Ambil perhatian
Akses ke halaman ini memerlukan kebenaran. Anda boleh cuba log masuk atau menukar direktori.
Akses ke halaman ini memerlukan kebenaran. Anda boleh cuba menukar direktori.
Ready to write your first client script to see things in action? Lets get started. We'll keep it simple.
Objective
After completing this walkthrough, you will know how to use JavaScript code in model-driven apps, which involves the following steps at a high level:
- Locate or create a solution to add your work to
- Write JavaScript code to address a business issue
- Upload your code as a web resource
- Associate your web resource to a form
- Configure form and field events
- Test your code
Step 1: Locate or create a solution
Solutions are the way that customizations can be transported from one environment to another. You should write and test your Javascript code in a development environment as part of an unmanaged solution. When you have finished testing, export the solution as a managed solution and import/install it in your production environment.
There may already be an existing solution that you should use. The model-driven app you want to customize with your script should already be part of a solution. You may edit that solution or create a new solution that depends on another existing solution.
To create a new solution:
Navigate to Power Apps.
In the left navigation pane, select Solutions and then select New solution.
In the fly-out dialog, specify Display name, Name, and Publisher.
Most companies will have an existing publisher that they will always use. You should use that publisher. If you are the very first person, you get to create your own.
Click New Publisher to open the New Publisher dialog. In this walkthrough, we will use a publisher with this definition:
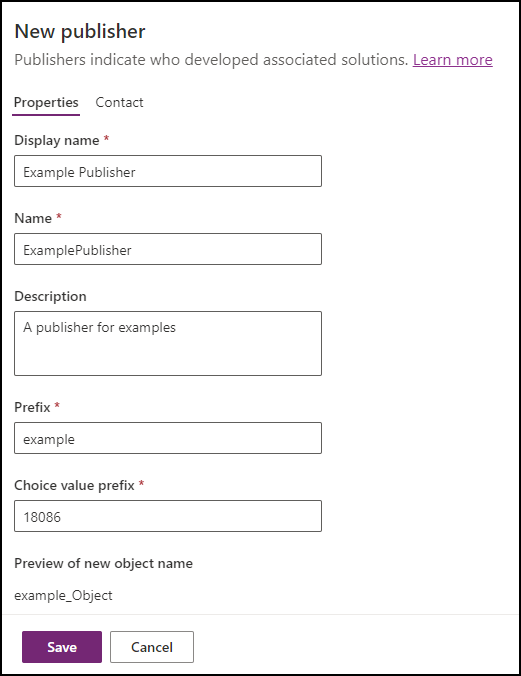
Notice the Prefix value. This should be something that identifies your company. In this case, we are using
example.This is the solution we will use in this walkthrough

Locate or add a model-driven app to your solution.
A new solution will not have any model-driven apps included in it. You will need to add an existing model-driven app or create a new one.
Note
For the purpose of this walkthrough, make sure the app includes the Account table. The scripts and instructions below expects fields found in a form for the Account table.
Option A: Add an existing model-driven app to your solution
- In your solution, select Add existing > App > Model-driven app.
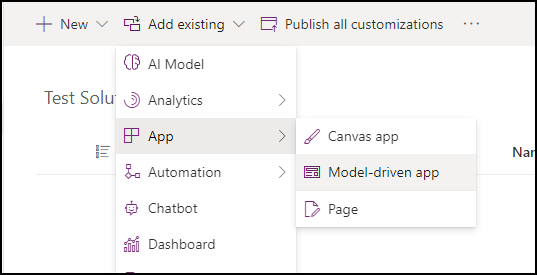
- Select an existing app and click Add.
Option B: Create a new model-driven app in your solution
In your solution, you can select New > App > Model-driven app.
See the Build your first model-driven app tutorial. Create an app that includes the Account table.
Step 2: Write your JavaScript code
The first step is to identify the business issue you are trying to address using client scripting. Once you have identified it, you need to write your JavaScript code containing the custom business logic that addresses your business issue.
Model-driven apps do not provide a JavaScript editor. Use an external authoring tool that provides features to specifically support editing JavaScript files, such as Notepad++, Visual Studio Code, or Microsoft Visual Studio.
This is the JavaScript code that this walkthrough uses:
// A namespace defined for the sample code
// As a best practice, you should always define
// a unique namespace for your libraries
var Example = window.Example || {};
(function () {
// Define some global variables
var myUniqueId = "_myUniqueId"; // Define an ID for the notification
var currentUserName = Xrm.Utility.getGlobalContext().userSettings.userName; // get current user name
var message = currentUserName + ": Your JavaScript code in action!";
// Code to run in the form OnLoad event
this.formOnLoad = function (executionContext) {
var formContext = executionContext.getFormContext();
// Display the form level notification as an INFO
formContext.ui.setFormNotification(message, "INFO", myUniqueId);
// Wait for 5 seconds before clearing the notification
window.setTimeout(function () { formContext.ui.clearFormNotification(myUniqueId); }, 5000);
}
// Code to run in the column OnChange event
this.attributeOnChange = function (executionContext) {
var formContext = executionContext.getFormContext();
// Automatically set some column values if the account name contains "Contoso"
var accountName = formContext.getAttribute("name").getValue();
if (accountName.toLowerCase().search("contoso") != -1) {
formContext.getAttribute("websiteurl").setValue("https://www.contoso.com");
formContext.getAttribute("telephone1").setValue("425-555-0100");
formContext.getAttribute("description").setValue("Website URL, Phone and Description set using custom script.");
}
}
// Code to run in the form OnSave event
this.formOnSave = function () {
// Display an alert dialog
Xrm.Navigation.openAlertDialog({ text: "Record saved." });
}
}).call(Example);
Copy this code into a text file and save it with the name: Example-form-script.js.
Detailed code explanation
Let's look at the code in detail:
Define namespace: The code starts by defining a namespace for your custom script. As a best practice, you should always create namespaced JavaScript libraries to avoid having your functions overridden by functions in another library.
var Example = window.Example || {};In this case, all the functions defined in this library can be used as
Example.[functionName]. You should choose a namespace that matches your solution publisher name.Define global variables: The following section defines some global variables to be used in the script. Context information is available globally using the Xrm.Utility.getGlobalContext method.
// Define some global variables var myUniqueId = "_myUniqueId"; // Define an ID for the notification var currentUserName = Xrm.Utility.getGlobalContext().userSettings.userName; // get current user name var message = currentUserName + ": Your JavaScript code in action!";Function to execute on the OnLoad event: This section contains the function that will be executed when the account form loads. For example, when you create a new account record or when you open an existing account record.
The
Example.formOnLoadfunction uses theexecutionContextparameter to get theformContextobject. When you attach your code with the form event later, you must remember to select the option to pass the execution context to this function.This function displays a form level notification using the formContext.ui.setFormNotification method.
Finally, this function uses the JavaScript setTimeOut method to delay the execution of the formContext.ui.clearFormNotification method to clear the notification after 5 seconds.
// Code to run in the form OnLoad event this.formOnLoad = function (executionContext) { var formContext = executionContext.getFormContext(); // Display the form level notification as an INFO formContext.ui.setFormNotification(message, "INFO", myUniqueId); // Wait for 5 seconds before clearing the notification window.setTimeout(function () { formContext.ui.clearFormNotification(myUniqueId); }, 5000); }Function to execute on the OnChange event: The
Example.attributeOnChangefunction will be associated with the Account Name column in the account form so that it gets executed only when you change the account name value.This function performs a case-insensitive search for
Contosoin the accountname, and if present, sets values for thewebsiteurl,telephone1, anddescriptioncolumns in the account form.// Code to run in the column OnChange event this.attributeOnChange = function (executionContext) { var formContext = executionContext.getFormContext(); // Automatically set some column values if the account name contains "Contoso" var accountName = formContext.getAttribute("name").getValue(); if (accountName.toLowerCase().search("contoso") != -1) { formContext.getAttribute("websiteurl").setValue("https://www.contoso.com"); formContext.getAttribute("telephone1").setValue("425-555-0100"); formContext.getAttribute("description").setValue("Website URL, Phone and Description set using custom script."); } }Function to execute on the OnSave event: The
Example.formOnSavefunction displays an alert dialog box using the Xrm.Navigation.openAlertDialog method. This dialog box displays a message with an OK button. The user can close the alert by clicking OK.Note
This function doesn't use the execution context because the Xrm.Navigation. methods don't require them.
// Code to run in the form OnSave event this.formOnSave = function () { // Display an alert dialog Xrm.Navigation.openAlertDialog({ text: "Record saved." }); }
Step 3: Upload your code as a web resource
Now that your code is ready, you need to upload it into your solution.
In your solution select New > More > Web resource
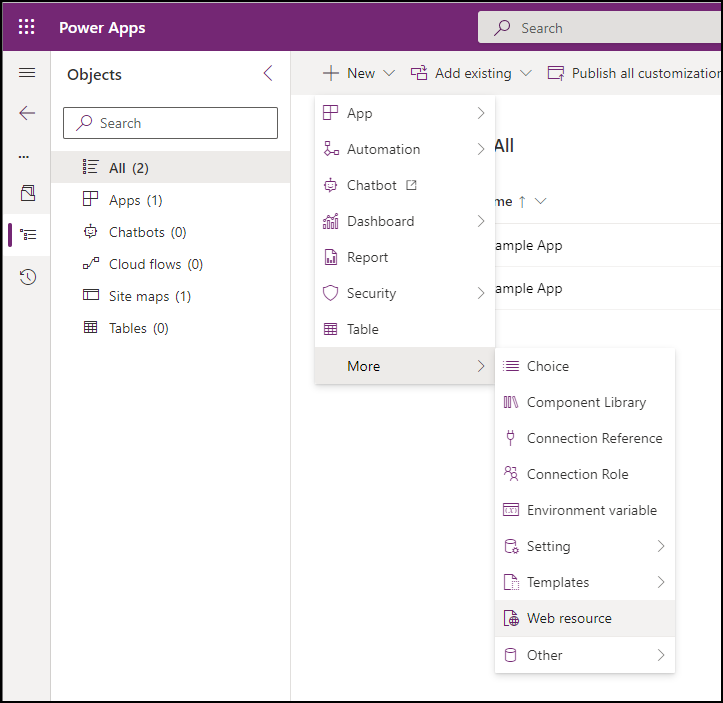
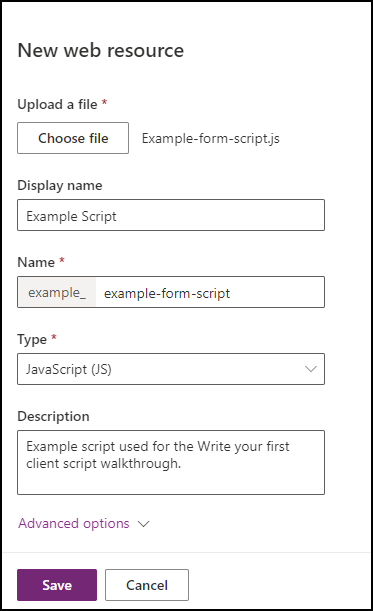
In the New web resource dialog, click Choose file and select the
Example-form-script.jsfile you saved earlier.Type in the Display name, Name, and optionally a Description. Make sure the Type is JavaScript (JS).
Note
- Notice how the Name has a prefix that matches the solution publisher customization prefix. There are other ways to create web resources, but creating a web resource this way ensures that the Web Resource is part of your solution.
- The name of the web resource is
example_example-form-script.
Step 4: Associate your web resource to a form
In your solution, select Objects > Apps > Your App and click Edit.
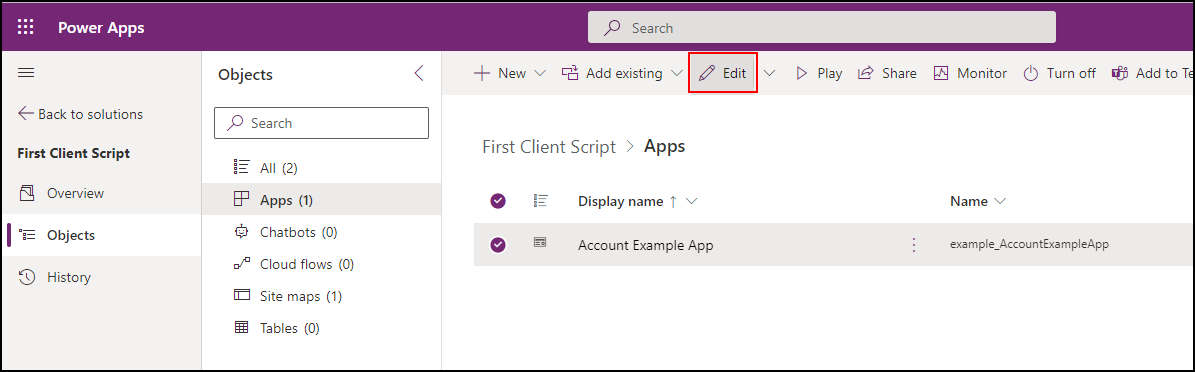
Expand Account and select the Account form, click the ellipses (...) to the right of the Information form and select Edit.
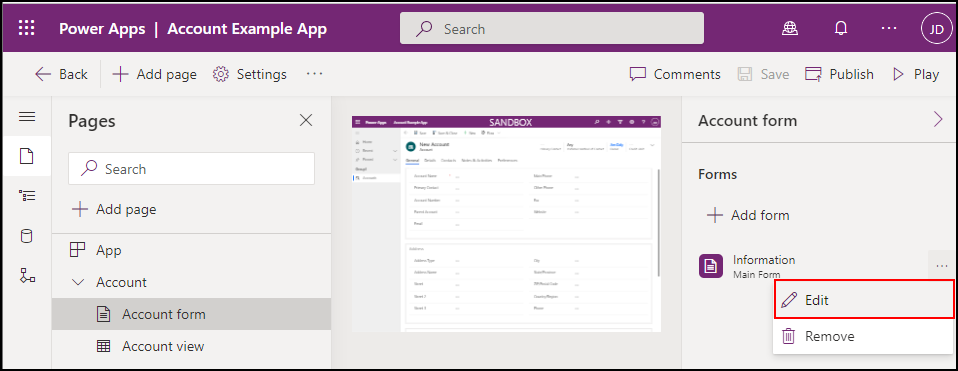
In the left navigation, select Form Libraries and click Add library.
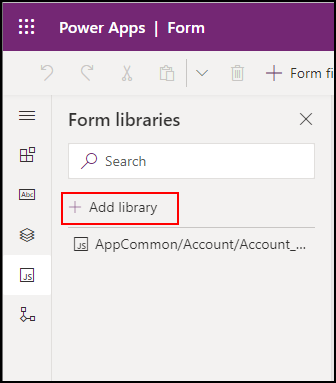
In the Add JavaScript Library dialog, search for the JavaScript web resource you created by name:
Example Script.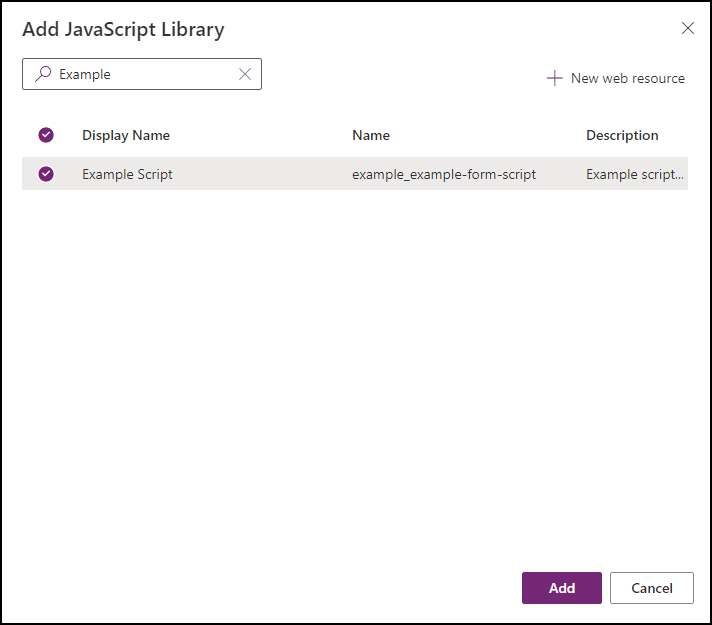
Select the Example Script web resource and click Add.
Step 5: Configure form and field events
Select the Events tab.
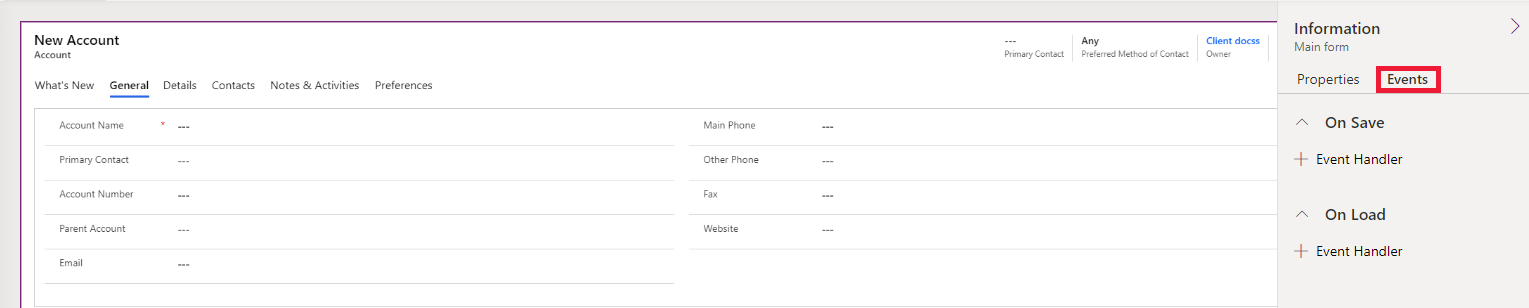
Configure form On Load event
Select On Load event handler and click + Event Handler.
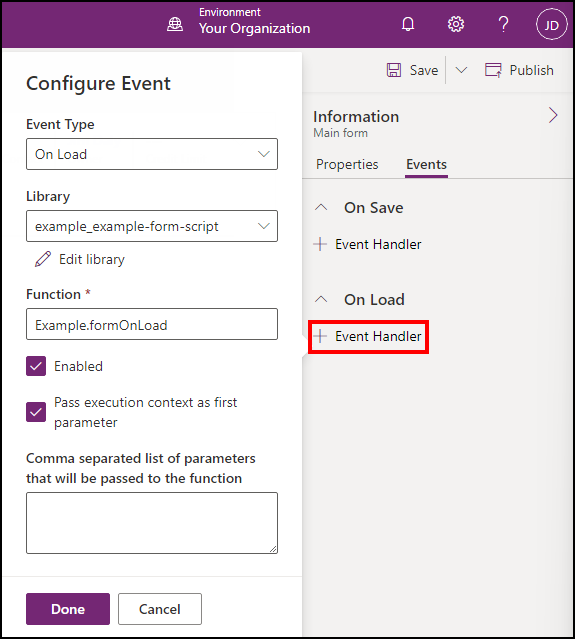
Make sure that:
- The Event Type is On Load.
- The example_example-form-script library is selected.
- Type the name of the function in the Function field. In this case
Example.formOnLoad. - Select Pass execution context as first parameter.
- Click Done.
Configure Form On Save event
Select On Save event handler and click + Event Handler.

Make sure that:
- The Event Type is On Save.
- The example_example-form-script library is selected.
- Type the name of the function in the Function field. In this case
Example.formOnSave.Note
It is not necessary to elect Pass execution context as first parameter for this function because it doesn't use it.
- Click Done
Configure Field On Change event
Select the Account Name field and the Events tab.
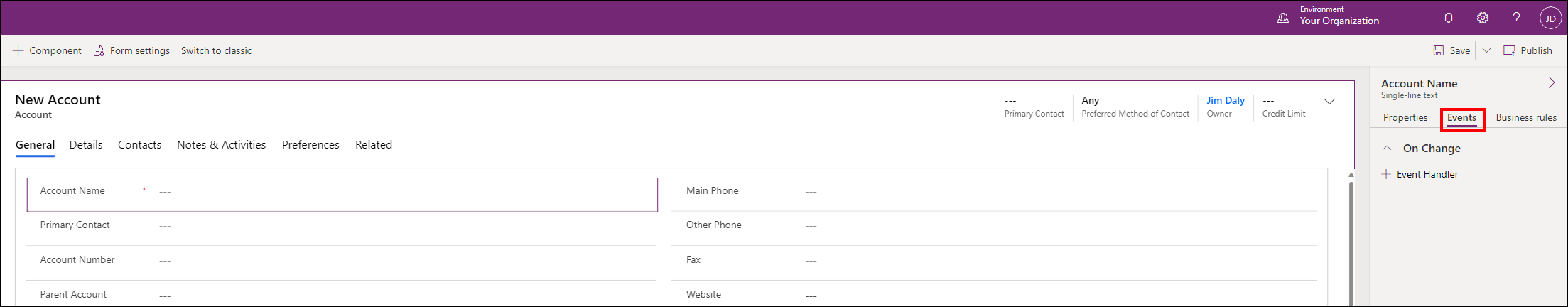
Select the On Change event handler and click + Event Handler.
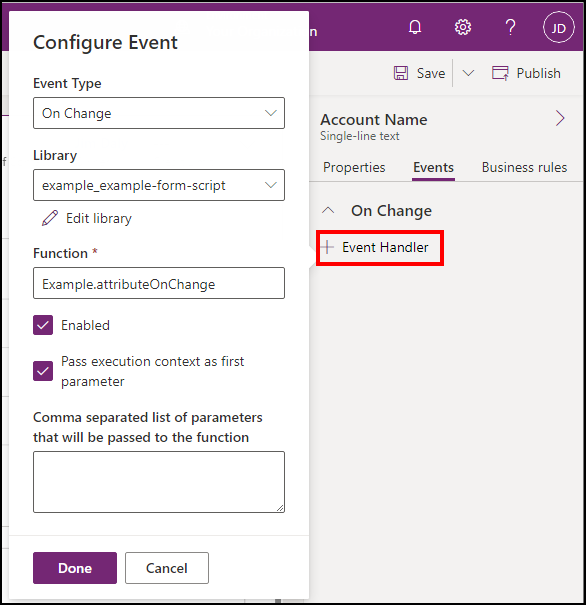
Make sure that:
- The Event Type is On Change.
- The example_example-form-script library is selected.
- Type the name of the function in the Function field. In this case
Example.attributeOnChange. - Select Pass execution context as first parameter.
- Click Done
Save and publish your changes
Save the form an click Publish.
Step 6: Test your code
It is recommended that you refresh your browser for the changes to take effect in your model-driven apps instance.
To test your code:
Navigate to Power Apps.
In the left navigation area select Apps.
Double-click the model-driven app you just edited, or select it and click Play.
Test form On Load function
Click on any account record in the list to open it.
Verify that the notification appears.
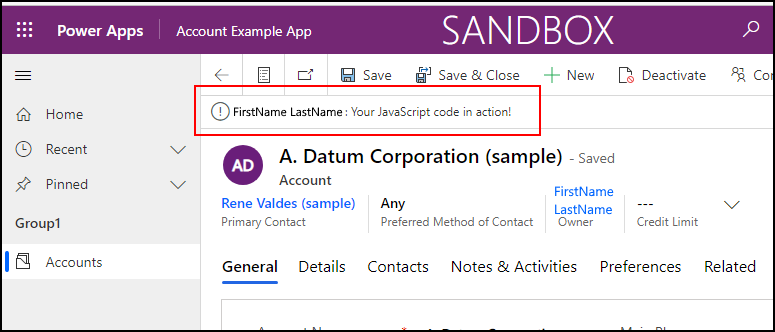
Verify the notification disappears in 5 seconds.
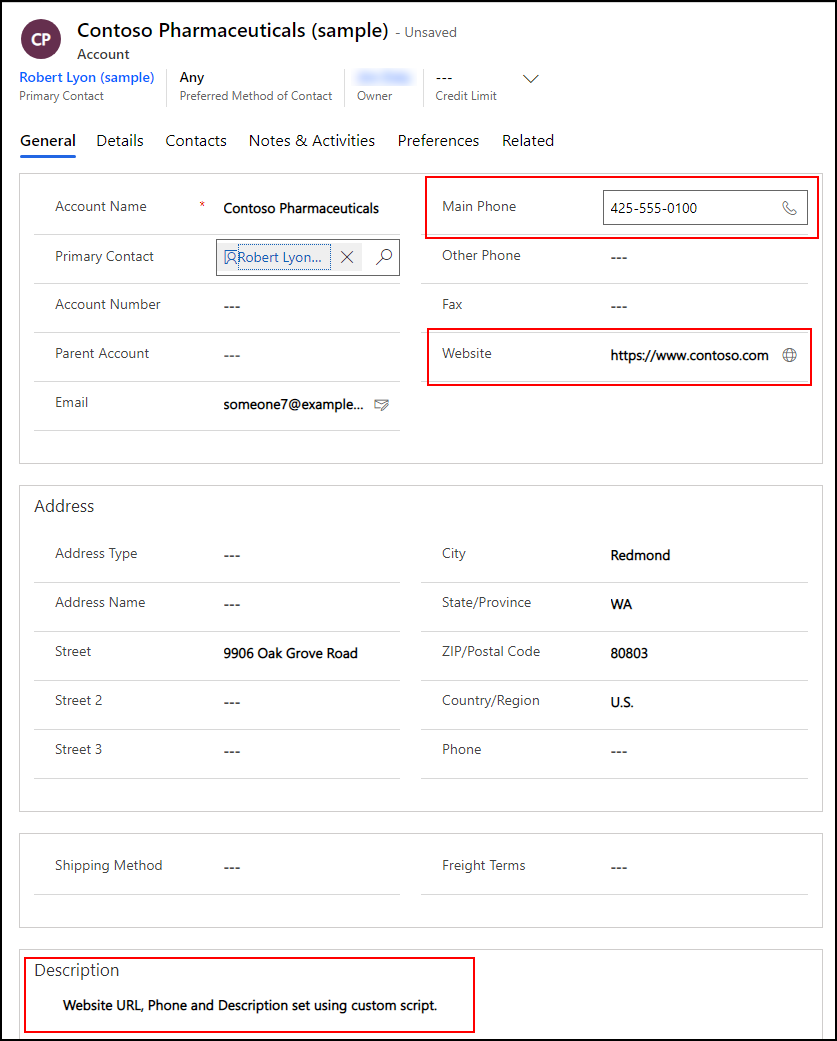
Test field On Change function
Edit the Account Name to include "Contoso" in the name and move to the next column by pressing TAB.
Verify the expected values set to the Main Phone, Website, and Description columns.
Test form On Save function
Click Save.
Verify that the alert dialog with a message that you configured in your code.
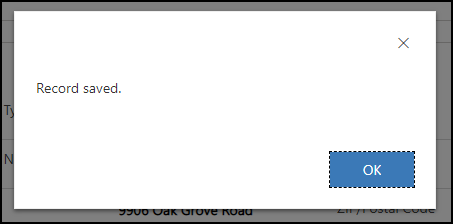
Click OK to close the alert.
Related articles
Debug JavaScript code for model-driven apps
Events in forms and grids in model-driven apps
Form OnLoad event
Form OnSave event (Client API reference) in model-driven apps
Column OnChange event (Client API reference)