Notitie
Voor toegang tot deze pagina is autorisatie vereist. U kunt proberen u aan te melden of de directory te wijzigen.
Voor toegang tot deze pagina is autorisatie vereist. U kunt proberen de mappen te wijzigen.
Een Git-opslagplaats of opslagplaats is een map waarin Git wijzigingen bijhoudt. Er kan een willekeurig aantal opslagplaatsen op een computer zijn, die elk in hun eigen map zijn opgeslagen. Elke Git-opslagplaats op een systeem is onafhankelijk, dus wijzigingen die zijn opgeslagen in de ene Git-opslagplaats, hebben geen invloed op de inhoud van een andere.
Een Git-opslagplaats bevat elke versie van elk bestand dat is opgeslagen in de opslagplaats. Dit verschilt van andere versiebeheersystemen die alleen de verschillen tussen bestanden opslaan. Git slaat de bestandsversies op in een verborgen .git-map naast andere informatie die nodig is om code te beheren. Git slaat deze bestanden zeer efficiënt op, dus het gebruik van een groot aantal versies betekent niet dat er veel schijfruimte wordt gebruikt. Door elke versie van een bestand op te slaan, kunt u Git-code beter samenvoegen en kunt u snel en eenvoudig werken met meerdere versies van code.
Ontwikkelaars werken met Git via opdrachten die zijn uitgegeven tijdens het werken in een lokale opslagplaats op de computer. Zelfs bij het delen van code of het ophalen van updates van het team, is het gedaan vanuit opdrachten die de lokale opslagplaats bijwerken. Dit lokaal gerichte ontwerp is wat Git een gedistribueerd versiebeheersysteem maakt. Elke opslagplaats is zelfstandig en de eigenaar van de opslagplaats is verantwoordelijk voor het up-to-date houden met wijzigingen van anderen.
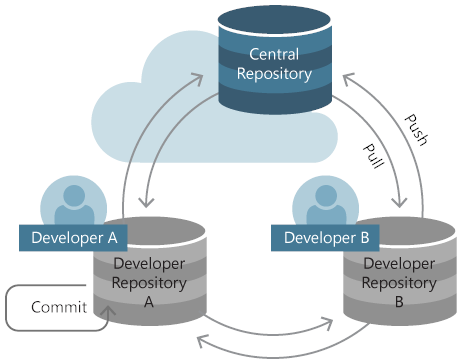
De meeste teams gebruiken een centrale opslagplaats die wordt gehost op een server waartoe iedereen toegang heeft om hun wijzigingen te coördineren. De centrale opslagplaats wordt meestal gehost in een oplossing voor broncodebeheer, zoals GitHub of Azure DevOps. Een beheeroplossing voor broncodebeheer voegt functies toe en maakt het samenwerken eenvoudiger.
Een nieuwe Git-opslagplaats maken
U hebt twee opties om een Git-opslagplaats te maken. U kunt er een maken op basis van de code in een map op een computer of een van een bestaande opslagplaats klonen. Als u werkt met code die zich alleen op de lokale computer bevindt, maakt u een lokale opslagplaats met behulp van de code in die map. Maar meestal wordt de code al gedeeld in een Git-opslagplaats, dus het klonen van de bestaande opslagplaats naar de lokale computer is de aanbevolen manier om te gaan.
Een nieuwe opslagplaats maken op basis van bestaande code
Gebruik de git init opdracht om een nieuwe opslagplaats te maken op basis van een bestaande map op de computer. Navigeer vanaf de opdrachtregel naar de hoofdmap met de code en voer het volgende uit:
> git init
om de repository te maken. Voeg vervolgens alle bestanden in de map toe aan de eerste doorvoering met behulp van de volgende opdrachten:
> git add --all
> git commit -m "Initial commit"
Een nieuwe opslagplaats maken vanuit een externe opslagplaats
Gebruik de git clone opdracht om de inhoud van een bestaande opslagplaats naar een map op de computer te kopiëren. Navigeer vanaf de opdrachtregel naar de map die de gekloonde opslagplaats bevat en voer vervolgens het volgende uit:
> git clone https://<fabrikam.visualstudio.com/DefaultCollection/Fabrikam/_git/FabrikamProject>
Zorg ervoor dat u de werkelijke URL naar de bestaande opslagplaats gebruikt in plaats van de tijdelijke aanduidings-URL die in dit voorbeeld wordt weergegeven. Deze URL, de kloon-URL genoemd, verwijst naar een server waarop het team wijzigingen coördineert. Haal deze URL op bij het team of via de knop voor klonen op de site waar de repository wordt gehost.
Het is niet nodig om bestanden toe te voegen of een initiële doorvoering te maken wanneer de opslagplaats wordt gekloond, omdat deze allemaal is gekopieerd, samen met de geschiedenis, uit de bestaande opslagplaats tijdens de kloonbewerking.
Volgende stappen
GitHub en Azure-opslagplaatsen bieden onbeperkte gratis openbare en persoonlijke Git-opslagplaatsen.
Visual Studio-gebruiker? Meer informatie over het maken en klonen van opslagplaatsen vanuit Visual Studio in deze Git-zelfstudie.