Outbound data integration
Outbound data integration involves making data in Microsoft Dataverse available to external systems.
Dataverse event publishing
Microsoft Dataverse provides an event model that enables integration with external systems. This model, known as the Dataverse Event Framework, supports triggering custom code and external actions in response to platform events.
The Event Framework allows solution architects and developers to register custom code or processes that run when specific events occur. While often used to trigger custom plug-ins, the framework can also facilitate outbound integrations with other systems.
To use the Event Framework effectively, be familiar with:
- Available event types
- How events are processed
- What data is available at each stage
- Applicable time and resource limits
- Performance monitoring practices
The framework supports four processing stages:
- Pre-validation – Occurs before the main operation and any security checks. Use this stage to validate or cancel operations early.
- Pre-operation – Runs within the transaction scope before the operation is committed. Use this stage to modify data.
- Main operation – Reserved for internal operations and supported only in custom APIs and virtual tables.
- Post-operation – Executes after the operation is complete and within the transaction. Commonly used for outbound integration.
Note
Integration typically uses the Post-operation stage with asynchronous execution.
The Event Framework can trigger:
- Plug-ins
- Classic workflows
- Power Automate cloud flows
- Azure Service Bus and Event Hubs messages
- Webhooks
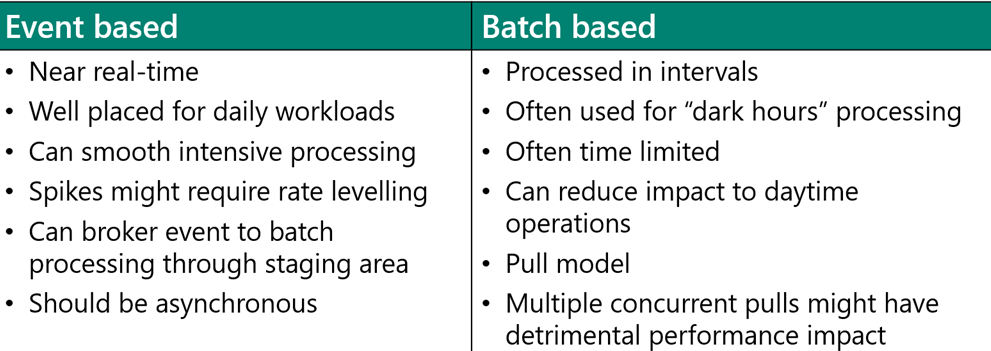
Event vs. batch
Solution architects should classify outbound data scenarios as event-driven or batch-based. The following diagram compares these two approaches:
Push pattern
The push pattern is commonly used for event-based processing. In this model, an event in Dataverse triggers a process that sends data to an external system.
To avoid performance issues and tight coupling, ensure that external calls triggered from Dataverse are optimized and nonblocking.
Important
Plug-ins are subject to a two-minute timeout. Use asynchronous processing for long-running tasks.
Pull pattern
The pull pattern relies on external systems initiating data retrieval from Dataverse, either on a schedule or in response to external events.
Note
The Recurrence trigger in Power Automate is frequently used in pull pattern implementations.
Change tracking
The change tracking feature in Dataverse enables efficient synchronization by identifying records that have changed since the last sync.
When enabled on a table, change tracking allows retrieval of only the modified rows, minimizing data transfer.
Note
Change tracking must be explicitly enabled for each table.
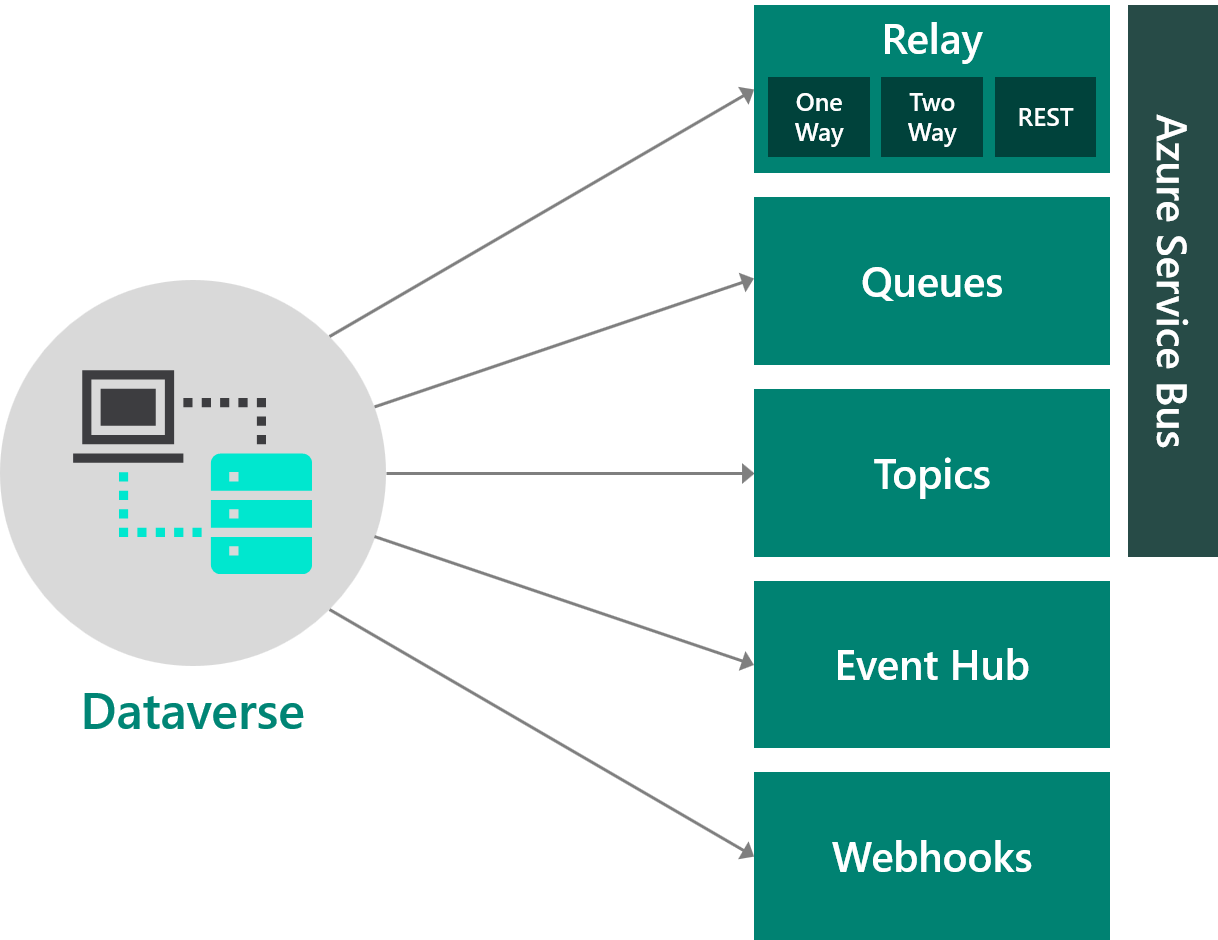
Azure integration
Dataverse supports outbound integration with Azure services through the Event Framework. The following diagram illustrates these integration points:
Azure Service Bus
Dataverse can publish messages to Microsoft Azure Service Bus, enabling secure, decoupled communication between systems. Benefits include:
- Load balancing across worker processes
- Secure routing and message transfer across service boundaries
- Coordination of high-reliability transactional workflows
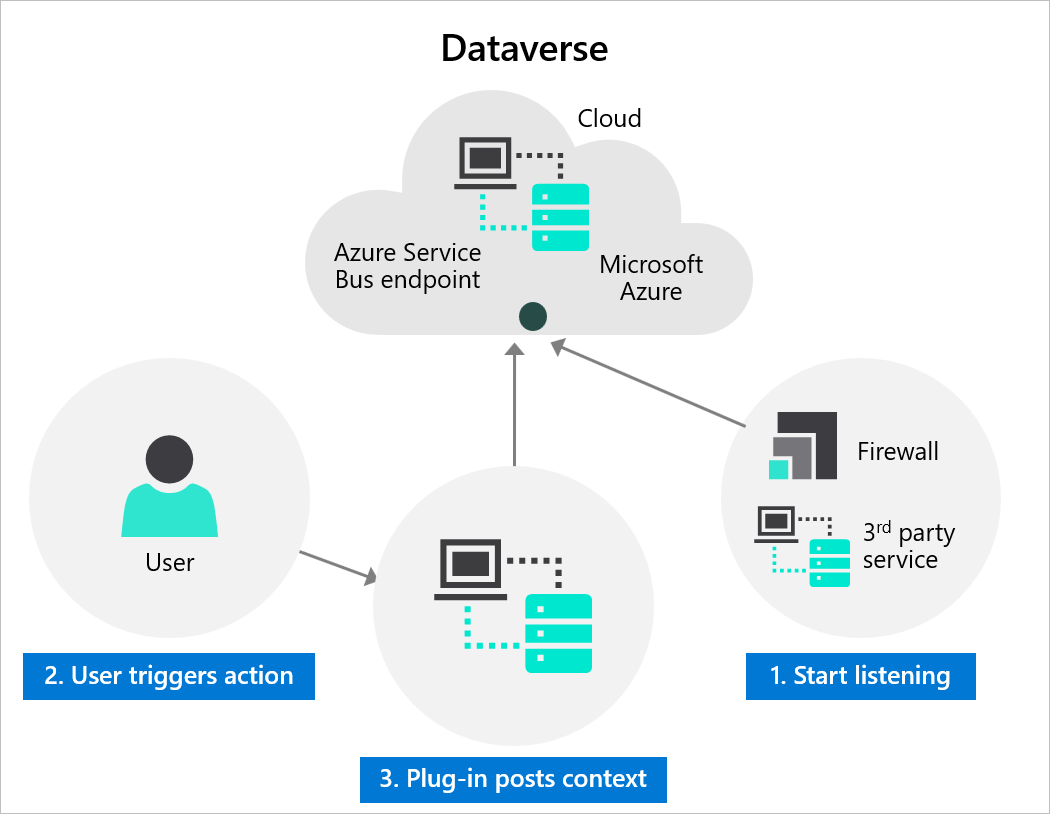
A listener application—such as an Azure Logic App or Azure Function—receives messages from the Service Bus and processes them based on the event context (such as table name, record ID, initiating user, and data changes).
Integration steps include:
- Registering an Azure Service Bus endpoint in Dataverse using the Plug-in Registration tool
- Defining steps to post messages on data events (such as record creation)
Listener implementations can include:
- A C# application polling messages from Service Bus
- An Azure Logic App triggered by new messages
- An Azure Function that responds to posted messages
Azure Service Bus is ideal when the receiving system has limited availability or must throttle high message volumes.
Message posting methods:
- Configuration-based (no code) – Define a step that sends event context to the Service Bus.
- Custom (code) – Develop and register a plug-in that posts a customized message to the Service Bus.
Use cases include:
- Building scalable cloud apps with messaging
- Managing burst traffic with message queues
- Decoupling systems for independent scaling
- Supporting ordered message delivery to multiple consumers
Azure Relay
Azure Relay enables secure, bidirectional communication between cloud and on-premises services without opening firewall ports or modifying network infrastructure.
Relay supports scenarios such as:
- One-way and request/response messaging
- Publish/subscribe for internet-scope event distribution
- Socket communication across network boundaries
Important
Azure Relay allows connected systems to exchange responses and acknowledgments over secure channels without requiring direct network access.
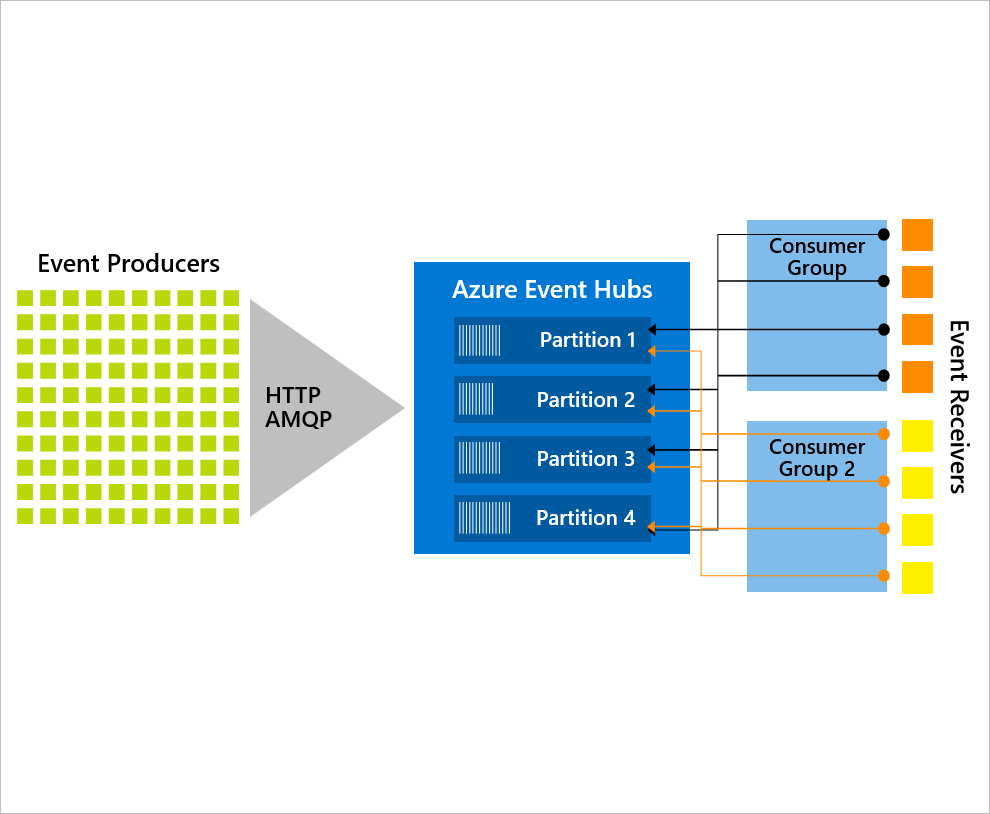
Azure Event Hubs
Azure Event Hubs is a high-throughput event ingestion service capable of handling millions of events per second.
It's well-suited for big data streaming and integrates with real-time analytics solutions. Use Event Hubs to:
- Broadcast events to multiple systems
- Filter messages via consumer groups
- Stream events into services like Microsoft Power BI
Note
Topics in Azure Service Bus offer similar functionality for message filtering and distribution.
Webhooks and Azure Functions
Webhooks provide a lightweight HTTP-based pattern for integrating Dataverse with external services.
Registered using the Plug-in Registration tool, webhooks send POST requests with JSON payloads to external endpoints when triggered by events.
Webhooks:
- Support both synchronous and asynchronous steps
- Use standard web technologies across platforms
- Can be secured with authentication headers or query string tokens
Azure Functions can serve as webhook endpoints to implement scalable integration logic.
Choosing between Webhooks and Service Bus
| Feature | Webhooks | Azure Service Bus |
|---|---|---|
| Scalability | Limited by endpoint capacity | High-throughput queuing |
| Message persistence | Requires custom retry | Built-in queuing and retries |
| Sync support | Supports sync and async | Async only |
| Simplicity | Lightweight | Enterprise-grade |
| Hosting | Any web app | Azure infrastructure |
Process integration: Power Automate vs. Azure Logic Apps
Power Automate cloud flows and Azure Logic Apps share a common runtime but differ in features and use cases.
Power Automate:
- Includes advanced Dataverse connector support
- Can be packaged as part of a solution
- Supports robotic process automation (RPA) with desktop flows
- Offers built-in approvals and notifications
- Subject to monthly flow run limits
Azure Logic Apps:
- Designed for enterprise integration (including EDI)
- Offers higher throughput and performance
- Supports robust error handling and monitoring via Azure tools
- Not packaged within Power Platform solutions
- Uses consumption-based or fixed pricing via Azure subscription