How to implement a many-to-many relationship using Linq to Sql ? Part II : add/remove support
In my previous post (https://blogs.msdn.com/mitsu/archive/2007/06/21/how-to-implement-a-many-to-many-relationship-using-linq-to-sql.aspx), I had proposed a simple solution for implementing many-to-many relationships using Linq to Sql.
Actually, this solution is a generic Linq solution. It's also working with just memory collections (not only Linq to Sql).
Many of you asked me for add/remove support.
Let's clarify a few things:
The current solution offers extensions to IList<T> and IBindingList.
Actually, the current solution is good enough when extending IList<T> and is very basic for IBindingList. Proxying (simulating) IList<T> is quite easy because we don't have a lot of possible technical issues. Proxying IBindingList with add/remove support is much more complicated.
For example, as we are virtually changing the item type (see ListSelector class), the notion of sorting becomes quite strange (we have to sort an OrderDetails collection from a Product property !!!).
Similarly, adding and removing don't have a real meaning from a Product entity.
In a many to many relationship, writing order.Products.Remove(n) should probably mean order.OrderDetails[n].Remove(). Of course we do not want to delete the associated product. The functional meaning is 'detaching' a product from it's many to many relationship with an order.
IList<T> contains the methods for adding and removing, so that's where we have to update the code. IBindingList is adding list change notifications necessary for binding.
The first thing is, there no universal solution because we don't know the real nature of the relationship. Sometimes, the link table has no functional meaning other than making the relationship. In that cases, the link table is only grouping foreign keys to join each table of the many-to-many relationship. Some other times, the link table contains other columns that have a functional meaning. For example, in a link table between an order and a product, the price is duplicated so it belongs to this specific order and stores the price at the time we had made the order.
What I am trying to say is we can not use an automatic logic to implement adding/removing.
So what I am proposing is to catch adding and removing from our IList entry points and to delegate those actions to external code.
Let's start with adding:
public class ListSelector<TSource, T> : IList<T>, IList
{
...
protected Action<IList<TSource>, T> onAdd;
...
public void Add(T item)
{
if (onAdd != null)
onAdd(source, item);
}
In the northwind case (Order/OrderDetails/Product), a good implementation for this delegate could be:
(ods, p) => ods.Add(
new Order_Detail { OrderID = currentOrder.OrderID, Product = p, Quantity=1 })
Of course we can notice that the goal is not to insert a Product (T) but an OrderDetail.
To make it easier to use, I have also added a new constructor so we can write:
public partial class Order
{
private ListSelector<Order_Detail, Product> products = null;
public ListSelector<Order_Detail, Product> Products
{
get
{
if (products == null)
products = this.Order_Details.GetNewBindingList()
.AsListSelector<Order_Detail, Product>(
od => od.Product,
(ods, p) => ods.Add(
new Order_Detail {
OrderID = this.OrderID,
Product = p, Quantity=1 })
We can notice that this syntax allows you to custom the OrderDetail creation. It's important because in our Northwind case, we had not only foreign keys but also Quantity and some other columns in the link table (OrderDetails). We can also notice that we had to know the Order to get the OrderID field. Fortunately, the lamba expression syntax allows us to share 'this.OrderID' from the host method scope. (same if we had used an anonymous method).
I will explain later in this post why I have used the GetNewBindingList method.
Now what about removing ? Removing is more complex because we have to find the entity before we remove it. (We start from a Product and we need to remove the corresponding OrderDetail).
The structure is very close to adding:
...
protected Action<IList<TSource>, T> onRemove;
...
public bool Remove(T item)
{
if (onRemove != null)
{
onRemove(source, item);
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
and the ListSelector is created that way:
public partial class Order
{
private ListSelector<Order_Detail, Product> products = null;
public ListSelector<Order_Detail, Product> Products
{
get
{
if (products == null)
products = this.Order_Details.GetNewBindingList()
.AsListSelector<Order_Detail, Product>(
od => od.Product,
(ods, p) => ods.Add(
new Order_Detail {
OrderID = this.OrderID,
Product = p, Quantity=1 },
delegate(IList<Order_Detail> ods, Product p)
{
var odToRemove = ods.Where(
od => od.ProductID == p.ProductID).Single();
Singleton<NorthwindDataContext>.Default
.Order_Details.DeleteOnSubmit(odToRemove);
ods.Remove(odToRemove);
})
return products;
}
}
As we need more that one instruction, I could not keep the lambda expression syntax. The anonymous method is quite the same here.
First we have to find the OrderDetail entity corresponding to the product.
Then, delete this entity. This is an issue because we have to 'talk' to Linq to Sql to declare this entity as to be removed on next SubmitChanges call. The issue is we don't have access to the datacontext at this point. I can imagine many different scenarios to make it visible here in the Order class but not to make this sample to much complicated, I have decided to give access to the current NorthwindDataContext through a static property.
Depending on your architecture, you can imagine other solutions. To preserve domain isolation, I would recommend to use an interface that would make abstraction of the persistence nature (Linq to Sql/DataContext/DeleteOnSubmit).
Just as a remark, here is the code of the generic singleton pattern I have used:
public class Singleton<T> where T : class, new()
{
private static T defaultInstance = null;
public static T Default
{
get
{
if (defaultInstance == null)
defaultInstance = new T();
return defaultInstance;
}
}
}
Last thing to explain, why did I have used 'this.Order_Details.GetNewBindingList().AsListSelector<Order_Detail, Product>(...);' ?
I have two AsListSelector extension methods. The first is extending IList<T> and the second one, IBindingList. As the extension method resolution is based on the reference type, I had to call AsListSelector from an IBindingList, so I can get binding notifications (add/remove).
The EntitySet class does not implement IBindingList but can provide an internal class that does !
When binding directly a Linq to Sql query to a winforms control, this class is provided implicitly:
grid.DataSource = q;
is equivalent to:
grid.DataSource = ((q as IListSource).GetList() as IBindingList);
To avoid multiple query execution when binding q many times, the result is cached in memory.
The GetNewBindingList method allows to get a fresh BindingList at each call.
Now we are done !
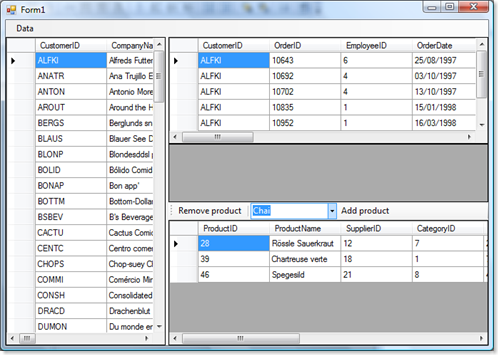
Let's modify the UI :
You have to use the main menu to submit the changes to the database 'Data>SubmitChanges'.
The whole source code is available on code gallery: https://code.msdn.microsoft.com/linqtosqlmanytomany
Comments
Anonymous
March 18, 2008
PingBack from http://blogs.msdn.com/mitsu/archive/2007/06/21/how-to-implement-a-many-to-many-relationship-using-linq-to-sql.aspxAnonymous
March 26, 2008
Very good post, I am using it with success. Thanks a lot.Anonymous
March 30, 2008
Welcome to the forty-second issue of Community Convergence. The last few weeks have been a busy time.Anonymous
April 07, 2008
Very nice! Thank you. I feel that the use of a static DataContext is unpleasant (the Singleton<T>). However I cannot come up with anything better.Anonymous
April 08, 2008
Nice post. I'm trying to use this in a web application where I want to create a different DataContext for each user, so that the changes can be submitted at an appropriate time. However, the singleton DataContext complains that the entity is not attached when I try to remove an item from the list, since I'm retrieving data from another DataContext. I'm thinking of rewriting the onRemove delegate to return the item from the many-to-many entity or passing in a DataContext to the onRemove method. Would that work?Anonymous
April 10, 2008
Hi Mitsu I've used your code to properly handle a many to many relationship and it's all working fine but for some reason I have a case where it's not possible to do an OrderBy(IEnumerable<T>) to the collection wrapping the linking entity. Here is the failing test: [Test] [ExpectedException(typeof(NullReferenceException))] public void CannotOrderBy() { Event ev = CreateValidateEvent(); ev.Participant.Add(CreateValidateParticipant()); ev.Participant.Add(CreateValidateParticipant()); var participants = ev.Participants.OrderBy(d => d.Name); Assert.IsTrue(list.Count() > 0); } and in Event class: public partial class Event { private ListSelector<EventParticipant, Participant> _participants = null; public IList<Participant> Participants { get { if (_participants == null) { _participants = this.EventParticipant.GetNewBindingList().AsListSelector<EventDrill, Participant>( ep => ep.Participant, (eps, p) => eps.Add(new EventParticipant { EventId = this.EventId, Participant = d }), delegate(IList<EventParticipant> eps, Participant p) { var pToRemove = eps.Where(ep => ep.ParticipantId == p.ParticipantId).Single(); // Registers EventParticipant entity for deletion IoC.Resolve<IDataContextProvider>().Get().GetTable<EventParticipant>().DeleteOnSubmit(pToRemove ); eps.Remove(pToRemove); }); } return _participants; } }Anonymous
April 10, 2008
Mitsu, I re-read your post and you mention that there may be issues with sorting and that's indeed something I came across (see my reply). Having a fair amount of experience with NHibernate, I can say that indeed the Linq To Sql mapping doesn't provide quite enough information, for instance: can one of the side not linked to a single entity from the other side, exact behavior of cascaded deletions, so that we can code a generic "pure" (ie a linking table without any other attributes than the foreign keys and maybe others that are not implemented by the types themselves like quantity in your example) implementation of a many to many class. I am fairly new to Linq and I am glad it does exist but I wonder now if we could do with constructs that allow clean definition of associations between entities that can provide compile and runtime checks.Anonymous
April 16, 2008
Hi Mitsu, as a little sidenote: the implementation isn't thread-safe. Otherwise thanks for your great work.Anonymous
April 16, 2008
The Singleton can be implemented as follows (based on code from http://www.yoda.arachsys.com/csharp/singleton.html): public sealed class Singleton<T> where T : class, new() { Singleton() { } public static T Instance { get { return Nested.instance; } } class Nested { // Explicit static constructor to tell C# compiler // not to mark type as beforefieldinit static Nested() { } internal static readonly T instance = new T(); } }Anonymous
April 17, 2008
The comment has been removedAnonymous
April 26, 2008
Mitsu Furata explores many-to-many relationships in LINQ to SQL in these two posts: How to implementAnonymous
May 08, 2008
How come, nobody complains about detail objects being fetched on a one-by-one basis? Lots of database roundtrips... Am I missing something?Anonymous
May 08, 2008
Hi Nelis, I don't see what you mean. Please could you detail more ? This solution is only a client side syntax simplification to allow direct access between to entities of a many to many relationship. (just in memory solution). It does not change the way data are physically loaded. If in your case you choose to use linq to sql deferred loading, it's your choice. If you prefer preloading details entities, you can use DataContext load options.Anonymous
May 11, 2008
In this article, I will show one possible solution to implement many-to-many relationship using Linq to Sql.Anonymous
May 19, 2008
Thank you for providing all of this helpful information. It would be very helpful to understand what's different about Linq to Entities that allows it to support many2many whilst Linq to SQL does not.Anonymous
May 26, 2008
In my previous post ( http://blogs.msdn.com/mitsu/archive/2007/06/21/how-to-implement-a-many-to-many-relationship-using-linq-to-sql.aspx ), I had proposed a simple solution for implementing many-to-many relationships using Linq to Sql. Actually, thisAnonymous
June 04, 2008
In my previous post ( http://blogs.msdn.com/mitsu/archive/2007/06/21/how-to-implement-a-many-to-many-relationship-using-linq-to-sql.aspx ), I had proposed a simple solution for implementing many-to-many relationships using Linq to Sql. Actually, thisAnonymous
June 16, 2008
Hi, This works great. How would I use it in a dynamic data appliaction? Dave Ebbo linked to this as a solution, but I am unsure how that would work. http://blogs.msdn.com/davidebb/archive/2007/12/12/dynamic-data-screencast-is-now-available.aspx Thanks ChrisAnonymous
September 23, 2008
The comment has been removedAnonymous
November 05, 2008
The comment has been removed