Create a real-time capable application
The easiest way to create a new real-time capable application is to start with the Blank template from the Visual Studio Code Azure Sphere extension and adjust the configuration to your project by following these steps:
Start Visual Studio Code. Select View > Command palette, and then type Azure Sphere: Generate New Project.
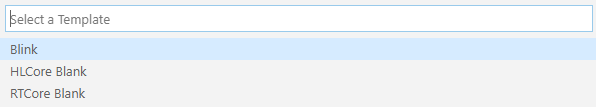
Choose RTCore Blank from the Templates menu.
Visual Studio Code then displays a File Explorer window. Navigate to the folder where you want to place the Blank application and specify a name for your project, for example, NewRTApp. Visual Studio Code creates the NewRTApp folder in your selected location and generates the build files for the blank application. You should see messages from CMake.
You can also create a new real-time capable application from any of the real-time capable Azure Sphere samples:
Clone the samples repo if you haven't already done so. Copy one of the high-level application folders and rename it for your project.
In the CMakeLists.txt file, change the project name to the name of your new folder. For example:
PROJECT(NewRTApp C)
The easiest way to create a new real-time capable application is to start with the Blank template from the Visual Studio Azure Sphere extension and adjust the configuration to your project by following these steps:
Start Visual Studio and select Create a new project.
Type
Azure Spherein the search box labeled Search for templates. Select Azure Sphere RTCore Blank from the returned list, then select Next.Specify a project name (for example, NewRTApp), a project file location, and a solution name (which can be the same as the project name), and then select Create. Visual Studio creates the NewRTApp folder in your selected location and generates the build files for the blank application. You should see messages from CMake.
You can also create a new real-time capable application from any of the high-level Azure Sphere samples:
Clone the samples repo if you haven't already done so. Copy one of the real-time capable application folders and rename it for your project.
In the CMakeLists.txt file, change the project name to the name of your new folder. For example:
PROJECT(NewRTApp C)
The easiest way to create a new real-time capable application is to start with the HelloWorld_RTApp_MT3620_BareMetal sample and adjust the configuration to your project by following these steps:
Clone the samples repo if you haven't already done so. Copy the HelloWorld_RTApp_MT3620_BareMetal folder and rename it for your project.
In the CMakeLists.txt file, change the project name to the name of your new folder. For example:
PROJECT(NewRTApp C)
Basic file structure of a real-time capable application
No matter how you create your application, all Azure Sphere applications share the following core files:
- Application source code in one or more files. Currently, only C language source code is supported.
- CMake build files. CMakeLists.txt is required. CMake, together with the ninja lightweight build utility, is used to control the Azure Sphere application build process.
- An app-manifest file describing the capabilities available to the application.
Real-time capable applications add at least one other file: a linker.ld file to specify precisely where various components of the application are to be loaded on the real-time core.
Write your code
- Write your application code, using the Azure Sphere RTApp samples as guides. The following topics describe specific implementation scenarios:
- In the app_manifest.json file:
- Set
Nameto your project name, - Set
ApplicationTypeto"RealTimeCapable" - Add any application-specific capabilities that your code requires, such as hardware resources or connections. If the RTApp communicates with a high-level app, add the component ID of the high-level application to the
AllowedApplicationConnectionscapability.
- Set
If you want to deploy your RTApp alongside a high-level partner app, add the component ID of the partner to the partnerComponents field of the configurations section of the launch.vs.json (Visual Studio) or .vscode/launch.json (Visual Studio Code) file :
"partnerComponents": [ "25025d2c-66da-4448-bae1-ac26fcdd3627" ]