Nata
Norint pasiekti šį puslapį, reikalingas leidimas. Galite pabandyti prisijungti arba pakeisti katalogus.
Norint pasiekti šį puslapį, reikalingas leidimas. Galite pabandyti pakeisti katalogus.
This quickstart shows you how to create and run a Stream Analytics job using Azure Stream Analytics tools for Visual Studio. The example job reads streaming data from an IoT Hub device. You define a job that calculates the average temperature when over 27° and writes the resulting output events to a new file in blob storage.
Note
- We strongly recommend using Stream Analytics tools for Visual Studio Code for best local development experience. There are known feature gaps in Stream Analytics tools for Visual Studio 2019 (version 2.6.3000.0) and it won't be improved going forward.
- Visual Studio and Visual Studio Code tools don't support jobs in the China East, China North, Germany Central, and Germany NorthEast regions.
Before you begin
If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a free account.
Sign in to the Azure portal.
Install Visual Studio 2019, Visual Studio 2015, or Visual Studio 2013 Update 4. Enterprise (Ultimate/Premium), Professional, and Community editions are supported. Express edition isn't supported.
Follow the installation instructions to install Stream Analytics tools for Visual Studio.
Prepare the input data
Before defining the Stream Analytics job, you should prepare the data, which is later configured as the job input. To prepare the input data required by the job, complete the following steps:
Sign in to the Azure portal.
Select Create a resource > Internet of Things > IoT Hub.
In the IoT Hub pane, enter the following information:
Setting Suggested value Description Subscription <Your subscription> Select the Azure subscription that you want to use. Resource group asaquickstart-resourcegroup Select Create New and enter a new resource-group name for your account. IoT Hub Name MyASAIoTHub Select a name for your IoT Hub. Region <Select the region that is closest to your users> Select a geographic location where you can host your IoT Hub. Use the location that's closest to your users. Tier Free For this quickstart, select Free if it's still available on your subscription. If the free tier is unavailable, choose the lowest tier available. For more information, see IoT Hub pricing. 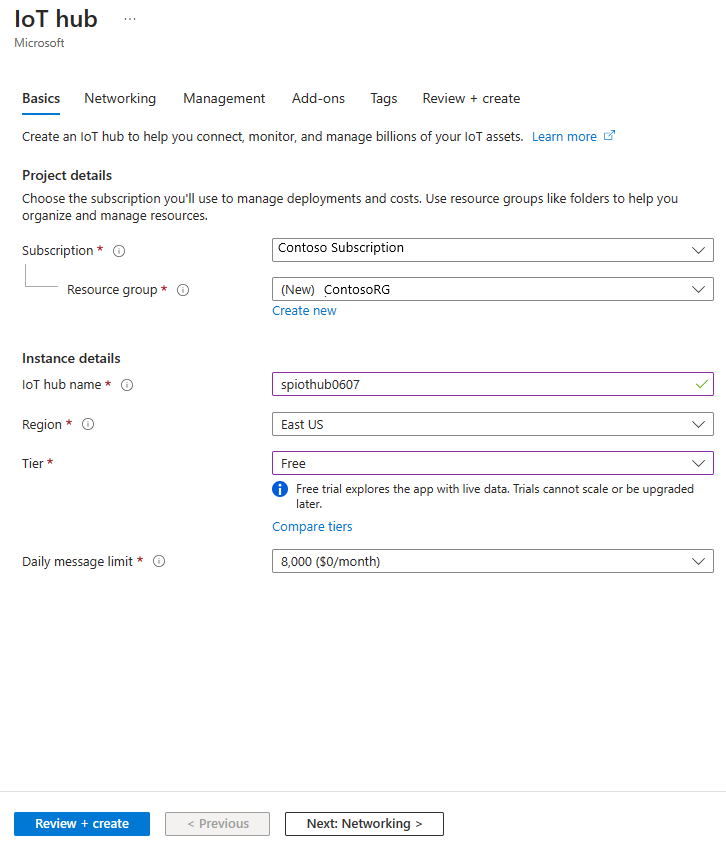
Select Review + create. Review your IoT Hub information and select Create. Your IoT Hub might take a few minutes to create. You can monitor the progress in the Notifications pane.
After the deployment completes, select Go to resource to navigate to the IoT Hub page for your IoT hub.
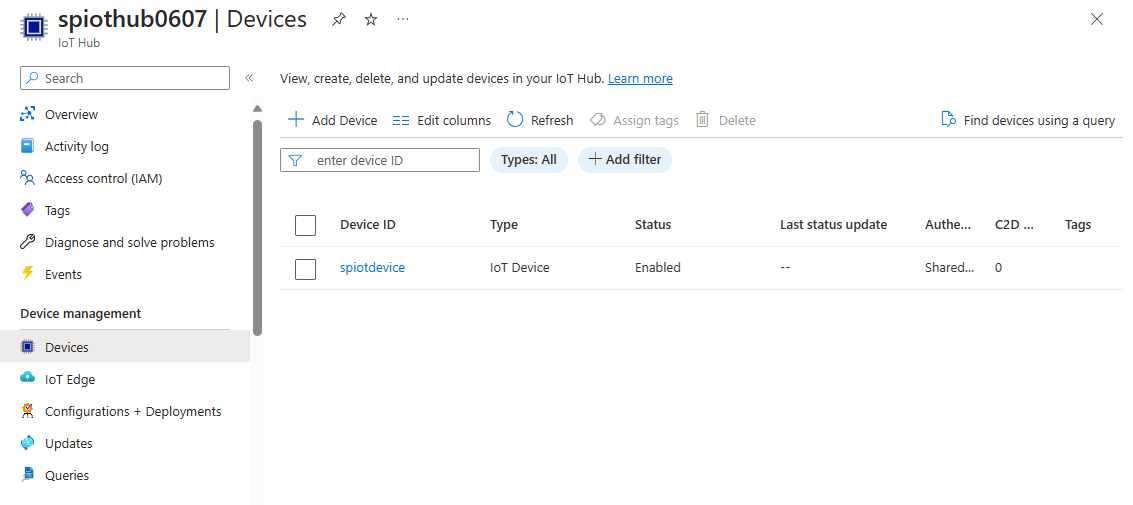
On the IoT Hub page, select Devices under Device management on the left navigation menu.
On the Devices page, select + Add device on the toolbar.
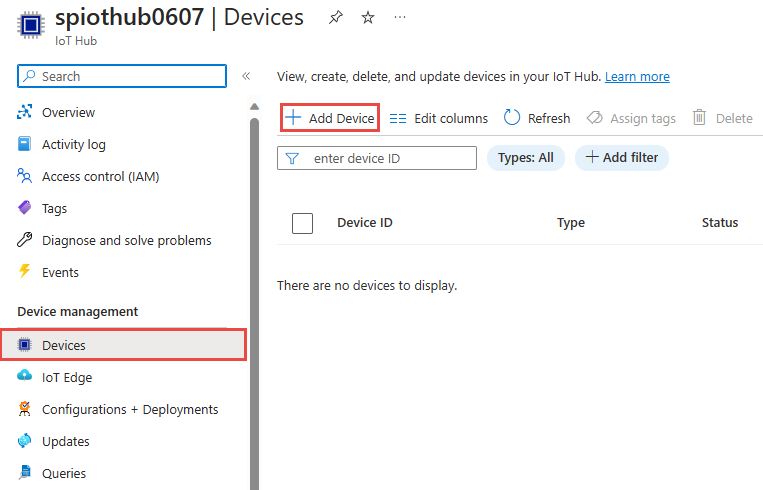
On the Create a device page, enter a name for the device, and select Save.
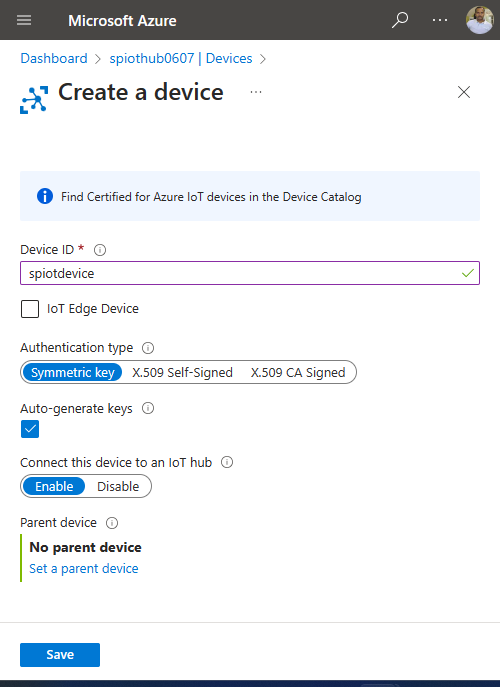
Once the device is created, open the device from the IoT devices list. If you don't see the device yet, refresh the page.
Copy the Primary connection string and save it to a notepad to use later.
Create blob storage
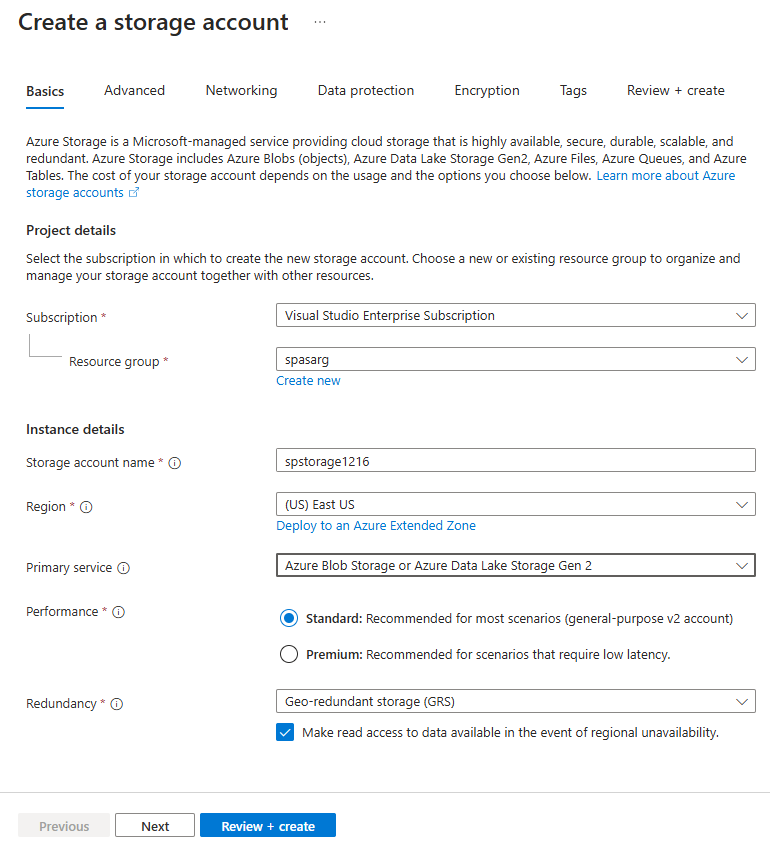
From the upper left-hand corner of the Azure portal, select Create a resource > Storage > Storage account.
In the Create storage account pane, enter a storage account name, location, and resource group. Choose the same location and resource group as the IoT Hub you created. Then select Review + create to create the account.
Once your storage account is created, select the Blob service tile on the Overview pane.
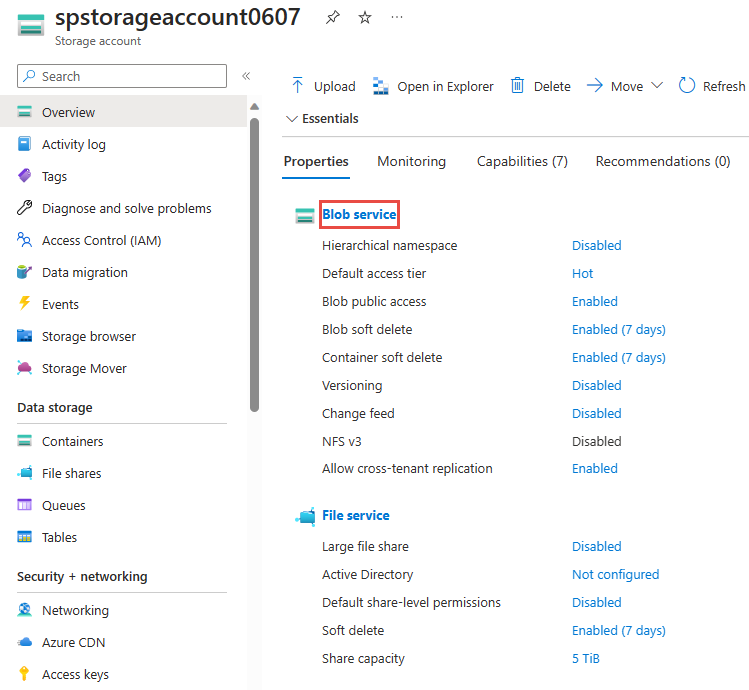
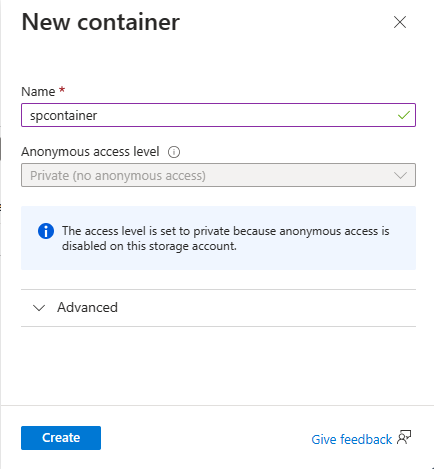
On the Blob service page, select + Container on the toolbar.
On the New container page, enter a name for your container, such as container1. Leave the Public access level as Private (no anonymous access) and select Create.
Create a Stream Analytics project
Start Visual Studio.
Select File > New Project.
In the templates list on the left, select Stream Analytics, and then select Azure Stream Analytics Application.
Input the project Name, Location, and Solution name, and select Create.

Notice the elements that are included in an Azure Stream Analytics project.
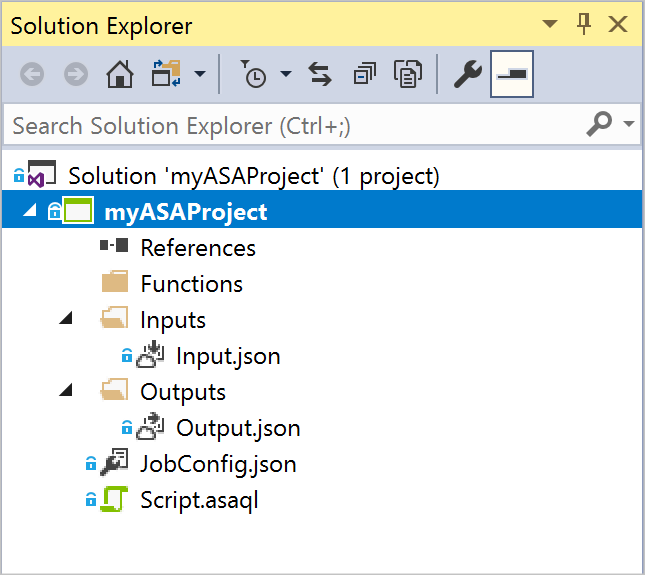
Choose the required subscription
- In Visual Studio, on the View menu, select Server Explorer.
- Right click on Azure, select Connect to Microsoft Azure Subscription, and then sign in with your Azure account.
Define input
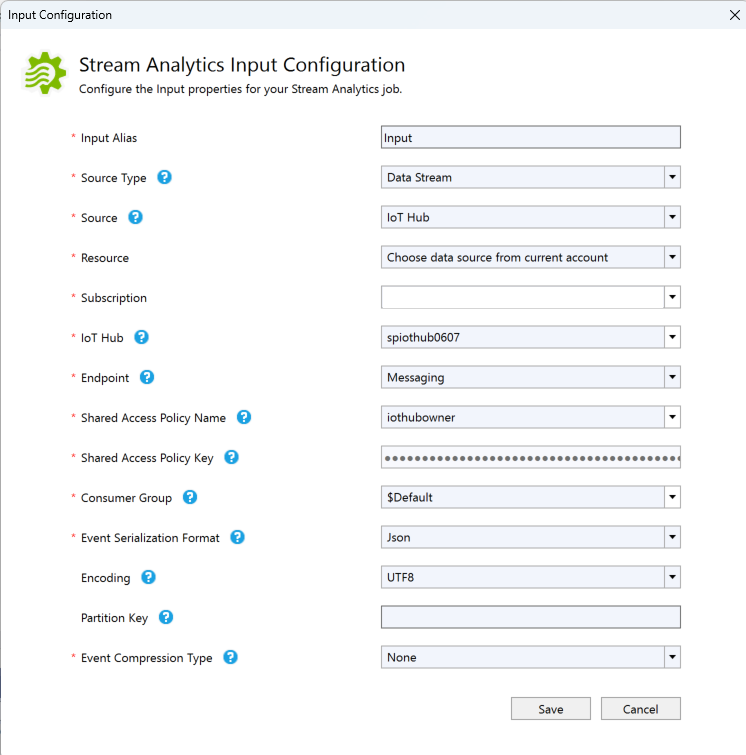
In Solution Explorer, expand the Inputs node and double-click Input.json.
Fill out the Stream Analytics Input Configuration with the following values:
Setting Suggested value Description Input Alias Input Enter a name to identify the job’s input. Source Type Data Stream Choose the appropriate input source: Data Stream or Reference Data. Source IoT Hub Choose the appropriate input source. Resource Choose data source from current account Choose to enter data manually or select an existing account. Subscription <Your subscription> Select the Azure subscription that has the IoT Hub you created. IoT Hub MyASAIoTHub Choose or enter the name of your IoT Hub. IoT Hub names are automatically detected if they're created in the same subscription. Leave other options to default values and select Save to save the settings.
Define output
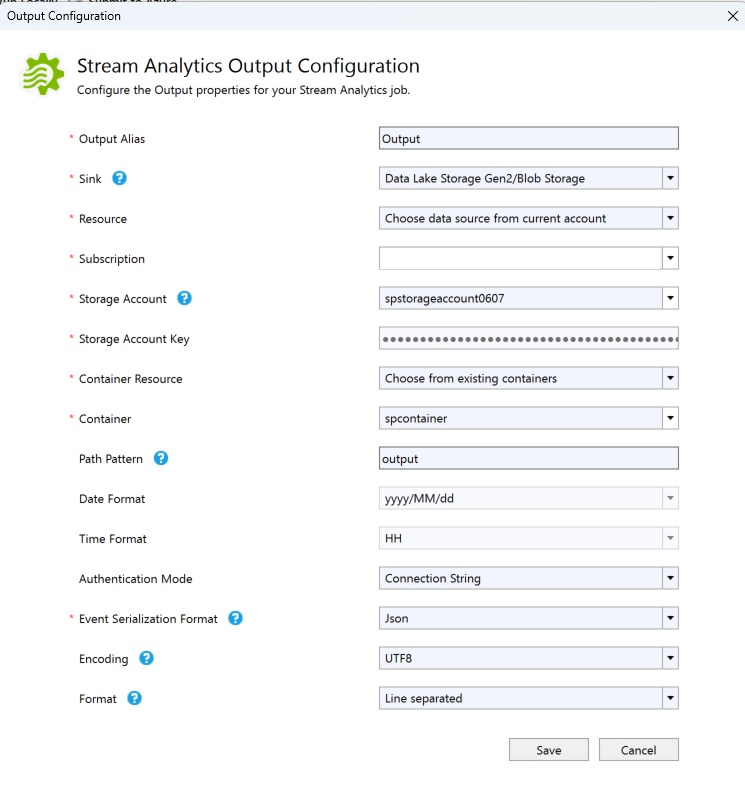
In Solution Explorer, expand the Outputs node and double-click Output.json.
Fill out the Stream Analytics Output Configuration with the following values:
Setting Suggested value Description Output Alias Output Enter a name to identify the job’s output. Sink Data Lake Storage Gen 2/Blob Storage Choose the appropriate sink. Resource Provide data source settings manually Choose to enter data manually or select an existing account. Subscription <Your subscription> Select the Azure subscription that has the storage account you created. The storage account can be in the same or in a different subscription. This example assumes that you have created storage account in the same subscription. Storage Account asaquickstartstorage Choose or enter the name of the storage account. Storage account names are automatically detected if they're created in the same subscription. Container container1 Select the existing container that you created in your storage account. Path Pattern output Enter the name of a file path to be created within the container. Leave other options to default values and select Save to save the settings.
Define the transformation query
Open Script.asaql from Solution Explorer in Visual Studio.
Add the following query:
SELECT * INTO Output FROM Input WHERE Temperature > 27
Submit a Stream Analytics query to Azure
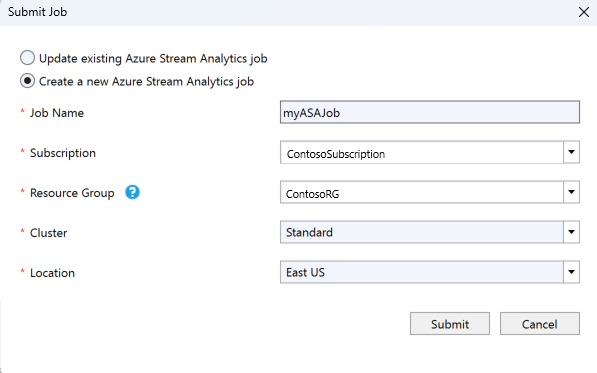
In the Query Editor, select Submit To Azure in the script editor.
In the Submit Job window, select Create a New Azure Stream Analytics job.
Enter a Job Name.
Choose the Azure Subscription.
Choose the Resource Group.
Keep the default value for Cluster.
Select the Location you used at the beginning of the Quickstart.
Then, select Submit.
Run the IoT simulator
Open the Raspberry Pi Azure IoT Online Simulator in a new browser tab or window.
Replace the placeholder in Line 15 with the Azure IoT Hub device connection string you saved in a previous section.
Select Run. The output should show the sensor data and messages that are being sent to your IoT Hub.

Start the Stream Analytics job and check output
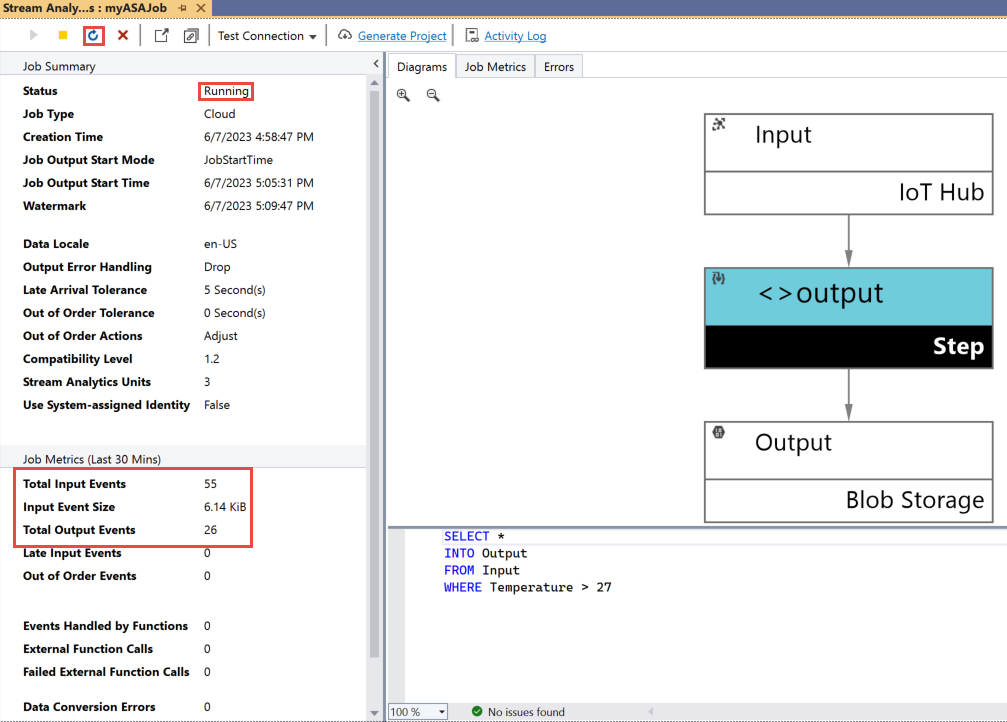
When your job is created, the job view opens automatically. Select the green arrow button to start the job,
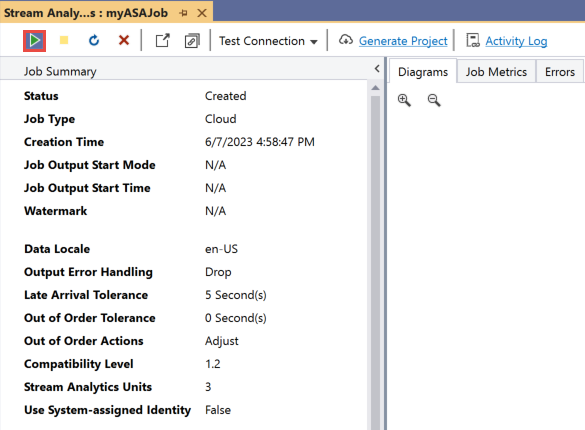
Change the Job output start mode to JobStartTime and select Start.
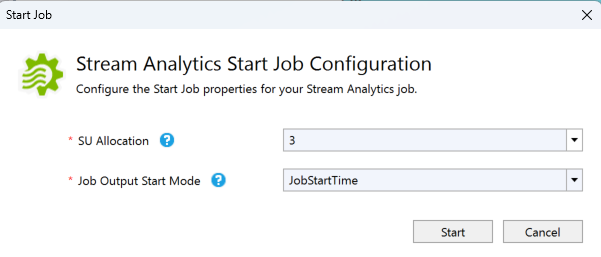
Note the job status has changed to Running, and there are input/output events. This may take a few minutes. Select the Refresh button on the toolbar to refresh metrics.
To view results, on the View menu, select Cloud Explorer, and navigate to the storage account in your resource group. Under Blob Containers, double-click container1, and then the output file path.

Clean up resources
When no longer needed, delete the resource group, the streaming job, and all related resources. Deleting the job avoids billing the streaming units consumed by the job. If you're planning to use the job in future, you can stop it and restart it later when you need. If you aren't going to continue to use this job, delete all resources created by this quickstart by using the following steps:
- From the left-hand menu in the Azure portal, select Resource groups and then select the name of the resource you created.
- On your resource group page, select Delete, type the name of the resource to delete in the text box, and then select Delete.
Next steps
In this quickstart, you deployed a simple Stream Analytics job using Visual Studio. You can also deploy Stream Analytics jobs using the Azure portal and PowerShell.
To learn about Azure Stream Analytics tools for Visual Studio, continue to the following article: