Accept active learning suggested questions in the knowledge base
Note
The QnA Maker service is being retired on the 31st of March, 2025. A newer version of the question and answering capability is now available as part of Azure AI Language. For question answering capabilities within the Language Service, see question answering. Starting 1st October, 2022 you won’t be able to create new QnA Maker resources. For information on migrating existing QnA Maker knowledge bases to question answering, consult the migration guide.
Active Learning alters the Knowledge Base or Search Service after you approve the suggestion, then save and train. If you approve the suggestion, it will be added as an alternate question.
Turn on active learning
In order to see suggested questions, you must turn on active learning for your QnA Maker resource.
View suggested questions
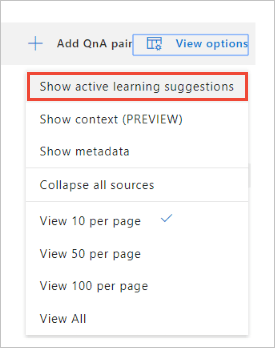
In order to see the suggested questions, on the Edit knowledge base page, select View Options, then select Show active learning suggestions. This option will be disabled if there are no suggestions present for any of the question and answer pairs.
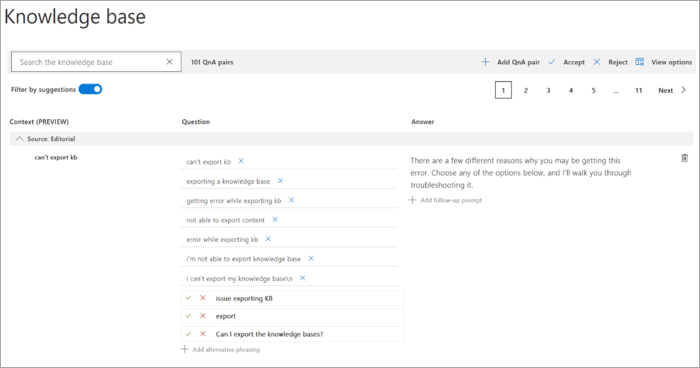
Filter the knowledge base with question and answer pairs to show only suggestions by selecting Filter by Suggestions.
Each QnA pair suggests the new question alternatives with a check mark,
✔, to accept the question or anxto reject the suggestions. Select the check mark to add the question.You can add or delete all suggestions by selecting Add all or Reject all in the contextual toolbar.
Select Save and Train to save the changes to the knowledge base.
Select Publish to allow the changes to be available from the GenerateAnswer API.
When 5 or more similar queries are clustered, every 30 minutes, QnA Maker suggests the alternate questions for you to accept or reject.
Active learning suggestions are saved in the exported knowledge base
When your app has active learning enabled, and you export the app, the SuggestedQuestions column in the tsv file retains the active learning data.
The SuggestedQuestions column is a JSON object of information of implicit, autosuggested, and explicit, usersuggested feedback. An example of this JSON object for a single user-submitted question of help is:
[
{
"clusterHead": "help",
"totalAutoSuggestedCount": 1,
"totalUserSuggestedCount": 0,
"alternateQuestionList": [
{
"question": "help",
"autoSuggestedCount": 1,
"userSuggestedCount": 0
}
]
}
]
When you reimport this app, the active learning continues to collect information and recommend suggestions for your knowledge base.
Architectural flow for using GenerateAnswer and Train APIs from a bot
A bot or other client application should use the following architectural flow to use active learning:
Bot gets the answer from the knowledge base with the GenerateAnswer API, using the
topproperty to get a number of answers.Bot determines explicit feedback:
- Using your own custom business logic, filter out low scores.
- In the bot or client-application, display list of possible answers to the user and get user's selected answer.
Bot sends selected answer back to QnA Maker with the Train API.
Use the top property in the GenerateAnswer request to get several matching answers
When submitting a question to QnA Maker for an answer, the top property of the JSON body sets the number of answers to return.
{
"question": "wi-fi",
"isTest": false,
"top": 3
}
Use the score property along with business logic to get list of answers to show user
When the client application (such as a chat bot) receives the response, the top 3 questions are returned. Use the score property to analyze the proximity between scores. This proximity range is determined by your own business logic.
{
"answers": [
{
"questions": [
"Wi-Fi Direct Status Indicator"
],
"answer": "**Wi-Fi Direct Status Indicator**\n\nStatus bar icons indicate your current Wi-Fi Direct connection status: \n\nWhen your device is connected to another device using Wi-Fi Direct, '$ \n\n+ *+ ' Wi-Fi Direct is displayed in the Status bar.",
"score": 74.21,
"id": 607,
"source": "Bugbash KB.pdf",
"metadata": []
},
{
"questions": [
"Wi-Fi - Connections"
],
"answer": "**Wi-Fi**\n\nWi-Fi is a term used for certain types of Wireless Local Area Networks (WLAN). Wi-Fi communication requires access to a wireless Access Point (AP).",
"score": 74.15,
"id": 599,
"source": "Bugbash KB.pdf",
"metadata": []
},
{
"questions": [
"Turn Wi-Fi On or Off"
],
"answer": "**Turn Wi-Fi On or Off**\n\nTurning Wi-Fi on makes your device able to discover and connect to compatible in-range wireless APs. \n\n1. From a Home screen, tap ::: Apps > e Settings .\n2. Tap Connections > Wi-Fi , and then tap On/Off to turn Wi-Fi on or off.",
"score": 69.99,
"id": 600,
"source": "Bugbash KB.pdf",
"metadata": []
}
]
}
Client application follow-up when questions have similar scores
Your client application displays the questions with an option for the user to select the single question that most represents their intention.
Once the user selects one of the existing questions, the client application sends the user's choice as feedback using the QnA Maker Train API. This feedback completes the active learning feedback loop.
Train API
Active learning feedback is sent to QnA Maker with the Train API POST request. The API signature is:
POST https://<QnA-Maker-resource-name>.azurewebsites.net/qnamaker/knowledgebases/<knowledge-base-ID>/train
Authorization: EndpointKey <endpoint-key>
Content-Type: application/json
{"feedbackRecords": [{"userId": "1","userQuestion": "<question-text>","qnaId": 1}]}
| HTTP request property | Name | Type | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| URL route parameter | Knowledge base ID | string | The GUID for your knowledge base. |
| Custom subdomain | QnAMaker resource name | string | The resource name is used as the custom subdomain for your QnA Maker. This is available on the Settings page after you publish the knowledge base. It is listed as the host. |
| Header | Content-Type | string | The media type of the body sent to the API. Default value is: application/json |
| Header | Authorization | string | Your endpoint key (EndpointKey xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx). |
| Post Body | JSON object | JSON | The training feedback |
The JSON body has several settings:
| JSON body property | Type | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
feedbackRecords |
array | List of feedback. |
userId |
string | The user ID of the person accepting the suggested questions. The user ID format is up to you. For example, an email address can be a valid user ID in your architecture. Optional. |
userQuestion |
string | Exact text of the user's query. Required. |
qnaID |
number | ID of question, found in the GenerateAnswer response. |
An example JSON body looks like:
{
"feedbackRecords": [
{
"userId": "1",
"userQuestion": "<question-text>",
"qnaId": 1
}
]
}
A successful response returns a status of 204 and no JSON response body.
Batch many feedback records into a single call
In the client-side application, such as a bot, you can store the data, then send many records in a single JSON body in the feedbackRecords array.
An example JSON body looks like:
{
"feedbackRecords": [
{
"userId": "1",
"userQuestion": "How do I ...",
"qnaId": 1
},
{
"userId": "2",
"userQuestion": "Where is ...",
"qnaId": 40
},
{
"userId": "3",
"userQuestion": "When do I ...",
"qnaId": 33
}
]
}
Bot framework sample code
Your bot framework code needs to call the Train API, if the user's query should be used for active learning. There are two pieces of code to write:
- Determine if query should be used for active learning
- Send query back to the QnA Maker Train API for active learning
In the Azure Bot sample, both of these activities have been programmed.
Example C# code for Train API with Bot Framework 4.x
The following code illustrates how to send information back to QnA Maker with the Train API.
public class FeedbackRecords
{
// <summary>
/// List of feedback records
/// </summary>
[JsonProperty("feedbackRecords")]
public FeedbackRecord[] Records { get; set; }
}
/// <summary>
/// Active learning feedback record
/// </summary>
public class FeedbackRecord
{
/// <summary>
/// User id
/// </summary>
public string UserId { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// User question
/// </summary>
public string UserQuestion { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// QnA Id
/// </summary>
public int QnaId { get; set; }
}
/// <summary>
/// Method to call REST-based QnAMaker Train API for Active Learning
/// </summary>
/// <param name="endpoint">Endpoint URI of the runtime</param>
/// <param name="FeedbackRecords">Feedback records train API</param>
/// <param name="kbId">Knowledgebase Id</param>
/// <param name="key">Endpoint key</param>
/// <param name="cancellationToken"> Cancellation token</param>
public async static void CallTrain(string endpoint, FeedbackRecords feedbackRecords, string kbId, string key, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
var uri = endpoint + "/knowledgebases/" + kbId + "/train/";
using (var client = new HttpClient())
{
using (var request = new HttpRequestMessage())
{
request.Method = HttpMethod.Post;
request.RequestUri = new Uri(uri);
request.Content = new StringContent(JsonConvert.SerializeObject(feedbackRecords), Encoding.UTF8, "application/json");
request.Headers.Add("Authorization", "EndpointKey " + key);
var response = await client.SendAsync(request, cancellationToken);
await response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
}
}
}
Example Node.js code for Train API with Bot Framework 4.x
The following code illustrates how to send information back to QnA Maker with the Train API.
async callTrain(stepContext){
var trainResponses = stepContext.values[this.qnaData];
var currentQuery = stepContext.values[this.currentQuery];
if(trainResponses.length > 1){
var reply = stepContext.context.activity.text;
var qnaResults = trainResponses.filter(r => r.questions[0] == reply);
if(qnaResults.length > 0){
stepContext.values[this.qnaData] = qnaResults;
var feedbackRecords = {
FeedbackRecords:[
{
UserId:stepContext.context.activity.id,
UserQuestion: currentQuery,
QnaId: qnaResults[0].id
}
]
};
// Call Active Learning Train API
this.activeLearningHelper.callTrain(this.qnaMaker.endpoint.host, feedbackRecords, this.qnaMaker.endpoint.knowledgeBaseId, this.qnaMaker.endpoint.endpointKey);
return await stepContext.next(qnaResults);
}
else{
return await stepContext.endDialog();
}
}
return await stepContext.next(stepContext.result);
}
Best practices
For best practices when using active learning, see Best practices.