Tutorial: Deploy applications using GitOps with Flux v2
This tutorial describes how to use GitOps in a Kubernetes cluster. GitOps with Flux v2 is enabled as a cluster extension in Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes clusters or Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) clusters. After the microsoft.flux cluster extension is installed, you can create one or more fluxConfigurations resources that sync your Git repository sources to the cluster and reconcile the cluster to the desired state. With GitOps, you can use your Git repository as the source of truth for cluster configuration and application deployment.
In this tutorial, we use an example GitOps configuration with two kustomizations, so that you can see how one kustomization can have a dependency on another. You can add more kustomizations and dependencies as needed, depending on your scenario.
Before you dive in, take a moment to learn how GitOps with Flux works conceptually.
Tip
While the source in this tutorial is a Git repository, Flux also provides support for other common file sources such as Helm repositories, Buckets, and Azure Blob Storage.
You can also create Flux configurations by using Bicep, ARM templates, or Terraform AzAPI provider. For more information, see Microsoft.KubernetesConfiguration fluxConfigurations.
Important
The microsoft.flux extension released major version 1.0.0. This includes the multi-tenancy feature. If you have existing GitOps Flux v2 configurations that use a previous version of the microsoft.flux extension, you can upgrade to the latest version manually using the Azure CLI: az k8s-extension create -g <RESOURCE_GROUP> -c <CLUSTER_NAME> -n flux --extension-type microsoft.flux -t <CLUSTER_TYPE> (use -t connectedClusters for Arc clusters and -t managedClusters for AKS clusters).
Prerequisites
To deploy applications using GitOps with Flux v2, you need:
For Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes clusters
An Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes connected cluster that's up and running. ARM64-based clusters are supported starting with
microsoft.fluxversion 1.7.0.Learn how to connect a Kubernetes cluster to Azure Arc. If you need to connect through an outbound proxy, then assure you install the Arc agents with proxy settings.
Read and write permissions on the
Microsoft.Kubernetes/connectedClustersresource type.
For Azure Kubernetes Service clusters
An MSI-based AKS cluster that's up and running.
Important
Ensure that the AKS cluster is created with MSI (not SPN), because the
microsoft.fluxextension won't work with SPN-based AKS clusters. For new AKS clusters created withaz aks create, the cluster is MSI-based by default. For already created SPN-based clusters that need to be converted to MSI, runaz aks update -g $RESOURCE_GROUP -n $CLUSTER_NAME --enable-managed-identity. For more information, see Use a managed identity in AKS.Read and write permissions on the
Microsoft.ContainerService/managedClustersresource type.
Common to both cluster types
Read and write permissions on these resource types:
Microsoft.KubernetesConfiguration/extensionsMicrosoft.KubernetesConfiguration/fluxConfigurations
Azure CLI version 2.15 or later. Install the Azure CLI or use the following commands to update to the latest version:
az version az upgradeThe Kubernetes command-line client, kubectl.
kubectlis already installed if you use Azure Cloud Shell.Install
kubectllocally using theaz aks install-clicommand:az aks install-cliRegistration of the following Azure resource providers:
az provider register --namespace Microsoft.Kubernetes az provider register --namespace Microsoft.ContainerService az provider register --namespace Microsoft.KubernetesConfigurationRegistration is an asynchronous process and should finish within 10 minutes. To monitor the registration process, use the following command:
az provider show -n Microsoft.KubernetesConfiguration -o table Namespace RegistrationPolicy RegistrationState --------------------------------- -------------------- ------------------- Microsoft.KubernetesConfiguration RegistrationRequired Registered
Version and region support
GitOps is currently supported in all regions that Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes supports. GitOps is currently supported in a subset of the regions that AKS supports. The GitOps service is adding new supported regions on a regular cadence.
The most recent version of the Flux v2 extension and the two previous versions (N-2) are supported. We generally recommend that you use the most recent version of the extension.
Network requirements
The GitOps agents require outbound (egress) TCP to the repo source on either port 22 (SSH) or port 443 (HTTPS) to function. The agents also require access to the following outbound URLs:
| Endpoint (DNS) | Description |
|---|---|
https://management.azure.com |
Required for the agent to communicate with the Kubernetes Configuration service. |
https://<region>.dp.kubernetesconfiguration.azure.com |
Data plane endpoint for the agent to push status and fetch configuration information. Depends on <region> (the supported regions mentioned earlier). |
https://login.microsoftonline.com |
Required to fetch and update Azure Resource Manager tokens. |
https://mcr.microsoft.com |
Required to pull container images for Flux controllers. |
Enable CLI extensions
Install the latest k8s-configuration and k8s-extension CLI extension packages:
az extension add -n k8s-configuration
az extension add -n k8s-extension
To update these packages to the latest versions:
az extension update -n k8s-configuration
az extension update -n k8s-extension
To see a list of all installed Azure CLI extensions and their versions, use the following command:
az extension list -o table
Experimental ExtensionType Name Path Preview Version
------------- -------------- ----------------- ----------------------------------------------------- -------- --------
False whl connectedk8s C:\Users\somename\.azure\cliextensions\connectedk8s False 1.2.7
False whl k8s-configuration C:\Users\somename\.azure\cliextensions\k8s-configuration False 1.5.0
False whl k8s-extension C:\Users\somename\.azure\cliextensions\k8s-extension False 1.1.0
Tip
For help resolving any errors, see the GitOps (Flux v2) section of Troubleshoot extension issues for Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes clusters.
Apply a Flux configuration
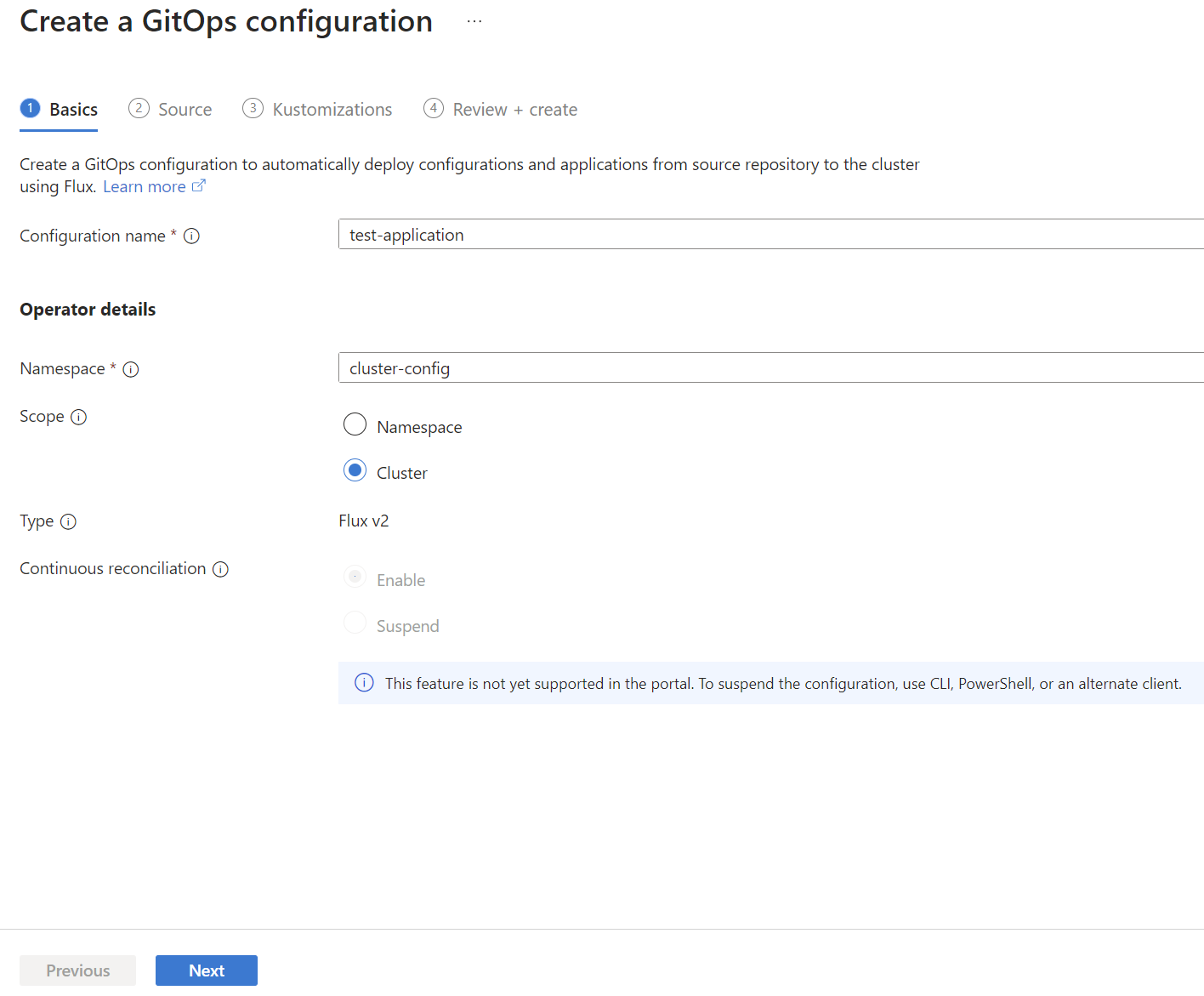
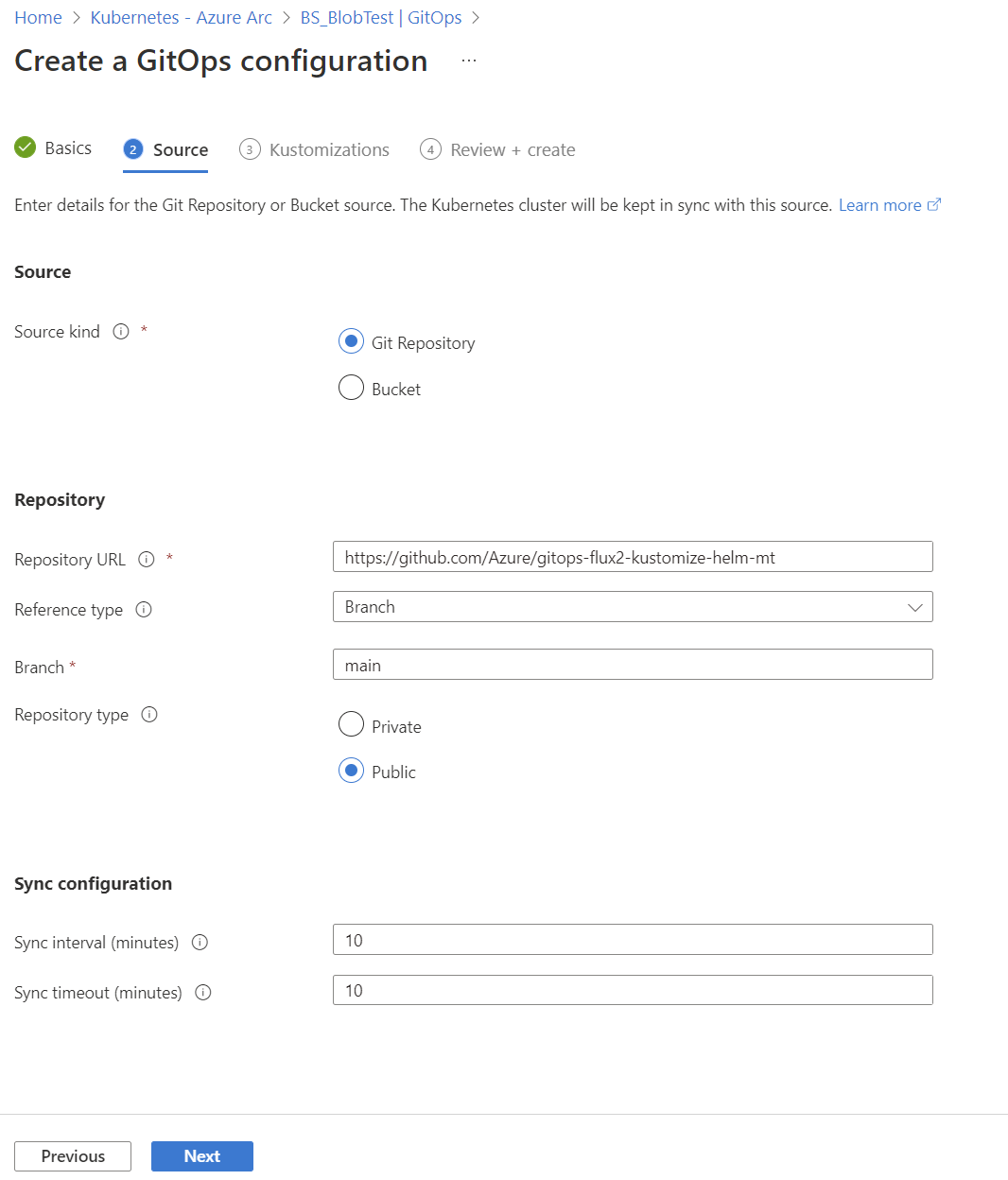
Use the k8s-configuration Azure CLI extension or the Azure portal to enable GitOps in an AKS or Arc-enabled Kubernetes cluster. For a demonstration, use the public gitops-flux2-kustomize-helm-mt repository.
Important
The demonstration repo is designed to simplify your use of this tutorial and illustrate some key principles. To keep up to date, the repo can get breaking changes occasionally from version upgrades. These changes won't affect your new application of this tutorial, only previous tutorial applications that have not been deleted. To learn how to handle these changes please see the breaking change disclaimer.
The following example uses the az k8s-configuration flux create command to apply a Flux configuration to a cluster, using the following values and settings:
- The resource group that contains the cluster is
flux-demo-rg. - The name of the Azure Arc cluster is
flux-demo-arc. - The cluster type is Azure Arc (
-t connectedClusters), but this example also works with AKS (-t managedClusters). - The name of the Flux configuration is
cluster-config. - The namespace for configuration installation is
cluster-config. - The URL for the public Git repository is
https://github.com/Azure/gitops-flux2-kustomize-helm-mt. - The Git repository branch is
main. - The scope of the configuration is
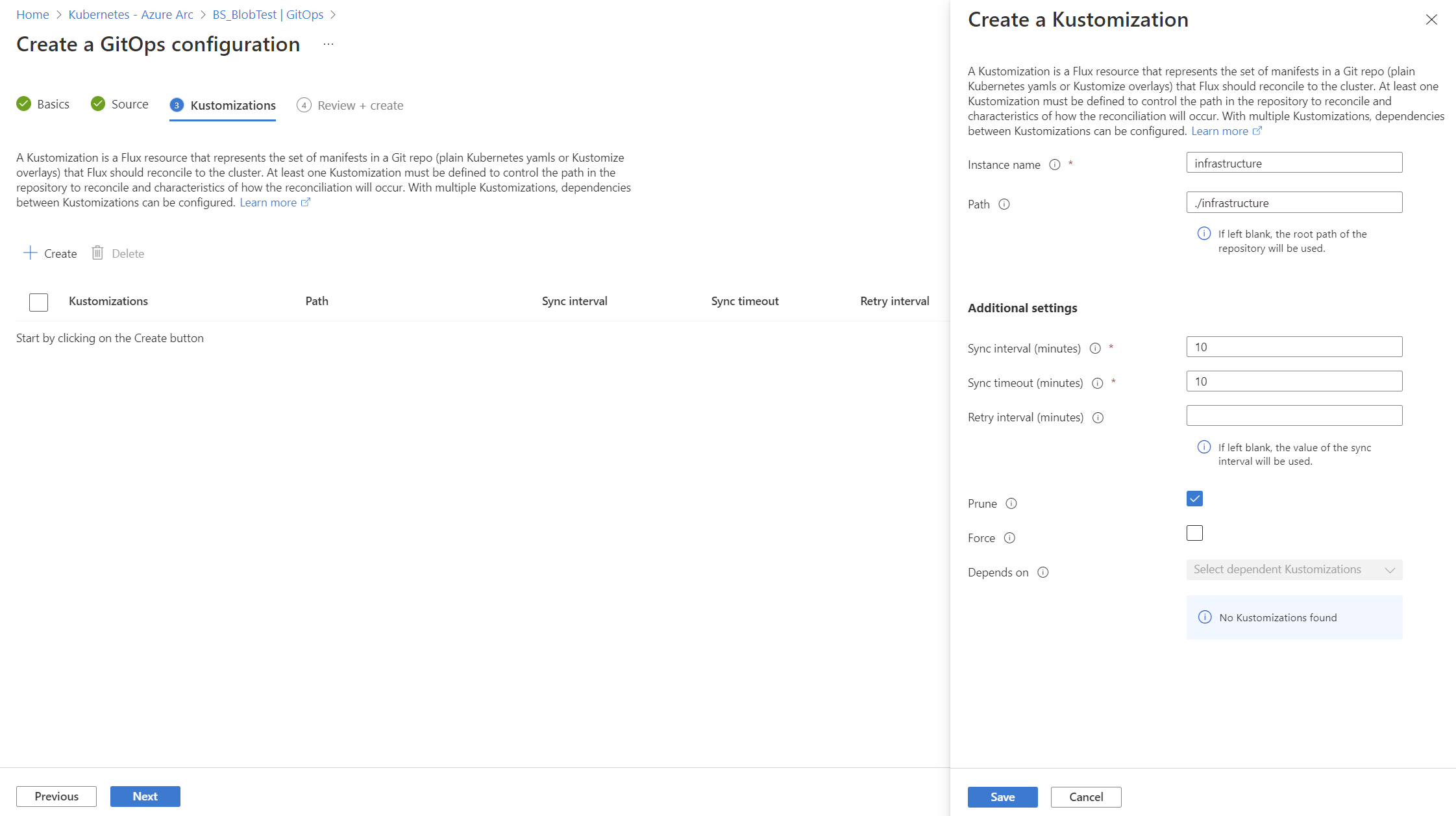
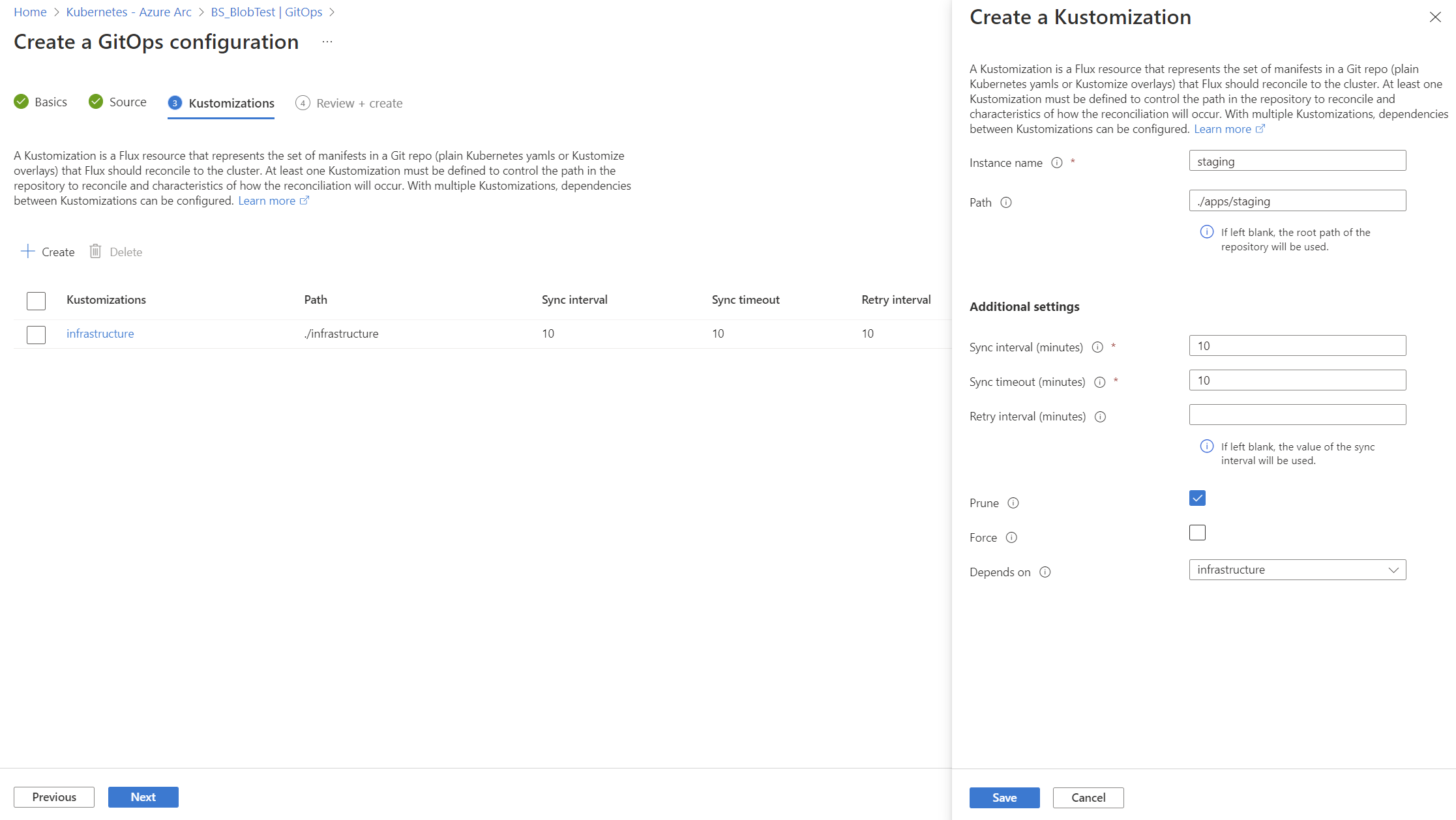
cluster. This scope gives the operators permissions to make changes throughout cluster. To usenamespacescope with this tutorial, see the changes needed. - Two kustomizations are specified with names
infraandapps. Each is associated with a path in the repository. - The
appskustomization depends on theinfrakustomization. (Theinfrakustomization must finish before theappskustomization runs.) - Set
prune=trueon both kustomizations. This setting ensures that the objects that Flux deployed to the cluster are cleaned up if they're removed from the repository, or if the Flux configuration or kustomizations are deleted.
az k8s-configuration flux create -g flux-demo-rg \
-c flux-demo-arc \
-n cluster-config \
--namespace cluster-config \
-t connectedClusters \
--scope cluster \
-u https://github.com/Azure/gitops-flux2-kustomize-helm-mt \
--branch main \
--kustomization name=infra path=./infrastructure prune=true \
--kustomization name=apps path=./apps/staging prune=true dependsOn=\["infra"\]
The microsoft.flux extension is installed on the cluster (if it wasn't already installed in a previous GitOps deployment).
Tip
The az k8s-configuration flux create command deploys the microsoft.flux extension to the cluster and creates the configuration. In some scenarios, you may want to create the flux extension instance separately before you create your configuration resources. To do so, use the az k8s-extension create command to create an instance of the extension on your cluster.
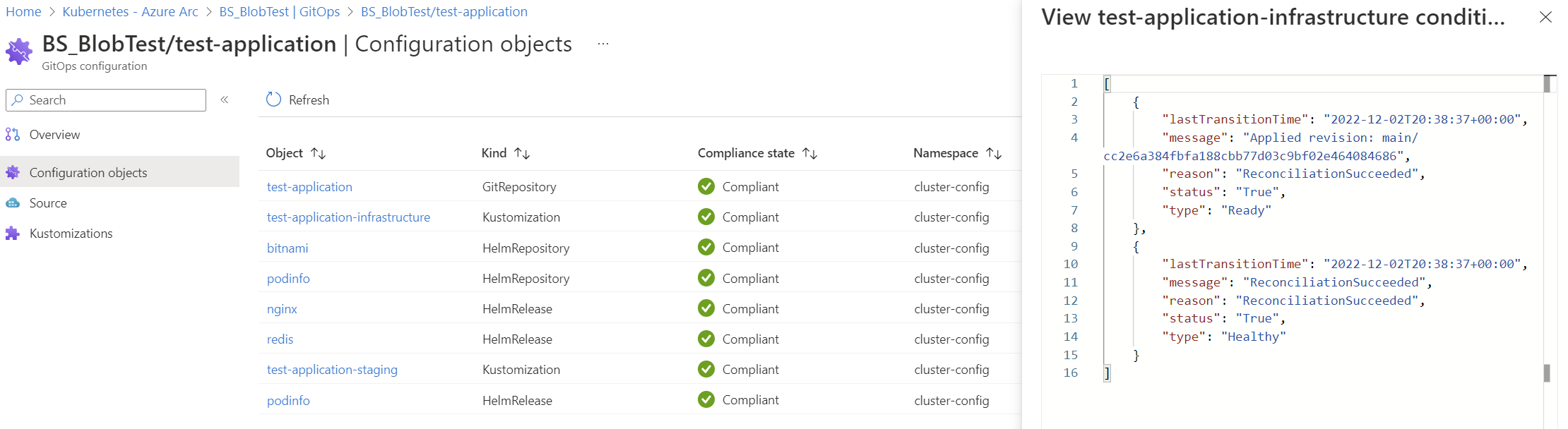
When the flux configuration is first installed, the initial compliance state may be Pending or Non-compliant because reconciliation is still ongoing. After a minute or so, query the configuration again to see the final compliance state.
az k8s-configuration flux show -g flux-demo-rg -c flux-demo-arc -n cluster-config -t connectedClusters
To confirm that the deployment was successful, run the following command:
az k8s-configuration flux show -g flux-demo-rg -c flux-demo-arc -n cluster-config -t connectedClusters
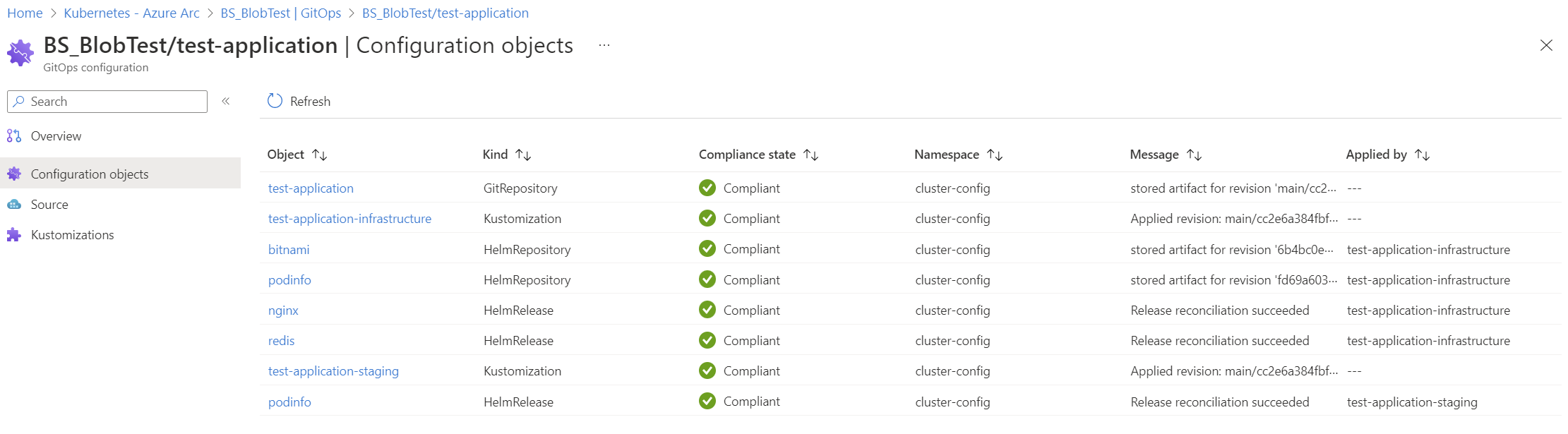
With a successful deployment the following namespaces are created:
flux-system: Holds the Flux extension controllers.cluster-config: Holds the Flux configuration objects.nginx,podinfo,redis: Namespaces for workloads described in manifests in the Git repository.
To confirm the namespaces, run the following command:
kubectl get namespaces
The flux-system namespace contains the Flux extension objects:
- Azure Flux controllers:
fluxconfig-agent,fluxconfig-controller - OSS Flux controllers:
source-controller,kustomize-controller,helm-controller,notification-controller
The Flux agent and controller pods should be in a running state. Confirm this using the following command:
kubectl get pods -n flux-system
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
fluxconfig-agent-9554ffb65-jqm8g 2/2 Running 0 21m
fluxconfig-controller-9d99c54c8-nztg8 2/2 Running 0 21m
helm-controller-59cc74dbc5-77772 1/1 Running 0 21m
kustomize-controller-5fb7d7b9d5-cjdhx 1/1 Running 0 21m
notification-controller-7d45678bc-fvlvr 1/1 Running 0 21m
source-controller-df7dc97cd-4drh2 1/1 Running 0 21m
The namespace cluster-config has the Flux configuration objects.
kubectl get crds
NAME CREATED AT
alerts.notification.toolkit.fluxcd.io 2022-04-06T17:15:48Z
arccertificates.clusterconfig.azure.com 2022-03-28T21:45:19Z
azureclusteridentityrequests.clusterconfig.azure.com 2022-03-28T21:45:19Z
azureextensionidentities.clusterconfig.azure.com 2022-03-28T21:45:19Z
buckets.source.toolkit.fluxcd.io 2022-04-06T17:15:48Z
connectedclusters.arc.azure.com 2022-03-28T21:45:19Z
customlocationsettings.clusterconfig.azure.com 2022-03-28T21:45:19Z
extensionconfigs.clusterconfig.azure.com 2022-03-28T21:45:19Z
fluxconfigs.clusterconfig.azure.com 2022-04-06T17:15:48Z
gitconfigs.clusterconfig.azure.com 2022-03-28T21:45:19Z
gitrepositories.source.toolkit.fluxcd.io 2022-04-06T17:15:48Z
helmcharts.source.toolkit.fluxcd.io 2022-04-06T17:15:48Z
helmreleases.helm.toolkit.fluxcd.io 2022-04-06T17:15:48Z
helmrepositories.source.toolkit.fluxcd.io 2022-04-06T17:15:48Z
imagepolicies.image.toolkit.fluxcd.io 2022-04-06T17:15:48Z
imagerepositories.image.toolkit.fluxcd.io 2022-04-06T17:15:48Z
imageupdateautomations.image.toolkit.fluxcd.io 2022-04-06T17:15:48Z
kustomizations.kustomize.toolkit.fluxcd.io 2022-04-06T17:15:48Z
providers.notification.toolkit.fluxcd.io 2022-04-06T17:15:48Z
receivers.notification.toolkit.fluxcd.io 2022-04-06T17:15:48Z
volumesnapshotclasses.snapshot.storage.k8s.io 2022-03-28T21:06:12Z
volumesnapshotcontents.snapshot.storage.k8s.io 2022-03-28T21:06:12Z
volumesnapshots.snapshot.storage.k8s.io 2022-03-28T21:06:12Z
websites.extensions.example.com 2022-03-30T23:42:32Z
Confirm other details of the configuration by using the following commands.
kubectl get fluxconfigs -A
NAMESPACE NAME SCOPE URL PROVISION AGE
cluster-config cluster-config cluster https://github.com/Azure/gitops-flux2-kustomize-helm-mt Succeeded 44m
kubectl get gitrepositories -A
NAMESPACE NAME URL READY STATUS AGE
cluster-config cluster-config https://github.com/Azure/gitops-flux2-kustomize-helm-mt True Fetched revision: main/4f1bdad4d0a54b939a5e3d52c51464f67e474fcf 45m
kubectl get helmreleases -A
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS AGE
cluster-config nginx True Release reconciliation succeeded 66m
cluster-config podinfo True Release reconciliation succeeded 66m
cluster-config redis True Release reconciliation succeeded 66m
kubectl get kustomizations -A
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS AGE
cluster-config cluster-config-apps True Applied revision: main/4f1bdad4d0a54b939a5e3d52c51464f67e474fcf 65m
cluster-config cluster-config-infra True Applied revision: main/4f1bdad4d0a54b939a5e3d52c51464f67e474fcf 65m
Workloads are deployed from manifests in the Git repository.
kubectl get deploy -n nginx
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
nginx-ingress-controller 1/1 1 1 67m
nginx-ingress-controller-default-backend 1/1 1 1 67m
kubectl get deploy -n podinfo
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
podinfo 1/1 1 1 68m
kubectl get all -n redis
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/redis-master-0 1/1 Running 0 68m
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/redis-headless ClusterIP None <none> 6379/TCP 68m
service/redis-master ClusterIP 10.0.13.182 <none> 6379/TCP 68m
NAME READY AGE
statefulset.apps/redis-master 1/1 68m
Control which controllers are deployed with the Flux cluster extension
For some scenarios, you may wish to change which Flux controllers are installed with the Flux cluster extension.
The source, helm, kustomize, and notification Flux controllers are installed by default. The image-automation and image-reflector controllers, used to update a Git repository when new container images are available, must be enabled explicitly.
You can use the k8s-extension command to change the default options:
--config source-controller.enabled=<true/false>(defaulttrue)--config helm-controller.enabled=<true/false>(defaulttrue)--config kustomize-controller.enabled=<true/false>(defaulttrue)--config notification-controller.enabled=<true/false>(defaulttrue)--config image-automation-controller.enabled=<true/false>(defaultfalse)--config image-reflector-controller.enabled=<true/false>(defaultfalse)
For instance, to disable notifications, you can set notification-controller.enabled to false.
This example command installs the image-reflector and image-automation controllers. If the Flux extension was created automatically when a Flux configuration was first created, the extension name is flux.
az k8s-extension create -g <cluster_resource_group> -c <cluster_name> -t <connectedClusters or managedClusters or provisionedClusters> --name flux --extension-type microsoft.flux --config image-automation-controller.enabled=true image-reflector-controller.enabled=true
Using Kubelet identity as authentication method for AKS clusters
For AKS clusters, one of the authentication options to use is kubelet identity. By default, AKS creates its own kubelet identity in the managed resource group. If you prefer, you can use a precreated kubelet managed identity. To do so, add the parameter --config useKubeletIdentity=true at the time of Flux extension installation.
az k8s-extension create --resource-group <resource-group> --cluster-name <cluster-name> --cluster-type managedClusters --name flux --extension-type microsoft.flux --config useKubeletIdentity=true
Red Hat OpenShift onboarding guidance
Flux controllers require a nonroot Security Context Constraint to properly provision pods on the cluster. These constraints must be added to the cluster before deploying the microsoft.flux extension.
NS="flux-system"
oc adm policy add-scc-to-user nonroot system:serviceaccount:$NS:kustomize-controller
oc adm policy add-scc-to-user nonroot system:serviceaccount:$NS:helm-controller
oc adm policy add-scc-to-user nonroot system:serviceaccount:$NS:source-controller
oc adm policy add-scc-to-user nonroot system:serviceaccount:$NS:notification-controller
oc adm policy add-scc-to-user nonroot system:serviceaccount:$NS:image-automation-controller
oc adm policy add-scc-to-user nonroot system:serviceaccount:$NS:image-reflector-controller
For more information on OpenShift guidance for onboarding Flux, see the Flux documentation.
Work with parameters
Flux supports many parameters to enable various scenarios. For a description of all parameters that Flux supports, see the official Flux documentation. Flux in Azure doesn't support all parameters yet. Let us know if a parameter you need is missing from the Azure implementation.
For information about available parameters and how to use them, see GitOps (Flux v2) supported parameters.
Work with local secret authentication reference
To use a local secret authentication reference, the secret must exist within the same namespace where the fluxConfiguration will be deployed. The secret must also contain all of the authentication parameters needed for the source.
For information on creating secrets for various fluxConfiguration sources, see Local secret for authentication with source.
Manage cluster configuration by using the Flux Kustomize controller
The Flux Kustomize controller is installed as part of the microsoft.flux cluster extension. It allows the declarative management of cluster configuration and application deployment by using Kubernetes manifests synced from a Git repository. These Kubernetes manifests can optionally include a kustomize.yaml file.
For usage details, see the following resources:
- Flux Kustomize controller
- Kustomize reference documents
- The kustomization file
- Kustomize project
- Kustomize guides
Manage Helm chart releases by using the Flux Helm controller
The Flux Helm controller is installed as part of the microsoft.flux cluster extension. It allows you to declaratively manage Helm chart releases with Kubernetes manifests that you maintain in your Git repository.
For usage details, see the following resources:
- Flux for Helm users
- Manage Helm releases
- Migrate to Flux v2 Helm from Flux v1 Helm
- Flux Helm controller
Tip
Because of how Helm handles index files, processing Helm charts is an expensive operation and can have very high memory footprint. As a result, reconciling a large number of Helm charts at once can cause memory spikes and OOMKilled errors. By default, the controller sets its memory limit at 1Gi and its memory requests at 64Mi. To increase this limit and requests due to a high number of large Helm chart reconciliations, run the following command after installing the microsoft.flux extension:
az k8s-extension update -g <resource-group> -c <cluster-name> -n flux -t connectedClusters --config source-controller.resources.limits.memory=2Gi source-controller.resources.requests.memory=300Mi
Use the GitRepository source for Helm charts
If your Helm charts are stored in the GitRepository source that you configure as part of the fluxConfigurations resource, you can indicate that the configured source should be used as the source of the Helm charts by adding clusterconfig.azure.com/use-managed-source: "true" to your HelmRelease.yaml file, as shown in the following example:
---
apiVersion: helm.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v2beta1
kind: HelmRelease
metadata:
name: somename
namespace: somenamespace
annotations:
clusterconfig.azure.com/use-managed-source: "true"
spec:
...
When you use this annotation, the deployed HelmRelease is patched with the reference to the configured source. Currently, only GitRepository source is supported.
Helm drift detection
Drift detection for Helm releases isn't enabled by default. Starting with microsoft.flux v1.7.5, you can enable Helm drift detection by running the following command:
az k8s-extension update --resource-group <resource-group> --cluster-name <cluster-name> --name flux --cluster-type <cluster-type> --config helm-controller.detectDrift=true
Strict post-build variable substitution
Strict post-build variable substitution is available starting with microsoft.flux v1.13.1.
To create a Flux extension with strict substitution policy enabled, run this command:
az k8s-extension create --resource-group <resource-group> --cluster-name <cluster-name> --cluster-type <cluster-type> --name flux --extension-type microsoft.flux --config kustomize-controller.strict-substitution-mode=true
To update an existing Flux extension to enable strict substitution policy, run this command:
az k8s-extension update --resource-group <resource-group> --cluster-name <cluster-name> --cluster-type <cluster-type> --name flux --config kustomize-controller.strict-substitution-mode=true
Vertical scaling
Support for vertical scaling is available starting with microsoft.flux v1.12.0. Currently, only specific parameters described in the Flux vertical scaling documentation are natively supported. Other parameters may be manually applied to the cluster.
To increase resource limits on controllers beyond the current limits, run this command, changing the specific resource type and value as needed:
az k8s-extension update --resource-group <resource-group> --cluster-name <cluster-name> --cluster-type <cluster-type> --name flux --config kustomize-controller.resources.limits.memory=2Gi kustomize-controller.resources.limits.cpu=2000m
To increase the number of reconciliations that can be performed in parallel, run this command:
az k8s-extension update --resource-group <resource-group> --cluster-name <cluster-name> --cluster-type <cluster-type> --name flux --config kustomize-controller.concurrent=6 kustomize-controller.requeue-dependency=50s
To enable in-memory build, run this command:
az k8s-extension update --resource-group <resource-group> --cluster-name <cluster-name> --cluster-type <cluster-type> --name flux --config kustomize-controller.enable-in-memory-build=true
Helm OOM watch
Starting with microsoft.flux v1.7.5, you can enable Helm OOM watch. For more information, see Enable Helm near OOM detection.
Be sure to review potential remediation strategies and apply them as needed when enabling this feature.
To enable OOM watch, run the following command:
az k8s-extension update --resource-group <resource-group> --cluster-name <cluster-name> --name flux --cluster-type <cluster-type> --config helm-controller.outOfMemoryWatch.enabled=true helm-controller.outOfMemoryWatch.memoryThreshold=70 helm-controller.outOfMemoryWatch.interval=700ms
If you don't specify values for memoryThreshold and outOfMemoryWatch, the default memory threshold is set to 95%, with the interval at which to check the memory utilization set to 500 ms.
Configurable log-level parameters
By default, the log-level for Flux controllers is set to info. Starting with microsoft.flux v1.8.3, you can modify these default settings using the k8s-extension command as follows:
--config helm-controller.log-level=<info/error/debug>
--config source-controller.log-level=<info/error/debug>
--config kustomize-controller.log-level=<info/error/debug>
--config notification-controller.log-level=<info/error/debug>
--config image-automation-controller.log-level=<info/error/debug>
--config image-reflector-controller.log-level=<info/error/debug>
Valid values are debug, info, or error. For instance, to change the log-level for the source-controller and kustomize-controller, use the following command:
az k8s-extension update --resource-group <resource-group> --cluster-name <cluster-name> --cluster-type <cluster-type> --name flux --config source-controller.log-level=error kustomize-controller.log-level=error
Starting with microsoft.flux v1.9.1, fluxconfig-agent and fluxconfig-controller support info and error log levels (but not debug). These can be modified by using the k8s-extension command as follows:
--config fluxconfig-agent.log-level=<info/error>
--config fluxconfig-controller.log-level=<info/error>
For example, the following command changes log-level to error:
az k8s-extension update --resource-group <resource-group> --cluster-name <cluster-name> --cluster-type <cluster-type> --name flux --config fluxconfig-agent.log-level=error fluxconfig-controller.log-level=error
Azure DevOps SSH-RSA deprecation
Azure DevOps announced the deprecation of SSH-RSA as a supported encryption method for connecting to Azure repositories using SSH. If you use SSH keys to connect to Azure repositories in Flux configurations, we recommend moving to more secure RSA-SHA2-256 or RSA-SHA2-512 keys.
When reconciling Flux configurations, you might see an error message indicating ssh-rsa is about to be deprecated or is unsupported. If so, update the host key algorithm used to establish SSH connections to Azure DevOps repositories from the Flux source-controller and image-automation-controller (if enabled) by using the az k8s-extension update command. For example:
az k8s-extension update --cluster-name <cluster-name> --resource-group <resource-group> --cluster-type <cluster-type> --name flux --config source-controller.ssh-host-key-args="--ssh-hostkey-algos=rsa-sha2-512,rsa-sha2-256"
az k8s-extension update --cluster-name <cluster-name> --resource-group <resource-group> --cluster-type <cluster-type> --name flux --config image-automation-controller.ssh-host-key-args="--ssh-hostkey-algos=rsa-sha2-512,rsa-sha2-256"
For more information on Azure DevOps SSH-RSA deprecation, see End of SSH-RSA support for Azure Repos.
Configure annotation on Flux extension pods
When configuring a solution other than Azure Firewall, network and FQDN/application rules are required for an AKS cluster. Starting with microsoft.flux v1.11.1, Flux controller pods can now set the annotation kubernetes.azure.com/set-kube-service-host-fqdn in their pod specifications. This allows traffic to the API Server's domain name even when a Layer 7 firewall is present, facilitating deployments during extension installation. To configure this annotation when using the Flux extension, use the following commands.
# Create flux extension with annotation
az k8s-extension create --resource-group <resource-group> --cluster-name <cluster-name> --cluster-type <cluster-type> --name flux --extension-type microsoft.flux --config setKubeServiceHostFqdn=true
# Update flux extension with annotation
az k8s-extension update --resource-group <resource-group> --cluster-name <cluster-name> --cluster-type <cluster-type> --name flux --config setKubeServiceHostFqdn=true
Workload identity in AKS clusters
Starting with microsoft.flux v1.8.0, you can create Flux configurations in AKS clusters with workload identity enabled. To do so, modify the flux extension as shown in the following steps.
Retrieve the OIDC issuer URL for your cluster.
Create a managed identity and note its client ID.
Create the flux extension on the cluster, using the following command:
az k8s-extension create --resource-group <resource_group_name> --cluster-name <aks_cluster_name> --cluster-type managedClusters --name flux --extension-type microsoft.flux --config workloadIdentity.enable=true workloadIdentity.azureClientId=<user_assigned_client_id>Establish a federated identity credential. For example:
# For source-controller az identity federated-credential create --name ${FEDERATED_IDENTITY_CREDENTIAL_NAME} --identity-name "${USER_ASSIGNED_IDENTITY_NAME}" --resource-group "${RESOURCE_GROUP}" --issuer "${AKS_OIDC_ISSUER}" --subject system:serviceaccount:"flux-system":"source-controller" --audience api://AzureADTokenExchange # For image-reflector controller if you plan to enable it during extension creation, it is not deployed by default az identity federated-credential create --name ${FEDERATED_IDENTITY_CREDENTIAL_NAME} --identity-name "${USER_ASSIGNED_IDENTITY_NAME}" --resource-group "${RESOURCE_GROUP}" --issuer "${AKS_OIDC_ISSUER}" --subject system:serviceaccount:"flux-system":"image-reflector-controller" --audience api://AzureADTokenExchange # For kustomize-controller az identity federated-credential create --name ${FEDERATED_IDENTITY_CREDENTIAL_NAME} --identity-name "${USER_ASSIGNED_IDENTITY_NAME}" --resource-group "${RESOURCE_GROUP}" --issuer "${AKS_OIDC_ISSUER}" --subject system:serviceaccount:"flux-system":"kustomize-controller" --audience api://AzureADTokenExchangeMake sure the custom resource that needs to use workload identity sets
.spec.providervalue toazurein the manifest. For example:apiVersion: source.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1beta2 kind: HelmRepository metadata: name: acrrepo spec: interval: 10m0s type: <helm_repository_type> url: <helm_repository_link> provider: azureBe sure to provide proper permissions for workload identity for the resource that you want source-controller or image-reflector controller to pull. For example, if using Azure Container Registry,
AcrPullpermissions are required.
Delete the Flux configuration and extension
Use the following commands to delete your Flux configurations and, if desired, the Flux extension itself.
Delete the Flux configurations
The following command deletes both the fluxConfigurations resource in Azure and the Flux configuration objects in the cluster. Because the Flux configuration was originally created with the prune=true parameter for the kustomization, all of the objects created in the cluster based on manifests in the Git repository are removed when the Flux configuration is removed. However, this command doesn't remove the Flux extension itself.
az k8s-configuration flux delete -g flux-demo-rg -c flux-demo-arc -n cluster-config -t connectedClusters --yes
Delete the Flux cluster extension
When you delete the Flux extension, both the microsoft.flux extension resource in Azure and the Flux extension objects in the cluster are removed.
Important
Be sure to delete all Flux configurations in the cluster before you delete the Flux extension. Deleting the extension without first deleting the Flux configurations may leave your cluster in an unstable condition.
If the Flux extension was created automatically when the Flux configuration was first created, the extension name is flux.
az k8s-extension delete -g flux-demo-rg -c flux-demo-arc -n flux -t connectedClusters --yes
Tip
These commands use -t connectedClusters, which is appropriate for an Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes cluster. For an AKS cluster, use -t managedClusters instead.
Next steps
- Read more about configurations and GitOps.
- Learn how to use Azure Policy to enforce GitOps at scale.
- Learn about monitoring GitOps (Flux v2) status and activity.