Notikumi
Veidojiet inteliģentas lietotnes
17. marts 21 - 21. marts 10
Pievienojieties meetup sērijai, lai kopā ar citiem izstrādātājiem un ekspertiem izveidotu mērogojamus AI risinājumus, kuru pamatā ir reālas lietošanas gadījumi.
Reģistrēties tūlītŠī pārlūkprogramma vairs netiek atbalstīta.
Jauniniet uz Microsoft Edge, lai izmantotu jaunāko līdzekļu, drošības atjauninājumu un tehniskā atbalsta sniegtās priekšrocības.
Azure DevOps Services | Azure DevOps Server 2022 - Azure DevOps Server 2019
Using Azure Artifacts, you can publish and download packages from feeds and public registries such as PyPi. This quickstart will guide you through creating a feed, configuring your project, and managing Python packages in your Azure Artifacts feed. In this article, you learn how to:
Create an Azure DevOps organization and a project if you haven't already.
Download and install Python.
If you don't have your own Python project, you can use the following sample Python project:
https://github.com/microsoft/python-package-template
To build your wheel and source distribution, run the following commands in your project directory:
pip install --upgrade build
python -m build
If your Python project has a setup.py file, you can also use this command to build your package:
python setup.py sdist bdist_wheel
Sign in to your Azure DevOps organization and navigate to your project.
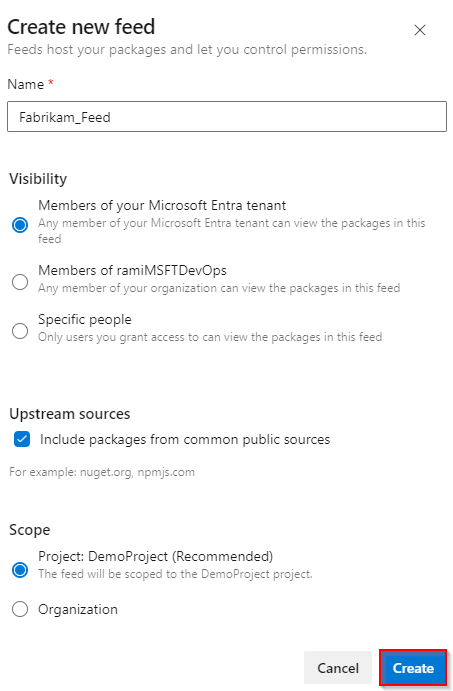
Select Artifacts, and then select Create Feed.
Provide a Name for your feed, choose the Visibility option that defines who can view your packages, check Include packages from common public sources if you want to include packages from sources like nuget.org or npmjs.com, and for Scope, decide whether the feed should be scoped to your project or the entire organization.
Select Create when you're done.
Sign in to your Azure DevOps server, and then go to your project.
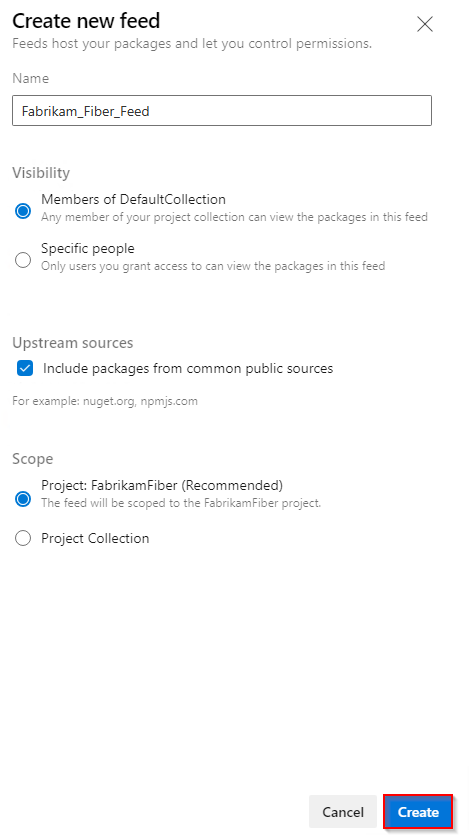
Select Artifacts, and then select Create Feed.
Provide a Name for your feed, choose the Visibility option that defines who can view your packages, check Include packages from common public sources if you want to include packages from sources like nuget.org or npmjs.com, and for Scope, decide whether the feed should be scoped to your project or the entire organization.
Select Create when you're done.
Select Create when you're done.
Sign in to your Azure DevOps server, and then go to your project.
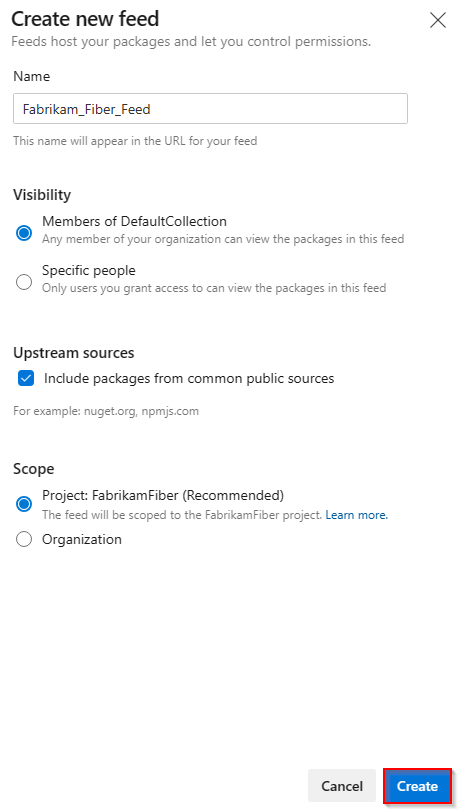
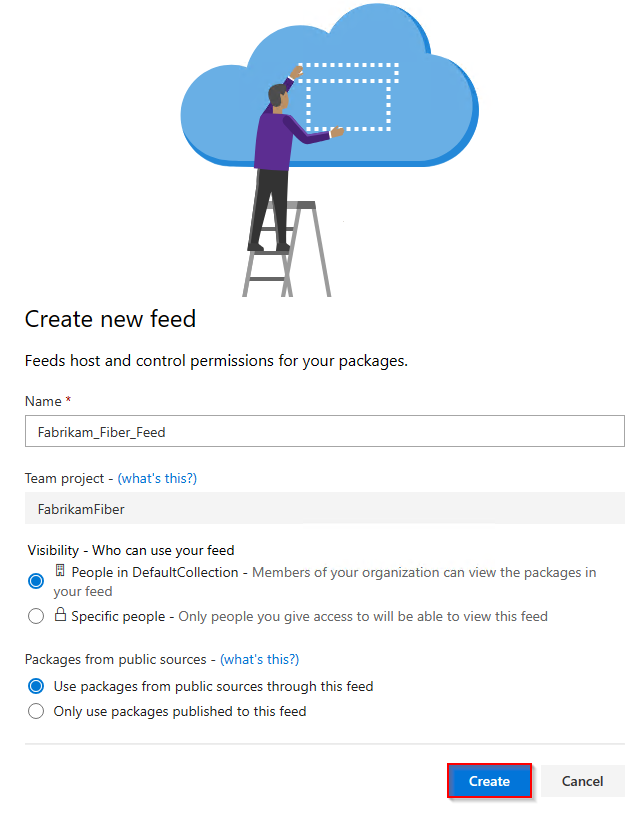
Select Artifacts, and then select New feed.
For Name, enter a descriptive name for your feed.
For Visibility, select an option to indicate who can view packages within the feed.
If you want to include packages from public sources, select the Use packages from public sources through this feed option.
Select Create when you're done.
Piezīme
By default, newly created feeds have their project's Build Service value set to Feed and Upstream Reader (Collaborator).
Sign in to your Azure DevOps organization, and then navigate to your project.
Select Artifacts, select your feed from the dropdown menu, and then select Connect to feed.
Select twine under the Python section.
If this is your first time using Azure Artifacts with twine, select Get the tools and follow the steps to install the prerequisites.
Add a pypirc file to your home directory and paste the provided snippet. Your file should look like this:
[distutils]
Index-servers =
FEED_NAME
[FEED_NAME]
Repository = https://pkgs.dev.azure.com/ORGANIZATION_NAME/PROJECT_NAME/_packaging/FEED_NAME/pypi/upload/
Piezīme
If your .pypirc file already contains credentials for the public PyPI index, we recommend removing the [pypi] section to prevent accidental publication of private packages to PyPI.
Run this command in your project directory to create source and wheel distributions:
python setup.py sdist bdist_wheel
Run the following command to publish your package. Use the -r FEED_NAME flag to ensure your private packages are not accidentally published to PyPI.
twine upload -r <FEED_NAME> dist/*
Run this command in your project directory to install your packages:
pip install
To install a specific package, run the following command, replacing the placeholder with the package name from your feed.
pip install <PACKAGE_NAME>
Notikumi
Veidojiet inteliģentas lietotnes
17. marts 21 - 21. marts 10
Pievienojieties meetup sērijai, lai kopā ar citiem izstrādātājiem un ekspertiem izveidotu mērogojamus AI risinājumus, kuru pamatā ir reālas lietošanas gadījumi.
Reģistrēties tūlītApmācība
Sertifikācija
Microsoft Certified: Azure Data Scientist Associate - Certifications
Manage data ingestion and preparation, model training and deployment, and machine learning solution monitoring with Python, Azure Machine Learning and MLflow.
Dokumentācija
Publish Python packages (CLI) - Azure Artifacts
Learn how to publish Python packages from the command-line interface.
Use packages from PyPI - Azure Artifacts
How to consume packages from Python package index with Azure Artifacts
Connect your Python project to an Azure Artifacts feed - Azure Artifacts
Learn how to set up your Python project and connect to an Azure Artifacts feed.