Obs!
Tilgang til denne siden krever autorisasjon. Du kan prøve å logge på eller endre kataloger.
Tilgang til denne siden krever autorisasjon. Du kan prøve å endre kataloger.
Azure Virtual Network Manager is a centralized management service that enables you to group, configure, deploy, and manage virtual networks globally across subscriptions and tenants. As organizations scale their cloud infrastructure, managing multiple virtual networks across different regions and subscriptions becomes increasingly complex. Azure Virtual Network Manager addresses this challenge by providing a unified pane of glass for network administration.
With Virtual Network Manager, you can define network groups to identify and logically segment your virtual networks. Then you can determine the connectivity, security, and routing configurations you want and apply them across all the selected virtual networks in network groups at once, ensuring consistent network policies across your entire infrastructure. You can also leverage Virtual Network Manager's capabilities to manage your organization's IP address space and democratize simple network connectivity troubleshooting.
How does Azure Virtual Network Manager work?
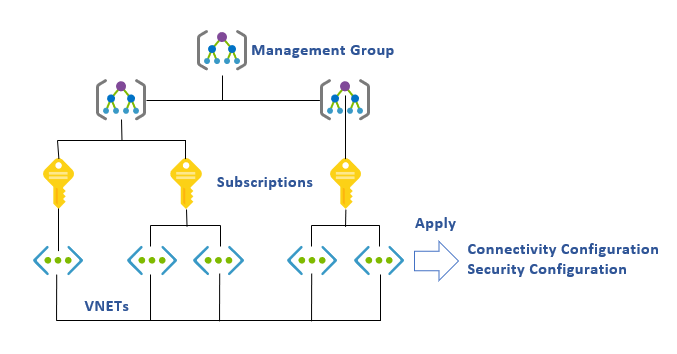
During the creation process, you define the scope for what your Azure Virtual Network Manager instance, or network manager, manages. Your network manager only has the delegated access for resource visibility, configuration deployment, and IP address management within this scope boundary. You can define a scope directly over a list of subscriptions. You may also use management groups to define your scope. Management groups provide hierarchical organization to your subscriptions. After defining your network manager's scope, you can deploy configuration types including Connectivity, Security admin, and Routing across grouped network resources within this scope. You can also use the network manager to manage your organization's IP address space and troubleshoot reachability issues across the Azure network resources within your network manager's scope.
After you deploy the network manager, you create a network group, which serves as a logical container of networking resources to apply configurations at scale. You can manually select individual virtual networks to be added to your network group, or you can use Azure Policy to define conditions that govern your group membership dynamically. For more information about Azure Policy initiatives, see Network groups and Azure Policy.
Next, you create configurations applied to those network groups based on your topology and security needs. A connectivity configuration enables you to create a mesh or a hub-and-spoke network topology using your network groups. A security admin configuration allows you to define a collection of security admin rules that you can apply onto one or more network groups, programming those rules across your virtual networks globally. A routing configuration lets you describe and orchestrate user-defined routes at scale to control traffic flow according to your desired routing behavior.
Once you create your desired network groups and configurations, you can deploy the configurations to any region of your choosing. Configurations do not take effect until they are deployed to regions containing your target network resources.
Azure Virtual Network Manager can be deployed and managed through the Azure portal, Azure CLI, Azure PowerShell, Bicep, or Terraform.
Key benefits
Centralized management: Manage connectivity and security policies globally across regions and subscriptions from a single pane of glass, reducing administrative overhead and ensuring consistency.
Simplified hub-and-spoke connectivity: Enable direct connectivity between spoke virtual networks in a hub-and-spoke configuration without the complexity of managing a mesh network or manually configuring additional peerings.
Enterprise-grade reliability: Azure Virtual Network Manager is a highly scalable and highly available service with redundancy and replication across the globe.
Advanced security controls: Create network security rules that are evaluated before network security group rules, providing granular control over traffic flow with global enforcement capabilities.
Optimized performance: Low latency and high bandwidth between resources in different virtual networks using virtual network peering.
Flexible deployment: Roll out network changes through a specific region sequence and frequency of your choosing for controlled and safe network updates and rollbacks.
Cost optimization: Reduce operational costs by automating network management tasks and eliminating the need for complex custom scripting solutions.
Centralized IP address management: Manage your organization's IP address space by automatically allocating non-overlapping IP address space from IP address pools to prevent address space conflicts across on-premises and multicloud environments.
Reachability verification: Validate Azure network policies and troubleshoot connectivity issues by analyzing reachability paths between Azure resources and identifying Azure policies and configurations disallowing network traffic.
Use cases
Learn more about common use cases for Azure Virtual Network Manager.
Regions
For current information on the regions where Azure Virtual Network Manager is available, see Azure Virtual Network Manager regions.
Pricing
For pricing details, see Azure Virtual Network Manager pricing.
New Azure Virtual Network Manager instances charge solely on the virtual network-based pricing described in the pricing page.
Azure Virtual Network Manager instances created before the release of the virtual network-based pricing continue to charge on the subscription-based pricing described in the pricing page. If you prefer for your Azure Virtual Network Manager instance to instead charge on the virtual network-based pricing, follow these steps to switch its pricing model through Azure Feature Exposure Control (AFEC).
- In the Azure portal, search for Preview features.
- On the Preview Features page, ensure the subscription selected is the subscription that contains your Azure Virtual Network Manager instance. Filter the features by Network manager.
- Select the feature named Network manager billing by virtual networks and register. The Azure Virtual Network Manager instance in the registered subscription now charges on the virtual network-based pricing.
Note
This virtual network-based pricing is generally available. Its enablement mechanism is available through AFEC for ease of setup and because the previous subscription-based pricing is not yet retired. The subscription-based pricing announced its retirement to pre-existing Azure Virtual Network Manager customers on February 6, 2025, and will be fully retired in February 6, 2028. Any Azure Virtual Network Manager instances still using the subscription-based pricing after February 6, 2028, will be automatically switched to the virtual network-based pricing.
FAQs
For FAQs, see Azure Virtual Network Manager FAQs.
Limits
For limits, see Azure Virtual Network Manager limits.
Service Level Agreement (SLA)
For SLA, see SLA for Azure Virtual Network Manager