Configure user authentication with Microsoft Entra ID
Adding authentication to your agent allows users to sign in, giving your agent access to a restricted resource or information.
This article covers how to configure Microsoft Entra ID as your service provider. To learn about other service providers and user authentication in general, see Configure user authentication in Copilot Studio.
If you have tenant administration rights, you can configure API permissions. Otherwise, you need to ask a tenant administrator to do it for you.
Prerequisites
Learn how to add user authentication to a topic
You complete the first several steps in the Azure portal, and complete the final two steps in Copilot Studio.
Create an app registration
Sign in to the Azure portal, using an admin account in the same tenant as your agent.
Go to App registrations.
Select New registration and enter a name for the registration. Don't alter existing app registrations.
It can be helpful later to use the name of your agent. For example, if your agent is called "Contoso sales help," you might name the app registration "ContosoSalesReg."
Under Supported account types, select Accounts in any organizational tenant (Any Microsoft Entra ID directory - Multitenant) and personal Microsoft accounts (e.g. Skype, Xbox).
Leave the Redirect URI section blank for now. Enter that information in the next steps.
Select Register.
After the registration is complete, go to Overview.
Copy the Application (client) ID and paste it in a temporary file. You need it in later steps.
Add the redirect URL
Under Manage, select Authentication.
Under Platform configurations, select Add a platform, and then select Web.
Under Redirect URIs, enter
https://token.botframework.com/.auth/web/redirect, and select Configure.This action takes you back to the Platform configurations page.
Under Redirect URIs for the Web platform, select Add URI.
Enter
https://europe.token.botframework.com/.auth/web/redirect, and select Save.Note
The authentication configuration pane in Copilot Studio might show the following redirect URL:
https://unitedstates.token.botframework.com/.auth/web/redirect. Using that URL makes the authentication fail; use the URI instead.In the Implicit grant and hybrid flows section, select both Access tokens (used for implicit flows) and ID tokens (used for implicit and hybrid flows).
Select Save.
Generate a client secret
Under Manage, select Certificates & secrets.
In the Client secrets section, select New client secret.
(Optional) Enter a description. One is provided if left blank.
Select the expiry period. Select the shortest period that's relevant for the life of your agent.
Select Add to create the secret.
Store the secret's Value in a secure temporary file. You need it when you configure your agent's authentication later on.
Tip
Don't leave the page before you copy the value of the client secret. If you do, the value is obfuscated and you must generate a new client secret.
Configure manual authentication
In Copilot Studio, go to Settings for your agent, and select Security.
Select Authentication.
Select Authenticate manually.
Leave Require users to sign in on.
Enter the following values for the properties:
Service provider: Select Azure Active Directory v2.
Client ID: Enter the application (client) ID that you copied earlier from the Azure portal.
Client secret: Enter the client secret you generated earlier from the Azure portal.
Scopes: Enter
profile openid.
Select Save to finish the configuration.
Configure API permissions
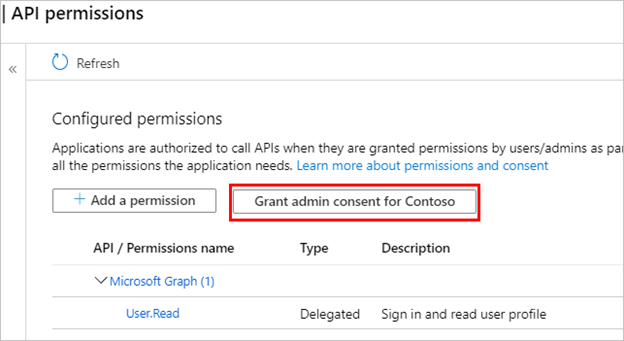
Go to API permissions.
Select Grant admin consent for <your tenant name>, and then select Yes. If the button isn't available, you might need to ask a tenant administrator to do enter it for you.
Important
To avoid users having to consent to each application, someone assigned at least the Application Administrator or Cloud Application Administrator role can grant tenant-wide consent to your application registrations.
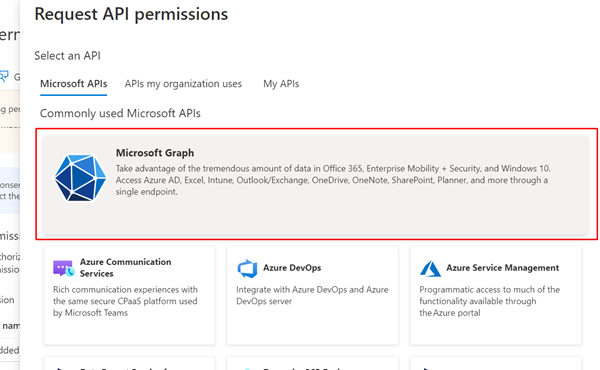
Select Add a permission, and then select Microsoft Graph.
Select Delegated permissions.
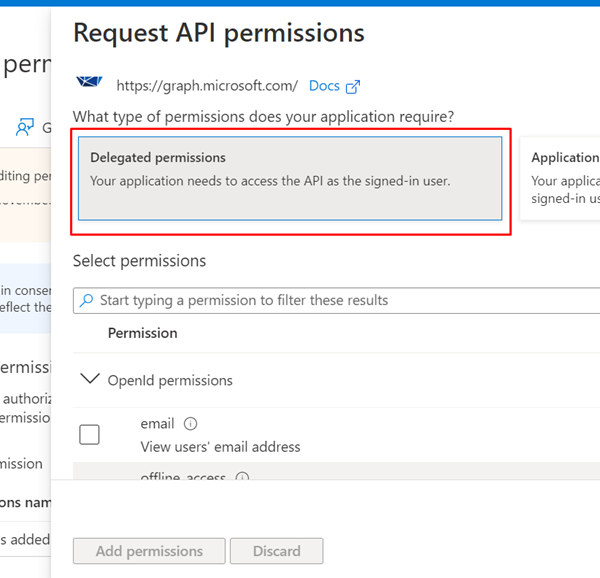
Expand OpenId permissions and turn on openid and profile.
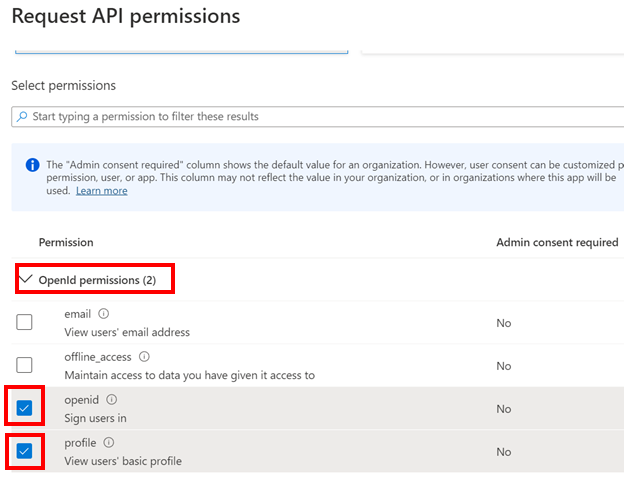
Select Add permissions.
Define a custom scope for your agent
Scopes allow you to determine user and admin roles and access rights. You create a custom scope for the canvas app registration that you create in a later step.
Go to Expose an API and select Add a scope.
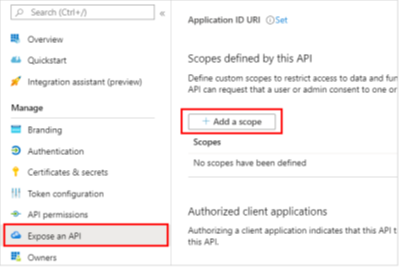
Set the following properties. You can leave the other properties blank.
Property Value Scope name Enter a name that makes sense in your environment, such as Test.ReadWho can consent? Select Admins and users Admin consent display name Enter a name that makes sense in your environment, such as Test.ReadAdmin consent description Enter Allows the app to sign the user in.State Select Enabled Select Add scope.
Configure authentication in Copilot Studio
In Copilot Studio, under Settings, select Security > Authentication.
Select Authenticate manually.
Leave Require users to sign in on.
Select a Service provider and provide the required values. See Configure manual authentication in Copilot Studio.
Select Save.
Tip
The token exchange URL is used to exchange the On-Behalf-Of (OBO) token for the requested access token. For more information, see Configure single sign-on with Microsoft Entra ID.
Note
The scopes should include profile openid and the following, depending on your use case:
Sites.Read.All Files.Read.Allfor SharePointExternalItem.Read.Allfor Graph Connectionhttps://[OrgURL]/user_impersonationfor Prompt Nodes and Dataverse structured data- For example, Dataverse Structure Data or Prompt Node should have the following scopes:
profile openid Sites.Read.All Files.Read.All https://myorg123.com/user_impersonation
Test your agent
Publish your agent.
In the Test agent pane, send a message to your agent.
When the agent responds, select Login.
A new browser tab opens, asking you to sign in.
Sign in, and then copy the displayed validation code.
Paste the code in the agent chat to complete the sign-in process.