Remote Desktop Gateway and Azure Multi-Factor Authentication Server using RADIUS
Often, Remote Desktop (RD) Gateway uses the local Network Policy Services (NPS) to authenticate users. This article describes how to route RADIUS requests out from the Remote Desktop Gateway (through the local NPS) to the Multi-Factor Authentication Server. The combination of Azure MFA and RD Gateway means that your users can access their work environments from anywhere while performing strong authentication.
Since Windows Authentication for terminal services is not supported for Server 2012 R2, use RD Gateway and RADIUS to integrate with MFA Server.
Install the Azure Multi-Factor Authentication Server on a separate server, which proxies the RADIUS request back to the NPS on the Remote Desktop Gateway Server. After NPS validates the username and password, it returns a response to the Multi-Factor Authentication Server. Then, the MFA Server performs the second factor of authentication and returns a result to the gateway.
Important
In September 2022, Microsoft announced deprecation of Azure Multi-Factor Authentication Server. Beginning September 30, 2024, Azure Multi-Factor Authentication Server deployments will no longer service multifactor authentication (MFA) requests, which could cause authentications to fail for your organization. To ensure uninterrupted authentication services and to remain in a supported state, organizations should migrate their users’ authentication data to the cloud-based Azure MFA service by using the latest Migration Utility included in the most recent Azure MFA Server update. For more information, see Azure MFA Server Migration.
To get started with cloud-based MFA, see Tutorial: Secure user sign-in events with Azure Multi-Factor Authentication.
If you use cloud-based MFA, see how to integrate with RADIUS authentication for Azure Multi-Factor Authentication.
Prerequisites
- A domain-joined Azure MFA Server. If you don't have one installed already, follow the steps in Getting started with the Azure Multi-Factor Authentication Server.
- An existing configured NPS Server.
- A Remote Desktop Gateway that authenticates with Network Policy Services.
Note
This article should be used with MFA Server deployments only, not Azure MFA (Cloud-based).
Configure the Remote Desktop Gateway
Configure the RD Gateway to send RADIUS authentication to an Azure Multi-Factor Authentication Server.
- In RD Gateway Manager, right-click the server name and select Properties.
- Go to the RD CAP Store tab and select Central server running NPS.
- Add one or more Azure Multi-Factor Authentication Servers as RADIUS servers by entering the name or IP address of each server.
- Create a shared secret for each server.
Configure NPS
The RD Gateway uses NPS to send the RADIUS request to Azure Multi-Factor Authentication. To configure NPS, first you change the timeout settings to prevent the RD Gateway from timing out before the two-step verification has completed. Then, you update NPS to receive RADIUS authentications from your MFA Server. Use the following procedure to configure NPS:
Modify the timeout policy
- In NPS, open the RADIUS Clients and Server menu in the left column and select Remote RADIUS Server Groups.
- Select the TS GATEWAY SERVER GROUP.
- Go to the Load Balancing tab.
- Change both the Number of seconds without response before request is considered dropped and the Number of seconds between requests when server is identified as unavailable to between 30 and 60 seconds. (If you find that the server still times out during authentication, you can come back here and increase the number of seconds.)
- Go to the Authentication/Account tab and check that the RADIUS ports specified match the ports that the Multi-Factor Authentication Server is listening on.
Prepare NPS to receive authentications from the MFA Server
- Right-click RADIUS Clients under RADIUS Clients and Servers in the left column and select New.
- Add the Azure Multi-Factor Authentication Server as a RADIUS client. Choose a Friendly name and specify a shared secret.
- Open the Policies menu in the left column and select Connection Request Policies. You should see a policy called TS GATEWAY AUTHORIZATION POLICY that was created when RD Gateway was configured. This policy forwards RADIUS requests to the Multi-Factor Authentication Server.
- Right-click TS GATEWAY AUTHORIZATION POLICY and select Duplicate Policy.
- Open the new policy and go to the Conditions tab.
- Add a condition that matches the Client Friendly Name with the Friendly name set in step 2 for the Azure Multi-Factor Authentication Server RADIUS client.
- Go to the Settings tab and select Authentication.
- Change the Authentication Provider to Authenticate requests on this server. This policy ensures that when NPS receives a RADIUS request from the Azure MFA Server, the authentication occurs locally instead of sending a RADIUS request back to the Azure Multi-Factor Authentication Server, which would result in a loop condition.
- To prevent a loop condition, make sure that the new policy is ordered ABOVE the original policy in the Connection Request Policies pane.
Configure Azure Multi-Factor Authentication
The Azure Multi-Factor Authentication Server is configured as a RADIUS proxy between RD Gateway and NPS. It should be installed on a domain-joined server that is separate from the RD Gateway server. Use the following procedure to configure the Azure Multi-Factor Authentication Server.
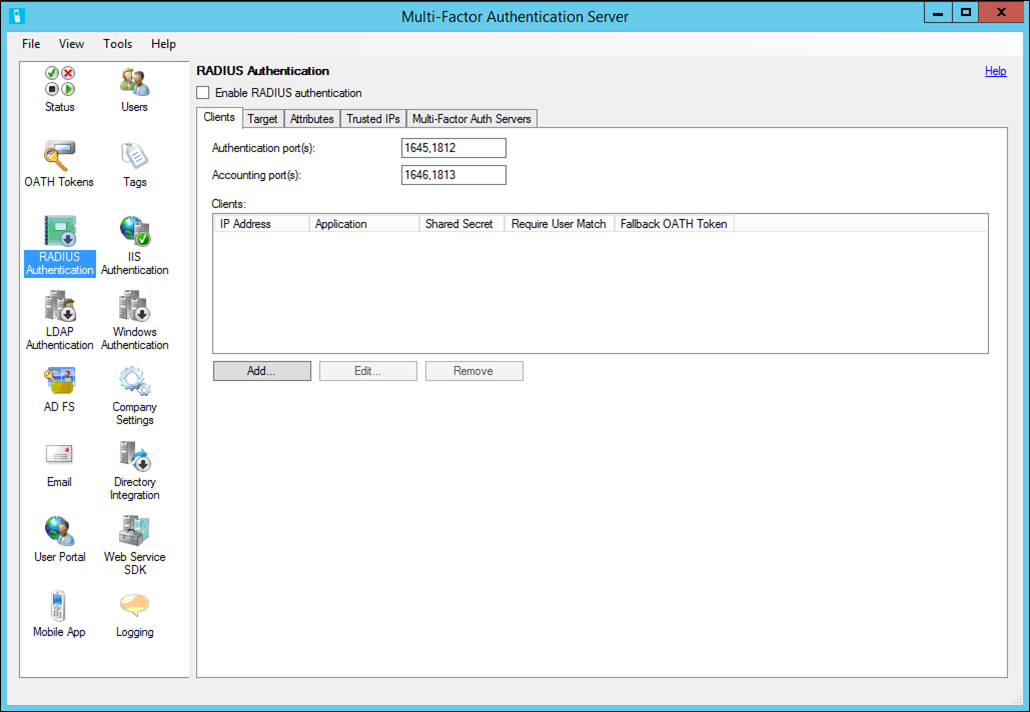
- Open the Azure Multi-Factor Authentication Server and select the RADIUS Authentication icon.
- Check the Enable RADIUS authentication checkbox.
- On the Clients tab, ensure the ports match what is configured in NPS then select Add.
- Add the RD Gateway server IP address, application name (optional), and a shared secret. The shared secret needs to be the same on both the Azure Multi-Factor Authentication Server and RD Gateway.
- Go to the Target tab and select the RADIUS server(s) radio button.
- Select Add and enter the IP address, shared secret, and ports of the NPS server. Unless using a central NPS, the RADIUS client and RADIUS target are the same. The shared secret must match the one setup in the RADIUS client section of the NPS server.
Next steps
Integrate Azure MFA and IIS web apps
Get answers in the Azure Multi-Factor Authentication FAQ