Python Tutorial: Deploy a linear regression model with SQL machine learning
Applies to:
SQL Server 2017 (14.x) and later
Azure SQL Managed Instance
In part four of this four-part tutorial series, you'll deploy a linear regression model developed in Python into a SQL Server database using Machine Learning Services or Big Data Clusters.
In part four of this four-part tutorial series, you'll deploy a linear regression model developed in Python into a SQL Server database using Machine Learning Services.
In part four of this four-part tutorial series, you'll deploy a linear regression model developed in Python into an Azure SQL Managed Instance database using Machine Learning Services.
In this article, you'll learn how to:
- Create a stored procedure that generates the machine learning model
- Store the model in a database table
- Create a stored procedure that makes predictions using the model
- Execute the model with new data
In part one, you learned how to restore the sample database.
In part two, you learned how to load the data from a database into a Python data frame, and prepare the data in Python.
In part three, you learned how to train a linear regression machine learning model in Python.
Prerequisites
- Part four of this tutorial assumes you have completed part one and its prerequisites.
Create a stored procedure that generates the model
Now, using the Python scripts you developed, create a stored procedure generate_rental_py_model that trains and generates the linear regression model using LinearRegression from scikit-learn.
Run the following T-SQL statement in Azure Data Studio to create the stored procedure to train the model.
-- Stored procedure that trains and generates a Python model using the rental_data and a linear regression algorithm
DROP PROCEDURE IF EXISTS generate_rental_py_model;
go
CREATE PROCEDURE generate_rental_py_model (@trained_model varbinary(max) OUTPUT)
AS
BEGIN
EXECUTE sp_execute_external_script
@language = N'Python'
, @script = N'
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
import pickle
df = rental_train_data
# Get all the columns from the dataframe.
columns = df.columns.tolist()
# Store the variable well be predicting on.
target = "RentalCount"
# Initialize the model class.
lin_model = LinearRegression()
# Fit the model to the training data.
lin_model.fit(df[columns], df[target])
# Before saving the model to the DB table, convert it to a binary object
trained_model = pickle.dumps(lin_model)'
, @input_data_1 = N'select "RentalCount", "Year", "Month", "Day", "WeekDay", "Snow", "Holiday" from dbo.rental_data where Year < 2015'
, @input_data_1_name = N'rental_train_data'
, @params = N'@trained_model varbinary(max) OUTPUT'
, @trained_model = @trained_model OUTPUT;
END;
GO
Store the model in a database table
Create a table in the TutorialDB database and then save the model to the table.
Run the following T-SQL statement in Azure Data Studio to create a table called dbo.rental_py_models which is used to store the model.
USE TutorialDB; DROP TABLE IF EXISTS dbo.rental_py_models; GO CREATE TABLE dbo.rental_py_models ( model_name VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL DEFAULT('default model') PRIMARY KEY, model VARBINARY(MAX) NOT NULL ); GOSave the model to the table as a binary object, with the model name linear_model.
DECLARE @model VARBINARY(MAX); EXECUTE generate_rental_py_model @model OUTPUT; INSERT INTO rental_py_models (model_name, model) VALUES('linear_model', @model);
Create a stored procedure that makes predictions
Create a stored procedure py_predict_rentalcount that makes predictions using the trained model and a set of new data. Run the T-SQL below in Azure Data Studio.
DROP PROCEDURE IF EXISTS py_predict_rentalcount; GO CREATE PROCEDURE py_predict_rentalcount (@model varchar(100)) AS BEGIN DECLARE @py_model varbinary(max) = (select model from rental_py_models where model_name = @model); EXECUTE sp_execute_external_script @language = N'Python', @script = N' # Import the scikit-learn function to compute error. from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error import pickle import pandas rental_model = pickle.loads(py_model) df = rental_score_data # Get all the columns from the dataframe. columns = df.columns.tolist() # Variable you will be predicting on. target = "RentalCount" # Generate the predictions for the test set. lin_predictions = rental_model.predict(df[columns]) print(lin_predictions) # Compute error between the test predictions and the actual values. lin_mse = mean_squared_error(lin_predictions, df[target]) #print(lin_mse) predictions_df = pandas.DataFrame(lin_predictions) OutputDataSet = pandas.concat([predictions_df, df["RentalCount"], df["Month"], df["Day"], df["WeekDay"], df["Snow"], df["Holiday"], df["Year"]], axis=1) ' , @input_data_1 = N'Select "RentalCount", "Year" ,"Month", "Day", "WeekDay", "Snow", "Holiday" from rental_data where Year = 2015' , @input_data_1_name = N'rental_score_data' , @params = N'@py_model varbinary(max)' , @py_model = @py_model with result sets (("RentalCount_Predicted" float, "RentalCount" float, "Month" float,"Day" float,"WeekDay" float,"Snow" float,"Holiday" float, "Year" float)); END; GOCreate a table for storing the predictions.
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS [dbo].[py_rental_predictions]; GO CREATE TABLE [dbo].[py_rental_predictions]( [RentalCount_Predicted] [int] NULL, [RentalCount_Actual] [int] NULL, [Month] [int] NULL, [Day] [int] NULL, [WeekDay] [int] NULL, [Snow] [int] NULL, [Holiday] [int] NULL, [Year] [int] NULL ) ON [PRIMARY] GOExecute the stored procedure to predict rental counts
--Insert the results of the predictions for test set into a table INSERT INTO py_rental_predictions EXEC py_predict_rentalcount 'linear_model'; -- Select contents of the table SELECT * FROM py_rental_predictions;You should see results similar to the following.
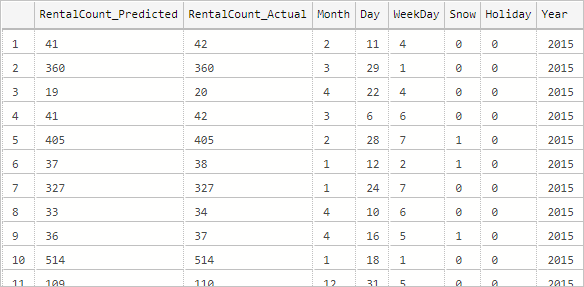
You have successfully created, trained, and deployed a model. You then used that model in a stored procedure to predict values based on new data.
Next steps
In part four of this tutorial series, you completed these steps:
- Create a stored procedure that generates the machine learning model
- Store the model in a database table
- Create a stored procedure that makes predictions using the model
- Execute the model with new data
To learn more about using Python with SQL machine learning, see: