Notitie
Voor toegang tot deze pagina is autorisatie vereist. U kunt proberen u aan te melden of mappen te wijzigen.
Voor toegang tot deze pagina is autorisatie vereist. U kunt proberen om mappen te wijzigen.
Van toepassing op:✅ Data-engineer ing en Datawetenschap in Microsoft Fabric
Meer informatie over het verzenden van Spark-sessietaken met behulp van de Livy-API voor Fabric Data Engineering.
Vereisten
Fabric Premium- of proefcapaciteit met een Lakehouse
Een externe client zoals Visual Studio Code met Jupyter Notebooks, PySpark en de Microsoft Authentication Library (MSAL) voor Python
Een Microsoft Entra-app-token. Een toepassing registreren met het Microsoft Identity Platform
Of een Microsoft Entra SPN-token. Toepassingsreferenties toevoegen en beheren in Microsoft Entra
Bepaalde gegevens in uw lakehouse, in dit voorbeeld wordt NYC Taxi & Limousine Commission green_tripdata_2022_08 een parquet-bestand geladen in de lakehouse
De Livy-API definieert een uniform eindpunt voor bewerkingen. Vervang de tijdelijke aanduidingen {Entra_TenantID}, {Entra_ClientID}, {Fabric_WorkspaceID}, {Fabric_LakehouseID} door de juiste waarden wanneer u de voorbeelden in dit artikel volgt.
Visual Studio Code configureren voor uw Livy API-sessie
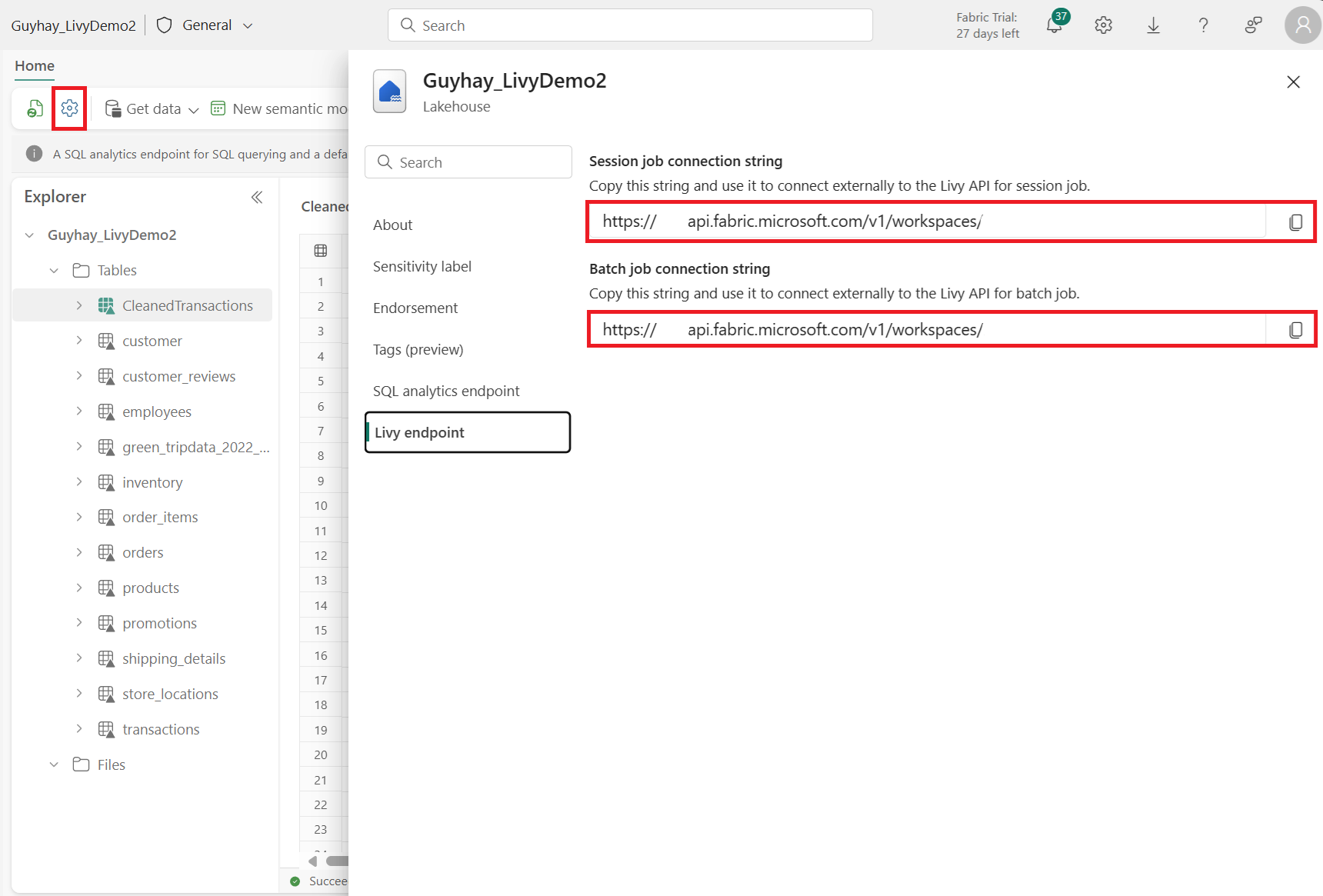
Selecteer Lakehouse-instellingen in uw Fabric Lakehouse.
Navigeer naar de Livy endpoint-sectie.
Kopieer de sessietaak verbindingsreeks (eerste rood vak in de afbeelding) naar uw code.
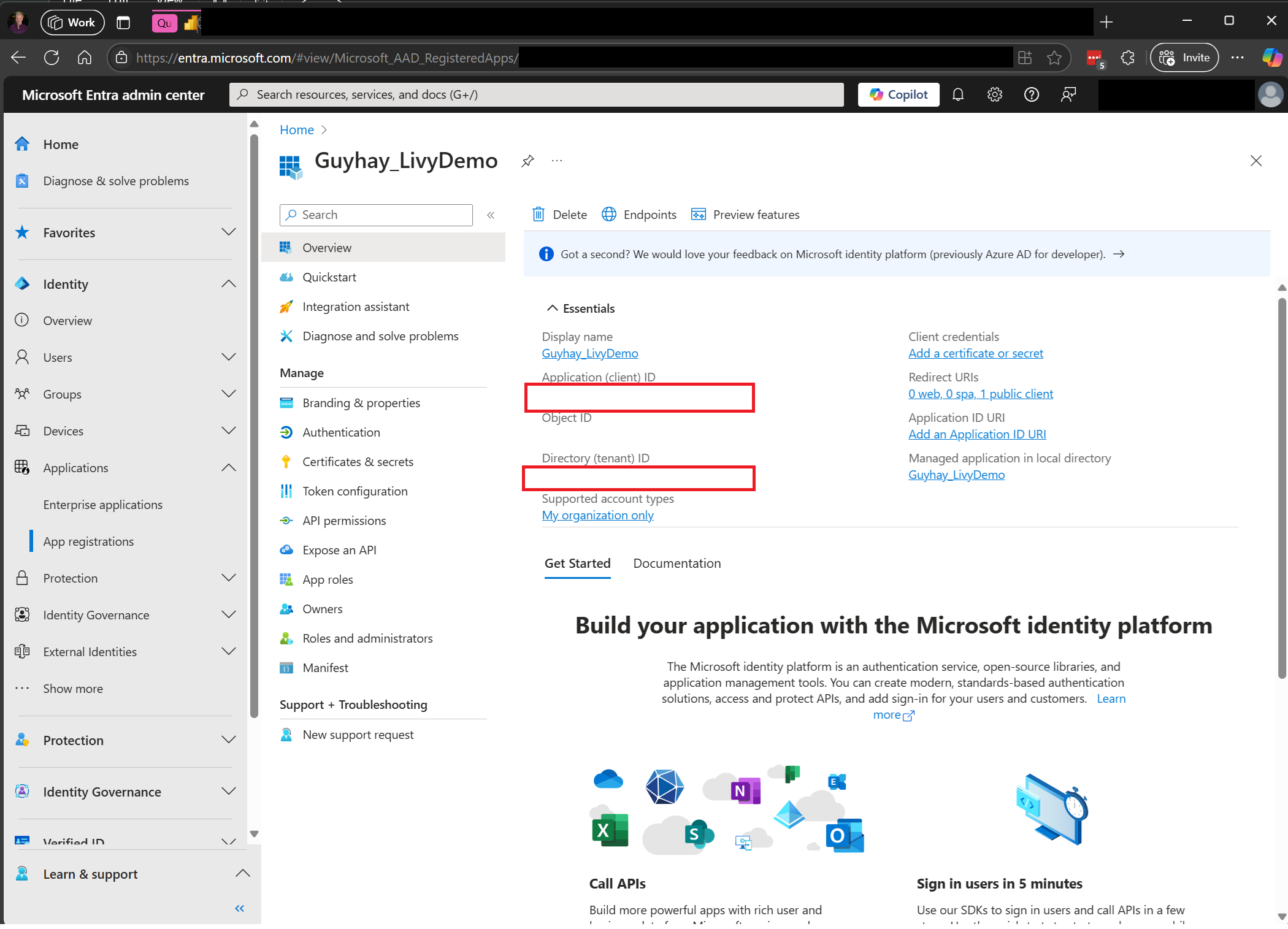
Navigeer naar het Microsoft Entra-beheercentrum en kopieer zowel de toepassings-id (client-id) als de map-id (tenant) naar uw code.
Een Livy API Spark-sessie verifiëren met behulp van een Microsoft Entra-gebruikerstoken of een Microsoft Entra SPN-token
Een Livy API Spark-sessie verifiëren met behulp van een Microsoft Entra SPN-token
Maak een
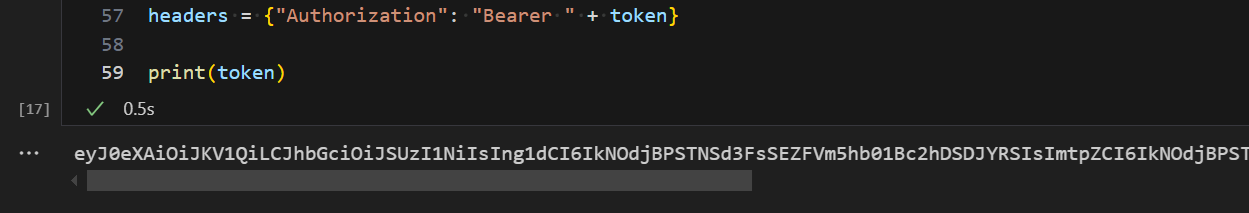
.ipynbnotebook in Visual Studio Code en voeg de volgende code in.import sys from msal import ConfidentialClientApplication # Configuration - Replace with your actual values tenant_id = "Entra_TenantID" # Microsoft Entra tenant ID client_id = "Entra_ClientID" # Service Principal Application ID # Certificate paths - Update these paths to your certificate files certificate_path = "PATH_TO_YOUR_CERTIFICATE.pem" # Public certificate file private_key_path = "PATH_TO_YOUR_PRIVATE_KEY.pem" # Private key file certificate_thumbprint = "YOUR_CERTIFICATE_THUMBPRINT" # Certificate thumbprint # OAuth settings audience = "https://analysis.windows.net/powerbi/api/.default" authority = f"https://login.windows.net/{tenant_id}" def get_access_token(client_id, audience, authority, certificate_path, private_key_path, certificate_thumbprint=None): """ Get an app-only access token for a Service Principal using OAuth 2.0 client credentials flow. This function uses certificate-based authentication which is more secure than client secrets. Args: client_id (str): The Service Principal's client ID audience (str): The audience for the token (resource scope) authority (str): The OAuth authority URL certificate_path (str): Path to the certificate file (.pem format) private_key_path (str): Path to the private key file (.pem format) certificate_thumbprint (str): Certificate thumbprint (optional but recommended) Returns: str: The access token for API authentication Raises: Exception: If token acquisition fails """ try: # Read the certificate from PEM file with open(certificate_path, "r", encoding="utf-8") as f: certificate_pem = f.read() # Read the private key from PEM file with open(private_key_path, "r", encoding="utf-8") as f: private_key_pem = f.read() # Create the confidential client application app = ConfidentialClientApplication( client_id=client_id, authority=authority, client_credential={ "private_key": private_key_pem, "thumbprint": certificate_thumbprint, "certificate": certificate_pem } ) # Acquire token using client credentials flow token_response = app.acquire_token_for_client(scopes=[audience]) if "access_token" in token_response: print("Successfully acquired access token") return token_response["access_token"] else: raise Exception(f"Failed to retrieve token: {token_response.get('error_description', 'Unknown error')}") except FileNotFoundError as e: print(f"Certificate file not found: {e}") sys.exit(1) except Exception as e: print(f"Error retrieving token: {e}", file=sys.stderr) sys.exit(1) # Get the access token token = get_access_token(client_id, audience, authority, certificate_path, private_key_path, certificate_thumbprint)Voer de notebookcel uit. U ziet dat het Microsoft Entra-token is geretourneerd.
Een Livy API Spark-sessie verifiëren met behulp van een Microsoft Entra-gebruikerstoken
Maak een
.ipynbnotebook in Visual Studio Code en voeg de volgende code in.from msal import PublicClientApplication import requests import time # Configuration - Replace with your actual values tenant_id = "Entra_TenantID" # Microsoft Entra tenant ID client_id = "Entra_ClientID" # Application ID (can be the same as above or different) # Required scopes for Microsoft Fabric API access scopes = [ "https://api.fabric.microsoft.com/Lakehouse.Execute.All", # Execute operations in lakehouses "https://api.fabric.microsoft.com/Lakehouse.Read.All", # Read lakehouse metadata "https://api.fabric.microsoft.com/Item.ReadWrite.All", # Read/write fabric items "https://api.fabric.microsoft.com/Workspace.ReadWrite.All", # Access workspace operations "https://api.fabric.microsoft.com/Code.AccessStorage.All", # Access storage from code "https://api.fabric.microsoft.com/Code.AccessAzureKeyvault.All", # Access Azure Key Vault "https://api.fabric.microsoft.com/Code.AccessAzureDataExplorer.All", # Access Azure Data Explorer "https://api.fabric.microsoft.com/Code.AccessAzureDataLake.All", # Access Azure Data Lake "https://api.fabric.microsoft.com/Code.AccessFabric.All" # General Fabric access ] def get_access_token(tenant_id, client_id, scopes): """ Get an access token using interactive authentication. This method will open a browser window for user authentication. Args: tenant_id (str): The Microsoft Entra tenant ID client_id (str): The application client ID scopes (list): List of required permission scopes Returns: str: The access token, or None if authentication fails """ app = PublicClientApplication( client_id, authority=f"https://login.microsoftonline.com/{tenant_id}" ) print("Opening browser for interactive authentication...") token_response = app.acquire_token_interactive(scopes=scopes) if "access_token" in token_response: print("Successfully authenticated") return token_response["access_token"] else: print(f"Authentication failed: {token_response.get('error_description', 'Unknown error')}") return None # Uncomment the lines below to use interactive authentication token = get_access_token(tenant_id, client_id, scopes) print("Access token acquired via interactive login")Voer de notebookcel uit. U ziet dat het Microsoft Entra-token is geretourneerd.
Een Livy API Spark-sessie maken
Voeg nog een notebookcel toe en voeg deze code in.
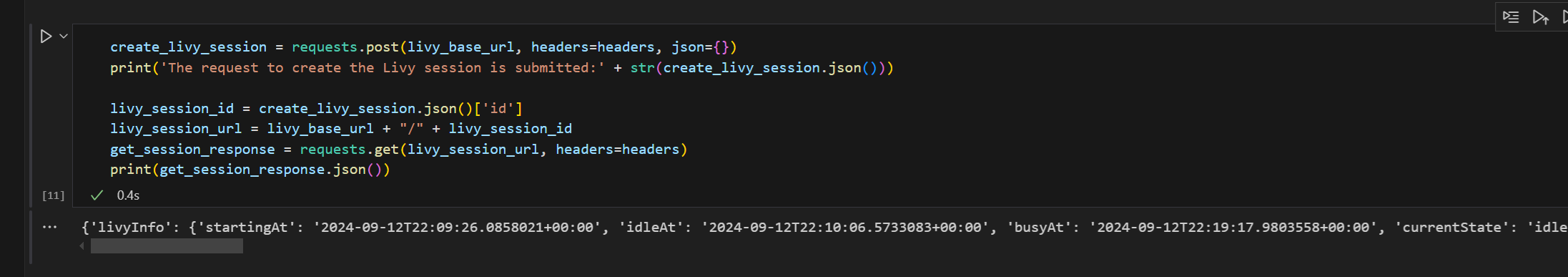
import json import requests api_base_url = "https://api.fabric.microsoft.com/" # Base URL for Fabric APIs # Fabric Resource IDs - Replace with your workspace and lakehouse IDs workspace_id = "Fabric_WorkspaceID" lakehouse_id = "Fabric_LakehouseID" # Construct the Livy API session URL # URL pattern: {base_url}/v1/workspaces/{workspace_id}/lakehouses/{lakehouse_id}/livyapi/versions/{api_version}/sessions livy_api_session_url = (f"{api_base_url}v1/workspaces/{workspace_id}/lakehouses/{lakehouse_id}/" f"livyapi/versions/2023-12-01/sessions") # Set up authentication headers headers = {"Authorization": f"Bearer {token}"} print(f"Livy API URL: {livy_api_session_url}") print("Creating Livy session...") try: # Create a new Livy session with default configuration create_livy_session = requests.post(livy_api_session_url, headers=headers, json={}) # Check if the request was successful if create_livy_session.status_code == 200: session_info = create_livy_session.json() print('Livy session creation request submitted successfully') print(f'Session Info: {json.dumps(session_info, indent=2)}') # Extract session ID for future operations livy_session_id = session_info['id'] livy_session_url = f"{livy_api_session_url}/{livy_session_id}" print(f"Session ID: {livy_session_id}") print(f"Session URL: {livy_session_url}") else: print(f"Failed to create session. Status code: {create_livy_session.status_code}") print(f"Response: {create_livy_session.text}") except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e: print(f"Network error occurred: {e}") except json.JSONDecodeError as e: print(f"JSON decode error: {e}") print(f"Response text: {create_livy_session.text}") except Exception as e: print(f"Unexpected error: {e}")Voer de notebookcel uit en u zult zien dat er één regel wordt afgedrukt zodra de Livy-sessie is aangemaakt.
U kunt verifiëren of de Livy-sessie is aangemaakt door gebruik te maken van [Het controleren van uw taken in de Bewakingshub](#View uw taken in de Monitoring Hub).
Integratie met Fabric-omgevingen
Deze Livy API-sessie wordt standaard uitgevoerd op basis van de standaardstartgroep voor de werkruimte. U kunt ook Infrastructuuromgevingen maken, configureren en gebruiken in Microsoft Fabric om de Spark-pool aan te passen die door de Livy API-sessie wordt gebruikt voor deze Spark-taken. Als u een Fabric-omgeving wilt gebruiken, update dan de vorige notebookcel met deze JSON payload.
create_livy_session = requests.post(livy_base_url, headers = headers, json = {
"conf" : {
"spark.fabric.environmentDetails" : "{\"id\" : \""EnvironmentID""}"}
}
)
Een spark.sql-instructie verzenden met behulp van de Spark-sessie van de Livy-API
Voeg nog een notebookcel toe en voeg deze code in.
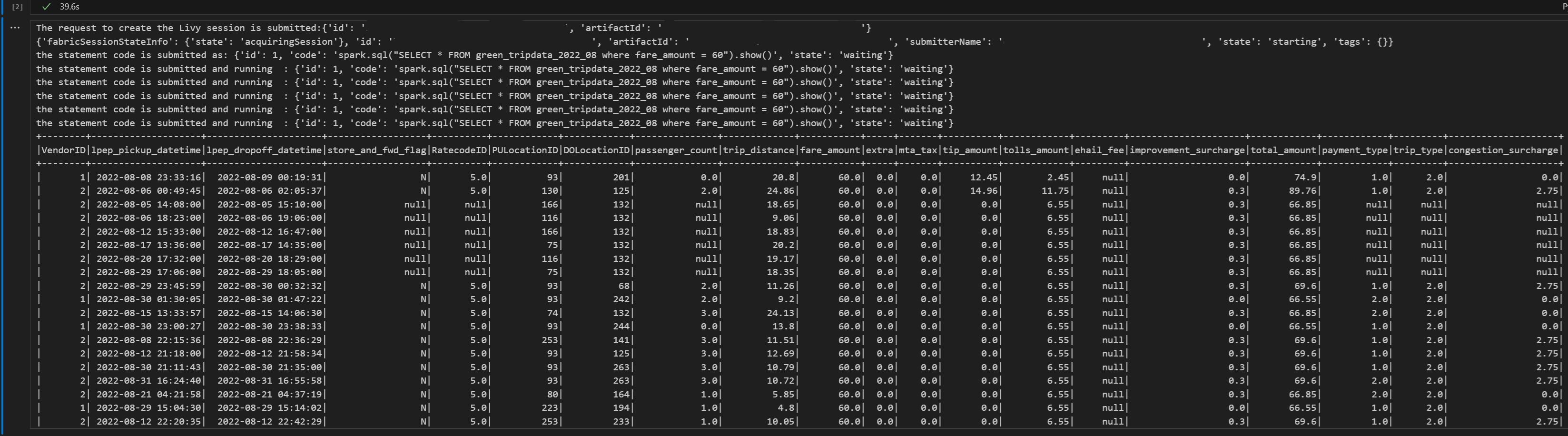
# call get session API import time table_name = "green_tripdata_2022" print("Checking session status...") # Get current session status get_session_response = requests.get(livy_session_url, headers=headers) session_status = get_session_response.json() print(f"Current session state: {session_status['state']}") # Wait for session to become idle (ready to accept statements) print("Waiting for session to become idle...") while session_status["state"] != "idle": print(f" Session state: {session_status['state']} - waiting 5 seconds...") time.sleep(5) get_session_response = requests.get(livy_session_url, headers=headers) session_status = get_session_response.json() print("Session is now idle and ready to accept statements") # Execute a Spark SQL statement execute_statement_url = f"{livy_session_url}/statements" # Define your Spark SQL query - Replace with your actual table and query payload_data = { "code": "spark.sql(\"SELECT * FROM {table_name} WHERE column_name = 'some_value' LIMIT 10\").show()", "kind": "spark" # Type of code (spark, pyspark, sql, etc.) } print("Submitting Spark SQL statement...") print(f"Query: {payload_data['code']}") try: # Submit the statement for execution execute_statement_response = requests.post(execute_statement_url, headers=headers, json=payload_data) if execute_statement_response.status_code == 200: statement_info = execute_statement_response.json() print('Statement submitted successfully') print(f"Statement Info: {json.dumps(statement_info, indent=2)}") # Get statement ID for monitoring statement_id = str(statement_info['id']) get_statement_url = f"{livy_session_url}/statements/{statement_id}" print(f"Statement ID: {statement_id}") # Monitor statement execution print("Monitoring statement execution...") get_statement_response = requests.get(get_statement_url, headers=headers) statement_status = get_statement_response.json() while statement_status["state"] != "available": print(f" Statement state: {statement_status['state']} - waiting 5 seconds...") time.sleep(5) get_statement_response = requests.get(get_statement_url, headers=headers) statement_status = get_statement_response.json() # Retrieve and display results print("Statement execution completed!") if 'output' in statement_status and 'data' in statement_status['output']: results = statement_status['output']['data']['text/plain'] print("Query Results:") print(results) else: print("No output data available") else: print(f"Failed to submit statement. Status code: {execute_statement_response.status_code}") print(f"Response: {execute_statement_response.text}") except Exception as e: print(f"Error executing statement: {e}")Voer de notebookcel uit. U zou meerdere oplopende regels moeten zien terwijl de taak wordt ingediend en de resultaten worden geretourneerd.
Een tweede spark.sql-instructie verzenden met behulp van de Spark-sessie van de Livy-API
Voeg nog een notebookcel toe en voeg deze code in.
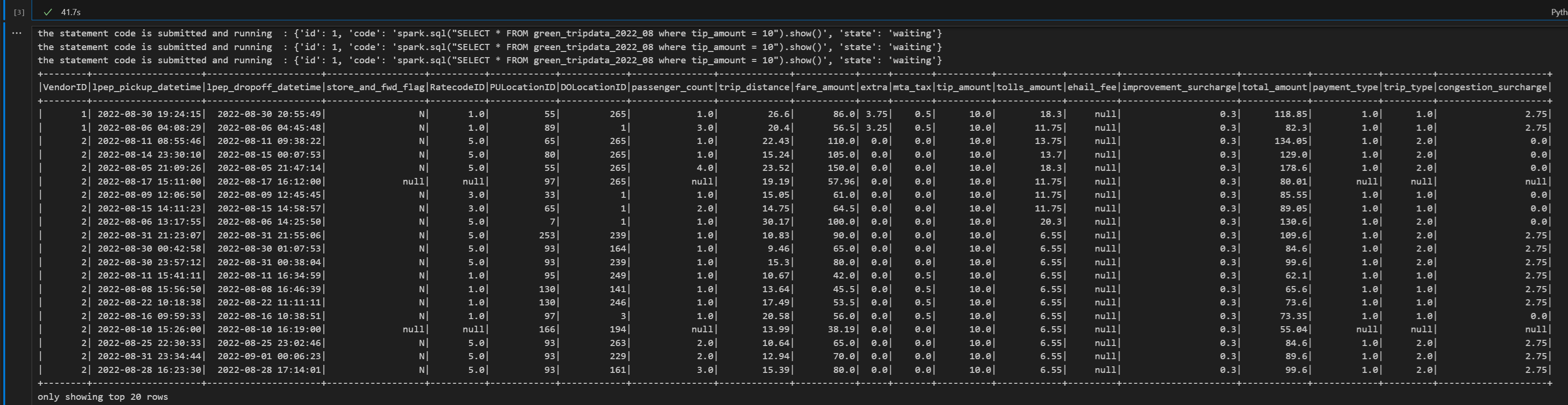
print("Executing additional Spark SQL statement...") # Wait for session to be idle again get_session_response = requests.get(livy_session_url, headers=headers) session_status = get_session_response.json() while session_status["state"] != "idle": print(f" Waiting for session to be idle... Current state: {session_status['state']}") time.sleep(5) get_session_response = requests.get(livy_session_url, headers=headers) session_status = get_session_response.json() # Execute another statement - Replace with your actual query payload_data = { "code": f"spark.sql(\"SELECT COUNT(*) as total_records FROM {table_name}\").show()", "kind": "spark" } print(f"Executing query: {payload_data['code']}") try: # Submit the second statement execute_statement_response = requests.post(execute_statement_url, headers=headers, json=payload_data) if execute_statement_response.status_code == 200: statement_info = execute_statement_response.json() print('Second statement submitted successfully') statement_id = str(statement_info['id']) get_statement_url = f"{livy_session_url}/statements/{statement_id}" # Monitor execution print("Monitoring statement execution...") get_statement_response = requests.get(get_statement_url, headers=headers) statement_status = get_statement_response.json() while statement_status["state"] != "available": print(f" Statement state: {statement_status['state']} - waiting 5 seconds...") time.sleep(5) get_statement_response = requests.get(get_statement_url, headers=headers) statement_status = get_statement_response.json() # Display results print("Second statement execution completed!") if 'output' in statement_status and 'data' in statement_status['output']: results = statement_status['output']['data']['text/plain'] print("Query Results:") print(results) else: print("No output data available") else: print(f"Failed to submit second statement. Status code: {execute_statement_response.status_code}") except Exception as e: print(f"Error executing second statement: {e}")Voer de notebookcel uit. U zou meerdere oplopende regels moeten zien terwijl de taak wordt ingediend en de resultaten worden geretourneerd.
De Livy-sessie beëindigen
Voeg nog een notebookcel toe en voeg deze code in.
print("Cleaning up Livy session...") try: # Check current session status before deletion get_session_response = requests.get(livy_session_url, headers=headers) if get_session_response.status_code == 200: session_info = get_session_response.json() print(f"Session state before deletion: {session_info.get('state', 'unknown')}") print(f"Deleting session at: {livy_session_url}") # Delete the session delete_response = requests.delete(livy_session_url, headers=headers) if delete_response.status_code == 200: print("Session deleted successfully") elif delete_response.status_code == 404: print("Session was already deleted or not found") else: print(f"Delete request completed with status code: {delete_response.status_code}") print(f"Response: {delete_response.text}") print(f"Delete response details: {delete_response}") except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e: print(f"Network error during session deletion: {e}") except Exception as e: print(f"Error during session cleanup: {e}")
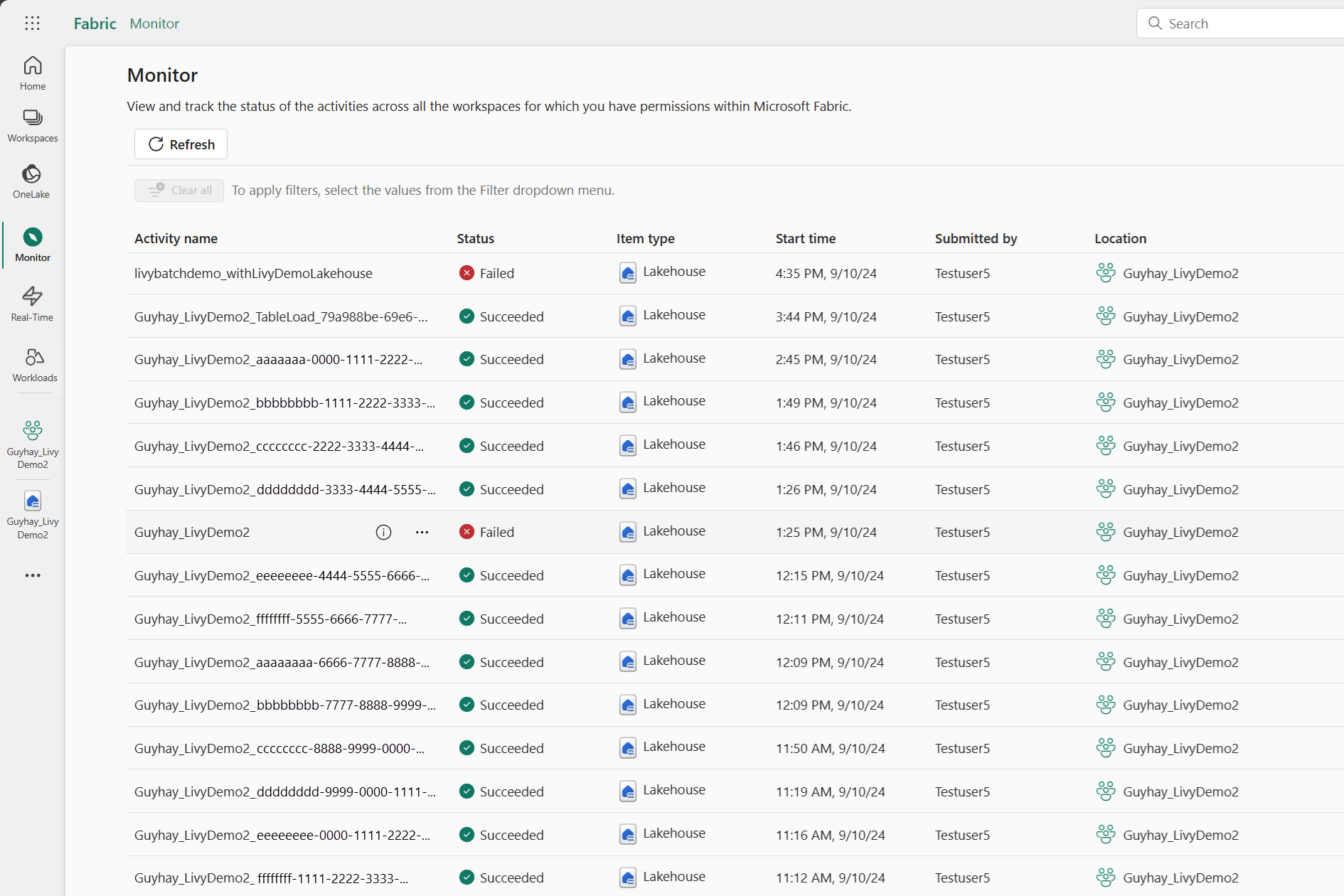
Uw taken weergeven in de Bewakingshub
U hebt toegang tot de Bewakingshub om verschillende Apache Spark-activiteiten weer te geven door Monitor te selecteren in de navigatiekoppelingen aan de linkerkant.
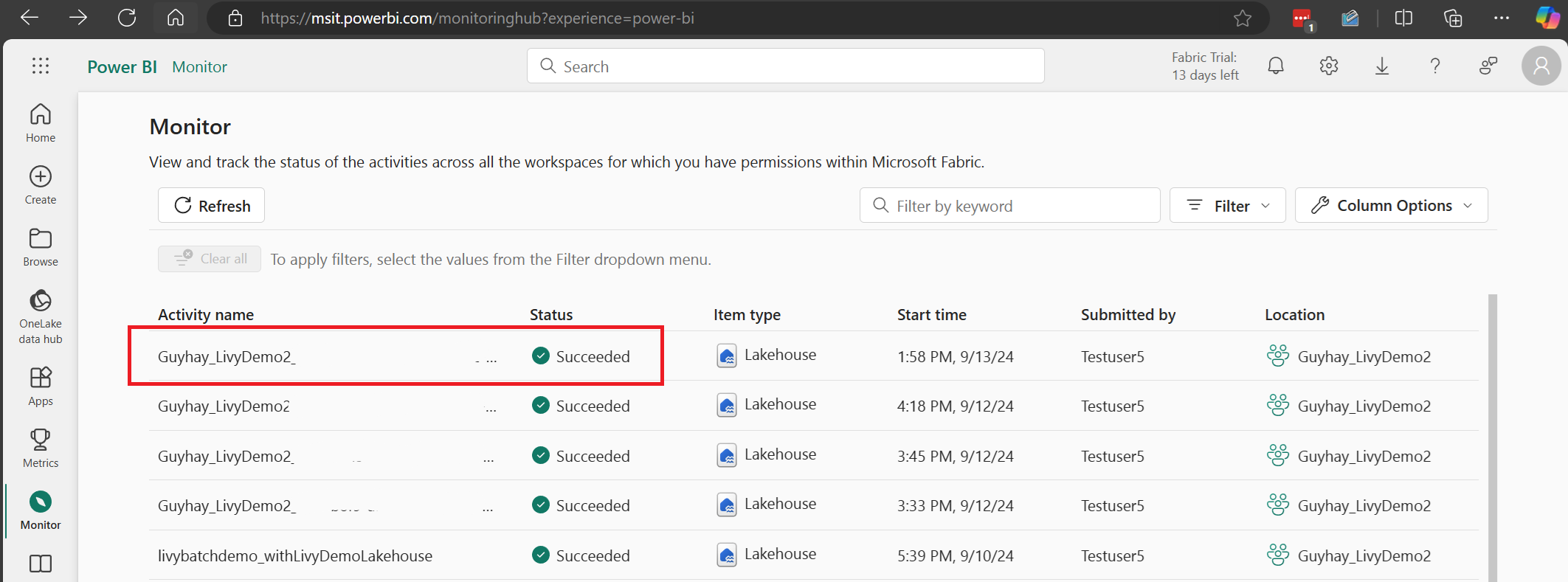
Wanneer de sessie wordt uitgevoerd of de voltooide status heeft, kunt u de sessiestatus bekijken door naar Monitor te navigeren.
Selecteer en open de naam van de meest recente activiteit.
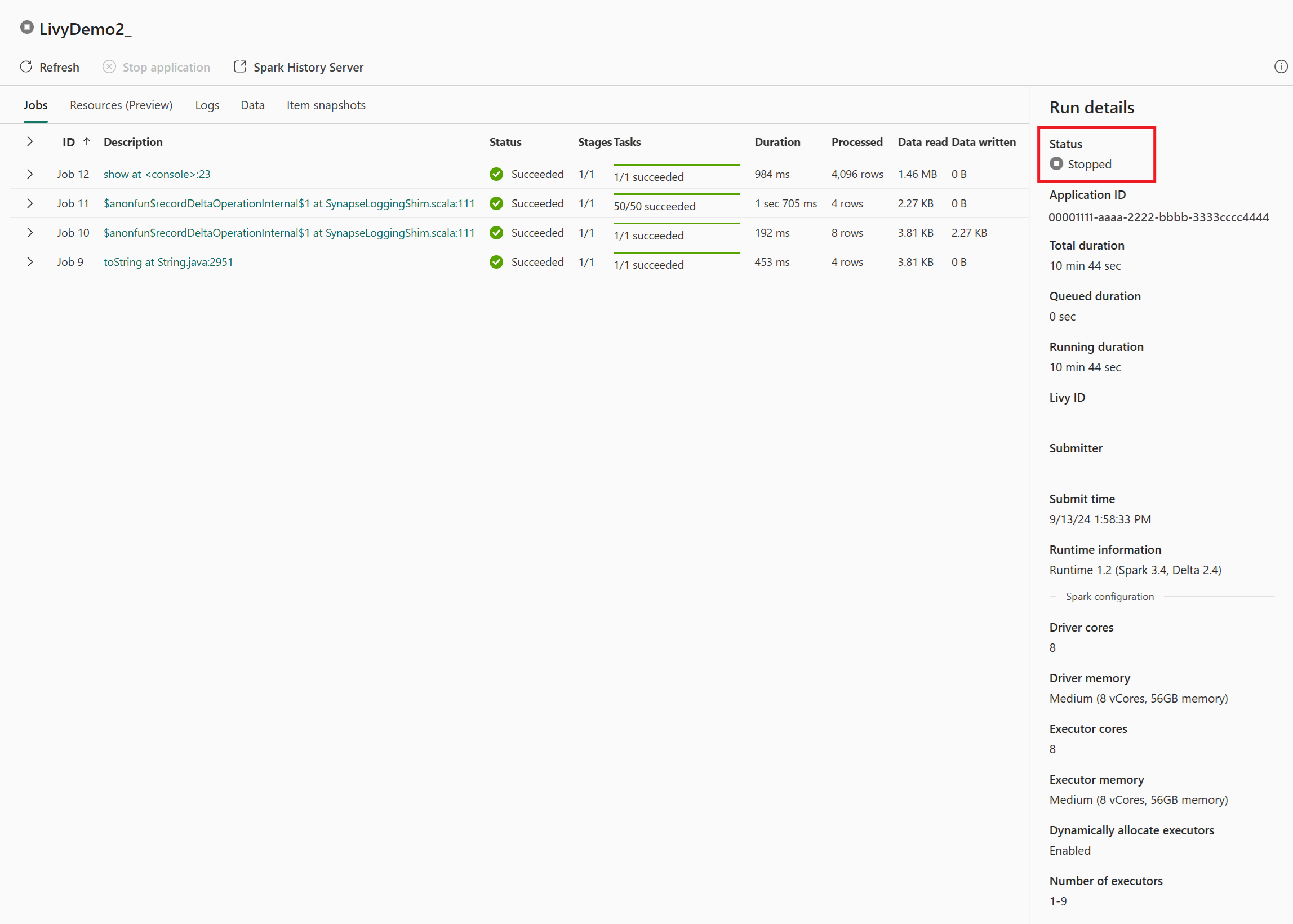
In dit geval van livy-API-sessie kunt u uw eerdere sessies zien, details uitvoeren, Spark-versies en configuratie. Let op de gestopte status rechtsboven.
Als u het hele proces wilt invatten, hebt u een externe client nodig, zoals Visual Studio Code, een Microsoft Entra-app/SPN-token, de URL van het Livy API-eindpunt, verificatie voor uw Lakehouse en ten slotte een Session Livy-API.