Nata
Norint pasiekti šį puslapį, reikalingas leidimas. Galite pabandyti prisijungti arba pakeisti katalogus.
Norint pasiekti šį puslapį, reikalingas leidimas. Galite pabandyti pakeisti katalogus.
Applies to:
SQL Server on Linux
SQL Server jobs are used to regularly perform the same sequence of commands in your SQL Server database. This tutorial provides an example of how to create a SQL Server Agent job on Linux using both Transact-SQL and SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS).
- Install SQL Server Agent on Linux
- Create a new job to perform daily database backups
- Schedule and run the job
- Perform the same steps in SSMS (optional)
For known issues with SQL Server Agent on Linux, see SQL Server on Linux: Known issues.
Prerequisites
The following prerequisites are required to complete this tutorial:
Linux machine with the following prerequisites:
- Quickstart: Install SQL Server and create a database on Red Hat Enterprise Linux
- Quickstart: Install SQL Server and create a database on SUSE Linux Enterprise Server
- Quickstart: Install SQL Server and create a database on Ubuntu with command-line tools.
Note
Starting in SQL Server 2025 (17.x), SUSE Linux Enterprise Server (SLES) isn't supported.
The following prerequisites are optional:
- Windows machine with SSMS:
- Install SQL Server Management Studio for optional SSMS steps.
Enable SQL Server Agent
To use SQL Server Agent on Linux, you must first enable SQL Server Agent on a machine that already has SQL Server installed.
To enable SQL Server Agent, run the following command.
sudo /opt/mssql/bin/mssql-conf set sqlagent.enabled trueRestart SQL Server with the following command:
sudo systemctl restart mssql-server
Note
Starting with SQL Server 2017 (14.x) CU 4, SQL Server Agent is included with the mssql-server package and is disabled by default. For Agent set up before CU 4, see Install SQL Server Agent on Linux.
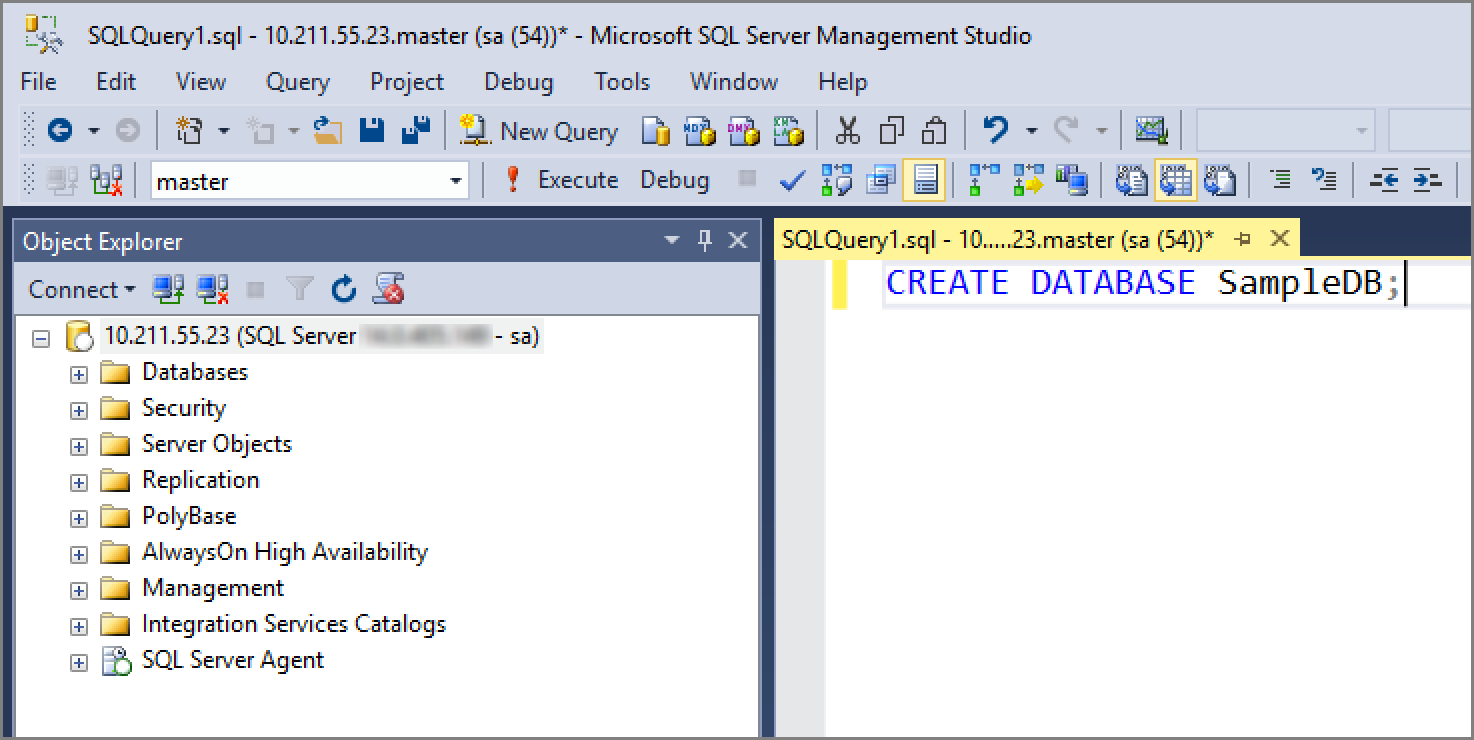
Create a sample database
Use the following steps to create a sample database named SampleDB. This database is used for the daily backup job.
On your Linux machine, open a bash terminal session.
Use sqlcmd to run a Transact-SQL
CREATE DATABASEcommand./opt/mssql-tools/bin/sqlcmd -S localhost -U sa -Q 'CREATE DATABASE SampleDB'Verify the database is created by listing the databases on your server.
/opt/mssql-tools/bin/sqlcmd -S localhost -U sa -Q 'SELECT name FROM sys.databases'
Create a job with Transact-SQL
The following steps create a SQL Server Agent job on Linux with Transact-SQL commands. The job runs a daily backup of the sample database, SampleDB.
Tip
You can use any T-SQL client to run these commands. For example, on Linux you can use Install the sqlcmd and bcp SQL Server command-line tools on Linux or SQL Server extension for Visual Studio Code. From a remote Windows Server, you can also run queries in SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) or use the UI interface for job management, which is described in the next section.
Use sp_add_job to create a job named
Daily SampleDB Backup.-- Adds a new job executed by the SQLServerAgent service -- called 'Daily SampleDB Backup' USE msdb; GO EXECUTE dbo.sp_add_job @job_name = N'Daily SampleDB Backup'; GOCall sp_add_jobstep to create a job step that creates a backup of the
SampleDBdatabase.EXECUTE sp_add_jobstep @job_name = N'Daily SampleDB Backup', @step_name = N'Backup database', @subsystem = N'TSQL', @command = N'BACKUP DATABASE SampleDB TO DISK = \ N''/var/opt/mssql/data/SampleDB.bak'' WITH NOFORMAT, NOINIT, \ NAME = ''SampleDB-full'', SKIP, NOREWIND, NOUNLOAD, STATS = 10', @retry_attempts = 5, @retry_interval = 5; GOThen create a daily schedule for your job with sp_add_schedule.
-- Creates a schedule called 'Daily' EXECUTE dbo.sp_add_schedule @schedule_name = N'Daily SampleDB', @freq_type = 4, @freq_interval = 1, @active_start_time = 233000; USE msdb; GOAttach the job schedule to the job with sp_attach_schedule.
-- Sets the 'Daily' schedule to the 'Daily SampleDB Backup' Job EXECUTE sp_attach_schedule @job_name = N'Daily SampleDB Backup', @schedule_name = N'Daily SampleDB'; GOUse sp_add_jobserver to assign the job to a target server. In this example, the target is the local server.
EXECUTE dbo.sp_add_jobserver @job_name = N'Daily SampleDB Backup', @server_name = N'(local)'; GOStart the job with sp_start_job.
EXECUTE dbo.sp_start_job N' Daily SampleDB Backup'; GO
Create a job with SSMS
You can also create and manage jobs remotely using SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) on Windows.
Start SSMS on Windows and connect to your Linux SQL Server instance. For more information, see Use SQL Server Management Studio on Windows to manage SQL Server on Linux.
Verify that you have created a sample database named
SampleDB.Verify that SQL Agent was Install SQL Server Agent on Linux and configured correctly. Look for the plus sign next to SQL Server Agent in the Object Explorer. If SQL Server Agent isn't enabled, try restarting the mssql-server service on Linux.
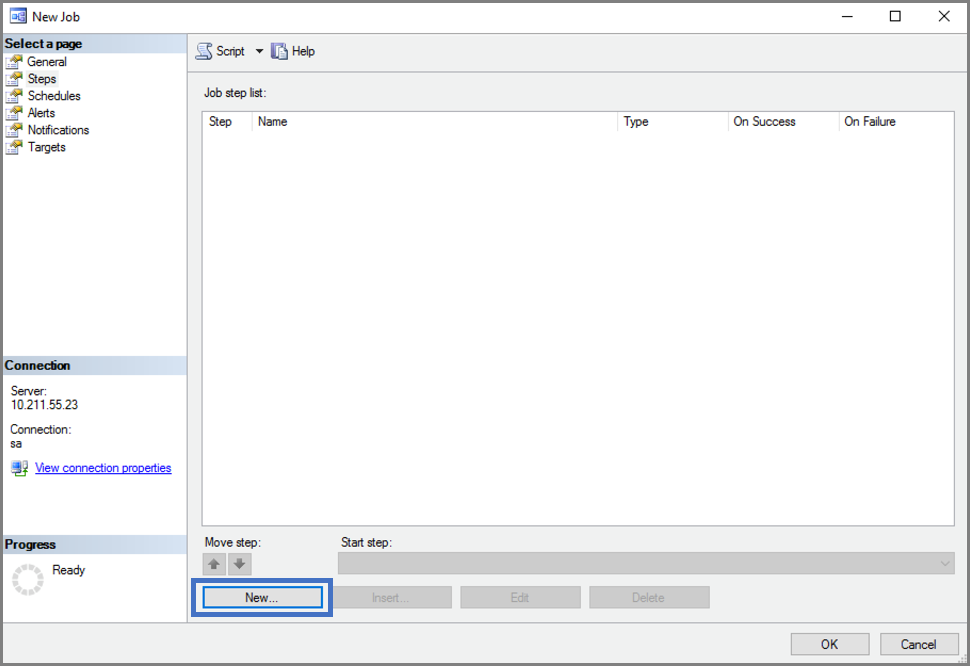
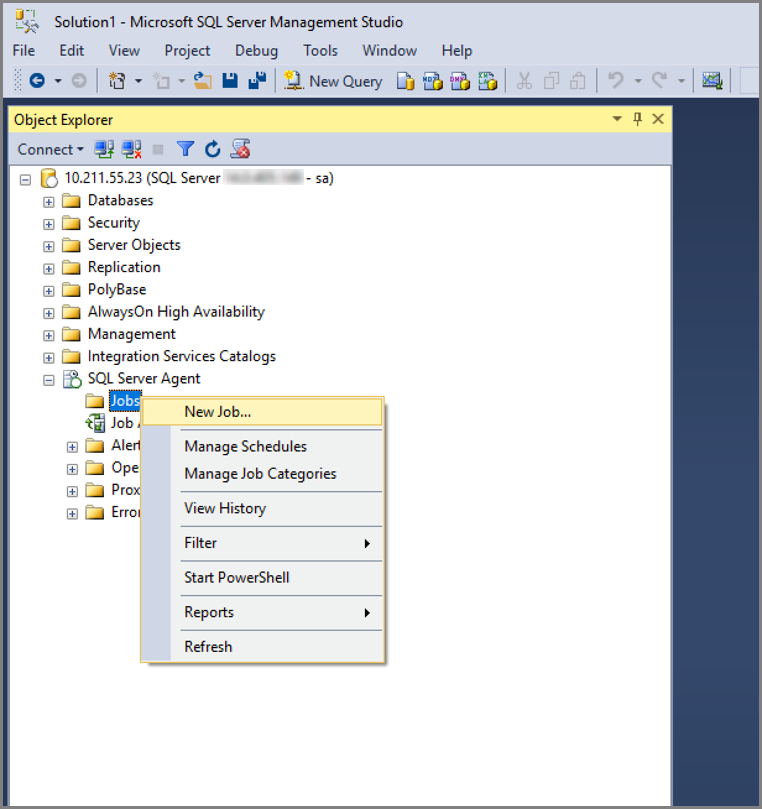
Create a new job.
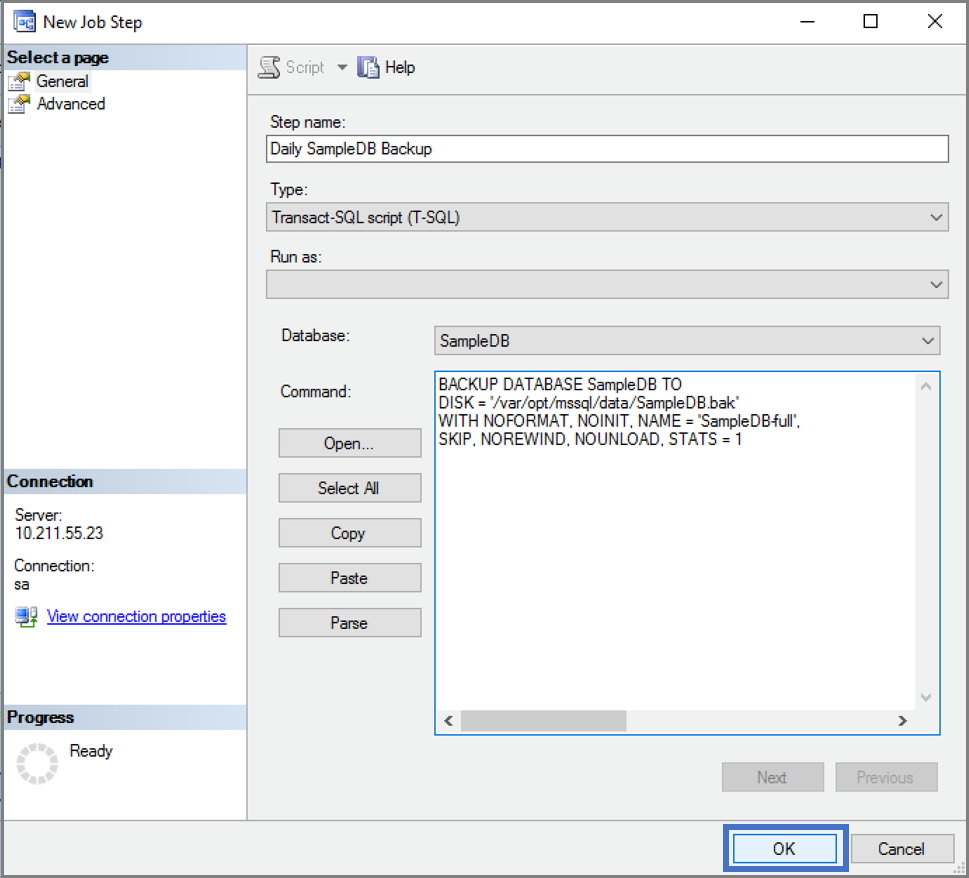
Give your job a name and create your job step.
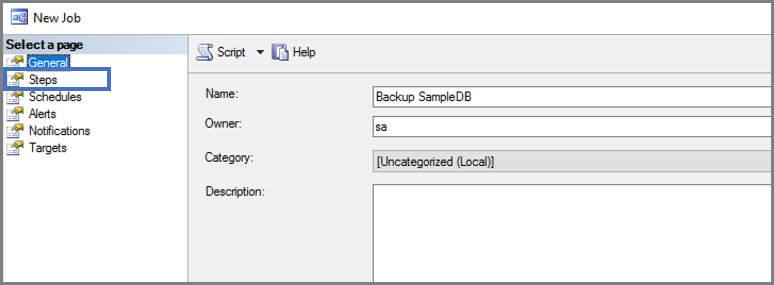
Specify what subsystem you want to use and what the job step should do.
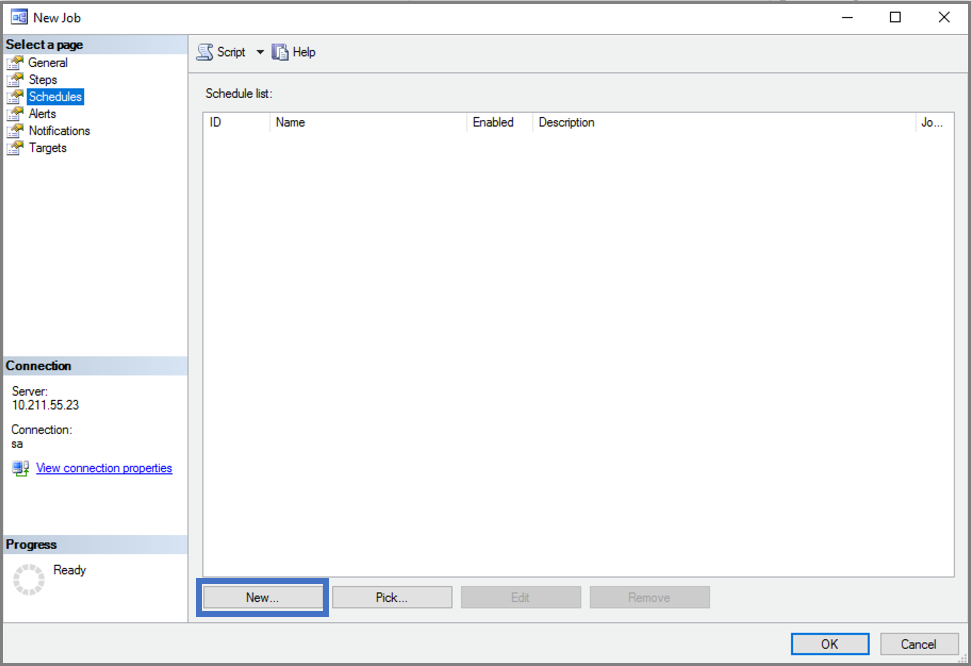
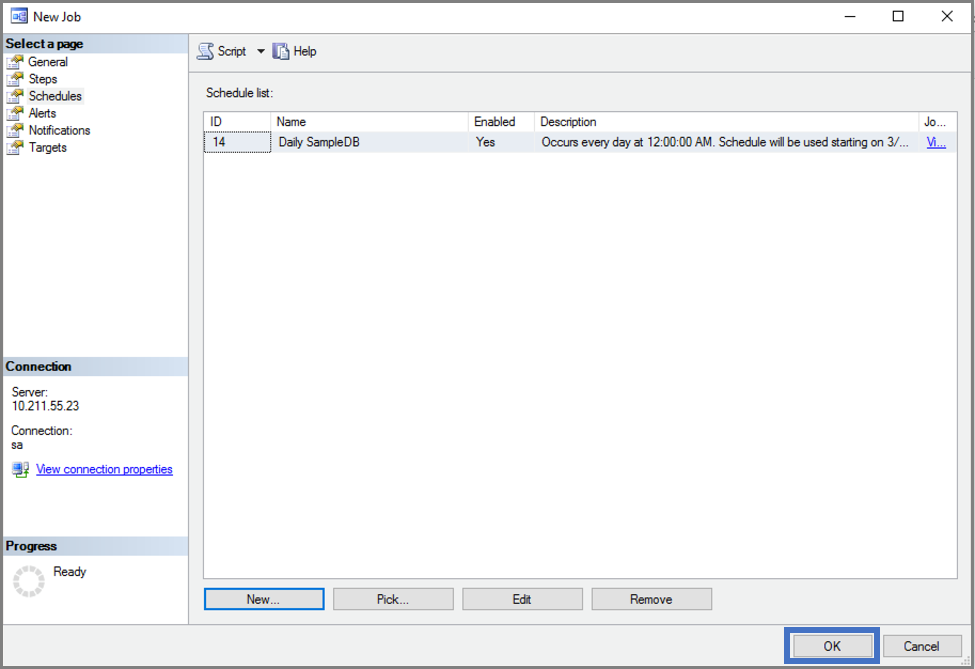
Create a new job schedule.
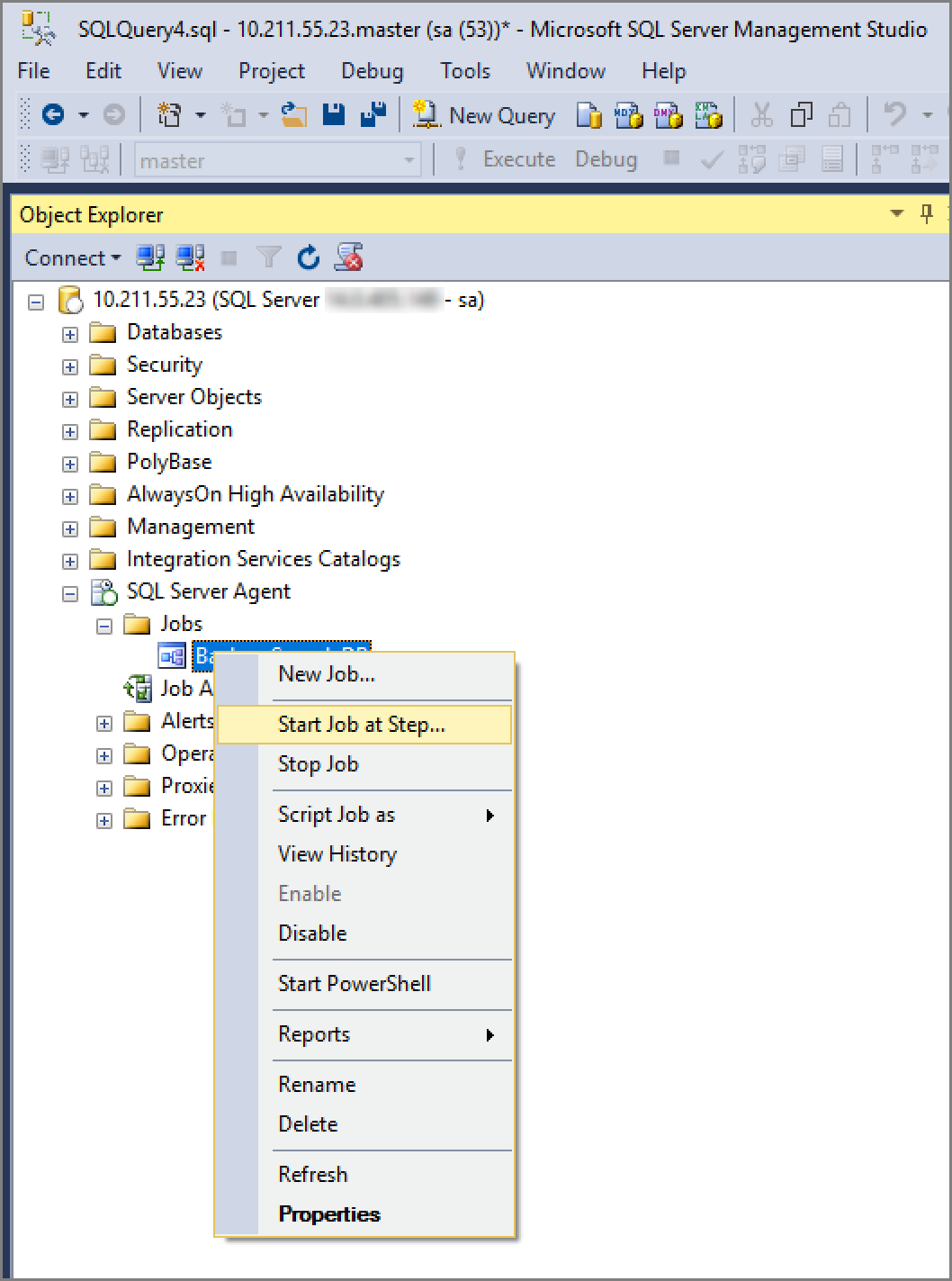
Start your job.
Next step
In this tutorial, you learned how to:
- Install SQL Server Agent on Linux
- Use Transact-SQL and system stored procedures to create jobs
- Create a job that performs daily database backups
- Use SSMS UI to create and manage jobs
Next, explore other capabilities for creating and managing jobs: