Notitie
Voor toegang tot deze pagina is autorisatie vereist. U kunt proberen u aan te melden of de directory te wijzigen.
Voor toegang tot deze pagina is autorisatie vereist. U kunt proberen de mappen te wijzigen.
Van toepassing op:SQL Server op Linux
Maak en beheer uw SQL Server-exemplaren systeemeigen in Kubernetes.
Implementeer SQL Server in docker-containers die worden beheerd door Kubernetes. In Kubernetes kan een container met een SQL Server-exemplaar automatisch worden hersteld als een clusterknooppunt mislukt.
SQL Server 2017 introduceert een Docker-image die op Kubernetes kan worden geïmplementeerd. U kunt de image configureren met een Kubernetes Persistent Volume Claim (PVC). Kubernetes bewaakt het SQL Server-proces in de container. Als het proces, de pod, de container of het knooppunt mislukt, bootstrapt Kubernetes automatisch een ander exemplaar op en maakt opnieuw verbinding met de opslag.
Container met SQL Server-exemplaar in Kubernetes
Kubernetes 1.6 en hoger biedt ondersteuning voor opslagklassen, permanente volumeclaims en het type Azure-schijfvolume.
In deze configuratie speelt Kubernetes de rol van de containerorchestrator.
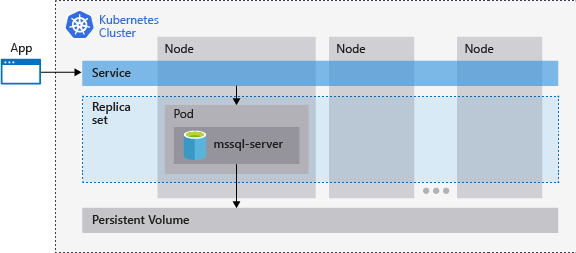
In het voorgaande diagram mssql-server bevindt zich een SQL Server-exemplaar (container) in een pod. Een replicaset ervoor zorgt dat de pod automatisch wordt hersteld na een storing in een knooppunt. Toepassingen maken verbinding met de service. In dit geval vertegenwoordigt de service een load balancer die als host fungeert voor een IP-adres dat niet hetzelfde is na het mislukken van de mssql-server.
Kubernetes organiseert de resources in het cluster. Wanneer een knooppunt dat als host fungeert voor een SQL Server-exemplaarcontainer mislukt, wordt een nieuwe container opgestart met een SQL Server-exemplaar en gekoppeld aan dezelfde permanente opslag.
SQL Server op Linux ondersteunt containers op Kubernetes, OpenShift en D2Hi.