Programowe tworzenie aplikacji LUIS przy użyciu Node.js
Ważne
Usługa LUIS zostanie wycofana 1 października 2025 r. i od 1 kwietnia 2023 r. nie będzie można utworzyć nowych zasobów usługi LUIS. Zalecamy migrację aplikacji LUIS do interpretacji języka konwersacyjnego, aby korzystać z ciągłej pomocy technicznej i wielojęzycznych możliwości produktów.
Usługa LUIS udostępnia programowy interfejs API, który wykonuje wszystko, co robi witryna internetowa usługi LUIS . Może to zaoszczędzić czas, gdy masz wstępnie istniejące dane i byłoby szybsze programowe tworzenie aplikacji usługi LUIS niż poprzez ręczne wprowadzanie informacji.
Uwaga
Ten dokument nie został zaktualizowany za pomocą tekstu i zrzutów ekranu dla najnowszego portalu usługi LUIS.
Wymagania wstępne
- Zaloguj się do witryny internetowej usługi LUIS i znajdź swój klucz tworzenia w Ustawienia konta. Ten klucz służy do wywoływania interfejsów API tworzenia.
- Jeśli nie masz subskrypcji platformy Azure, przed rozpoczęciem utwórz bezpłatne konto.
- Ten artykuł rozpoczyna się od pliku CSV dla hipotetycznych plików dziennika firmy żądań użytkowników. Pobierz go tutaj.
- Zainstaluj najnowszą wersję Node.js. Pobierz go stąd.
- [Zalecane] Program Visual Studio Code dla funkcji IntelliSense i debugowanie, pobierz go tutaj bezpłatnie.
Cały kod w tym artykule jest dostępny w repozytorium GitHub Azure-Samples Language Understanding.
Mapowanie istniejących danych na intencje i jednostki
Nawet jeśli masz system, który nie został utworzony z myślą o usłudze LUIS, jeśli zawiera on dane tekstowe mapujące różne elementy, które użytkownicy chcą wykonać, może być możliwe utworzenie mapowania z istniejących kategorii danych wejściowych użytkownika do intencji w usłudze LUIS. Jeśli możesz zidentyfikować ważne wyrazy lub frazy w tym, co mówili użytkownicy, te słowa mogą być mapowanie na jednostki.
Otwórz plik IoT.csv. Zawiera on dziennik zapytań użytkowników do hipotetycznej usługi automatyzacji domu, w tym sposobu ich kategoryzowania, tego, co powiedział użytkownik, a niektóre kolumny z przydatnymi informacjami wyciągniętymi z nich.
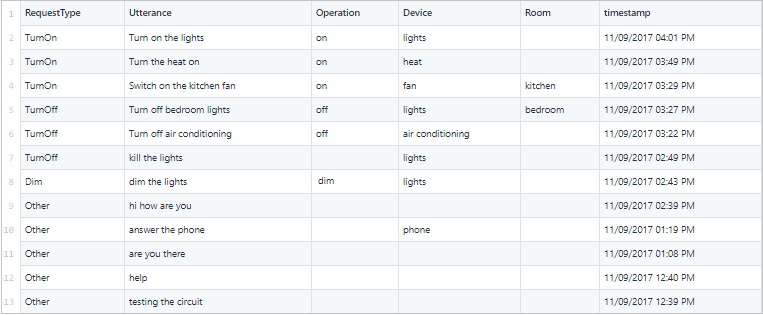
Zobaczysz, że kolumna RequestType może być intencjami, a kolumna Request (Żądanie ) zawiera przykładową wypowiedź. Inne pola mogą być jednostkami, jeśli wystąpią w wypowiedzi. Ponieważ istnieją intencje, jednostki i przykładowe wypowiedzi, masz wymagania dotyczące prostej, przykładowej aplikacji.
Kroki generowania aplikacji LUIS na podstawie danych innych niż luis
Aby wygenerować nową aplikację usługi LUIS z pliku CSV:
- Przeanalizuj dane z pliku CSV:
- Przekonwertuj na format, który można przekazać do usługi LUIS przy użyciu interfejsu API tworzenia.
- Z analizowanych danych zbierz informacje o intencjach i jednostkach.
- Wykonaj wywołania interfejsu API tworzenia do:
- Utwórz aplikację.
- Dodaj intencje i jednostki, które zostały zebrane z analizowanych danych.
- Po utworzeniu aplikacji usługi LUIS możesz dodać przykładowe wypowiedzi z analizowanych danych.
Ten przepływ programu można zobaczyć w ostatniej części index.js pliku. Skopiuj lub pobierz ten kod i zapisz go w pliku index.js.
Ważne
Pamiętaj, aby usunąć klucz z kodu po zakończeniu i nigdy nie publikować go publicznie. W przypadku środowiska produkcyjnego użyj bezpiecznego sposobu przechowywania i uzyskiwania dostępu do poświadczeń, takich jak usługa Azure Key Vault. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji, zobacz artykuł Dotyczący zabezpieczeń usług Azure AI.
var path = require('path');
const parse = require('./_parse');
const createApp = require('./_create');
const addEntities = require('./_entities');
const addIntents = require('./_intents');
const upload = require('./_upload');
// Change these values
const LUIS_authoringKey = "YOUR_AUTHORING_KEY";
const LUIS_appName = "Sample App - build from IoT csv file";
const LUIS_appCulture = "en-us";
const LUIS_versionId = "0.1";
// NOTE: final output of add-utterances api named utterances.upload.json
const downloadFile = "./IoT.csv";
const uploadFile = "./utterances.json"
// The app ID is returned from LUIS when your app is created
var LUIS_appId = ""; // default app ID
var intents = [];
var entities = [];
/* add utterances parameters */
var configAddUtterances = {
LUIS_subscriptionKey: LUIS_authoringKey,
LUIS_appId: LUIS_appId,
LUIS_versionId: LUIS_versionId,
inFile: path.join(__dirname, uploadFile),
batchSize: 100,
uri: "https://westus.api.cognitive.microsoft.com/luis/api/v2.0/apps/{appId}/versions/{versionId}/examples"
};
/* create app parameters */
var configCreateApp = {
LUIS_subscriptionKey: LUIS_authoringKey,
LUIS_versionId: LUIS_versionId,
appName: LUIS_appName,
culture: LUIS_appCulture,
uri: "https://westus.api.cognitive.microsoft.com/luis/api/v2.0/apps/"
};
/* add intents parameters */
var configAddIntents = {
LUIS_subscriptionKey: LUIS_authoringKey,
LUIS_appId: LUIS_appId,
LUIS_versionId: LUIS_versionId,
intentList: intents,
uri: "https://westus.api.cognitive.microsoft.com/luis/api/v2.0/apps/{appId}/versions/{versionId}/intents"
};
/* add entities parameters */
var configAddEntities = {
LUIS_subscriptionKey: LUIS_authoringKey,
LUIS_appId: LUIS_appId,
LUIS_versionId: LUIS_versionId,
entityList: entities,
uri: "https://westus.api.cognitive.microsoft.com/luis/api/v2.0/apps/{appId}/versions/{versionId}/entities"
};
/* input and output files for parsing CSV */
var configParse = {
inFile: path.join(__dirname, downloadFile),
outFile: path.join(__dirname, uploadFile)
};
// Parse CSV
parse(configParse)
.then((model) => {
// Save intent and entity names from parse
intents = model.intents;
entities = model.entities;
// Create the LUIS app
return createApp(configCreateApp);
}).then((appId) => {
// Add intents
LUIS_appId = appId;
configAddIntents.LUIS_appId = appId;
configAddIntents.intentList = intents;
return addIntents(configAddIntents);
}).then(() => {
// Add entities
configAddEntities.LUIS_appId = LUIS_appId;
configAddEntities.entityList = entities;
return addEntities(configAddEntities);
}).then(() => {
// Add example utterances to the intents in the app
configAddUtterances.LUIS_appId = LUIS_appId;
return upload(configAddUtterances);
}).catch(err => {
console.log(err.message);
});
Analizowanie woluminu CSV
Wpisy kolumn zawierające wypowiedzi w pliku CSV muszą być analizowane w formacie JSON, który może zrozumieć usługa LUIS. Ten format JSON musi zawierać intentName pole identyfikujące intencję wypowiedzi. Musi również zawierać entityLabels pole, które może być puste, jeśli w wypowiedzi nie ma żadnych jednostek.
Na przykład wpis "Włącz światła" mapuje na ten kod JSON:
{
"text": "Turn on the lights",
"intentName": "TurnOn",
"entityLabels": [
{
"entityName": "Operation",
"startCharIndex": 5,
"endCharIndex": 6
},
{
"entityName": "Device",
"startCharIndex": 12,
"endCharIndex": 17
}
]
}
W tym przykładzie element intentName pochodzi z żądania użytkownika w nagłówku kolumny Żądanie w pliku CSV i entityName pochodzi z innych kolumn z kluczowymi informacjami. Jeśli na przykład istnieje wpis operacji lub urządzenia, a ten ciąg również występuje w rzeczywistym żądaniu, można go oznaczyć jako jednostkę. Poniższy kod demonstruje ten proces analizowania. Możesz skopiować lub pobrać go i zapisać go w pliku _parse.js.
// node 7.x
// built with streams for larger files
const fse = require('fs-extra');
const path = require('path');
const lineReader = require('line-reader');
const babyparse = require('babyparse');
const Promise = require('bluebird');
const intent_column = 0;
const utterance_column = 1;
var entityNames = [];
var eachLine = Promise.promisify(lineReader.eachLine);
function listOfIntents(intents) {
return intents.reduce(function (a, d) {
if (a.indexOf(d.intentName) === -1) {
a.push(d.intentName);
}
return a;
}, []);
}
function listOfEntities(utterances) {
return utterances.reduce(function (a, d) {
d.entityLabels.forEach(function(entityLabel) {
if (a.indexOf(entityLabel.entityName) === -1) {
a.push(entityLabel.entityName);
}
}, this);
return a;
}, []);
}
var utterance = function (rowAsString) {
let json = {
"text": "",
"intentName": "",
"entityLabels": [],
};
if (!rowAsString) return json;
let dataRow = babyparse.parse(rowAsString);
// Get intent name and utterance text
json.intentName = dataRow.data[0][intent_column];
json.text = dataRow.data[0][utterance_column];
// For each column heading that may be an entity, search for the element in this column in the utterance.
entityNames.forEach(function (entityName) {
entityToFind = dataRow.data[0][entityName.column];
if (entityToFind != "") {
strInd = json.text.indexOf(entityToFind);
if (strInd > -1) {
let entityLabel = {
"entityName": entityName.name,
"startCharIndex": strInd,
"endCharIndex": strInd + entityToFind.length - 1
}
json.entityLabels.push(entityLabel);
}
}
}, this);
return json;
};
const convert = async (config) => {
try {
var i = 0;
// get inFile stream
inFileStream = await fse.createReadStream(config.inFile, 'utf-8')
// create out file
var myOutFile = await fse.createWriteStream(config.outFile, 'utf-8');
var utterances = [];
// read 1 line at a time
return eachLine(inFileStream, (line) => {
// skip first line with headers
if (i++ == 0) {
// csv to baby parser object
let dataRow = babyparse.parse(line);
// populate entityType list
var index = 0;
dataRow.data[0].forEach(function (element) {
if ((index != intent_column) && (index != utterance_column)) {
entityNames.push({ name: element, column: index });
}
index++;
}, this);
return;
}
// transform utterance from csv to json
utterances.push(utterance(line));
}).then(() => {
console.log("intents: " + JSON.stringify(listOfIntents(utterances)));
console.log("entities: " + JSON.stringify(listOfEntities(utterances)));
myOutFile.write(JSON.stringify({ "converted_date": new Date().toLocaleString(), "utterances": utterances }));
myOutFile.end();
console.log("parse done");
console.log("JSON file should contain utterances. Next step is to create an app with the intents and entities it found.");
var model =
{
intents: listOfIntents(utterances),
entities: listOfEntities(utterances)
}
return model;
});
} catch (err) {
throw err;
}
}
module.exports = convert;
Tworzenie aplikacji usługi LUIS
Po przeanalizowaniu danych w formacie JSON dodaj je do aplikacji usługi LUIS. Poniższy kod tworzy aplikację usługi LUIS. Skopiuj lub pobierz go i zapisz go w pliku _create.js.
// node 7.x
// uses async/await - promises
var rp = require('request-promise');
var fse = require('fs-extra');
var path = require('path');
// main function to call
// Call Apps_Create
var createApp = async (config) => {
try {
// JSON for the request body
// { "name": MyAppName, "culture": "en-us"}
var jsonBody = {
"name": config.appName,
"culture": config.culture
};
// Create a LUIS app
var createAppPromise = callCreateApp({
uri: config.uri,
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key': config.LUIS_subscriptionKey
},
json: true,
body: jsonBody
});
let results = await createAppPromise;
// Create app returns an app ID
let appId = results.response;
console.log(`Called createApp, created app with ID ${appId}`);
return appId;
} catch (err) {
console.log(`Error creating app: ${err.message} `);
throw err;
}
}
// Send JSON as the body of the POST request to the API
var callCreateApp = async (options) => {
try {
var response;
if (options.method === 'POST') {
response = await rp.post(options);
} else if (options.method === 'GET') { // TODO: There's no GET for create app
response = await rp.get(options);
}
// response from successful create should be the new app ID
return { response };
} catch (err) {
throw err;
}
}
module.exports = createApp;
Dodawanie intencji
Gdy masz aplikację, musisz ją uruchomić. Poniższy kod tworzy aplikację usługi LUIS. Skopiuj lub pobierz go i zapisz go w pliku _intents.js.
var rp = require('request-promise');
var fse = require('fs-extra');
var path = require('path');
var request = require('requestretry');
// time delay between requests
const delayMS = 1000;
// retry recount
const maxRetry = 5;
// retry request if error or 429 received
var retryStrategy = function (err, response, body) {
let shouldRetry = err || (response.statusCode === 429);
if (shouldRetry) console.log("retrying add intent...");
return shouldRetry;
}
// Call add-intents
var addIntents = async (config) => {
var intentPromises = [];
config.uri = config.uri.replace("{appId}", config.LUIS_appId).replace("{versionId}", config.LUIS_versionId);
config.intentList.forEach(function (intent) {
config.intentName = intent;
try {
// JSON for the request body
var jsonBody = {
"name": config.intentName,
};
// Create an intent
var addIntentPromise = callAddIntent({
// uri: config.uri,
url: config.uri,
fullResponse: false,
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key': config.LUIS_subscriptionKey
},
json: true,
body: jsonBody,
maxAttempts: maxRetry,
retryDelay: delayMS,
retryStrategy: retryStrategy
});
intentPromises.push(addIntentPromise);
console.log(`Called addIntents for intent named ${intent}.`);
} catch (err) {
console.log(`Error in addIntents: ${err.message} `);
}
}, this);
let results = await Promise.all(intentPromises);
console.log(`Results of all promises = ${JSON.stringify(results)}`);
let response = results;
}
// Send JSON as the body of the POST request to the API
var callAddIntent = async (options) => {
try {
var response;
response = await request(options);
return { response: response };
} catch (err) {
console.log(`Error in callAddIntent: ${err.message} `);
}
}
module.exports = addIntents;
Dodawanie jednostek
Poniższy kod dodaje jednostki do aplikacji USŁUGI LUIS. Skopiuj lub pobierz go i zapisz go w pliku _entities.js.
// node 7.x
// uses async/await - promises
const request = require("requestretry");
var rp = require('request-promise');
var fse = require('fs-extra');
var path = require('path');
// time delay between requests
const delayMS = 1000;
// retry recount
const maxRetry = 5;
// retry request if error or 429 received
var retryStrategy = function (err, response, body) {
let shouldRetry = err || (response.statusCode === 429);
if (shouldRetry) console.log("retrying add entity...");
return shouldRetry;
}
// main function to call
// Call add-entities
var addEntities = async (config) => {
var entityPromises = [];
config.uri = config.uri.replace("{appId}", config.LUIS_appId).replace("{versionId}", config.LUIS_versionId);
config.entityList.forEach(function (entity) {
try {
config.entityName = entity;
// JSON for the request body
// { "name": MyEntityName}
var jsonBody = {
"name": config.entityName,
};
// Create an app
var addEntityPromise = callAddEntity({
url: config.uri,
fullResponse: false,
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key': config.LUIS_subscriptionKey
},
json: true,
body: jsonBody,
maxAttempts: maxRetry,
retryDelay: delayMS,
retryStrategy: retryStrategy
});
entityPromises.push(addEntityPromise);
console.log(`called addEntity for entity named ${entity}.`);
} catch (err) {
console.log(`Error in addEntities: ${err.message} `);
//throw err;
}
}, this);
let results = await Promise.all(entityPromises);
console.log(`Results of all promises = ${JSON.stringify(results)}`);
let response = results;// await fse.writeJson(createResults.json, results);
}
// Send JSON as the body of the POST request to the API
var callAddEntity = async (options) => {
try {
var response;
response = await request(options);
return { response: response };
} catch (err) {
console.log(`error in callAddEntity: ${err.message}`);
}
}
module.exports = addEntities;
Dodawanie wypowiedzi
Po zdefiniowaniu jednostek i intencji w aplikacji usługi LUIS możesz dodać wypowiedzi. Poniższy kod używa interfejsu API Utterances_AddBatch , który umożliwia dodanie maksymalnie 100 wypowiedzi naraz. Skopiuj lub pobierz go i zapisz go w pliku _upload.js.
// node 7.x
// uses async/await - promises
var rp = require('request-promise');
var fse = require('fs-extra');
var path = require('path');
var request = require('requestretry');
// time delay between requests
const delayMS = 500;
// retry recount
const maxRetry = 5;
// retry request if error or 429 received
var retryStrategy = function (err, response, body) {
let shouldRetry = err || (response.statusCode === 429);
if (shouldRetry) console.log("retrying add examples...");
return shouldRetry;
}
// main function to call
var upload = async (config) => {
try{
// read in utterances
var entireBatch = await fse.readJson(config.inFile);
// break items into pages to fit max batch size
var pages = getPagesForBatch(entireBatch.utterances, config.batchSize);
var uploadPromises = [];
// load up promise array
pages.forEach(page => {
config.uri = "https://westus.api.cognitive.microsoft.com/luis/api/v2.0/apps/{appId}/versions/{versionId}/examples".replace("{appId}", config.LUIS_appId).replace("{versionId}", config.LUIS_versionId)
var pagePromise = sendBatchToApi({
url: config.uri,
fullResponse: false,
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key': config.LUIS_subscriptionKey
},
json: true,
body: page,
maxAttempts: maxRetry,
retryDelay: delayMS,
retryStrategy: retryStrategy
});
uploadPromises.push(pagePromise);
})
//execute promise array
let results = await Promise.all(uploadPromises)
console.log(`\n\nResults of all promises = ${JSON.stringify(results)}`);
let response = await fse.writeJson(config.inFile.replace('.json','.upload.json'),results);
console.log("upload done");
} catch(err){
throw err;
}
}
// turn whole batch into pages batch
// because API can only deal with N items in batch
var getPagesForBatch = (batch, maxItems) => {
try{
var pages = [];
var currentPage = 0;
var pageCount = (batch.length % maxItems == 0) ? Math.round(batch.length / maxItems) : Math.round((batch.length / maxItems) + 1);
for (let i = 0;i<pageCount;i++){
var currentStart = currentPage * maxItems;
var currentEnd = currentStart + maxItems;
var pagedBatch = batch.slice(currentStart,currentEnd);
var j = 0;
pagedBatch.forEach(item=>{
item.ExampleId = j++;
});
pages.push(pagedBatch);
currentPage++;
}
return pages;
}catch(err){
throw(err);
}
}
// send json batch as post.body to API
var sendBatchToApi = async (options) => {
try {
var response = await request(options);
//return {page: options.body, response:response};
return {response:response};
}catch(err){
throw err;
}
}
module.exports = upload;
Uruchamianie kodu
Instalowanie zależności Node.js
Zainstaluj zależności Node.js w terminalu/wierszu polecenia.
> npm install
Zmienianie Ustawienia konfiguracji
Aby użyć tej aplikacji, musisz zmienić wartości w pliku index.js na własny klucz punktu końcowego i podać nazwę, którą aplikacja ma mieć. Możesz również ustawić kulturę aplikacji lub zmienić numer wersji.
Otwórz plik index.js i zmień te wartości w górnej części pliku.
// Change these values
const LUIS_programmaticKey = "YOUR_AUTHORING_KEY";
const LUIS_appName = "Sample App";
const LUIS_appCulture = "en-us";
const LUIS_versionId = "0.1";
Uruchamianie skryptu
Uruchom skrypt z poziomu wiersza polecenia/terminalu z Node.js.
> node index.js
Or
> npm start
Postęp aplikacji
Gdy aplikacja jest uruchomiona, wiersz polecenia pokazuje postęp. Dane wyjściowe wiersza polecenia zawierają format odpowiedzi z usługi LUIS.
> node index.js
intents: ["TurnOn","TurnOff","Dim","Other"]
entities: ["Operation","Device","Room"]
parse done
JSON file should contain utterances. Next step is to create an app with the intents and entities it found.
Called createApp, created app with ID 314b306c-0033-4e09-92ab-94fe5ed158a2
Called addIntents for intent named TurnOn.
Called addIntents for intent named TurnOff.
Called addIntents for intent named Dim.
Called addIntents for intent named Other.
Results of all calls to addIntent = [{"response":"e7eaf224-8c61-44ed-a6b0-2ab4dc56f1d0"},{"response":"a8a17efd-f01c-488d-ad44-a31a818cf7d7"},{"response":"bc7c32fc-14a0-4b72-bad4-d345d807f965"},{"response":"727a8d73-cd3b-4096-bc8d-d7cfba12eb44"}]
called addEntity for entity named Operation.
called addEntity for entity named Device.
called addEntity for entity named Room.
Results of all calls to addEntity= [{"response":"6a7e914f-911d-4c6c-a5bc-377afdce4390"},{"response":"56c35237-593d-47f6-9d01-2912fa488760"},{"response":"f1dd440c-2ce3-4a20-a817-a57273f169f3"}]
retrying add examples...
Results of add utterances = [{"response":[{"value":{"UtteranceText":"turn on the lights","ExampleId":-67649},"hasError":false},{"value":{"UtteranceText":"turn the heat on","ExampleId":-69067},"hasError":false},{"value":{"UtteranceText":"switch on the kitchen fan","ExampleId":-3395901},"hasError":false},{"value":{"UtteranceText":"turn off bedroom lights","ExampleId":-85402},"hasError":false},{"value":{"UtteranceText":"turn off air conditioning","ExampleId":-8991572},"hasError":false},{"value":{"UtteranceText":"kill the lights","ExampleId":-70124},"hasError":false},{"value":{"UtteranceText":"dim the lights","ExampleId":-174358},"hasError":false},{"value":{"UtteranceText":"hi how are you","ExampleId":-143722},"hasError":false},{"value":{"UtteranceText":"answer the phone","ExampleId":-69939},"hasError":false},{"value":{"UtteranceText":"are you there","ExampleId":-149588},"hasError":false},{"value":{"UtteranceText":"help","ExampleId":-81949},"hasError":false},{"value":{"UtteranceText":"testing the circuit","ExampleId":-11548708},"hasError":false}]}]
upload done
Otwieranie aplikacji luis
Po zakończeniu działania skryptu możesz zalogować się do usługi LUIS i wyświetlić aplikację usługi LUIS utworzoną w Moje aplikacje. Powinny być widoczne wypowiedzi dodane w intencjach TurnOn, TurnOff i None .
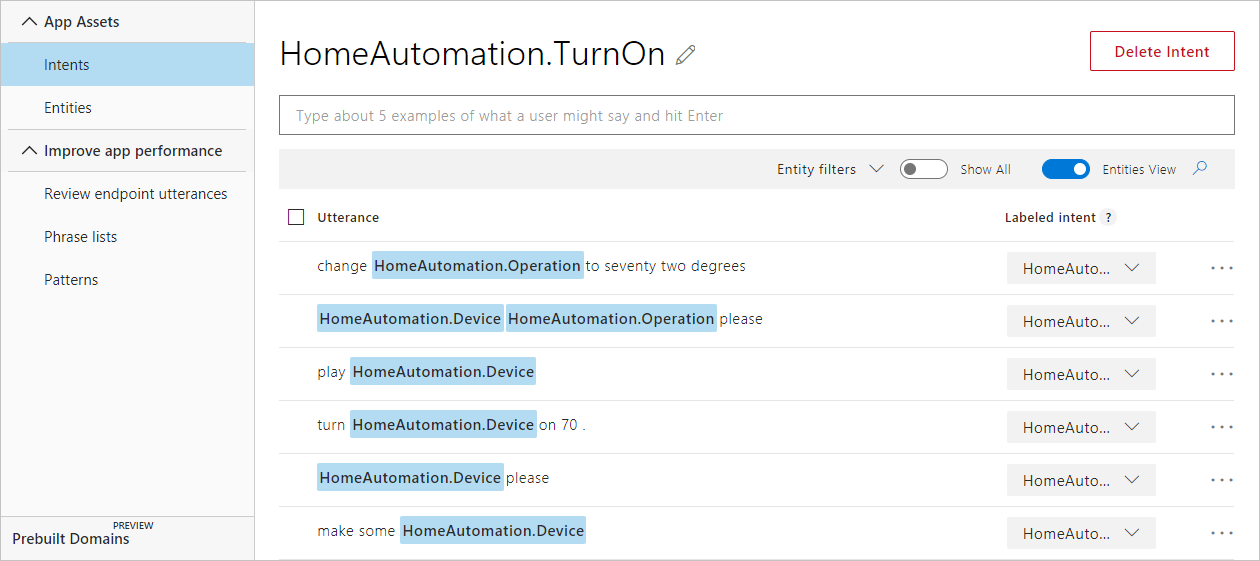
Następne kroki
Przetestuj i przeszkolij aplikację w witrynie internetowej usługi LUIS.
Dodatkowe zasoby
Ta przykładowa aplikacja używa następujących interfejsów API usługi LUIS: