Nata
Norint pasiekti šį puslapį, reikalingas leidimas. Galite pabandyti prisijungti arba pakeisti katalogus.
Norint pasiekti šį puslapį, reikalingas leidimas. Galite pabandyti pakeisti katalogus.
You can view, export, and download transcripts of customer interactions with your agent in both Power Apps and Copilot Studio. The information that each app exports is slightly different.
Important
Makers with the Environment maker role don't automatically have access to transcripts.
This article covers downloading conversation transcripts in Power Apps and using them to create reports in Power BI. To download transcripts directly in Copilot Studio, see Download conversation transcripts in Copilot Studio.
By default, Power Apps downloads conversation transcripts from the last 30 days. You can change the retention period.
Note
Agent responses that use SharePoint as a knowledge source and use documents that include sensitive data are not included in the conversation transcript.
Conversation transcripts aren't written for:
- Microsoft Dataverse for Teams environments
- Dataverse developer environments
- Microsoft 365 Copilot agents
Prerequisite
- To view conversation transcripts, you need the Bot Transcript Viewer security role. Only admins can grant the Bot Transcript Viewer security role.
View and export conversation transcripts from the Power Apps portal
Sign in to Power Apps.
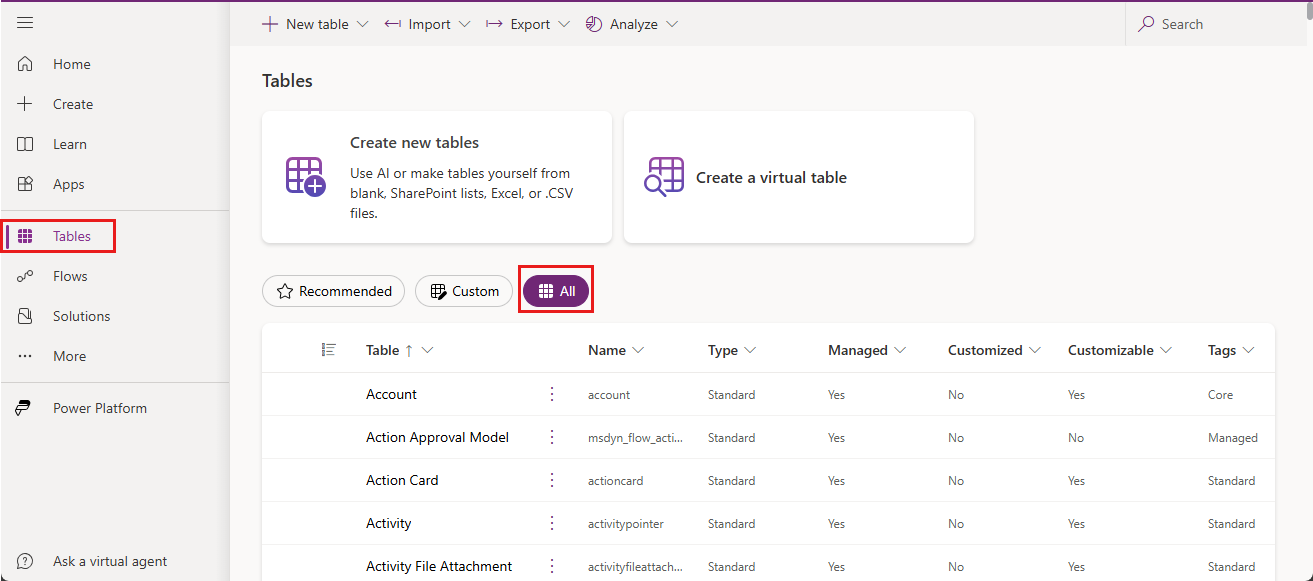
In the side pane, select Tables, and then select All.
Enter "conversation" in the Search box.
Select the ConversationTranscript table.
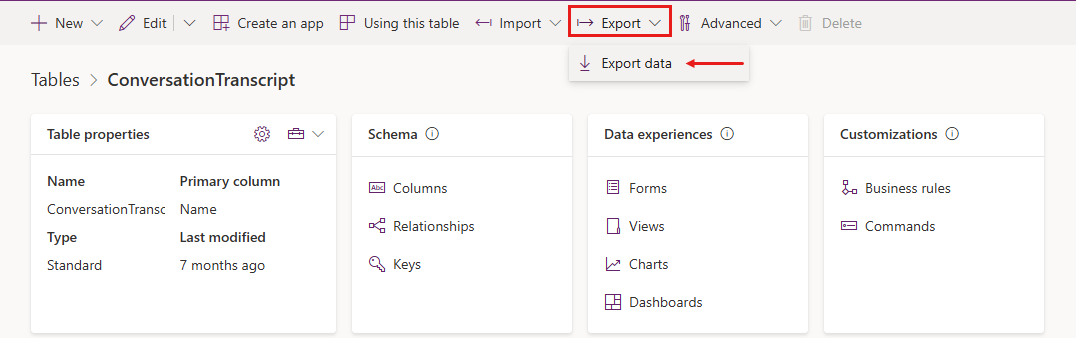
A page for the ConversationTranscript table opens.
On the top menu bar, select Export > Export data.
It takes a few minutes to compile the data for export.
Wait a couple of minutes for Power Apps to prepare the data for export, and then select Download exported data.
The file is saved as a ZIP archive to your browser's default download location.
Understand conversation transcripts
The conversation transcript exists as a Dataverse table you can download as a CSV (comma-separated values) file. The logic that determines when and how the system records information to conversation transcripts is:
- The system saves a conversation to a transcript record after 30 minutes of inactivity. If the conversation resumes after the inactivity time, the system saves the new activities to a new record with the same
Namevalue but with a newConversationStartTimevalue. - For agents published to the Telephony channel, conversations time out three minutes after an End Conversation event.
- Each record has a limit of 1 MB for the transcript (
Contentcolumn). When a transcript is larger than this limit, the system splits the transcript into multiple records, all having the sameNameandConversationStartTimevalues, but with differentMetadata.BatchIdvalues. - To merge transcripts, take all records with the same
NameandConversationStartTimevalues, and then sort these records byBatchId.
The following table describes the most important fields in your conversation transcripts.
| Field | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
Content |
The entire transcript in JSON format | See Content field |
ConversationStartTime |
The time the conversation started (not the time the transcript record was written to the data store) | 2021-04-19T20:39:09Z |
ConversationTranscript |
The unique identifier of the row in the Dataverse table | 28eccb77-xxxx-4a63-985f-ffaaadd6f391 |
Metadata |
JSON that includes the agent ID, tenant ID, agent name, and batch ID | {"BotId": "aaaabbbb-0000-cccc-1111-dddd2222eeee", "AADTenantId": "bbbbcccc-1111-dddd-2222-eeee3333ffff", "BotName": "Test Bot", "BatchId":2} |
Name |
The name of the custom row created from ConversationId followed by BotId |
8YYe8iif49ZKkycZLe7HUO_198eca5f-1145-4ae6-8c08-835d884a8688 |
Bot_ConversationTranscript |
The agent ID | aaaabbbb-0000-cccc-1111-dddd2222eeee |
Created on |
The date and time the transcript record was created | 2021-04-20T02:40:13Z |
Content field
The Content field is a raw log of all the activities that users had with the agent. Common activity types include message and event:
- Message activities represent the content shown in a conversation. Message activities can contain text, speech, interactive cards, and binary or unknown attachments.
- Event activities communicate programmatic information from a client or channel to the agent.
For more information on activity types, see Bot Framework Activity schema.
The following table describes some of the key fields in the content JSON:
| Key | Description |
|---|---|
ID |
The unique GUID of the activity object |
valueType |
The type of value stored in the activity; dictates what information the activity is providing (Common activity value types) |
timestamp |
The timestamp of when the activity was generated, in Epoch format (the number of seconds since midnight UTC January 1, 1970) |
type |
The type of activity; for example, message, event, or trace |
replyToId |
The ID of the activity that the current activity is responding to |
from |
Contains fields id and role:
The id can be used to calculate the number of active users that are interacting with the agent if the canvas is passing in a unique ID of the user. If the canvas doesn't pass an ID, a unique ID per conversation is passed. For security and privacy, the system hashes the ID before writing the ID to the transcript. |
channelId |
The ID of the channel where the activity is coming from; for example, directline, msteams, or facebook |
textFormat |
The format of the text; for example, plain or markdown |
attachments |
Dynamic rich data associated with the activity; for example, AdaptiveCards, HeroCards, or Carousel data |
text |
The text for message activities |
value |
Fields specific to the activity based on the value type; this field is where most of the useful information exists |
channeldata |
Contains channel data:
|
name |
The name of the event activity; for example, SetPVAContext |
Common activity value types
| Activity value type | Description |
|---|---|
ConversationInfo |
Whether the conversation is from the Copilot Studio test pane (isDesignMode) and the locale of the conversation |
CSATSurveyRequest |
The user is presented with a customer satisfaction (CSAT) survey |
CSATSurveyResponse |
The user responds to a CSAT survey |
DialogRedirect |
The user is redirected to another topic |
ImpliedSuccess |
The user reached a question node in the topic, where one of the conditions points to the Confirmed Success CSAT system topic (classic bots only) or calls the End of Conversation system topic |
IntentRecognition |
The user triggered a topic |
PRRSurveyRequest |
The user was asked if the topic answered their question from the End of Conversation topic |
PRRSurveyResponse |
The user's response to whether the topic answered their question from the End of Conversation topic |
SessionInfo |
The type (unengaged or engaged), outcome (Escalated, Resolved, Abandon), session start and end time (startTimeUtc, endTimeUtc), and the turn count of the session |
VariableAssignment |
A value is assigned to a variable |
Enhanced transcripts
You can configure agents to generate enhanced transcripts that include node-level data. This data helps track the flow of a conversation within a topic. For example, in a manage orders topic, users might choose between submitting a new order or retrieving an existing one. Node-level data enables analysis of user behavior across these options.
Turn on enhanced transcripts
Open your agent.
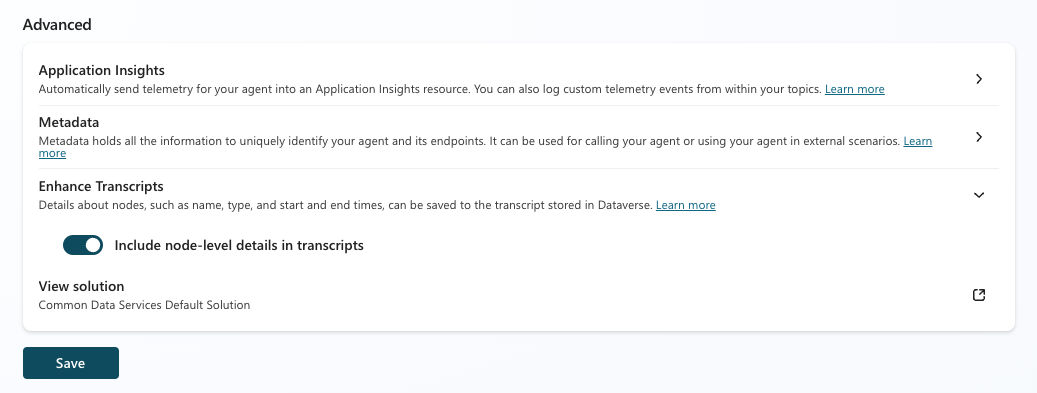
Go to Settings > Advanced.
Select Enhance Transcripts, and then turn on Include node-level details in transcripts.
Node-level data
When you turn on enhanced transcripts, the transcript includes a nodeTraceData activity type for each node that a topic invokes. The following table describes the key fields in the nodeTraceData activity value.
| Key | Description |
|---|---|
nodeID |
The node identifier |
nodeType |
The node type, for example, SendActivity or SearchAndSummarizeContent |
startTime |
The timestamp when the node was invoked |
endTime |
The timestamp when the node finished executing |
topicDisplayName |
The topic invoking the node |
Custom analytics
Some scenarios, like filtering conversations based on a custom variable, require a custom approach for analytics. To build custom analytics solutions, customers can ingest the raw transcripts into their data pipelines or use an add-on, like the Copilot Studio Kit.
The Conversation KPIs solution in Copilot Studio Kit automatically parses transcripts and populates aggregated data into Dataverse tables.
Change the default retention period
A Power Apps bulk-deleting job automatically removes agent transcripts that are older than 30 days. To keep the transcripts longer, cancel the existing job and create a new one that runs on a different schedule.
Cancel the existing bulk delete job
In Power Apps, select Settings > Advanced settings.
The Dynamics 365 portal opens in a new tab.
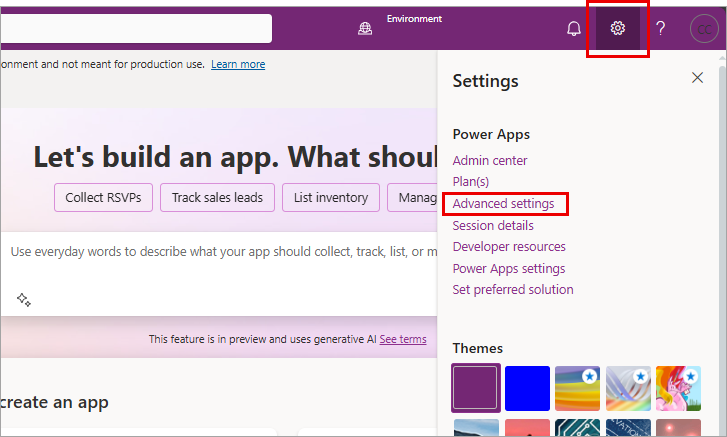
Select the caret next to Settings. Under System, select Data Management.
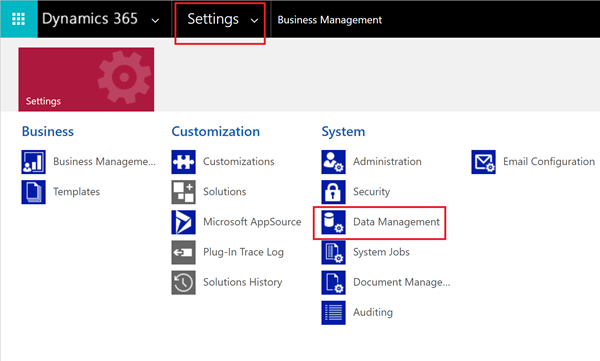
Select Bulk Record Deletion.
In the View list, select Recurring Bulk Deletion System Jobs.
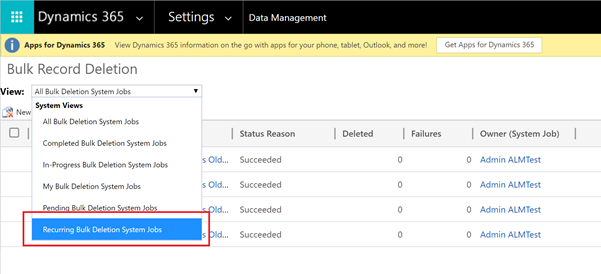
Select the Bulk Delete Conversation Transcript Records Older Than 1 Month job.
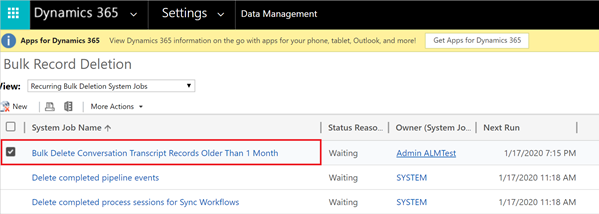
In the More Actions list, select Cancel.
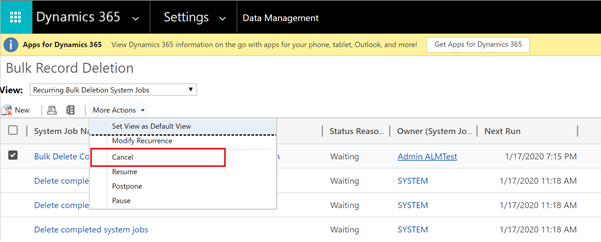
Create a new bulk delete job
Select New to start the Bulk Deletion Wizard. In the wizard, select Next.
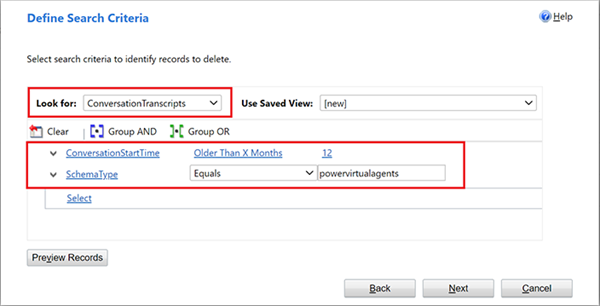
Set the following search criteria:
- In the Look for list, select ConversationTranscripts.
- Select ConversationStartTime, select Older Than X Months, and enter "12".
This setting keeps the transcripts for 12 months. Choose a different comparison and value if you want. - Select SchemaType, keep equals, and enter "powervirtualagents".
Select Next.
Enter a name for the job, select Run this job after every, and enter 1. Choose a different schedule if you don't want the job to run every day.
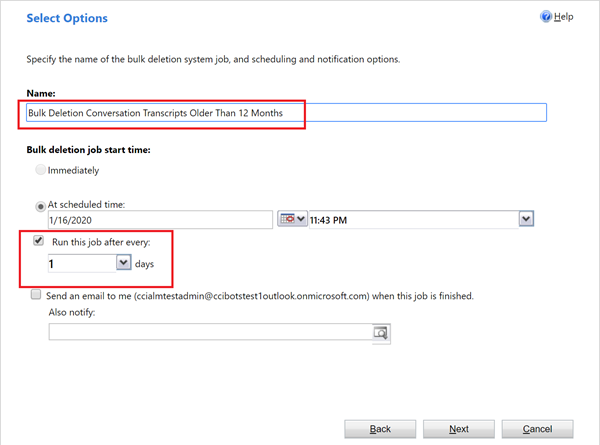
Select Next, and then select Submit.
Why can't I see my conversation transcripts in the ConversationTranscript Power Apps table?
Administrators can prevent the saving of transcripts to Dataverse. For more information on how transcripts are saved and how to manage access, see Control transcript access.
Important
Transcripts aren't stored for agents deployed in developer environments.
Tips for getting the most out of your conversation transcripts
Use variables to store data relevant to your agent content or agent user. By parsing the variable and its value from the conversation transcript, you can filter or slice the data by the variable.
Conversation transcripts might refer to content by ID only. For example, in a Redirect node, the destination topic is only referred to by its ID. To get the name of this topic, look up its ID in the agent content.