Troubleshoot private endpoints
This guide can help you troubleshoot connectivity, operational, and cluster creation issues for a cluster using private endpoints. If you're experiencing connectivity issues to private endpoints, use the following troubleshooting guidance.
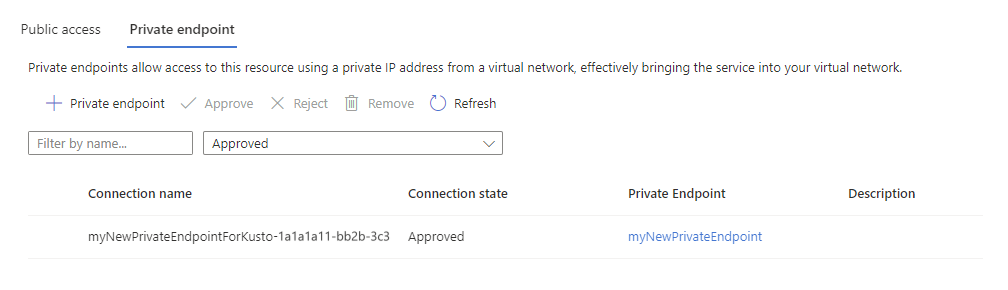
Check the connection state
Make sure that the private endpoint's connection state is set to approved.
In the Azure portal, navigate to your cluster and then select Networking
Select Private endpoint. In the table, in the Connection state column, verify that the private endpoint is approved.
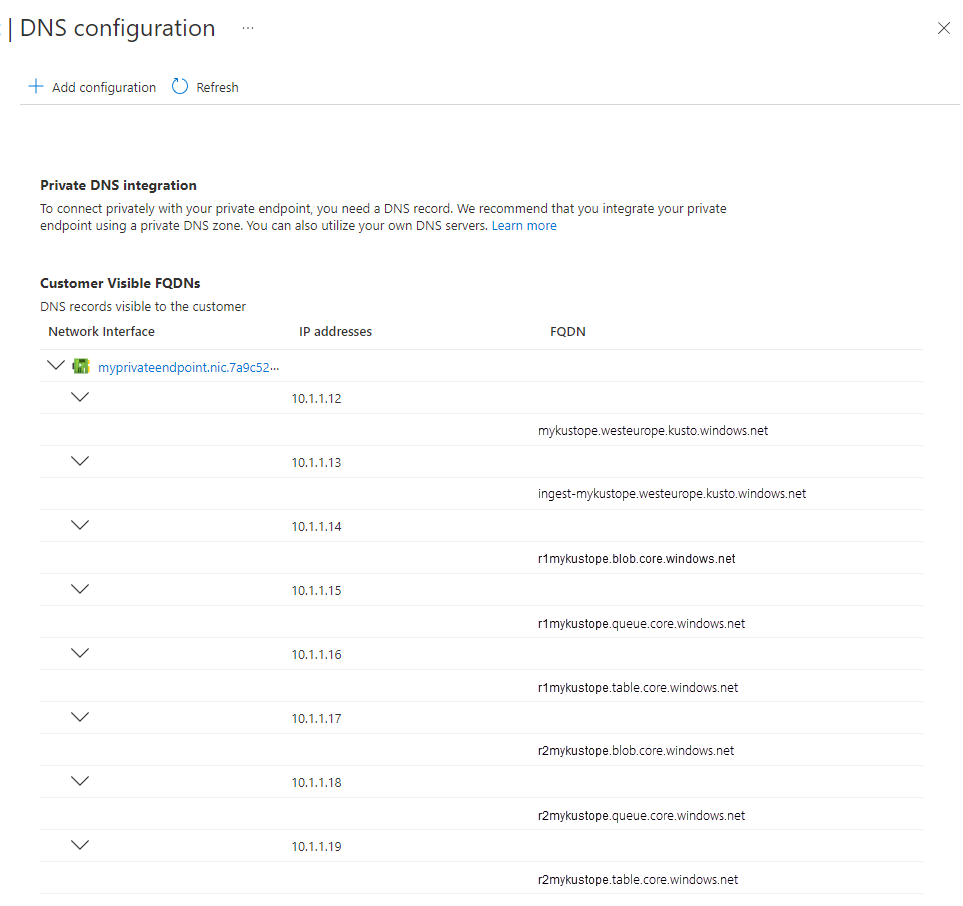
Run checks from within the virtual network
Use the following checks to investigate connectivity issues from within the same virtual network. We recommended deploying a virtual machine in the same virtual network where you created the private endpoint. Once you logged into the machine, you can run the following tests.
Check name resolution
Make sure that the name resolution is working properly.
Iterate over all FQDNs of the private endpoint DNS configuration and run the tests using nslookup, Test-NetConnection, or other similar tools to verify that each DNS matches its corresponding IP address.
Check DNS resolution
In addition, run the following command to verify that the DNS name of each FQDN matches its corresponding IP address.
#replace the <...> placeholders with the correct values
nslookup <cluster-name>.<cluster-region>.kusto.windows.net
#Results in the following output:
Server:'Server'
Address:'Address'
Non-authoritative answer:
<cluster-name>.<cluster-region>.kusto.windows.netcanonical name = <cluster-name>.privatelink.<cluster-region>.kusto.windows.net.
Name:<cluster-name>.privatelink.<cluster-region>.kusto.windows.net
Address: 'Address'
If you find an FQDN that doesn't match its corresponding IP address, you need to fix your custom DNS server. If you aren't using a custom DNS server, create a support ticket.
Connectivity checks
Check if you can establish a TCP connection every FQDN of the private endpoint DNS. Run the following tests on all FQDNs mentioned in the DNS configuration of the private endpoint.
#replace the <...> placeholders with the correct values
Test-NetConnection -ComputerName <cluster-name>.<cluster-region>.kusto.windows.net -Port 443
#Results in the following output:
ComputerName : <cluster-name>.<cluster-region>.kusto.windows.net
RemoteAddress : 'RemoteAddress'
RemotePort : 443
InterfaceAlias : Ethernet
SourceAddress : 'SourceAddress'
TcpTestSucceeded : True
A successful result returns TcpTestSucceeded : True, which means that the caller was able to establish a TCP connection to the cluster.
Check the health of the cluster
The last step of the troubleshooting is to test the health of the cluster.
#replace the <...> placeholders with the correct values
#engine
Invoke-RestMethod https://<cluster-name>.<cluster-region>.kusto.windows.net/v1/rest/ping
Pong! IP address: 'IPv6IPaddress1'
#data management
Invoke-RestMethod https://ingest-<cluster-name>.<cluster-region>.kusto.windows.net/v1/rest/ping
Pong! IP address: 'IPv6IPaddress2'
A successful result must return Pong! and an IPv6 address.
Other troubleshooting tips
If after trying all these checks you're still experiencing an issue, try using the private endpoint troubleshooting guide to diagnose it.
Troubleshoot managed private endpoints
For managed private endpoints, the only check you can do it to verify that the connection status of all managed private endpoint is Approved. Otherwise, the cluster won't be able to connect to the corresponding services.
To verify that the managed private endpoint's connection state is set to approved, do the following:
In the Azure portal, navigate to your cluster and then select Networking
Select Private endpoint connections. In the table, in the Connection state column, verify that the managed private endpoint is approved.
If you are unable to create a managed private endpoint, make sure the subscription is registered for the Microsoft.Network resource provider:
In the Azure portal, navigate to your subscription and then select Resource Providers
Search for Microsoft.Network and register the resource provider.
Other troubleshooting guidelines
If all the checks were successful and you still aren't able to establish a connection to the cluster, then you should contact your corporate security team that is responsible for firewalls and networking in general.
Potential reasons for failure include:
- Misconfiguration of the firewall appliance
- Misconfiguration of User Defined Routes in your Azure Virtual Network
- A misconfigured proxy on the client machine
- A misconfigured proxy between the client and the cluster