Create a route-based VPN gateway using CLI
This article helps you quickly create a route-based Azure VPN gateway using the Azure CLI. A VPN gateway is used when creating a VPN connection to your on-premises network. You can also use a VPN gateway to connect VNets.
In this article you'll create a VNet, a subnet, a gateway subnet, and a route-based VPN gateway (virtual network gateway). Creating a gateway can often take 45 minutes or more, depending on the selected gateway SKU. Once the gateway creation has completed, you can then create connections. These steps require an Azure subscription.
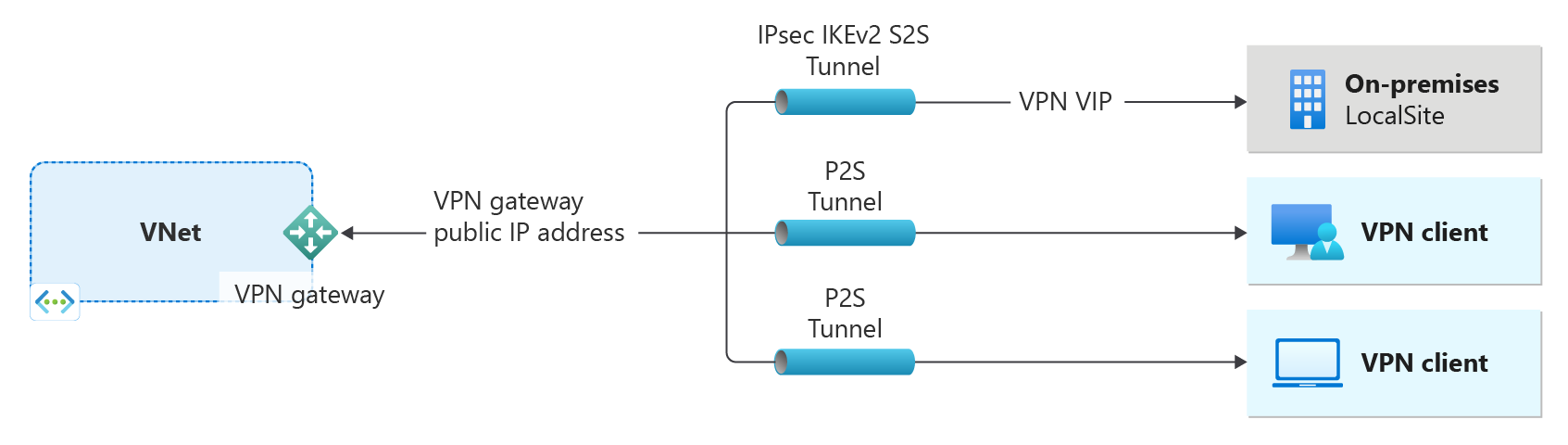
A VPN gateway is just one part of a connection architecture to help you securely access resources within a virtual network.
- The left side of the diagram shows the virtual network and the VPN gateway that you create by using the steps in this article.
- You can later add different types of connections, as shown on the right side of the diagram. For example, you can create site-to-site and point-to-site connections. To view different design architectures that you can build, see VPN gateway design.
If you don't have an Azure subscription, create an Azure free account before you begin.
Prerequisites
Use the Bash environment in Azure Cloud Shell. For more information, see Quickstart for Bash in Azure Cloud Shell.
If you prefer to run CLI reference commands locally, install the Azure CLI. If you're running on Windows or macOS, consider running Azure CLI in a Docker container. For more information, see How to run the Azure CLI in a Docker container.
If you're using a local installation, sign in to the Azure CLI by using the az login command. To finish the authentication process, follow the steps displayed in your terminal. For other sign-in options, see Sign in with the Azure CLI.
When you're prompted, install the Azure CLI extension on first use. For more information about extensions, see Use extensions with the Azure CLI.
Run az version to find the version and dependent libraries that are installed. To upgrade to the latest version, run az upgrade.
- This article requires version 2.0.4 or later of the Azure CLI. If using Azure Cloud Shell, the latest version is already installed.
Create a resource group
Create a resource group using the az group create command. A resource group is a logical container into which Azure resources are deployed and managed.
az group create --name TestRG1 --location eastus
Create a virtual network
Create a virtual network using the az network vnet create command. The following example creates a virtual network named VNet1 in the EastUS location:
az network vnet create \
-n VNet1 \
-g TestRG1 \
-l eastus \
--address-prefix 10.1.0.0/16 \
--subnet-name Frontend \
--subnet-prefix 10.1.0.0/24
Add a gateway subnet
The gateway subnet contains the reserved IP addresses that the virtual network gateway services use. Use the following examples to add a gateway subnet:
az network vnet subnet create \
--vnet-name VNet1 \
-n GatewaySubnet \
-g TestRG1 \
--address-prefix 10.1.255.0/27
Request a public IP address
A VPN gateway must have a public IP address. The public IP address is allocated to the VPN gateway that you create for your virtual network. Use the following example to request a public IP address using the az network public-ip create command:
az network public-ip create \
-n VNet1GWIP \
-g TestRG1 \
Create the VPN gateway
Create the VPN gateway using the az network vnet-gateway create command.
If you run this command by using the --no-wait parameter, you don't see any feedback or output. The --no-wait parameter allows the gateway to be created in the background. It doesn't mean that the VPN gateway is created immediately.
az network vnet-gateway create \
-n VNet1GW \
-l eastus \
--public-ip-address VNet1GWIP \
-g TestRG1 \
--vnet VNet1 \
--gateway-type Vpn \
--sku VpnGw2 \
--vpn-gateway-generation Generation2 \
--no-wait
A VPN gateway can take 45 minutes or more to create.
View the VPN gateway
az network vnet-gateway show \
-n VNet1GW \
-g TestRG1
The response looks similar to this:
{
"activeActive": false,
"bgpSettings": {
"asn": 65515,
"bgpPeeringAddress": "10.1.255.30",
"bgpPeeringAddresses": [
{
"customBgpIpAddresses": [],
"defaultBgpIpAddresses": [
"10.1.255.30"
],
"ipconfigurationId": "/subscriptions/<subscription ID>/resourceGroups/TestRG1/providers/Microsoft.Network/virtualNetworkGateways/VNet1GW/ipConfigurations/vnetGatewayConfig0",
"tunnelIpAddresses": [
"20.228.164.35"
]
}
],
"peerWeight": 0
},
"disableIPSecReplayProtection": false,
"enableBgp": false,
"enableBgpRouteTranslationForNat": false,
"enablePrivateIpAddress": false,
"etag": "W/\"6c61f8cb-d90f-4796-8697\"",
"gatewayType": "Vpn",
"id": "/subscriptions/<subscription ID>/resourceGroups/TestRG1/providers/Microsoft.Network/virtualNetworkGateways/VNet1GW",
"ipConfigurations": [
{
"etag": "W/\"6c61f8cb-d90f-4796-8697\"",
"id": "/subscriptions/<subscription ID>/resourceGroups/TestRG1/providers/Microsoft.Network/virtualNetworkGateways/VNet1GW/ipConfigurations/vnetGatewayConfig0",
"name": "vnetGatewayConfig0",
"privateIPAllocationMethod": "Dynamic",
"provisioningState": "Succeeded",
"publicIPAddress": {
"id": "/subscriptions/<subscription ID>/resourceGroups/TestRG1/providers/Microsoft.Network/publicIPAddresses/VNet1GWIP",
"resourceGroup": "TestRG1"
},
"resourceGroup": "TestRG1",
"subnet": {
"id": "/subscriptions/<subscription ID>/resourceGroups/TestRG1/providers/Microsoft.Network/virtualNetworks/VNet1/subnets/GatewaySubnet",
"resourceGroup": "TestRG1"
}
}
],
"location": "eastus",
"name": "VNet1GW",
"natRules": [],
"provisioningState": "Succeeded",
"resourceGroup": "TestRG1",
"resourceGuid": "69c269e3-622c-4123-9231",
"sku": {
"capacity": 2,
"name": "VpnGw2",
"tier": "VpnGw2"
},
"type": "Microsoft.Network/virtualNetworkGateways",
"vpnGatewayGeneration": "Generation2",
"vpnType": "RouteBased"
}
View the public IP address
To view the public IP address assigned to your gateway, use the following example:
az network public-ip show \
--name VNet1GWIP \
--resource-group TestRG1
The value associated with the ipAddress field is the public IP address of your VPN gateway.
Example response:
{
"dnsSettings": null,
"etag": "W/\"69c269e3-622c-4123-9231\"",
"id": "/subscriptions/<subscription ID>/resourceGroups/TestRG1/providers/Microsoft.Network/publicIPAddresses/VNet1GWIP",
"idleTimeoutInMinutes": 4,
"ipAddress": "13.90.195.184",
"ipConfiguration": {
"etag": null,
"id": "/subscriptions/<subscription ID>/resourceGroups/TestRG1/providers/Microsoft.Network/virtualNetworkGateways/VNet1GW/ipConfigurations/vnetGatewayConfig0",
Clean up resources
When you no longer need the resources you created, use az group delete to delete the resource group. This deletes the resource group and all of the resources it contains.
az group delete --name TestRG1 --yes
Next steps
Once the gateway has finished creating, you can create a connection between your virtual network and another VNet. Or, create a connection between your virtual network and an on-premises location.