Copy and transform data in Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL by using Azure Data Factory
APPLIES TO:  Azure Data Factory
Azure Data Factory  Azure Synapse Analytics
Azure Synapse Analytics
Tip
Try out Data Factory in Microsoft Fabric, an all-in-one analytics solution for enterprises. Microsoft Fabric covers everything from data movement to data science, real-time analytics, business intelligence, and reporting. Learn how to start a new trial for free!
This article outlines how to use Copy Activity in Azure Data Factory to copy data from and to Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL, and use Data Flow to transform data in Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL. To learn more, read the introductory articles for Azure Data Factory and Azure Synapse Analytics.
Note
This connector only support Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL. For Azure Cosmos DB for MongoDB, refer to connector for Azure Cosmos DB for MongoDB. Other API types are not supported now.
Supported capabilities
This Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL connector is supported for the following capabilities:
| Supported capabilities | IR | Managed private endpoint |
|---|---|---|
| Copy activity (source/sink) | ① ② | ✓ |
| Mapping data flow (source/sink) | ① | ✓ |
| Lookup activity | ① ② | ✓ |
① Azure integration runtime ② Self-hosted integration runtime
For Copy activity, this Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL connector supports:
- Copy data from and to the Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL using key, service principal, or managed identities for Azure resources authentications.
- Write to Azure Cosmos DB as insert or upsert.
- Import and export JSON documents as-is, or copy data from or to a tabular dataset. Examples include a SQL database and a CSV file. To copy documents as-is to or from JSON files or to or from another Azure Cosmos DB collection, see Import and export JSON documents.
Data Factory and Synapse pipelines integrate with the Azure Cosmos DB bulk executor library to provide the best performance when you write to Azure Cosmos DB.
Tip
The Data Migration video walks you through the steps of copying data from Azure Blob storage to Azure Cosmos DB. The video also describes performance-tuning considerations for ingesting data to Azure Cosmos DB in general.
Get started
To perform the Copy activity with a pipeline, you can use one of the following tools or SDKs:
- The Copy Data tool
- The Azure portal
- The .NET SDK
- The Python SDK
- Azure PowerShell
- The REST API
- The Azure Resource Manager template
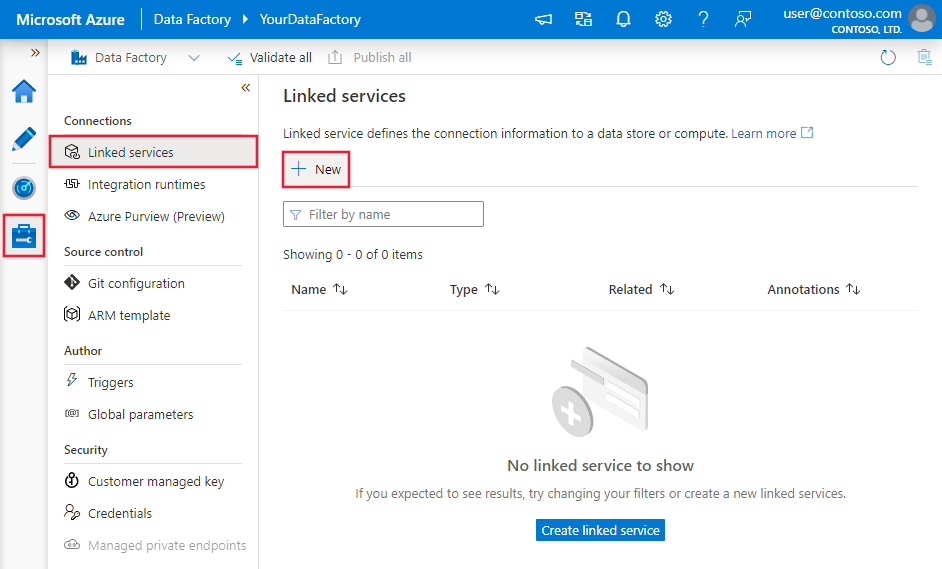
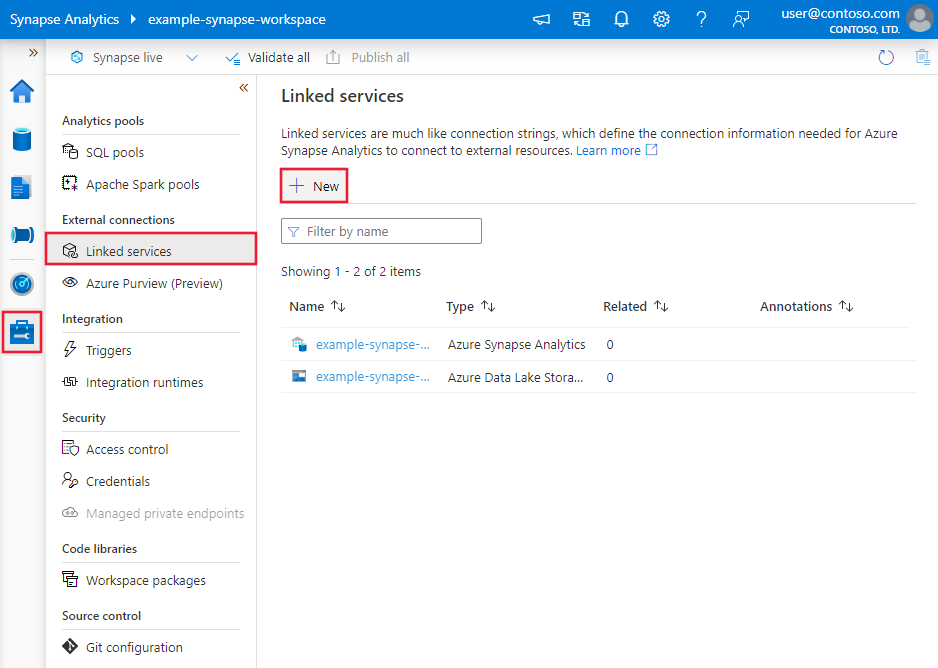
Create a linked service to Azure Cosmos DB using UI
Use the following steps to create a linked service to Azure Cosmos DB in the Azure portal UI.
Browse to the Manage tab in your Azure Data Factory or Synapse workspace and select Linked Services, then click New:
Search for Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL and select the Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL connector.

Configure the service details, test the connection, and create the new linked service.

Connector configuration details
The following sections provide details about properties you can use to define entities that are specific to Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL.
Linked service properties
The Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL connector supports the following authentication types. See the corresponding sections for details:
- Key authentication
- Service principal authentication
- System-assigned managed identity authentication
- User-assigned managed identity authentication
Key authentication
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property must be set to CosmosDb. | Yes |
| connectionString | Specify information that's required to connect to the Azure Cosmos DB database. Note: You must specify database information in the connection string as shown in the examples that follow. You can also put account key in Azure Key Vault and pull the accountKey configuration out of the connection string. Refer to the following samples and Store credentials in Azure Key Vault article with more details. |
Yes |
| connectVia | The Integration Runtime to use to connect to the data store. You can use the Azure Integration Runtime or a self-hosted integration runtime (if your data store is located in a private network). If this property isn't specified, the default Azure Integration Runtime is used. | No |
Example
{
"name": "CosmosDbSQLAPILinkedService",
"properties": {
"type": "CosmosDb",
"typeProperties": {
"connectionString": "AccountEndpoint=<EndpointUrl>;AccountKey=<AccessKey>;Database=<Database>"
},
"connectVia": {
"referenceName": "<name of Integration Runtime>",
"type": "IntegrationRuntimeReference"
}
}
}
Example: store account key in Azure Key Vault
{
"name": "CosmosDbSQLAPILinkedService",
"properties": {
"type": "CosmosDb",
"typeProperties": {
"connectionString": "AccountEndpoint=<EndpointUrl>;Database=<Database>",
"accountKey": {
"type": "AzureKeyVaultSecret",
"store": {
"referenceName": "<Azure Key Vault linked service name>",
"type": "LinkedServiceReference"
},
"secretName": "<secretName>"
}
},
"connectVia": {
"referenceName": "<name of Integration Runtime>",
"type": "IntegrationRuntimeReference"
}
}
}
Service principal authentication
Note
Currently, the service principal authentication is not supported in data flow.
To use service principal authentication, follow these steps.
Register an application with the Microsoft identity platform. To learn how, see Quickstart: Register an application with the Microsoft identity platform. Make note of these values, which you use to define the linked service:
- Application ID
- Application key
- Tenant ID
Grant the service principal proper permission. See examples on how permission works in Azure Cosmos DB from Access control lists on files and directories. More specifically, create a role definition, and assign the role to the service principal via service principal object ID.
These properties are supported for the linked service:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property must be set to CosmosDb. | Yes |
| accountEndpoint | Specify the account endpoint URL for the Azure Cosmos DB instance. | Yes |
| database | Specify the name of the database. | Yes |
| servicePrincipalId | Specify the application's client ID. | Yes |
| servicePrincipalCredentialType | The credential type to use for service principal authentication. Allowed values are ServicePrincipalKey and ServicePrincipalCert. | Yes |
| servicePrincipalCredential | The service principal credential. When you use ServicePrincipalKey as the credential type, specify the application's key. Mark this field as SecureString to store it securely, or reference a secret stored in Azure Key Vault. When you use ServicePrincipalCert as the credential, reference a certificate in Azure Key Vault, and ensure the certificate content type is PKCS #12. |
Yes |
| tenant | Specify the tenant information (domain name or tenant ID) under which your application resides. Retrieve it by hovering the mouse in the upper-right corner of the Azure portal. | Yes |
| azureCloudType | For service principal authentication, specify the type of Azure cloud environment to which your Microsoft Entra application is registered. Allowed values are AzurePublic, AzureChina, AzureUsGovernment, and AzureGermany. By default, the service's cloud environment is used. |
No |
| connectVia | The integration runtime to be used to connect to the data store. You can use the Azure integration runtime or a self-hosted integration runtime if your data store is in a private network. If not specified, the default Azure integration runtime is used. | No |
Example: using service principal key authentication
You can also store service principal key in Azure Key Vault.
{
"name": "CosmosDbSQLAPILinkedService",
"properties": {
"type": "CosmosDb",
"typeProperties": {
"accountEndpoint": "<account endpoint>",
"database": "<database name>",
"servicePrincipalId": "<service principal id>",
"servicePrincipalCredentialType": "ServicePrincipalKey",
"servicePrincipalCredential": {
"type": "SecureString",
"value": "<service principal key>"
},
"tenant": "<tenant info, e.g. microsoft.onmicrosoft.com>"
},
"connectVia": {
"referenceName": "<name of Integration Runtime>",
"type": "IntegrationRuntimeReference"
}
}
}
Example: using service principal certificate authentication
{
"name": "CosmosDbSQLAPILinkedService",
"properties": {
"type": "CosmosDb",
"typeProperties": {
"accountEndpoint": "<account endpoint>",
"database": "<database name>",
"servicePrincipalId": "<service principal id>",
"servicePrincipalCredentialType": "ServicePrincipalCert",
"servicePrincipalCredential": {
"type": "AzureKeyVaultSecret",
"store": {
"referenceName": "<AKV reference>",
"type": "LinkedServiceReference"
},
"secretName": "<certificate name in AKV>"
},
"tenant": "<tenant info, e.g. microsoft.onmicrosoft.com>"
},
"connectVia": {
"referenceName": "<name of Integration Runtime>",
"type": "IntegrationRuntimeReference"
}
}
}
System-assigned managed identity authentication
Note
Currently, the system-assigned managed identity authentication is supported in data flows through the use of advanced properties in JSON format.
A data factory or Synapse pipeline can be associated with a system-assigned managed identity for Azure resources, which represents this specific service instance. You can directly use this managed identity for Azure Cosmos DB authentication, similar to using your own service principal. It allows this designated resource to access and copy data to or from your Azure Cosmos DB instance.
To use system-assigned managed identities for Azure resource authentication, follow these steps.
Retrieve the system-assigned managed identity information by copying the value of the managed identity object ID generated along with your service.
Grant the system-assigned managed identity proper permission. See examples on how permission works in Azure Cosmos DB from Access control lists on files and directories. More specifically, create a role definition, and assign the role to the system-assigned managed identity.
These properties are supported for the linked service:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property must be set to CosmosDb. | Yes |
| accountEndpoint | Specify the account endpoint URL for the Azure Cosmos DB instance. | Yes |
| database | Specify the name of the database. | Yes |
| connectVia | The integration runtime to be used to connect to the data store. You can use the Azure integration runtime or a self-hosted integration runtime if your data store is in a private network. If not specified, the default Azure integration runtime is used. | No |
| subscriptionId | Specify the subscription id for the Azure Cosmos DB instance | No for Copy Activity, Yes for Mapping Data Flow |
| tenantId | Specify the tenant id for the Azure Cosmos DB instance | No for Copy Activity, Yes for Mapping Data Flow |
| resourceGroup | Specify the resource group name for the Azure Cosmos DB instance | No for Copy Activity, Yes for Mapping Data Flow |
Example:
{
"name": "CosmosDbSQLAPILinkedService",
"properties": {
"type": "CosmosDb",
"typeProperties": {
"accountEndpoint": "<account endpoint>",
"database": "<database name>",
"subscriptionId": "<subscription id>",
"tenantId": "<tenant id>",
"resourceGroup": "<resource group>"
},
"connectVia": {
"referenceName": "<name of Integration Runtime>",
"type": "IntegrationRuntimeReference"
}
}
}
User-assigned managed identity authentication
Note
Currently, user-assigned managed identity authentication is supported in data flows through the use of advanced properties in JSON format.
A data factory or Synapse pipeline can be associated with a user-assigned managed identities, which represents this specific service instance. You can directly use this managed identity for Azure Cosmos DB authentication, similar to using your own service principal. It allows this designated resource to access and copy data to or from your Azure Cosmos DB instance.
To use user-assigned managed identities for Azure resource authentication, follow these steps.
Create one or multiple user-assigned managed identities and grant the user-assigned managed identity proper permission. See examples on how permission works in Azure Cosmos DB from Access control lists on files and directories. More specifically, create a role definition, and assign the role to the user-assigned managed identity.
Assign one or multiple user-assigned managed identities to your data factory and create credentials for each user-assigned managed identity.
These properties are supported for the linked service:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property must be set to CosmosDb. | Yes |
| accountEndpoint | Specify the account endpoint URL for the Azure Cosmos DB instance. | Yes |
| database | Specify the name of the database. | Yes |
| credentials | Specify the user-assigned managed identity as the credential object. | Yes |
| connectVia | The integration runtime to be used to connect to the data store. You can use the Azure integration runtime or a self-hosted integration runtime if your data store is in a private network. If not specified, the default Azure integration runtime is used. | No |
| subscriptionId | Specify the subscription id for the Azure Cosmos DB instance | No for Copy Activity, Yes for Mapping Data Flow |
| tenantId | Specify the tenant id for the Azure Cosmos DB instance | No for Copy Activity, Yes for Mapping Data Flow |
| resourceGroup | Specify the resource group name for the Azure Cosmos DB instance | No for Copy Activity, Yes for Mapping Data Flow |
Example:
{
"name": "CosmosDbSQLAPILinkedService",
"properties": {
"type": "CosmosDb",
"typeProperties": {
"accountEndpoint": "<account endpoint>",
"database": "<database name>",
"credential": {
"referenceName": "credential1",
"type": "CredentialReference"
},
"subscriptionId": "<subscription id>",
"tenantId": "<tenant id>",
"resourceGroup": "<resource group>"
},
"connectVia": {
"referenceName": "<name of Integration Runtime>",
"type": "IntegrationRuntimeReference"
}
}
}
Dataset properties
For a full list of sections and properties that are available for defining datasets, see Datasets and linked services.
The following properties are supported for Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL dataset:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property of the dataset must be set to CosmosDbSqlApiCollection. | Yes |
| collectionName | The name of the Azure Cosmos DB document collection. | Yes |
If you use "DocumentDbCollection" type dataset, it is still supported as-is for backward compatibility for Copy and Lookup activity, it's not supported for Data Flow. You are suggested to use the new model going forward.
Example
{
"name": "CosmosDbSQLAPIDataset",
"properties": {
"type": "CosmosDbSqlApiCollection",
"linkedServiceName":{
"referenceName": "<Azure Cosmos DB linked service name>",
"type": "LinkedServiceReference"
},
"schema": [],
"typeProperties": {
"collectionName": "<collection name>"
}
}
}
Copy Activity properties
This section provides a list of properties that the Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL source and sink support. For a full list of sections and properties that are available for defining activities, see Pipelines.
Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL as source
To copy data from Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL, set the source type in Copy Activity to DocumentDbCollectionSource.
The following properties are supported in the Copy Activity source section:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property of the copy activity source must be set to CosmosDbSqlApiSource. | Yes |
| query | Specify the Azure Cosmos DB query to read data. Example: SELECT c.BusinessEntityID, c.Name.First AS FirstName, c.Name.Middle AS MiddleName, c.Name.Last AS LastName, c.Suffix, c.EmailPromotion FROM c WHERE c.ModifiedDate > \"2009-01-01T00:00:00\" |
No If not specified, this SQL statement is executed: select <columns defined in structure> from mycollection |
| preferredRegions | The preferred list of regions to connect to when retrieving data from Azure Cosmos DB. | No |
| pageSize | The number of documents per page of the query result. Default is "-1" which means uses the service side dynamic page size up to 1000. | No |
| detectDatetime | Whether to detect datetime from the string values in the documents. Allowed values are: true (default), false. | No |
If you use "DocumentDbCollectionSource" type source, it is still supported as-is for backward compatibility. You are suggested to use the new model going forward which provide richer capabilities to copy data from Azure Cosmos DB.
Example
"activities":[
{
"name": "CopyFromCosmosDBSQLAPI",
"type": "Copy",
"inputs": [
{
"referenceName": "<Cosmos DB for NoSQL input dataset name>",
"type": "DatasetReference"
}
],
"outputs": [
{
"referenceName": "<output dataset name>",
"type": "DatasetReference"
}
],
"typeProperties": {
"source": {
"type": "CosmosDbSqlApiSource",
"query": "SELECT c.BusinessEntityID, c.Name.First AS FirstName, c.Name.Middle AS MiddleName, c.Name.Last AS LastName, c.Suffix, c.EmailPromotion FROM c WHERE c.ModifiedDate > \"2009-01-01T00:00:00\"",
"preferredRegions": [
"East US"
]
},
"sink": {
"type": "<sink type>"
}
}
}
]
When copying data from Azure Cosmos DB, unless you want to export JSON documents as-is, the best practice is to specify the mapping in copy activity. The service honors the mapping you specified on the activity - if a row doesn't contain a value for a column, a null value is provided for the column value. If you don't specify a mapping, the service infers the schema by using the first row in the data. If the first row doesn't contain the full schema, some columns will be missing in the result of the activity operation.
Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL as sink
To copy data to Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL, set the sink type in Copy Activity to DocumentDbCollectionSink.
The following properties are supported in the Copy Activity sink section:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property of the Copy Activity sink must be set to CosmosDbSqlApiSink. | Yes |
| writeBehavior | Describes how to write data to Azure Cosmos DB. Allowed values: insert and upsert. The behavior of upsert is to replace the document if a document with the same ID already exists; otherwise, insert the document. Note: The service automatically generates an ID for a document if an ID isn't specified either in the original document or by column mapping. This means that you must ensure that, for upsert to work as expected, your document has an ID. |
No (the default is insert) |
| writeBatchSize | The service uses the Azure Cosmos DB bulk executor library to write data to Azure Cosmos DB. The writeBatchSize property controls the size of documents the service provides to the library. You can try increasing the value for writeBatchSize to improve performance and decreasing the value if your document size being large - see below tips. | No (the default is 10,000) |
| disableMetricsCollection | The service collects metrics such as Azure Cosmos DB RUs for copy performance optimization and recommendations. If you are concerned with this behavior, specify true to turn it off. |
No (default is false) |
| maxConcurrentConnections | The upper limit of concurrent connections established to the data store during the activity run. Specify a value only when you want to limit concurrent connections. | No |
Tip
To import JSON documents as-is, refer to Import or export JSON documents section; to copy from tabular-shaped data, refer to Migrate from relational database to Azure Cosmos DB.
Tip
Azure Cosmos DB limits single request's size to 2MB. The formula is Request Size = Single Document Size * Write Batch Size. If you hit error saying "Request size is too large.", reduce the writeBatchSize value in copy sink configuration.
If you use "DocumentDbCollectionSink" type source, it is still supported as-is for backward compatibility. You are suggested to use the new model going forward which provide richer capabilities to copy data from Azure Cosmos DB.
Example
"activities":[
{
"name": "CopyToCosmosDBSQLAPI",
"type": "Copy",
"inputs": [
{
"referenceName": "<input dataset name>",
"type": "DatasetReference"
}
],
"outputs": [
{
"referenceName": "<Document DB output dataset name>",
"type": "DatasetReference"
}
],
"typeProperties": {
"source": {
"type": "<source type>"
},
"sink": {
"type": "CosmosDbSqlApiSink",
"writeBehavior": "upsert"
}
}
}
]
Schema mapping
To copy data from Azure Cosmos DB to tabular sink or reversed, refer to schema mapping.
Mapping data flow properties
When transforming data in mapping data flow, you can read and write to collections in Azure Cosmos DB. For more information, see the source transformation and sink transformation in mapping data flows.
Note
The Azure Cosmos DB serverless is not supported in mapping data flow.
Source transformation
Settings specific to Azure Cosmos DB are available in the Source Options tab of the source transformation.
Include system columns: If true, id, _ts, and other system columns will be included in your data flow metadata from Azure Cosmos DB. When updating collections, it is important to include this so that you can grab the existing row ID.
Page size: The number of documents per page of the query result. Default is "-1" which uses the service dynamic page up to 1000.
Throughput: Set an optional value for the number of RUs you'd like to apply to your Azure Cosmos DB collection for each execution of this data flow during the read operation. Minimum is 400.
Preferred regions: Choose the preferred read regions for this process.
Change feed: If true, you will get data from Azure Cosmos DB change feed which is a persistent record of changes to a container in the order they occur from last run automatically. When you set it true, do not set both Infer drifted column types and Allow schema drift as true at the same time. For more details, see Azure Cosmos DB change feed).
Start from beginning: If true, you will get initial load of full snapshot data in the first run, followed by capturing changed data in next runs. If false, the initial load will be skipped in the first run, followed by capturing changed data in next runs. The setting is aligned with the same setting name in Azure Cosmos DB reference. For more details, see Azure Cosmos DB change feed.
Sink transformation
Settings specific to Azure Cosmos DB are available in the Settings tab of the sink transformation.
Update method: Determines what operations are allowed on your database destination. The default is to only allow inserts. To update, upsert, or delete rows, an alter-row transformation is required to tag rows for those actions. For updates, upserts and deletes, a key column or columns must be set to determine which row to alter.
Collection action: Determines whether to recreate the destination collection prior to writing.
- None: No action will be done to the collection.
- Recreate: The collection will get dropped and recreated
Batch size: An integer that represents how many objects are being written to Azure Cosmos DB collection in each batch. Usually, starting with the default batch size is sufficient. To further tune this value, note:
- Azure Cosmos DB limits single request's size to 2MB. The formula is "Request Size = Single Document Size * Batch Size". If you hit error saying "Request size is too large", reduce the batch size value.
- The larger the batch size, the better throughput the service can achieve, while make sure you allocate enough RUs to empower your workload.
Partition key: Enter a string that represents the partition key for your collection. Example: /movies/title
Throughput: Set an optional value for the number of RUs you'd like to apply to your Azure Cosmos DB collection for each execution of this data flow. Minimum is 400.
Write throughput budget: An integer that represents the RUs you want to allocate for this Data Flow write operation, out of the total throughput allocated to the collection.
Note
To limit the RU usage, please set the Cosmos DB Throughput(autoscale) to Manual.
Lookup activity properties
To learn details about the properties, check Lookup activity.
Import and export JSON documents
You can use this Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL connector to easily:
- Copy documents between two Azure Cosmos DB collections as-is.
- Import JSON documents from various sources to Azure Cosmos DB, including from Azure Blob storage, Azure Data Lake Store, and other file-based stores that the service supports.
- Export JSON documents from an Azure Cosmos DB collection to various file-based stores.
To achieve schema-agnostic copy:
- When you use the Copy Data tool, select the Export as-is to JSON files or Azure Cosmos DB collection option.
- When you use activity authoring, choose JSON format with the corresponding file store for source or sink.
Migrate from relational database to Azure Cosmos DB
When migrating from a relational database e.g. SQL Server to Azure Cosmos DB, copy activity can easily map tabular data from source to flatten JSON documents in Azure Cosmos DB. In some cases, you may want to redesign the data model to optimize it for the NoSQL use-cases according to Data modeling in Azure Cosmos DB, for example, to de-normalize the data by embedding all of the related sub-items within one JSON document. For such case, refer to this article with a walk-through on how to achieve it using the copy activity.
Azure Cosmos DB change feed
Azure Data Factory can get data from Azure Cosmos DB change feed by enabling it in the mapping data flow source transformation. With this connector option, you can read change feeds and apply transformations before loading transformed data into destination datasets of your choice. You do not have to use Azure functions to read the change feed and then write custom transformations. You can use this option to move data from one container to another, prepare change feed driven material views for fit purpose or automate container backup or recovery based on change feed, and enable many more such use cases using visual drag and drop capability of Azure Data Factory.
Make sure you keep the pipeline and activity name unchanged, so that the checkpoint can be recorded by ADF for you to get changed data from the last run automatically. If you change your pipeline name or activity name, the checkpoint will be reset, which leads you to start from beginning or get changes from now in the next run.
When you debug the pipeline, this feature works the same. Be aware that the checkpoint will be reset when you refresh your browser during the debug run. After you are satisfied with the pipeline result from debug run, you can go ahead to publish and trigger the pipeline. At the moment when you first time trigger your published pipeline, it automatically restarts from the beginning or gets changes from now on.
In the monitoring section, you always have the chance to rerun a pipeline. When you are doing so, the changed data is always captured from the previous checkpoint of your selected pipeline run.
In addition, Azure Cosmos DB analytical store now supports Change Data Capture (CDC) for Azure Cosmos DB API for NoSQL and Azure Cosmos DB API for Mongo DB (public preview). Azure Cosmos DB analytical store allows you to efficiently consume a continuous and incremental feed of changed (inserted, updated, and deleted) data from analytical store.
Related content
For a list of data stores that Copy Activity supports as sources and sinks, see supported data stores.