmlToAccountList(accountsXml); } // If the UserAccountList does not contain the sampleUser Initialize the sample users // This is only needed as it in a Hand on Lab to demonstrate a user migrating // In the real world user accounts would just be in a database if (!_mockDatabaseUserAccountsList.Any(f = > f.Username.Equals("sampleUsername"))) { //If the list is empty InitializeSampleUserAccountsAsync and return the list await InitializeSampleUserAccountsAsync(); } }이제 모의 저장소의 사용자 계정 목록을 저장하고 로드할 수 있습니다. 애플리케이션의 다른 부분에서는 이 목록에 액세스할 수 있어야 하므로 이 데이터를 검색하는 몇 가지 방법이 있어야 합니다. InitializeSampleUserAccountsAsync 메서드 아래에 다음 메서드를 추가하여 데이터를 가져옵니다. 사용자 ID, 단일 사용자, 특정 Windows Hello 디바이스에 대한 사용자 목록을 가져오고 특정 디바이스에서 사용자의 공개 키를 가져올 수 있습니다.
public Guid GetUserId(string username) { if (_mockDatabaseUserAccountsList.Any()) { UserAccount account = _mockDatabaseUserAccountsList.FirstOrDefault(f => f.Username.Equals(username)); if (account != null) { return account.UserId; } } return Guid.Empty; } public UserAccount GetUserAccount(Guid userId) { return _mockDatabaseUserAccountsList.FirstOrDefault(f => f.UserId.Equals(userId)); } public List<UserAccount> GetUserAccountsForDevice(Guid deviceId) { var usersForDevice = new List<UserAccount>(); foreach (UserAccount account in _mockDatabaseUserAccountsList) { if (account.WindowsHelloDevices.Any(f => f.DeviceId.Equals(deviceId))) { usersForDevice.Add(account); } } return usersForDevice; } public byte[] GetPublicKey(Guid userId, Guid deviceId) { UserAccount account = _mockDatabaseUserAccountsList.FirstOrDefault(f => f.UserId.Equals(userId)); if (account != null) { if (account.WindowsHelloDevices.Any()) { return account.WindowsHelloDevices.FirstOrDefault(p => p.DeviceId.Equals(deviceId)).PublicKey; } } return null; }다음 구현 방법은 계정을 추가하고, 계정을 제거하고, 디바이스를 제거하는 간단한 작업을 처리합니다. Windows Hello는 디바이스별이므로 디바이스를 제거해야 합니다. 로그인하는 각 디바이스에 대해 Windows Hello에서 새 공개 및 프라이빗 키 쌍을 만듭니다. 로그인하는 각 디바이스에 대해 다른 암호를 갖는 것과 같으며, 유일한 것은 모든 암호를 기억할 필요가 없다는 것입니다. 서버에서 수행합니다. MockStore.cs 다음 메서드를 추가합니다.
public async Task<UserAccount> AddAccountAsync(string username) { UserAccount newAccount = null; try { newAccount = new UserAccount() { UserId = Guid.NewGuid(), Username = username, }; _mockDatabaseUserAccountsList.Add(newAccount); await SaveAccountListAsync(); } catch (Exception) { throw; } return newAccount; } public async Task<bool> RemoveAccountAsync(Guid userId) { UserAccount userAccount = GetUserAccount(userId); if (userAccount != null) { _mockDatabaseUserAccountsList.Remove(userAccount); await SaveAccountListAsync(); return true; } return false; } public async Task<bool> RemoveDeviceAsync(Guid userId, Guid deviceId) { UserAccount userAccount = GetUserAccount(userId); WindowsHelloDevice deviceToRemove = null; if (userAccount != null) { foreach (WindowsHelloDevice device in userAccount.WindowsHelloDevices) { if (device.DeviceId.Equals(deviceId)) { deviceToRemove = device; break; } } } if (deviceToRemove != null) { //Remove the WindowsHelloDevice userAccount.WindowsHelloDevices.Remove(deviceToRemove); await SaveAccountListAsync(); } return true; }MockStore 클래스에서 Windows Hello 관련 정보를 기존 UserAccount에 추가하는 메서드를 추가합니다. 이 메서드는 "WindowsHelloUpdateDetailsAsync"라고 하며 매개 변수를 사용하여 사용자 및 Windows Hello 세부 정보를 식별합니다. KeyAttestationResult는 WindowsHelloDevice를 만들 때 주석 처리되어 비활성화되었습니다. 실제 애플리케이션에서는 반드시 필요합니다.
using System.Threading.Tasks; using Windows.Security.Credentials; public async Task WindowsHelloUpdateDetailsAsync(Guid userId, Guid deviceId, byte[] publicKey, KeyCredentialAttestationResult keyAttestationResult) { UserAccount existingUserAccount = GetUserAccount(userId); if (existingUserAccount != null) { if (!existingUserAccount.WindowsHelloDevices.Any(f => f.DeviceId.Equals(deviceId))) { existingUserAccount.WindowsHelloDevices.Add(new WindowsHelloDevice() { DeviceId = deviceId, PublicKey = publicKey, // KeyAttestationResult = keyAttestationResult }); } } await SaveAccountListAsync(); }이제 MockStore 클래스는 프라이빗으로 간주되어야 하는 데이터베이스를 나타내기 때문에 완료되었습니다. MockStore에 액세스하려면 데이터베이스 데이터를 조작하기 위해 AuthService 클래스가 필요합니다. AuthService 폴더에서 "AuthService.cs"이라는 새 클래스를 만듭니다. 클래스 범위를 public으로 변경하고 단일 인스턴스 패턴을 추가하여 하나의 인스턴스만 만들어지도록 합니다.
namespace WindowsHelloLogin.AuthService { public class AuthService { // Singleton instance of the AuthService // The AuthService is a mock of what a real world server and service implementation would be private static AuthService _instance; public static AuthService Instance { get { if (null == _instance) { _instance = new AuthService(); } return _instance; } } private AuthService() { } } }AuthService 클래스는 MockStore 클래스의 인스턴스를 만들고 MockStore 개체의 속성에 대한 액세스를 제공해야 합니다.
namespace WindowsHelloLogin.AuthService { public class AuthService { //Singleton instance of the AuthService //The AuthService is a mock of what a real world server and database implementation would be private static AuthService _instance; public static AuthService Instance { get { if (null == _instance) { _instance = new AuthService(); } return _instance; } } private AuthService() { } private MockStore _mockStore = new(); public Guid GetUserId(string username) { return _mockStore.GetUserId(username); } public UserAccount GetUserAccount(Guid userId) { return _mockStore.GetUserAccount(userId); } public List<UserAccount> GetUserAccountsForDevice(Guid deviceId) { return _mockStore.GetUserAccountsForDevice(deviceId); } } }MockStore 개체의 Windows Hello 세부 정보 메서드 추가, 제거 및 업데이트에 액세스하려면 AuthService 클래스의 메서드가 필요합니다. AuthService 클래스 정의의 끝에 다음 메서드를 추가합니다.
using System.Threading.Tasks; using Windows.Security.Credentials; public async Task RegisterAsync(string username) { await _mockStore.AddAccountAsync(username); } public async Task<bool> WindowsHelloRemoveUserAsync(Guid userId) { return await _mockStore.RemoveAccountAsync(userId); } public async Task<bool> WindowsHelloRemoveDeviceAsync(Guid userId, Guid deviceId) { return await _mockStore.RemoveDeviceAsync(userId, deviceId); } public async Task WindowsHelloUpdateDetailsAsync(Guid userId, Guid deviceId, byte[] publicKey, KeyCredentialAttestationResult keyAttestationResult) { await _mockStore.WindowsHelloUpdateDetailsAsync(userId, deviceId, publicKey, keyAttestationResult); }AuthService 클래스는 자격 증명의 유효성을 검사하는 메서드를 제공해야 합니다. 이 메서드는 사용자 이름과 암호를 사용하고 계정이 있고 암호가 유효한지 확인합니다. 기존 시스템에는 사용자에게 권한이 부여되었는지 확인하는 이와 동일한 메서드가 있습니다. 다음 ValidateCredentials 메서드를 AuthService.cs 파일에 추가합니다.
public bool ValidateCredentials(string username, string password) { if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(username) && !string.IsNullOrEmpty(password)) { // This would be used for existing accounts migrating to use Windows Hello Guid userId = GetUserId(username); if (userId != Guid.Empty) { UserAccount account = GetUserAccount(userId); if (account != null) { if (string.Equals(password, account.Password)) { return true; } } } } return false; }AuthService 클래스에는 사용자가 자신이 주장하는 사용자인지 여부를 확인하기 위해 클라이언트에 챌린지를 반환하는 요청 챌린지 메서드가 필요합니다. 그런 다음, 클라이언트에서 서명된 챌린지를 다시 받으려면 AuthService 클래스에서 다른 메서드가 필요합니다. 이 실습에서는 서명된 챌린지가 완료되었는지를 판단하는 방법이 완전히 구현되지 않았습니다. 기존 인증 시스템에 대한 Windows Hello의 모든 구현은 약간 다릅니다. 서버에 저장된 공개 키는 클라이언트가 서버에 반환한 결과와 일치해야 합니다. 이러한 두 가지 메서드를 AuthService.cs 추가합니다.
using Windows.Security.Cryptography; using Windows.Storage.Streams; public IBuffer WindowsHelloRequestChallenge() { return CryptographicBuffer.ConvertStringToBinary("ServerChallenge", BinaryStringEncoding.Utf8); } public bool SendServerSignedChallenge(Guid userId, Guid deviceId, byte[] signedChallenge) { // Depending on your company polices and procedures this step will be different // It is at this point you will need to validate the signedChallenge that is sent back from the client. // Validation is used to ensure the correct user is trying to access this account. // The validation process will use the signedChallenge and the stored PublicKey // for the username and the specific device signin is called from. // Based on the validation result you will return a bool value to allow access to continue or to block the account. // For this sample validation will not happen as a best practice solution does not apply and will need to // be configured for each company. // Simply just return true. // You could get the User's Public Key with something similar to the following: byte[] userPublicKey = _mockStore.GetPublicKey(userId, deviceId); return true; }
연습 2: 클라이언트 쪽 논리
이 연습에서는 AuthService 클래스를 사용하도록 첫 번째 랩에서 클라이언트 쪽 보기 및 도우미 클래스를 변경합니다. 실제 환경에서 AuthService 는 인증 서버가 되며 Web API를 사용하여 서버에서 데이터를 보내고 받아야 합니다. 이 실습의 경우 클라이언트와 서버는 모두 작업을 단순하게 유지하기 위해 로컬입니다. Windows Hello API를 사용하는 방법을 알아보기 위한 것입니다.
MainPage.xaml.cs AuthService 클래스가 계정 목록을 로드하는 MockStore의 인스턴스를 만들 때 로드된 메서드에서 AccountHelper.LoadAccountListAsync 메서드 호출을 제거할 수 있습니다. 이제 메서드가
Loaded아래 코드 조각과 같이 표시됩니다. 대기 중인 항목이 없기 때문에 비동기 메서드 정의가 제거됩니다.private void MainPage_Loaded(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) { Frame.Navigate(typeof(UserSelection)); }암호를 입력하도록 로그인 페이지 인터페이스를 업데이트합니다. 이 실습 랩에서는 Windows Hello를 사용하도록 기존 시스템을 마이그레이션할 수 있고 기존 계정에는 사용자 이름과 암호가 있는 방법을 보여 줍니다. 또한 기본 암호를 포함하도록 XAML 아래쪽의 설명을 업데이트합니다. Login.xaml에서 다음 XAML을 업데이트합니다.
<Grid> <StackPanel> <TextBlock Text="Login" FontSize="36" Margin="4" TextAlignment="Center"/> <TextBlock x:Name="ErrorMessage" Text="" FontSize="20" Margin="4" Foreground="Red" TextAlignment="Center"/> <TextBlock Text="Enter your credentials below" Margin="0,0,0,20" TextWrapping="Wrap" Width="300" TextAlignment="Center" VerticalAlignment="Center" FontSize="16"/> <StackPanel Orientation="Horizontal" HorizontalAlignment="Center"> <!-- Username Input --> <TextBlock x:Name="UserNameTextBlock" Text="Username: " FontSize="20" Margin="4" Width="100"/> <TextBox x:Name="UsernameTextBox" PlaceholderText="sampleUsername" Width="200" Margin="4"/> </StackPanel> <StackPanel Orientation="Horizontal" HorizontalAlignment="Center"> <!-- Password Input --> <TextBlock x:Name="PasswordTextBlock" Text="Password: " FontSize="20" Margin="4" Width="100"/> <PasswordBox x:Name="PasswordBox" PlaceholderText="samplePassword" Width="200" Margin="4"/> </StackPanel> <Button x:Name="LoginButton" Content="Login" Background="DodgerBlue" Foreground="White" Click="LoginButton_Click" Width="80" HorizontalAlignment="Center" Margin="0,20"/> <TextBlock Text="Don't have an account?" TextAlignment="Center" VerticalAlignment="Center" FontSize="16"/> <TextBlock x:Name="RegisterButtonTextBlock" Text="Register now" PointerPressed="RegisterButtonTextBlock_OnPointerPressed" Foreground="DodgerBlue" TextAlignment="Center" VerticalAlignment="Center" FontSize="16"/> <Border x:Name="WindowsHelloStatus" Background="#22B14C" Margin="0,20" Height="100"> <TextBlock x:Name="WindowsHelloStatusText" Text="Windows Hello is ready to use!" Margin="4" TextAlignment="Center" VerticalAlignment="Center" FontSize="20"/> </Border> <TextBlock x:Name="LoginExplanation" FontSize="24" TextAlignment="Center" TextWrapping="Wrap" Text="Please Note: To demonstrate a login, validation will only occur using the default username 'sampleUsername' and default password 'samplePassword'"/> </StackPanel> </Grid>로그인 클래스의 코드 숨김 파일에서 클래스 상단에 위치한
Account프라이빗 변수를UserAccount로 변경해야 합니다. 형식을OnNavigateTo.로 캐스팅하도록UserAccount이벤트를 변경합니다. 다음 "using" 문도 필요합니다.using WindowsHelloLogin.AuthService; namespace WindowsHelloLogin.Views { public sealed partial class Login : Page { private UserAccount _account; private bool _isExistingAccount; public Login() { this.InitializeComponent(); } protected override async void OnNavigatedTo(NavigationEventArgs e) { //Check Windows Hello is setup and available on this machine if (await WindowsHelloHelper.WindowsHelloAvailableCheckAsync()) { if (e.Parameter != null) { _isExistingAccount = true; //Set the account to the existing account being passed in _account = (UserAccount)e.Parameter; UsernameTextBox.Text = _account.Username; await SignInWindowsHelloAsync(); } } } private async void LoginButton_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) { ErrorMessage.Text = ""; await SignInWindowsHelloAsync(); } } }로그인 페이지에서 이전
UserAccount개체 대신 개체를 사용Account하므로 일부 메서드의 매개 변수 형식으로 사용UserAccount하려면 WindowsHelloHelper.cs 업데이트해야 합니다. CreateWindowsHelloKeyAsync, RemoveWindowsHelloAccountAsync 및 GetWindowsHelloAuthenticationMessageAsync 메서드에 대해 다음 매개 변수를 변경해야 합니다. 클래스UserAccount에GuidUserId에 대한 항목이 있으므로 더 정확하게 하기 위해 더 많은 위치에서 ID를 사용하기 시작합니다.public static async Task<bool> CreateWindowsHelloKeyAsync(Guid userId, string username) { KeyCredentialRetrievalResult keyCreationResult = await KeyCredentialManager.RequestCreateAsync(username, KeyCredentialCreationOption.ReplaceExisting); return true; } public static async Task RemoveWindowsHelloAccountAsync(UserAccount account) { } public static async Task<bool> GetWindowsHelloAuthenticationMessageAsync(UserAccount account) { KeyCredentialRetrievalResult openKeyResult = await KeyCredentialManager.OpenAsync(account.Username); //Calling OpenAsync will allow the user access to what is available in the app and will not require user credentials again. //If you wanted to force the user to sign in again you can use the following: //var consentResult = await Windows.Security.Credentials.UI.UserConsentVerifier.RequestVerificationAsync(account.Username); //This will ask for the either the password of the currently signed in Microsoft Account or the PIN used for Windows Hello. if (openKeyResult.Status == KeyCredentialStatus.Success) { //If OpenAsync has succeeded, the next thing to think about is whether the client application requires access to backend services. //If it does here you would Request a challenge from the Server. The client would sign this challenge and the server //would check the signed challenge. If it is correct it would allow the user access to the backend. //You would likely make a new method called RequestSignAsync to handle all this //for example, RequestSignAsync(openKeyResult); //Refer to the second Windows Hello sample for information on how to do this. //For this sample there is not concept of a server implemented so just return true. return true; } else if (openKeyResult.Status == KeyCredentialStatus.NotFound) { //If the _account is not found at this stage. It could be one of two errors. //1. Windows Hello has been disabled //2. Windows Hello has been disabled and re-enabled cause the Windows Hello Key to change. //Calling CreateWindowsHelloKeyAsync and passing through the account will attempt to replace the existing Windows Hello Key for that account. //If the error really is that Windows Hello is disabled then the CreateWindowsHelloKeyAsync method will output that error. if (await CreateWindowsHelloKeyAsync(account.UserId, account.Username)) { //If the Windows Hello Key was again successfully created, Windows Hello has just been reset. //Now that the Windows Hello Key has been reset for the account retry sign in. return await GetWindowsHelloAuthenticationMessageAsync(account); } } // Can't use Windows Hello right now, try again later return false; }accountHelper 대신 AuthService를 사용하려면 Login.xaml.cs 파일의 SignInWindowsHelloAsync 메서드를 업데이트해야 합니다. 자격 증명의 유효성 검사는 AuthService를 통해 수행됩니다. 이 실습의 경우 구성된 유일한 계정은 "sampleUsername"입니다. 이 계정은 MockStore.cs InitializeSampleUserAccountsAsync 메서드에서 만들어집니다. 아래 코드 조각을 반영하도록 Login.xaml.cs SignInWindowsHelloAsync 메서드를 업데이트합니다.
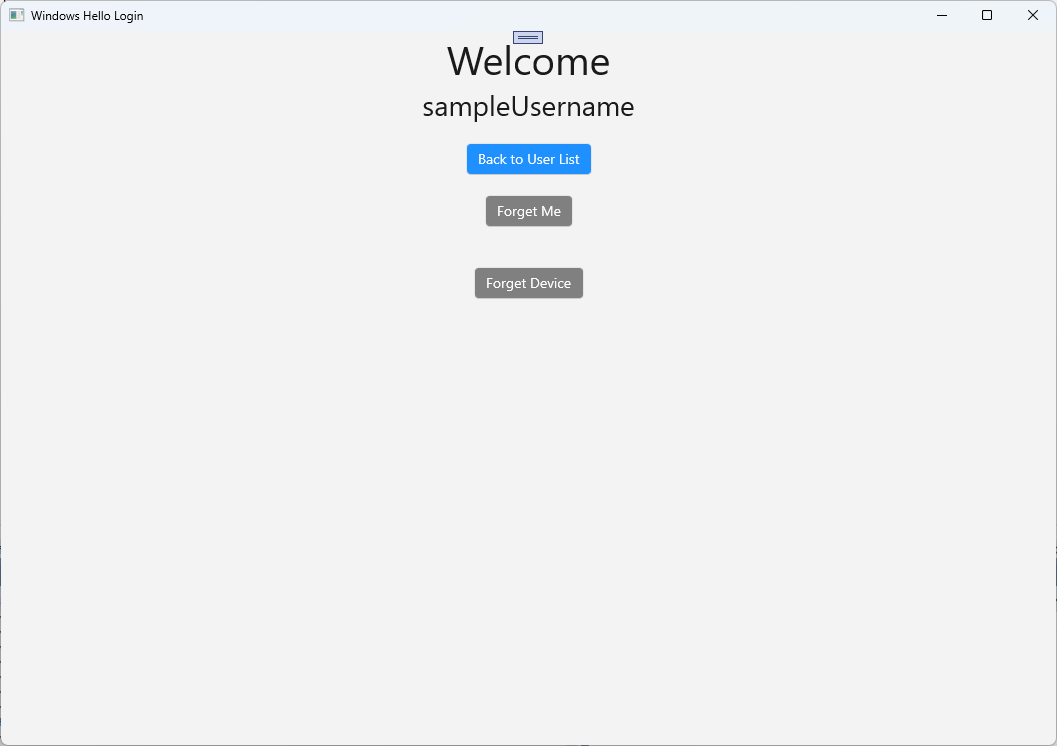
private async Task SignInWindowsHelloAsync() { if (_isExistingAccount) { if (await WindowsHelloHelper.GetWindowsHelloAuthenticationMessageAsync(_account)) { Frame.Navigate(typeof(Welcome), _account); } } else if (AuthService.AuthService.Instance.ValidateCredentials(UsernameTextBox.Text, PasswordBox.Password)) { Guid userId = AuthService.AuthService.Instance.GetUserId(UsernameTextBox.Text); if (userId != Guid.Empty) { //Now that the account exists on server try and create the necessary details and add them to the account if (await WindowsHelloHelper.CreateWindowsHelloKeyAsync(userId, UsernameTextBox.Text)) { Debug.WriteLine("Successfully signed in with Windows Hello!"); //Navigate to the Welcome Screen. _account = AuthService.AuthService.Instance.GetUserAccount(userId); Frame.Navigate(typeof(Welcome), _account); } else { //The Windows Hello account creation failed. //Remove the account from the server as the details were not configured await AuthService.AuthService.Instance.WindowsHelloRemoveUserAsync(userId); ErrorMessage.Text = "Account Creation Failed"; } } } else { ErrorMessage.Text = "Invalid Credentials"; } }Windows Hello는 각 디바이스의 각 계정에 대해 다른 공개 및 프라이빗 키 쌍을 만들기 때문에 시작 페이지에서 로그인한 계정에 등록된 디바이스 목록을 표시하고 각 디바이스를 잊어버릴 수 있도록 해야 합니다. Welcome.xaml에서
ForgetButton아래에 다음 XAML을 추가합니다. 그러면 디바이스 잊기 단추, 오류 텍스트 영역 및 모든 디바이스를 표시하는 목록이 구현됩니다.<Grid> <StackPanel> <TextBlock x:Name="Title" Text="Welcome" FontSize="40" TextAlignment="Center"/> <TextBlock x:Name="UserNameText" FontSize="28" TextAlignment="Center"/> <Button x:Name="BackToUserListButton" Content="Back to User List" Click="Button_Restart_Click" HorizontalAlignment="Center" Margin="0,20" Foreground="White" Background="DodgerBlue"/> <Button x:Name="ForgetButton" Content="Forget Me" Click="Button_Forget_User_Click" Foreground="White" Background="Gray" HorizontalAlignment="Center"/> <Button x:Name="ForgetDeviceButton" Content="Forget Device" Click="Button_Forget_Device_Click" Foreground="White" Background="Gray" Margin="0,40,0,20" HorizontalAlignment="Center"/> <TextBlock x:Name="ForgetDeviceErrorTextBlock" Text="Select a device first" TextWrapping="Wrap" Width="300" Foreground="Red" TextAlignment="Center" VerticalAlignment="Center" FontSize="16" Visibility="Collapsed"/> <ListView x:Name="UserListView" MaxHeight="500" MinWidth="350" Width="350" HorizontalAlignment="Center"> <ListView.ItemTemplate> <DataTemplate> <Grid Background="Gray" Height="50" Width="350" HorizontalAlignment="Center" VerticalAlignment="Stretch" > <TextBlock Text="{Binding DeviceId}" HorizontalAlignment="Center" TextAlignment="Center" VerticalAlignment="Center" Foreground="White"/> </Grid> </DataTemplate> </ListView.ItemTemplate> </ListView> </StackPanel> </Grid>Welcome.xaml.cs 파일에서 클래스 맨 위에 있는 프라이빗
Account변수를 프라이빗UserAccount변수로 변경해야 합니다. 그런 다음OnNavigatedTo를 사용하도록 메서드를 업데이트 하고 현재 계정에 대한 정보를 검색합니다. 계정 정보를 가지고 있으면 목록의ItemsSource을(를) 설정하여 장치를 표시할 수 있습니다. AuthService 네임스페이스에 대한 참조를 추가해야 합니다.using WindowsHelloLogin.AuthService; namespace WindowsHelloLogin.Views { public sealed partial class Welcome : Page { private UserAccount _activeAccount; public Welcome() { InitializeComponent(); } protected override void OnNavigatedTo(NavigationEventArgs e) { _activeAccount = (UserAccount)e.Parameter; if (_activeAccount != null) { UserAccount account = AuthService.AuthService.Instance.GetUserAccount(_activeAccount.UserId); if (account != null) { UserListView.ItemsSource = account.WindowsHelloDevices; UserNameText.Text = account.Username; } } } } }계정을 제거할 때 AuthService 를 사용하므로 메서드의 AccountHelper 에 대한 참조를
Button_Forget_User_Click제거할 수 있습니다. 이제 메서드가 아래와 같이 표시됩니다.private async void Button_Forget_User_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) { //Remove it from Windows Hello await WindowsHelloHelper.RemoveWindowsHelloAccountAsync(_activeAccount); Debug.WriteLine($"User {_activeAccount.Username} deleted."); //Navigate back to UserSelection page. Frame.Navigate(typeof(UserSelection)); }WindowsHelloHelper 메서드는 AuthService를 사용하여 계정을 제거하지 않습니다. AuthService를 호출하고 userId를 전달해야 합니다.
public static async Task RemoveWindowsHelloAccountAsync(UserAccount account) { //Open the account with Windows Hello KeyCredentialRetrievalResult keyOpenResult = await KeyCredentialManager.OpenAsync(account.Username); if (keyOpenResult.Status == KeyCredentialStatus.Success) { // In the real world you would send key information to server to unregister await AuthService.AuthService.Instance.WindowsHelloRemoveUserAsync(account.UserId); } //Then delete the account from the machines list of Windows Hello Accounts await KeyCredentialManager.DeleteAsync(account.Username); }시작 페이지 구현을 완료하려면 WindowsHelloHelper.cs 디바이스를 제거할 수 있는 메서드를 만들어야 합니다. AuthService에서 WindowsHelloRemoveDeviceAsync를 호출하는 새 메서드를 만듭니다.
public static async Task RemoveWindowsHelloDeviceAsync(UserAccount account, Guid deviceId) { await AuthService.AuthService.Instance.WindowsHelloRemoveDeviceAsync(account.UserId, deviceId); }Welcome.xaml.cs에서 Button_Forget_Device_Click 이벤트 처리기를 구현하십시오. 그러면 디바이스 목록에서 선택한 디바이스를 사용하고 Windows Hello 도우미를 사용하여 제거 디바이스를 호출합니다. 이벤트 처리기를 비동기로 만드는 것을 잊지 마세요.
private async void Button_Forget_Device_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) { WindowsHelloDevice selectedDevice = UserListView.SelectedItem as WindowsHelloDevice; if (selectedDevice != null) { //Remove it from Windows Hello await WindowsHelloHelper.RemoveWindowsHelloDeviceAsync(_activeAccount, selectedDevice.DeviceId); Debug.WriteLine($"User {_activeAccount.Username} deleted."); if (!UserListView.Items.Any()) { //Navigate back to UserSelection page. Frame.Navigate(typeof(UserSelection)); } } else { ForgetDeviceErrorTextBlock.Visibility = Visibility.Visible; } }업데이트할 다음 페이지는 UserSelection 페이지입니다. UserSelection 페이지는 AuthService를 사용하여 현재 디바이스에 대한 모든 사용자 계정을 검색해야 합니다. 현재는 해당 디바이스에 대한 사용자 계정을 반환할 수 있도록 디바이스 ID를 AuthService 에 전달할 방법이 없습니다. Utils 폴더에서 "Helpers.cs"이라는 새 클래스를 만듭니다. 클래스 범위를 public static으로 변경한 다음 현재 디바이스 ID를 검색할 수 있는 다음 메서드를 추가합니다.
using System; using Windows.Security.ExchangeActiveSyncProvisioning; namespace WindowsHelloLogin.Utils { public static class Helpers { public static Guid GetDeviceId() { //Get the Device ID to pass to the server var deviceInformation = new EasClientDeviceInformation(); return deviceInformation.Id; } } }UserSelection 페이지 클래스에서는 사용자 인터페이스가 아니라 코드 비하인드만 변경해야 합니다. UserSelection.xaml.cs 파일에서 UserSelection_Loaded 메서드와 UserSelectionChanged 메서드를
UserAccount클래스 대신Account클래스를 사용하도록 업데이트합니다. 또한 AuthService를 통해 이 디바이스에 대한 모든 사용자를 가져와야 합니다.using System.Linq; using WindowsHelloLogin.AuthService; namespace WindowsHelloLogin.Views { public sealed partial class UserSelection : Page { public UserSelection() { InitializeComponent(); Loaded += UserSelection_Loaded; } private void UserSelection_Loaded(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) { List<UserAccount> accounts = AuthService.AuthService.Instance.GetUserAccountsForDevice(Helpers.GetDeviceId()); if (accounts.Any()) { UserListView.ItemsSource = accounts; UserListView.SelectionChanged += UserSelectionChanged; } else { //If there are no accounts navigate to the Login page Frame.Navigate(typeof(Login)); } } /// <summary> /// Function called when an account is selected in the list of accounts /// Navigates to the Login page and passes the chosen account /// </summary> private void UserSelectionChanged(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) { if (((ListView)sender).SelectedValue != null) { UserAccount account = (UserAccount)((ListView)sender).SelectedValue; if (account != null) { Debug.WriteLine($"Account {account.Username} selected!"); } Frame.Navigate(typeof(Login), account); } } } }WindowsHelloRegister 페이지에는 코드 숨김 파일이 업데이트되어야 합니다. 사용자 인터페이스는 변경할 필요가 없습니다. WindowsHelloRegister.xaml.cs 더 이상 필요하지 않으므로 클래스 맨 위에 있는 프라이빗
Account변수를 제거합니다. AuthService를 사용하도록 RegisterButton_Click_Async 이벤트 처리기를 업데이트합니다. 이 메서드는 새 UserAccount 를 만든 다음 해당 계정 세부 정보를 시도하고 업데이트합니다. Windows Hello에서 키를 만들지 못하면 등록 프로세스가 실패하면 계정이 제거됩니다.private async void RegisterButton_Click_Async(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) { ErrorMessage.Text = ""; //Validate entered credentials are acceptable if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(UsernameTextBox.Text)) { //Register an Account on the AuthService so that we can get back a userId await AuthService.AuthService.Instance.RegisterAsync(UsernameTextBox.Text); Guid userId = AuthService.AuthService.Instance.GetUserId(UsernameTextBox.Text); if (userId != Guid.Empty) { //Now that the account exists on server try and create the necessary details and add them to the account if (await WindowsHelloHelper.CreateWindowsHelloKeyAsync(userId, UsernameTextBox.Text)) { //Navigate to the Welcome Screen. Frame.Navigate(typeof(Welcome), AuthService.AuthService.Instance.GetUserAccount(userId)); } else { //The Windows Hello account creation failed. //Remove the account from the server as the details were not configured await AuthService.AuthService.Instance.WindowsHelloRemoveUserAsync(userId); ErrorMessage.Text = "Account Creation Failed"; } } } else { ErrorMessage.Text = "Please enter a username"; } }애플리케이션을 빌드하고 실행합니다. "sampleUsername" 및 "samplePassword" 자격 증명을 사용하여 샘플 사용자 계정에 로그인합니다. 시작 화면에서 디바이스 잊기 단추가 표시되지만 디바이스가 없는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다. Windows Hello로 작업하도록 사용자를 만들거나 마이그레이션하는 경우 계정 정보가 AuthService로 푸시되지 않습니다.
AuthService에 Windows Hello 계정 정보를 얻으려면 WindowsHelloHelper.cs 업데이트해야 합니다. CreateWindowsHelloKeyAsync 메서드에서 성공한 경우에만 반환하는
true대신 KeyAttestation을 가져오는 새 메서드를 호출해야 합니다. 이 실습 랩은 AuthService에서 이 정보를 기록하지 않지만 클라이언트 쪽에서 이 정보를 가져오는 방법을 알아봅니다. 다음과 같이 CreateWindowsHelloKeyAsync 메서드를 업데이트합니다.public static async Task<bool> CreateWindowsHelloKeyAsync(Guid userId, string username) { KeyCredentialRetrievalResult keyCreationResult = await KeyCredentialManager.RequestCreateAsync(username, KeyCredentialCreationOption.ReplaceExisting); switch (keyCreationResult.Status) { case KeyCredentialStatus.Success: Debug.WriteLine("Successfully made key"); await GetKeyAttestationAsync(userId, keyCreationResult); return true; case KeyCredentialStatus.UserCanceled: Debug.WriteLine("User cancelled sign-in process."); break; case KeyCredentialStatus.NotFound: // User needs to setup Windows Hello Debug.WriteLine($"Windows Hello is not set up!{Environment.NewLine}Please go to Windows Settings and set up a PIN to use it."); break; default: break; } return false; }WindowsHelloHelper.cs GetKeyAttestationAsync 메서드를 만듭니다. 이 메서드는 특정 디바이스의 각 계정에 대해 Windows Hello에서 제공할 수 있는 모든 필요한 정보를 가져오는 방법을 보여 줍니다.
using Windows.Storage.Streams; private static async Task GetKeyAttestationAsync(Guid userId, KeyCredentialRetrievalResult keyCreationResult) { KeyCredential userKey = keyCreationResult.Credential; IBuffer publicKey = userKey.RetrievePublicKey(); KeyCredentialAttestationResult keyAttestationResult = await userKey.GetAttestationAsync(); IBuffer keyAttestation = null; IBuffer certificateChain = null; bool keyAttestationIncluded = false; bool keyAttestationCanBeRetrievedLater = false; KeyCredentialAttestationStatus keyAttestationRetryType = 0; if (keyAttestationResult.Status == KeyCredentialAttestationStatus.Success) { keyAttestationIncluded = true; keyAttestation = keyAttestationResult.AttestationBuffer; certificateChain = keyAttestationResult.CertificateChainBuffer; Debug.WriteLine("Successfully made key and attestation"); } else if (keyAttestationResult.Status == KeyCredentialAttestationStatus.TemporaryFailure) { keyAttestationRetryType = KeyCredentialAttestationStatus.TemporaryFailure; keyAttestationCanBeRetrievedLater = true; Debug.WriteLine("Successfully made key but not attestation"); } else if (keyAttestationResult.Status == KeyCredentialAttestationStatus.NotSupported) { keyAttestationRetryType = KeyCredentialAttestationStatus.NotSupported; keyAttestationCanBeRetrievedLater = false; Debug.WriteLine("Key created, but key attestation not supported"); } Guid deviceId = Helpers.GetDeviceId(); //Update the Windows Hello details with the information we have just fetched above. //await UpdateWindowsHelloDetailsAsync(userId, deviceId, publicKey.ToArray(), keyAttestationResult); }GetKeyAttestationAsync 메서드에서 방금 추가한 마지막 줄이 주석 처리되었음을 알 수 있습니다. 이 마지막 줄은 모든 Windows Hello 정보를 AuthService로 보내는 새 메서드입니다. 실제 환경에서는 Web API를 통해 이를 실제 서버로 보내야 합니다.
using System.Runtime.InteropServices.WindowsRuntime; using System.Threading.Tasks; public static async Task<bool> UpdateWindowsHelloDetailsAsync(Guid userId, Guid deviceId, byte[] publicKey, KeyCredentialAttestationResult keyAttestationResult) { //In the real world, you would use an API to add Windows Hello signing info to server for the signed in account. //For this tutorial, we do not implement a Web API for our server and simply mock the server locally. //The CreateWindowsHelloKey method handles adding the Windows Hello account locally to the device using the KeyCredential Manager //Using the userId the existing account should be found and updated. await AuthService.AuthService.Instance.WindowsHelloUpdateDetailsAsync(userId, deviceId, publicKey, keyAttestationResult); return true; }Windows Hello 정보가 AuthService로 전송되도록 GetKeyAttestationAsync 메서드의 마지막 줄의 주석 처리를 제거합니다.
애플리케이션을 빌드 및 실행하고 이전과 같이 기본 자격 증명으로 로그인합니다. 이제 시작 페이지에서 디바이스 ID가 표시되는 것을 볼 수 있습니다. 여기에 표시될 다른 디바이스에 로그인한 경우(클라우드 호스팅 인증 서비스가 있는 경우) 이 실습의 경우 실제 디바이스 ID가 표시됩니다. 실제 구현에서는 사용자가 이해하고 각 디바이스를 식별하는 데 사용할 수 있는 친숙한 이름을 표시하려고 합니다.
이 실습을 완료하려면 사용자 선택 페이지에서 선택하고 다시 로그인할 때 사용자에게 요청 및 챌린지가 필요합니다. AuthService에는 챌린지를 요청하기 위해 만든 두 가지 메서드가 있으며, 하나는 서명된 챌린지를 사용합니다. WindowsHelloHelper.cs RequestSignAsync라는 새 메서드를 만듭니다. 이렇게 하면 AuthService에서 챌린지를 요청하고, Windows Hello API를 사용하여 해당 챌린지에 로컬로 서명하고, 서명된 챌린지를 AuthService에 보냅니다. 이 실습에서 AuthService는 서명된 챌린지를 받으면
true을/를 반환합니다. 실제 구현에서는 올바른 디바이스에서 올바른 사용자가 챌린지에 서명했는지 확인하는 확인 메커니즘을 구현해야 합니다. 아래 메서드를 WindowsHelloHelper.cs 추가합니다.private static async Task<bool> RequestSignAsync(Guid userId, KeyCredentialRetrievalResult openKeyResult) { // Calling userKey.RequestSignAsync() prompts the uses to enter the PIN or use Biometrics (Windows Hello). // The app would use the private key from the user account to sign the sign-in request (challenge) // The client would then send it back to the server and await the servers response. IBuffer challengeMessage = AuthService.AuthService.Instance.WindowsHelloRequestChallenge(); KeyCredential userKey = openKeyResult.Credential; KeyCredentialOperationResult signResult = await userKey.RequestSignAsync(challengeMessage); if (signResult.Status == KeyCredentialStatus.Success) { // If the challenge from the server is signed successfully // send the signed challenge back to the server and await the servers response return AuthService.AuthService.Instance.SendServerSignedChallenge( userId, Helpers.GetDeviceId(), signResult.Result.ToArray()); } else if (signResult.Status == KeyCredentialStatus.UserCanceled) { // User cancelled the Windows Hello PIN entry. } else if (signResult.Status == KeyCredentialStatus.NotFound) { // Must recreate Windows Hello key } else if (signResult.Status == KeyCredentialStatus.SecurityDeviceLocked) { // Can't use Windows Hello right now, remember that hardware failed and suggest restart } else if (signResult.Status == KeyCredentialStatus.UnknownError) { // Can't use Windows Hello right now, try again later } return false; }WindowsHelloHelper 클래스의 GetWindowsHelloAuthenticationMessageAsync 메서드에서 RequestSignAsync 메서드를 호출합니다.
public static async Task<bool> GetWindowsHelloAuthenticationMessageAsync(UserAccount account) { KeyCredentialRetrievalResult openKeyResult = await KeyCredentialManager.OpenAsync(account.Username); // Calling OpenAsync will allow the user access to what is available in the app and will not require user credentials again. // If you wanted to force the user to sign in again you can use the following: // var consentResult = await Windows.Security.Credentials.UI.UserConsentVerifier.RequestVerificationAsync(account.Username); // This will ask for the either the password of the currently signed in Microsoft Account or the PIN used for Windows Hello. if (openKeyResult.Status == KeyCredentialStatus.Success) { //If OpenAsync has succeeded, the next thing to think about is whether the client application requires access to backend services. //If it does here you would Request a challenge from the Server. The client would sign this challenge and the server //would check the signed challenge. If it is correct it would allow the user access to the backend. //You would likely make a new method called RequestSignAsync to handle all this //for example, RequestSignAsync(openKeyResult); //Refer to the second Windows Hello sample for information on how to do this. return await RequestSignAsync(account.UserId, openKeyResult); } else if (openKeyResult.Status == KeyCredentialStatus.NotFound) { //If the _account is not found at this stage. It could be one of two errors. //1. Windows Hello has been disabled //2. Windows Hello has been disabled and re-enabled cause the Windows Hello Key to change. //Calling CreateWindowsHelloKeyAsync and passing through the account will attempt to replace the existing Windows Hello Key for that account. //If the error really is that Windows Hello is disabled then the CreateWindowsHelloKeyAsync method will output that error. if (await CreateWindowsHelloKeyAsync(account.UserId, account.Username)) { //If the Windows Hello Key was again successfully created, Windows Hello has just been reset. //Now that the Windows Hello Key has been reset for the _account retry sign in. return await GetWindowsHelloAuthenticationMessageAsync(account); } } // Can't use Windows Hello right now, try again later return false; }이 연습 전체에서 AuthService를 사용하도록 클라이언트 쪽 애플리케이션을 업데이트했습니다. 이렇게 하면 Account 클래스 및 AccountHelper 클래스가 필요하지 않습니다. Utils 폴더에서 Account 클래스, Models 폴더 및 AccountHelper 클래스를 삭제합니다. 솔루션이 성공적으로 빌드되기 전에 애플리케이션 전체에서
WindowsHelloLogin.Models네임스페이스에 대한 모든 참조를 제거해야 합니다.애플리케이션을 빌드 및 실행하고 모의 서비스 및 데이터베이스와 함께 Windows Hello를 사용해 보세요.
이 실습 랩에서는 Windows 컴퓨터에서 인증을 사용할 때 Windows Hello API를 사용하여 암호의 필요성을 바꾸는 방법을 알아보았습니다. 기존 시스템에서 암호를 유지하고 분실한 암호를 지원하는 데 사람들이 소비하는 에너지를 생각해보면, 이러한 새로운 인증 방법인 Windows Hello 시스템으로 전환하는 것이 얼마나 유익한지 알 수 있습니다.
서비스 및 서버 쪽에서 인증을 구현하는 방법에 대한 세부 정보를 연습으로 남겨 드립니다. 대부분의 개발자는 Windows Hello 작업을 시작하기 위해 마이그레이션해야 하는 기존 시스템을 갖게 될 것으로 예상됩니다. 이러한 각 시스템의 세부 정보는 다릅니다.
관련 항목
Windows developer
