Wskazówki: tworzenie sieci przetwarzania obrazów
W tym dokumencie pokazano, jak utworzyć sieć bloków komunikatów asynchronicznych, które wykonują przetwarzanie obrazów.
Sieć określa, które operacje mają być wykonywane na obrazie na podstawie jej cech. W tym przykładzie użyto modelu przepływu danych do kierowania obrazów za pośrednictwem sieci. W modelu przepływu danych niezależne składniki programu komunikują się ze sobą, wysyłając komunikaty. Gdy składnik odbiera komunikat, może wykonać jakąś akcję, a następnie przekazać wynik tej akcji do innego składnika. Porównaj to z modelem przepływu sterowania, w którym aplikacja używa struktur sterujących, na przykład instrukcji warunkowych, pętli itd., aby kontrolować kolejność operacji w programie.
Sieć oparta na przepływie danych tworzy potok zadań. Każdy etap potoku współbieżnie wykonuje część ogólnego zadania. Analogią do tego jest linia montażowa do produkcji samochodów. Gdy każdy pojazd przechodzi przez linię montażową, jedna stacja montuje ramę, druga instaluje silnik itd. Dzięki włączeniu jednoczesnego montażu wielu pojazdów linia montażowa zapewnia lepszą przepływność niż montaż kompletnych pojazdów pojedynczo.
Wymagania wstępne
Przed rozpoczęciem tego przewodnika zapoznaj się z następującymi dokumentami:
Zalecamy również zapoznanie się z podstawowymi elementami GDI+ przed rozpoczęciem tego przewodnika.
Sekcje
Ten przewodnik zawiera następujące sekcje:
Definiowanie funkcji przetwarzania obrazów
W tej sekcji przedstawiono funkcje obsługi używane przez sieć przetwarzania obrazów do pracy z obrazami odczytywanymi z dysku.
Następujące funkcje i GetRGB MakeColor, wyodrębnić i połączyć poszczególne składniki danego koloru, odpowiednio.
// Retrieves the red, green, and blue components from the given
// color value.
void GetRGB(DWORD color, BYTE& r, BYTE& g, BYTE& b)
{
r = static_cast<BYTE>((color & 0x00ff0000) >> 16);
g = static_cast<BYTE>((color & 0x0000ff00) >> 8);
b = static_cast<BYTE>((color & 0x000000ff));
}
// Creates a single color value from the provided red, green,
// and blue components.
DWORD MakeColor(BYTE r, BYTE g, BYTE b)
{
return (r<<16) | (g<<8) | (b);
}
Następująca funkcja ProcessImage, wywołuje dany obiekt std::function , aby przekształcić wartość koloru każdego piksela w obiekcie GDI+ Bitmap . Funkcja ProcessImage używa współbieżności::p arallel_for algorytmu do przetwarzania każdego wiersza mapy bitowej równolegle.
// Calls the provided function for each pixel in a Bitmap object.
void ProcessImage(Bitmap* bmp, const function<void (DWORD&)>& f)
{
int width = bmp->GetWidth();
int height = bmp->GetHeight();
// Lock the bitmap.
BitmapData bitmapData;
Rect rect(0, 0, bmp->GetWidth(), bmp->GetHeight());
bmp->LockBits(&rect, ImageLockModeWrite, PixelFormat32bppRGB, &bitmapData);
// Get a pointer to the bitmap data.
DWORD* image_bits = (DWORD*)bitmapData.Scan0;
// Call the function for each pixel in the image.
parallel_for (0, height, [&, width](int y)
{
for (int x = 0; x < width; ++x)
{
// Get the current pixel value.
DWORD* curr_pixel = image_bits + (y * width) + x;
// Call the function.
f(*curr_pixel);
}
});
// Unlock the bitmap.
bmp->UnlockBits(&bitmapData);
}
Następujące funkcje, Grayscale, , SepiatoneColorMask, i Darken, wywołają ProcessImage funkcję , aby przekształcić wartość koloru każdego piksela Bitmap w obiekcie. Każda z tych funkcji używa wyrażenia lambda do zdefiniowania transformacji kolorów jednego piksela.
// Converts the given image to grayscale.
Bitmap* Grayscale(Bitmap* bmp)
{
ProcessImage(bmp,
[](DWORD& color) {
BYTE r, g, b;
GetRGB(color, r, g, b);
// Set each color component to the average of
// the original components.
BYTE c = (static_cast<WORD>(r) + g + b) / 3;
color = MakeColor(c, c, c);
}
);
return bmp;
}
// Applies sepia toning to the provided image.
Bitmap* Sepiatone(Bitmap* bmp)
{
ProcessImage(bmp,
[](DWORD& color) {
BYTE r0, g0, b0;
GetRGB(color, r0, g0, b0);
WORD r1 = static_cast<WORD>((r0 * .393) + (g0 *.769) + (b0 * .189));
WORD g1 = static_cast<WORD>((r0 * .349) + (g0 *.686) + (b0 * .168));
WORD b1 = static_cast<WORD>((r0 * .272) + (g0 *.534) + (b0 * .131));
color = MakeColor(min(0xff, r1), min(0xff, g1), min(0xff, b1));
}
);
return bmp;
}
// Applies the given color mask to each pixel in the provided image.
Bitmap* ColorMask(Bitmap* bmp, DWORD mask)
{
ProcessImage(bmp,
[mask](DWORD& color) {
color = color & mask;
}
);
return bmp;
}
// Darkens the provided image by the given amount.
Bitmap* Darken(Bitmap* bmp, unsigned int percent)
{
if (percent > 100)
throw invalid_argument("Darken: percent must less than 100.");
double factor = percent / 100.0;
ProcessImage(bmp,
[factor](DWORD& color) {
BYTE r, g, b;
GetRGB(color, r, g, b);
r = static_cast<BYTE>(factor*r);
g = static_cast<BYTE>(factor*g);
b = static_cast<BYTE>(factor*b);
color = MakeColor(r, g, b);
}
);
return bmp;
}
Następująca funkcja , GetColorDominancewywołuje ProcessImage również funkcję . Jednak zamiast zmieniać wartość każdego koloru, ta funkcja używa współbieżności::połączonych obiektów do obliczenia, czy czerwony, zielony lub niebieski składnik koloru dominuje na obrazie.
// Determines which color component (red, green, or blue) is most dominant
// in the given image and returns a corresponding color mask.
DWORD GetColorDominance(Bitmap* bmp)
{
// The ProcessImage function processes the image in parallel.
// The following combinable objects enable the callback function
// to increment the color counts without using a lock.
combinable<unsigned int> reds;
combinable<unsigned int> greens;
combinable<unsigned int> blues;
ProcessImage(bmp,
[&](DWORD& color) {
BYTE r, g, b;
GetRGB(color, r, g, b);
if (r >= g && r >= b)
reds.local()++;
else if (g >= r && g >= b)
greens.local()++;
else
blues.local()++;
}
);
// Determine which color is dominant and return the corresponding
// color mask.
unsigned int r = reds.combine(plus<unsigned int>());
unsigned int g = greens.combine(plus<unsigned int>());
unsigned int b = blues.combine(plus<unsigned int>());
if (r + r >= g + b)
return 0x00ff0000;
else if (g + g >= r + b)
return 0x0000ff00;
else
return 0x000000ff;
}
Następująca funkcja GetEncoderClsidpobiera identyfikator klasy dla danego typu MIME kodera. Aplikacja używa tej funkcji do pobierania kodera dla mapy bitowej.
// Retrieves the class identifier for the given MIME type of an encoder.
int GetEncoderClsid(const WCHAR* format, CLSID* pClsid)
{
UINT num = 0; // number of image encoders
UINT size = 0; // size of the image encoder array in bytes
ImageCodecInfo* pImageCodecInfo = nullptr;
GetImageEncodersSize(&num, &size);
if(size == 0)
return -1; // Failure
pImageCodecInfo = (ImageCodecInfo*)(malloc(size));
if(pImageCodecInfo == nullptr)
return -1; // Failure
GetImageEncoders(num, size, pImageCodecInfo);
for(UINT j = 0; j < num; ++j)
{
if( wcscmp(pImageCodecInfo[j].MimeType, format) == 0 )
{
*pClsid = pImageCodecInfo[j].Clsid;
free(pImageCodecInfo);
return j; // Success
}
}
free(pImageCodecInfo);
return -1; // Failure
}
[Top]
Tworzenie sieci przetwarzania obrazów
W tej sekcji opisano sposób tworzenia sieci bloków komunikatów asynchronicznych, które wykonują przetwarzanie obrazów na każdym obrazie JPEG (.jpg) w danym katalogu. Sieć wykonuje następujące operacje przetwarzania obrazów:
W przypadku dowolnego obrazu utworzonego przez tom przekonwertuj na skala szarości.
W przypadku każdego obrazu, który ma czerwony kolor dominujący, usuń zielone i niebieskie składniki, a następnie zaciemnić go.
W przypadku dowolnego innego obrazu zastosuj tonowanie sepii.
Sieć stosuje tylko pierwszą operację przetwarzania obrazów zgodną z jednym z tych warunków. Jeśli na przykład obraz jest utworzony przez Tom i ma czerwony kolor dominujący, obraz jest konwertowany tylko na skala szarości.
Gdy sieć wykonuje każdą operację przetwarzania obrazów, zapisuje obraz na dysku jako plik mapy bitowej (.bmp).
W poniższych krokach pokazano, jak utworzyć funkcję, która implementuje tę sieć przetwarzania obrazów i stosuje tę sieć do każdego obrazu JPEG w danym katalogu.
Aby utworzyć sieć przetwarzania obrazów
Utwórz funkcję ,
ProcessImagesktóra przyjmuje nazwę katalogu na dysku.void ProcessImages(const wstring& directory) { }ProcessImagesW funkcji utwórz zmiennącountdown_event. Klasa zostanie wyświetlonacountdown_eventw dalszej części tego przewodnika.// Holds the number of active image processing operations and // signals to the main thread that processing is complete. countdown_event active(0);Utwórz obiekt std::map, który kojarzy
Bitmapobiekt z oryginalną nazwą pliku.// Maps Bitmap objects to their original file names. map<Bitmap*, wstring> bitmap_file_names;Dodaj następujący kod, aby zdefiniować elementy członkowskie sieci przetwarzania obrazów.
// // Create the nodes of the network. // // Loads Bitmap objects from disk. transformer<wstring, Bitmap*> load_bitmap( [&](wstring file_name) -> Bitmap* { Bitmap* bmp = new Bitmap(file_name.c_str()); if (bmp != nullptr) bitmap_file_names.insert(make_pair(bmp, file_name)); return bmp; } ); // Holds loaded Bitmap objects. unbounded_buffer<Bitmap*> loaded_bitmaps; // Converts images that are authored by Tom to grayscale. transformer<Bitmap*, Bitmap*> grayscale( [](Bitmap* bmp) { return Grayscale(bmp); }, nullptr, [](Bitmap* bmp) -> bool { if (bmp == nullptr) return false; // Retrieve the artist name from metadata. UINT size = bmp->GetPropertyItemSize(PropertyTagArtist); if (size == 0) // Image does not have the Artist property. return false; PropertyItem* artistProperty = (PropertyItem*) malloc(size); bmp->GetPropertyItem(PropertyTagArtist, size, artistProperty); string artist(reinterpret_cast<char*>(artistProperty->value)); free(artistProperty); return (artist.find("Tom ") == 0); } ); // Removes the green and blue color components from images that have red as // their dominant color. transformer<Bitmap*, Bitmap*> colormask( [](Bitmap* bmp) { return ColorMask(bmp, 0x00ff0000); }, nullptr, [](Bitmap* bmp) -> bool { if (bmp == nullptr) return false; return (GetColorDominance(bmp) == 0x00ff0000); } ); // Darkens the color of the provided Bitmap object. transformer<Bitmap*, Bitmap*> darken([](Bitmap* bmp) { return Darken(bmp, 50); }); // Applies sepia toning to the remaining images. transformer<Bitmap*, Bitmap*> sepiatone( [](Bitmap* bmp) { return Sepiatone(bmp); }, nullptr, [](Bitmap* bmp) -> bool { return bmp != nullptr; } ); // Saves Bitmap objects to disk. transformer<Bitmap*, Bitmap*> save_bitmap([&](Bitmap* bmp) -> Bitmap* { // Replace the file extension with .bmp. wstring file_name = bitmap_file_names[bmp]; file_name.replace(file_name.rfind(L'.') + 1, 3, L"bmp"); // Save the processed image. CLSID bmpClsid; GetEncoderClsid(L"image/bmp", &bmpClsid); bmp->Save(file_name.c_str(), &bmpClsid); return bmp; }); // Deletes Bitmap objects. transformer<Bitmap*, Bitmap*> delete_bitmap([](Bitmap* bmp) -> Bitmap* { delete bmp; return nullptr; }); // Decrements the event counter. call<Bitmap*> decrement([&](Bitmap* _) { active.signal(); });Dodaj następujący kod, aby połączyć sieć.
// // Connect the network. // load_bitmap.link_target(&loaded_bitmaps); loaded_bitmaps.link_target(&grayscale); loaded_bitmaps.link_target(&colormask); colormask.link_target(&darken); loaded_bitmaps.link_target(&sepiatone); loaded_bitmaps.link_target(&decrement); grayscale.link_target(&save_bitmap); darken.link_target(&save_bitmap); sepiatone.link_target(&save_bitmap); save_bitmap.link_target(&delete_bitmap); delete_bitmap.link_target(&decrement);Dodaj następujący kod, aby wysłać do głowy sieci pełną ścieżkę każdego pliku JPEG w katalogu.
// Traverse all files in the directory. wstring searchPattern = directory; searchPattern.append(L"\\*"); WIN32_FIND_DATA fileFindData; HANDLE hFind = FindFirstFile(searchPattern.c_str(), &fileFindData); if (hFind == INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE) return; do { if (!(fileFindData.dwFileAttributes & FILE_ATTRIBUTE_DIRECTORY)) { wstring file = fileFindData.cFileName; // Process only JPEG files. if (file.rfind(L".jpg") == file.length() - 4) { // Form the full path to the file. wstring full_path(directory); full_path.append(L"\\"); full_path.append(file); // Increment the count of work items. active.add_count(); // Send the path name to the network. send(load_bitmap, full_path); } } } while (FindNextFile(hFind, &fileFindData) != 0); FindClose(hFind);Poczekaj, aż zmienna
countdown_eventosiągnie zero.// Wait for all operations to finish. active.wait();
W poniższej tabeli opisano elementy członkowskie sieci.
| Element członkowski | opis |
|---|---|
load_bitmap |
Obiekt concurrency::transformer , który ładuje Bitmap obiekt z dysku i dodaje wpis do map obiektu w celu skojarzenia obrazu z oryginalną nazwą pliku. |
loaded_bitmaps |
Współbieżność ::unbounded_buffer obiekt, który wysyła załadowane obrazy do filtrów przetwarzania obrazów. |
grayscale |
transformer Obiekt, który konwertuje obrazy utworzone przez tom na skala szarości. Używa metadanych obrazu do określenia jego autora. |
colormask |
transformer Obiekt, który usuwa składniki koloru zielonego i niebieskiego z obrazów, które mają czerwony jako dominujący kolor. |
darken |
transformer Obiekt, który ciemnieje obrazy, które mają czerwony jako dominujący kolor. |
sepiatone |
transformer Obiekt, który stosuje tonowanie sepii do obrazów, które nie są tworzone przez Tom i nie są głównie czerwone. |
save_bitmap |
transformer Obiekt, który zapisuje przetworzone na image dysku jako mapę bitową. save_bitmap Pobiera oryginalną nazwę pliku z map obiektu i zmienia jego rozszerzenie nazwy pliku na .bmp. |
delete_bitmap |
transformer Obiekt, który zwalnia pamięć dla obrazów. |
decrement |
Obiekt concurrency::call , który działa jako węzeł terminalu w sieci. Dekrementuje countdown_event obiekt w celu sygnalizowania głównej aplikacji, że obraz został przetworzony. |
Bufor komunikatów loaded_bitmaps jest ważny, ponieważ jako unbounded_buffer obiekt oferuje Bitmap obiekty wielu odbiornikom. Gdy blok docelowy Bitmap akceptuje obiekt, unbounded_buffer obiekt nie oferuje tego Bitmap obiektu innym obiektom docelowym. W związku z tym kolejność łączenia obiektów z obiektem unbounded_buffer jest ważna. Komunikaty grayscale, colormaski sepiatone blokują każdy z nich używa filtru do akceptowania tylko niektórych Bitmap obiektów. Bufor decrement komunikatów jest ważnym elementem docelowym buforu loaded_bitmaps komunikatów, ponieważ akceptuje wszystkie Bitmap obiekty, które są odrzucane przez inne komunikatów. Obiekt unbounded_buffer jest wymagany do propagowania komunikatów w kolejności. unbounded_buffer W związku z tym obiekt blokuje do momentu, aż nowy blok docelowy zostanie z nim połączony i zaakceptuje komunikat, jeśli bieżący blok docelowy nie akceptuje tego komunikatu.
Jeśli aplikacja wymaga, aby wiele bloków komunikatów przetwarzało komunikat, zamiast tylko jednego bloku komunikatów, który najpierw akceptuje komunikat, możesz użyć innego typu bloku komunikatów, takiego jak overwrite_buffer. Klasa overwrite_buffer przechowuje jeden komunikat naraz, ale propaguje ten komunikat do każdego z jego celów.
Poniższa ilustracja przedstawia sieć przetwarzania obrazów:
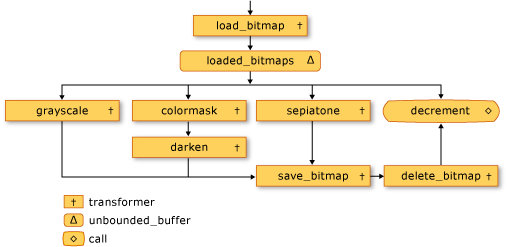
Obiekt countdown_event w tym przykładzie umożliwia sieci przetwarzania obrazów informowanie głównej aplikacji o przetworzeniu wszystkich obrazów. Klasa countdown_event używa obiektu concurrency::event , aby zasygnalizować, gdy wartość licznika osiągnie zero. Główna aplikacja zwiększa licznik za każdym razem, gdy wysyła nazwę pliku do sieci. Węzeł terminalu sieci dekrementuje licznik po przetworzeniu każdego obrazu. Po przejściu przez określony katalog przez główną aplikację czeka, aż countdown_event obiekt zasygnalizuje, że jego licznik osiągnął zero.
W poniższym przykładzie przedstawiono klasę countdown_event :
// A synchronization primitive that is signaled when its
// count reaches zero.
class countdown_event
{
public:
countdown_event(unsigned int count = 0)
: _current(static_cast<long>(count))
{
// Set the event if the initial count is zero.
if (_current == 0L)
_event.set();
}
// Decrements the event counter.
void signal() {
if(InterlockedDecrement(&_current) == 0L) {
_event.set();
}
}
// Increments the event counter.
void add_count() {
if(InterlockedIncrement(&_current) == 1L) {
_event.reset();
}
}
// Blocks the current context until the event is set.
void wait() {
_event.wait();
}
private:
// The current count.
volatile long _current;
// The event that is set when the counter reaches zero.
event _event;
// Disable copy constructor.
countdown_event(const countdown_event&);
// Disable assignment.
countdown_event const & operator=(countdown_event const&);
};
[Top]
Kompletny przykład
Poniższy kod przedstawia kompletny przykład. Funkcja wmain zarządza biblioteką GDI+ i wywołuje ProcessImages funkcję w celu przetworzenia plików JPEG w Sample Pictures katalogu.
// image-processing-network.cpp
// compile with: /DUNICODE /EHsc image-processing-network.cpp /link gdiplus.lib
#include <windows.h>
#include <gdiplus.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <agents.h>
#include <ppl.h>
using namespace concurrency;
using namespace Gdiplus;
using namespace std;
// Retrieves the red, green, and blue components from the given
// color value.
void GetRGB(DWORD color, BYTE& r, BYTE& g, BYTE& b)
{
r = static_cast<BYTE>((color & 0x00ff0000) >> 16);
g = static_cast<BYTE>((color & 0x0000ff00) >> 8);
b = static_cast<BYTE>((color & 0x000000ff));
}
// Creates a single color value from the provided red, green,
// and blue components.
DWORD MakeColor(BYTE r, BYTE g, BYTE b)
{
return (r<<16) | (g<<8) | (b);
}
// Calls the provided function for each pixel in a Bitmap object.
void ProcessImage(Bitmap* bmp, const function<void (DWORD&)>& f)
{
int width = bmp->GetWidth();
int height = bmp->GetHeight();
// Lock the bitmap.
BitmapData bitmapData;
Rect rect(0, 0, bmp->GetWidth(), bmp->GetHeight());
bmp->LockBits(&rect, ImageLockModeWrite, PixelFormat32bppRGB, &bitmapData);
// Get a pointer to the bitmap data.
DWORD* image_bits = (DWORD*)bitmapData.Scan0;
// Call the function for each pixel in the image.
parallel_for (0, height, [&, width](int y)
{
for (int x = 0; x < width; ++x)
{
// Get the current pixel value.
DWORD* curr_pixel = image_bits + (y * width) + x;
// Call the function.
f(*curr_pixel);
}
});
// Unlock the bitmap.
bmp->UnlockBits(&bitmapData);
}
// Converts the given image to grayscale.
Bitmap* Grayscale(Bitmap* bmp)
{
ProcessImage(bmp,
[](DWORD& color) {
BYTE r, g, b;
GetRGB(color, r, g, b);
// Set each color component to the average of
// the original components.
BYTE c = (static_cast<WORD>(r) + g + b) / 3;
color = MakeColor(c, c, c);
}
);
return bmp;
}
// Applies sepia toning to the provided image.
Bitmap* Sepiatone(Bitmap* bmp)
{
ProcessImage(bmp,
[](DWORD& color) {
BYTE r0, g0, b0;
GetRGB(color, r0, g0, b0);
WORD r1 = static_cast<WORD>((r0 * .393) + (g0 *.769) + (b0 * .189));
WORD g1 = static_cast<WORD>((r0 * .349) + (g0 *.686) + (b0 * .168));
WORD b1 = static_cast<WORD>((r0 * .272) + (g0 *.534) + (b0 * .131));
color = MakeColor(min(0xff, r1), min(0xff, g1), min(0xff, b1));
}
);
return bmp;
}
// Applies the given color mask to each pixel in the provided image.
Bitmap* ColorMask(Bitmap* bmp, DWORD mask)
{
ProcessImage(bmp,
[mask](DWORD& color) {
color = color & mask;
}
);
return bmp;
}
// Darkens the provided image by the given amount.
Bitmap* Darken(Bitmap* bmp, unsigned int percent)
{
if (percent > 100)
throw invalid_argument("Darken: percent must less than 100.");
double factor = percent / 100.0;
ProcessImage(bmp,
[factor](DWORD& color) {
BYTE r, g, b;
GetRGB(color, r, g, b);
r = static_cast<BYTE>(factor*r);
g = static_cast<BYTE>(factor*g);
b = static_cast<BYTE>(factor*b);
color = MakeColor(r, g, b);
}
);
return bmp;
}
// Determines which color component (red, green, or blue) is most dominant
// in the given image and returns a corresponding color mask.
DWORD GetColorDominance(Bitmap* bmp)
{
// The ProcessImage function processes the image in parallel.
// The following combinable objects enable the callback function
// to increment the color counts without using a lock.
combinable<unsigned int> reds;
combinable<unsigned int> greens;
combinable<unsigned int> blues;
ProcessImage(bmp,
[&](DWORD& color) {
BYTE r, g, b;
GetRGB(color, r, g, b);
if (r >= g && r >= b)
reds.local()++;
else if (g >= r && g >= b)
greens.local()++;
else
blues.local()++;
}
);
// Determine which color is dominant and return the corresponding
// color mask.
unsigned int r = reds.combine(plus<unsigned int>());
unsigned int g = greens.combine(plus<unsigned int>());
unsigned int b = blues.combine(plus<unsigned int>());
if (r + r >= g + b)
return 0x00ff0000;
else if (g + g >= r + b)
return 0x0000ff00;
else
return 0x000000ff;
}
// Retrieves the class identifier for the given MIME type of an encoder.
int GetEncoderClsid(const WCHAR* format, CLSID* pClsid)
{
UINT num = 0; // number of image encoders
UINT size = 0; // size of the image encoder array in bytes
ImageCodecInfo* pImageCodecInfo = nullptr;
GetImageEncodersSize(&num, &size);
if(size == 0)
return -1; // Failure
pImageCodecInfo = (ImageCodecInfo*)(malloc(size));
if(pImageCodecInfo == nullptr)
return -1; // Failure
GetImageEncoders(num, size, pImageCodecInfo);
for(UINT j = 0; j < num; ++j)
{
if( wcscmp(pImageCodecInfo[j].MimeType, format) == 0 )
{
*pClsid = pImageCodecInfo[j].Clsid;
free(pImageCodecInfo);
return j; // Success
}
}
free(pImageCodecInfo);
return -1; // Failure
}
// A synchronization primitive that is signaled when its
// count reaches zero.
class countdown_event
{
public:
countdown_event(unsigned int count = 0)
: _current(static_cast<long>(count))
{
// Set the event if the initial count is zero.
if (_current == 0L)
_event.set();
}
// Decrements the event counter.
void signal() {
if(InterlockedDecrement(&_current) == 0L) {
_event.set();
}
}
// Increments the event counter.
void add_count() {
if(InterlockedIncrement(&_current) == 1L) {
_event.reset();
}
}
// Blocks the current context until the event is set.
void wait() {
_event.wait();
}
private:
// The current count.
volatile long _current;
// The event that is set when the counter reaches zero.
event _event;
// Disable copy constructor.
countdown_event(const countdown_event&);
// Disable assignment.
countdown_event const & operator=(countdown_event const&);
};
// Demonstrates how to set up a message network that performs a series of
// image processing operations on each JPEG image in the given directory and
// saves each altered image as a Windows bitmap.
void ProcessImages(const wstring& directory)
{
// Holds the number of active image processing operations and
// signals to the main thread that processing is complete.
countdown_event active(0);
// Maps Bitmap objects to their original file names.
map<Bitmap*, wstring> bitmap_file_names;
//
// Create the nodes of the network.
//
// Loads Bitmap objects from disk.
transformer<wstring, Bitmap*> load_bitmap(
[&](wstring file_name) -> Bitmap* {
Bitmap* bmp = new Bitmap(file_name.c_str());
if (bmp != nullptr)
bitmap_file_names.insert(make_pair(bmp, file_name));
return bmp;
}
);
// Holds loaded Bitmap objects.
unbounded_buffer<Bitmap*> loaded_bitmaps;
// Converts images that are authored by Tom to grayscale.
transformer<Bitmap*, Bitmap*> grayscale(
[](Bitmap* bmp) {
return Grayscale(bmp);
},
nullptr,
[](Bitmap* bmp) -> bool {
if (bmp == nullptr)
return false;
// Retrieve the artist name from metadata.
UINT size = bmp->GetPropertyItemSize(PropertyTagArtist);
if (size == 0)
// Image does not have the Artist property.
return false;
PropertyItem* artistProperty = (PropertyItem*) malloc(size);
bmp->GetPropertyItem(PropertyTagArtist, size, artistProperty);
string artist(reinterpret_cast<char*>(artistProperty->value));
free(artistProperty);
return (artist.find("Tom ") == 0);
}
);
// Removes the green and blue color components from images that have red as
// their dominant color.
transformer<Bitmap*, Bitmap*> colormask(
[](Bitmap* bmp) {
return ColorMask(bmp, 0x00ff0000);
},
nullptr,
[](Bitmap* bmp) -> bool {
if (bmp == nullptr)
return false;
return (GetColorDominance(bmp) == 0x00ff0000);
}
);
// Darkens the color of the provided Bitmap object.
transformer<Bitmap*, Bitmap*> darken([](Bitmap* bmp) {
return Darken(bmp, 50);
});
// Applies sepia toning to the remaining images.
transformer<Bitmap*, Bitmap*> sepiatone(
[](Bitmap* bmp) {
return Sepiatone(bmp);
},
nullptr,
[](Bitmap* bmp) -> bool { return bmp != nullptr; }
);
// Saves Bitmap objects to disk.
transformer<Bitmap*, Bitmap*> save_bitmap([&](Bitmap* bmp) -> Bitmap* {
// Replace the file extension with .bmp.
wstring file_name = bitmap_file_names[bmp];
file_name.replace(file_name.rfind(L'.') + 1, 3, L"bmp");
// Save the processed image.
CLSID bmpClsid;
GetEncoderClsid(L"image/bmp", &bmpClsid);
bmp->Save(file_name.c_str(), &bmpClsid);
return bmp;
});
// Deletes Bitmap objects.
transformer<Bitmap*, Bitmap*> delete_bitmap([](Bitmap* bmp) -> Bitmap* {
delete bmp;
return nullptr;
});
// Decrements the event counter.
call<Bitmap*> decrement([&](Bitmap* _) {
active.signal();
});
//
// Connect the network.
//
load_bitmap.link_target(&loaded_bitmaps);
loaded_bitmaps.link_target(&grayscale);
loaded_bitmaps.link_target(&colormask);
colormask.link_target(&darken);
loaded_bitmaps.link_target(&sepiatone);
loaded_bitmaps.link_target(&decrement);
grayscale.link_target(&save_bitmap);
darken.link_target(&save_bitmap);
sepiatone.link_target(&save_bitmap);
save_bitmap.link_target(&delete_bitmap);
delete_bitmap.link_target(&decrement);
// Traverse all files in the directory.
wstring searchPattern = directory;
searchPattern.append(L"\\*");
WIN32_FIND_DATA fileFindData;
HANDLE hFind = FindFirstFile(searchPattern.c_str(), &fileFindData);
if (hFind == INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE)
return;
do
{
if (!(fileFindData.dwFileAttributes & FILE_ATTRIBUTE_DIRECTORY))
{
wstring file = fileFindData.cFileName;
// Process only JPEG files.
if (file.rfind(L".jpg") == file.length() - 4)
{
// Form the full path to the file.
wstring full_path(directory);
full_path.append(L"\\");
full_path.append(file);
// Increment the count of work items.
active.add_count();
// Send the path name to the network.
send(load_bitmap, full_path);
}
}
}
while (FindNextFile(hFind, &fileFindData) != 0);
FindClose(hFind);
// Wait for all operations to finish.
active.wait();
}
int wmain()
{
GdiplusStartupInput gdiplusStartupInput;
ULONG_PTR gdiplusToken;
// Initialize GDI+.
GdiplusStartup(&gdiplusToken, &gdiplusStartupInput, nullptr);
// Perform image processing.
// TODO: Change this path if necessary.
ProcessImages(L"C:\\Users\\Public\\Pictures\\Sample Pictures");
// Shutdown GDI+.
GdiplusShutdown(gdiplusToken);
}
Na poniższej ilustracji przedstawiono przykładowe dane wyjściowe. Każdy obraz źródłowy znajduje się powyżej odpowiadającego mu zmodyfikowanego obrazu.

Lighthouse jest autorem tom Alphin i dlatego jest konwertowany na skala szarości. Chrysanthemum, , DesertKoalai Tulips mają czerwony jako dominujący kolor i dlatego mają usunięte niebieskie i zielone składniki kolorów i są ciemniejsze. Hydrangeas, Jellyfishi Penguins są zgodne z kryteriami domyślnymi, a zatem są to sepia toned.
[Top]
Kompilowanie kodu
Skopiuj przykładowy kod i wklej go w projekcie programu Visual Studio lub wklej go w pliku o nazwie image-processing-network.cpp , a następnie uruchom następujące polecenie w oknie wiersza polecenia programu Visual Studio.
cl.exe /DUNICODE /EHsc image-processing-network.cpp /link gdiplus.lib